Effect of UV Irradiation on the Structural Variation of Metal Oxide-Silica Nanocomposites for Enhanced Removal of Erythromycin at Neutral pH
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Texture and Morphology of the Pristine Nanocomposite
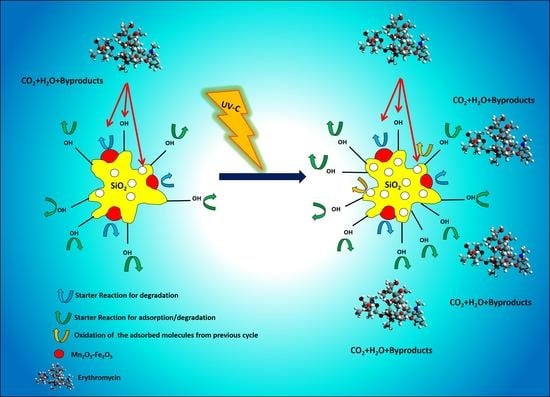
2.2. Performance of Pristine and UV-Treated Nanocomposites for Removal of ERY
2.3. Comparison of Structural Variation in Pristine and UV-Treated Nanocomposite
2.4. Degradation By-Products Using the Regenerated Nanocomposite after the Last Cycle
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Synthesis of Metal Oxide Silica Nanocomposites
3.3. Experimental Procedure
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Humayun, M.; Wang, C.; Luo, W. Recent Progress in the Synthesis and Applications of Composite Photocatalysts: A Critical Review. Small Methods 2022, 6, 2101395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, M.; Kumar, R.; Kishor, K.; Mlsna, T.; Pittman, C.U., Jr.; Mohan, D. Pharmaceuticals of emerging concern in aquatic systems: Chemistry, occurrence, effects, and removal methods. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 3510–3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bao, T.; Damtie, M.M.; Hosseinzadeh, A.; Frost, R.L.; Yu, Z.M.; Jin, J.; Wu, K. Catalytic degradation of P-chlorophenol by muscovite-supported nano zero valent iron composite: Synthesis, characterization, and mechanism studies. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 195, 105735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafhauser, B.H.; Kristofco, L.A.; de Oliveira, C.M.R.; Brooks, B.W. Global review and analysis of erythromycin in the environment: Occurrence, bioaccumulation and antibiotic resistance hazards. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 238, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michael-Kordatou, I.; Iacovou, M.; Frontistis, Z.; Hapeshi, E.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Fatta-Kassinos, D. Erythromycin oxidation and ERY-resistant Escherichia coli inactivation in urban wastewater by sulfate radical-based oxidation process under UV-C irradiation. Water Res. 2015, 85, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, L.; Zhuan, R.; Chen, D.; Wang, J.; Shen, Y. Degradation of macrolide antibiotic erythromycin and reduction of antimicrobial activity using persulfate activated by gamma radiation in different water matrices. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 361, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Pleiter, M.; Gonzalo, S.; Rodea-Palomares, I.; Leganés, F.; Rosal, R.; Boltes, K.; Marco, E.; Fernández-Piñas, F. Toxicity of five antibiotics and their mixtures towards photosynthetic aquatic organisms: Implications for environmental risk assessment. Water Res. 2013, 47, 2050–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Nie, X.; Liu, W.; Snoeijs, P.; Guan, C.; Tsui, M.T.K. Toxic effects of erythromycin, ciprofloxacin and sulfamethoxazole on photosynthetic apparatus in Selenastrum capricornutum. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2011, 74, 1027–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lu, G.; Ding, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y. Tissue distribution, bioconcentration, metabolism, and effects of erythromycin in crucian carp (Carassius auratus). Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 490, 914–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, T.; Damtie, M.M.; Wei, W.; Phong Vo, H.N.; Nguyen, K.H.; Hosseinzadeh, A.; Cho, K.; Yu, Z.M.; Jin, J.; Wei, X.L.; et al. Simultaneous adsorption and degradation of bisphenol A on magnetic illite clay composite: Eco-friendly preparation, characterizations, and catalytic mechanism. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 287, 125068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, T.X.; Choi, H. Adsorptive removal of selected pharmaceuticals by mesoporous silica SBA-15. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáenz-Roblero, B.; Durán, J.E.; Masís-Mora, M.; Ramírez-Morales, D.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, C.E. Removal of cimetidine, ketoprofen and naproxen by heterogeneous catalytic ozonation over volcanic sand at low pH. