Highly Hydrophilic Ti−Beta Zeolite with Ti−Rich Exterior as Efficient Catalyst for Cyclohexene Epoxidation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
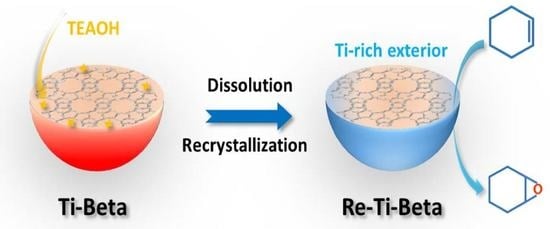
2.1. Synthesis of Re−Ti−Beta Catalyst by Post−Modification
2.2. Characterization of Catalysts
2.2.1. Textural Properties of Re−Ti−Beta Catalyst
2.2.2. Coordination State and Location of Ti Active Sites
2.2.3. Hydrophilicity/Hydrophobicity Property
2.3. Catalytic Performance in the Cyclohexene Epoxidation Reaction
2.4. The Reusability of Re−Ti−Beta
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Catalyst Preparation
3.2.1. Preparation of the Parent Ti−Beta Zeolite via Structural Reconstruction Method
3.2.2. Preparation of Re−Ti−Beta by Post−Modification of Ti−Beta
3.3. Characterization Methods
3.4. Liquid−Phase Epoxidation of Cyclohexene
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Takeuchi, Y.; Asano, T.; Tsuzaki, K.; Wada, K. Catalytic asymmetric amination of meso−epoxide using soy polysaccharide (soyafibe S−DN). Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2018, 91, 678–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, T.; Zhao, G.F.; Liu, Y.; Lu, Y. Catalytic distillation for one−step cyclohexyl acetate production and cyclohexene−cyclohexane separation via esterification of cyclohexene with acetic acid over microfibrous−structured Nafion−SiO2/SS−fiber packings. Chem. Eng. Process. 2018, 131, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.Y.; Nguyen, V.H.; Wu, J.C.S.; Calvino−Casilda, V.; Bañares, M.A.; Bai, H. Real−Time Raman Monitoring during Photocatalytic Epoxidation of Cyclohexene over V−Ti/MCM−41 Catalysts. Catalysts 2015, 5, 518–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.Z.; Guan, X.Z. Studies on the electrochemical epoxidation of cyclohexene. Chem. J. Chinese, U. 1998, 10, 1260–1262. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, O.; Pattisson, S.; Macginley, J.; Engel, R.V.; Whiston, K.; Taylor, S.H.; Hutchings, G.J. The Low Temperature Solvent−Free Aerobic Oxidation of Cyclohexene to Cyclohexane Diol over Highly Active Au/Graphite and Au/Graphene Catalysts. Catalysts 2018, 8, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, X.T.; Ji, H.B.; Xu, J.C.; Pei, L.X.; Yao, X.D. Enzymatic−like mediated olefins epoxidation by molecular oxygen under mild conditions. Tetrahedron Lett. 2007, 48, 2691–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktas, A.; Saka, E.T.; Biyiklioglu, Z.; Acar, I.; Kantekin, H. Investigation of catalytic activity of new co (II) phthalocyanine complexes in cyclohexene oxidation using different type of oxidants. J. Organomet. Chem. 2013, 745, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taramasso, M.; Perego, G.; Notari, B. Preparation of Porous Crystalline Synthetic Material Comprised of Silicon and Titanium Oxides. U.S. Patent 4410501, 13 October 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, P.; Tatsumi, T.; Komatsu, T.; Yashima, T. Hydrothermal synthesis of a novel titanosilicate with MWW topology. Chem. Lett. 2000, 29, 774–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Komatsu, T.; Yashima, T. Characterization of titanium species incorporated into dealuminated mordenites by means of IR spectroscopy and 18O−exchange technique. J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 10316–10322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jappar, N.; Xia, Q.H.; Tatsumi, T. Oxidation activity of Ti−Beta synthesized by a dry−gel conversion method. J. Catal. 1998, 180, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morey, M.S.; Ơbrien, S.; Schwarz, S.; Stucky, G.D. Hydrothermal and postsynthesis surface modification of cubic, MCM−48, and ultralarge pore SBA−15 mesoporous silica with titanium. Chem. Mater. 2000, 12, 898–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corma, A.; Navarro, M.T.; Perez−Pariente, J. Synthesis of an ultralarge pore titanium silicate isomorphous to MCM−41 and its application as a catalyst for selective oxidation of hydrocarbons. Chem. Commun. 1994, 147–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corma, A.; Camblor, M.A.; Esteve, P.; Martinez, A.; Perezpariente, J. Activity of Ti−Beta catalyst for the selective oxidation of alkenes and alkanes. J. Catal. 1994, 145, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Waal, J.C.; Rigutto, M.S.; Van Bekkum, H. Zeolite titanium beta as a selective catalyst in the epoxidation of bulky alkenes. Appl. Catal. A 1998, 167, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camblor, M.A.; Costantini, M.; Corma, A.; Gilbert, L.; Esteve, P.; Martínez, A.; Valencia, S. Synthesis and catalytic activity of aluminium−free zeolite Ti−β oxidation catalysts. Chem. Commun. 1996, 1339–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasco, T.; Camblor, M.A.; Corma, A.; Esteve, P.; Martínez, A.; Prieto, C.; Valencia, S. Unseeded synthesis of Al−free Ti−β zeolite in fluoride medium: A hydrophobic selective oxidation catalyst. Chem. Commun. 1996, 2367–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasco, T.; Camblor, M.A.; Corma, A.; Esteve, P.; Guil, J.M.; Martínez, A.; Perdigón−Melón, J.A.; Valencia, S. Direct synthesis and characterization of hydrophobic aluminum−free Ti−Beta zeolite. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, K.Y.; Li, X.L.; Ye, G.; Du, Y.C.; Sun, Y.Y.; Xu, W. Ti−containing hierarchical Beta with highly