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 37, 101461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoub, H.; Roques-Carmes, T.; Potier, O.; Koubaissy, B.; Pontvianne, S.; Lenouvel, A.; Guignard, C.; Mousset, E.; Poirot, H.; Toufaily, J.; et al. Iron-impregnated zeolite catalyst for efficient removal of micropollutants at very low concentration from Meurthe river. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 34950–34967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, M.; Saini, V.K.; Suthar, S. Removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) from water by adsorption on aluminum pillared clay. J. Porous Mater. 2020, 27, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasetya, N.; Li, K. MOF-808 and its hollow fibre adsorbents for efficient diclofenac removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 417, 129216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaria, G.; Calisto, V.; Silva, C.P.; Gil, M.V.; Otero, M.; Esteves, V.I. Fixed-bed performance of a waste-derived granular activated carbon for the removal of micropollutants from municipal wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 683, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, A.; Liu, G.; Yousaf, B.; Arif, M.; Ahmed, R.; Irshad, S.; Cheema, A.I.; Rashid, A.; Gulzaman, H. Recent trends in advanced oxidation process-based degradation of erythromycin: Pollution status, eco-toxicity and degradation mechanism in aquatic ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 772, 145389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, L.; Gamallo, M.; González-Gómez, M.; Vázquez-Vázquez, C.; Rivas, J.; Pintado, M.; Moreira, M. Insight into antibiotics removal: Exploring the photocatalytic performance of a Fe3O4/ZnO nanocomposite in a novel magnetic sequential batch reactor. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 237, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaffari, Y.; Beak, S.; Bae, J.; Kim, S.; Saifuddin, M.; Kim, K.S. One-step fabrication of novel ultra porous Mn2O3-Fe2O3@ SiO2: A versatile material for removal of organic pollutants from industrial wastewater at neutral pH. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 285, 120259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maletić, M.; Vukčević, M.; Kalijadis, A.; Janković-Častvan, I.; Dapčević, A.; Laušević, Z.; Laušević, M. Hydrothermal synthesis of TiO2/carbon composites and their application for removal of organic pollutants. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 4388–4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vignesh, K.; Rajarajan, M.; Suganthi, A. Photocatalytic degradation of erythromycin under visible light by zinc phthalocyanine-modified titania nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Processing 2014, 23, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayadi, M.H.; Sobhani, S.; Shekari, H. Photocatalytic degradation of azithromycin using GO@ Fe3O4/ZnO/SnO2 nanocomposites. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 232, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanchikova, N.; Pestryakov, A.; Farias, M.; Diaz, J.A.; Avalos, M.; Navarrete, J. Formation of TEM-and XRD-undetectable gold clusters accompanying big gold particles on TiO2–SiO2 supports. Solid State Sci. 2008, 10, 908–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Nengzi, L.-C.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, G.; Gou, J.; Cheng, X. Degradation of tartrazine by peroxymonosulfate through magnetic Fe2O3/Mn2O3 composites activation. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 2730–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Liu, L.; Yang, F.; Zhang, Y. Evaluation of cooling property of high density polyethylene (HDPE)/titanium dioxide (TiO2) composites after accelerated ultraviolet (UV) irradiation. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2015, 143, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasseh, N.; Panahi, A.H.; Esmati, M.; Daglioglu, N.; Asadi, A.; Rajati, H.; Khodadoost, F. Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline from aqueous solution by a novel magnetically separable FeNi3/SiO2/ZnO nano-composite under simulated sunlight: Efficiency, stability, and kinetic studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 301, 112434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motlagh, M.M.; Hassanzadeh-Tabrizi, S.; Saffar-Teluri, A. Influence of Mn2O3 content on the textural and catalytic properties of Mn2O3/Al2O3/SiO2 nanocatalyst. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 16177–16181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, A.; Fakhari, M.; Safaei, Z.; Khodeai, M.; Repo, E.; Asadi, A. Ionic liquid-decorated Fe3O4@ SiO2 nanocomposite coated on talc sheets: An efficient adsorbent for methylene blue in aqueous solution. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2020, 121, 108204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, S.P.; Elangovan, S.; Okubo, T.; Sokolov, I. Morphology control of mesoporous silica particles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 11168–11173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, B.M.; Khan, A.; Yamada, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Loridant, S.; Volta, J.-C. Surface characterization of CeO2/SiO2 and V2O5/CeO2/SiO2 catalysts by Raman, XPS, and other techniques. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 10964–10972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flak, D.; Chen, Q.; Mun, B.S.; Liu, Z.; Rękas, M.; Braun, A. In situ ambient pressure XPS observation of surface chemistry and electronic structure of α-Fe2O3 and γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 455, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Q.; Song, X.; Qian, Y. Synthesis of porous and hollow microspheres of nanocrystalline Mn2O3. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2006, 418, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimouni, I.; Bouziani, A.; Naciri, Y.; Boujnah, M.; El Belghiti, M.A.; El Azzouzi, M. Effect of heat treatment on the photocatalytic activity of α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles: Towards diclofenac elimination. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 29, 7984–7996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Process | Experimental Condition | Removal Efficiency | Reusability/Regeneration | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERY | TiO2/carbon | Catalyst dosage: 1 g/L, initial concentration: 10 mg dm−3, pH: not mentioned | 87% | 1 | [20] |
| ERY | ZnO/Fe3O4 | Catalyst dosage: 50–800 mg/L, initial concentration: 10–100 μg/L, pH: 5 | 36% | 8 | [18] |
| ERY | Znpc–TiO2 | Catalyst dosage: 0.4 g/L, initial concentration: 1 × 105 M, pH: 5 | 74.21% | 5 | [21] |
| azithromycin (ERY derivative) | GO@Fe3O4/ZnO/SnO2 | Catalyst dosage: 1 g/L, initial concentration: 30 mg/L, pH: 3 | 90.06% | 6 | [22] |
| ERY | Mn2O3-Fe2O3@SiO2 | Catalyst dosage: 0.5 g/L, initial concentration: 2 mg/L, pH: neutral | 99.57 | 10 | This work |
| Product | BET (m2/g) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Pore Diameter (nm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pristine | 891.58 | 0.982 | 5.4 |
| 2 | UV-irradiated (20 min) | 1025.190 | 1.039 | 4.9 |
| 3 | UV-irradiated (180 min) | 1038.67 | 1.053 | 4.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghaffari, Y.; Beak, S.; Bae, J.; Saifuddin, M.; Kim, K.S. Effect of UV Irradiation on the Structural Variation of Metal Oxide-Silica Nanocomposites for Enhanced Removal of Erythromycin at Neutral pH. Catalysts 2022, 12, 424. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12040424
Ghaffari Y, Beak S, Bae J, Saifuddin M, Kim KS. Effect of UV Irradiation on the Structural Variation of Metal Oxide-Silica Nanocomposites for Enhanced Removal of Erythromycin at Neutral pH. Catalysts. 2022; 12(4):424. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12040424
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhaffari, Yasaman, Soyoung Beak, Jiyeol Bae, Md Saifuddin, and Kwang Soo Kim. 2022. "Effect of UV Irradiation on the Structural Variation of Metal Oxide-Silica Nanocomposites for Enhanced Removal of Erythromycin at Neutral pH" Catalysts 12, no. 4: 424. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12040424
APA StyleGhaffari, Y., Beak, S., Bae, J., Saifuddin, M., & Kim, K. S. (2022). Effect of UV Irradiation on the Structural Variation of Metal Oxide-Silica Nanocomposites for Enhanced Removal of Erythromycin at Neutral pH. Catalysts, 12(4), 424. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12040424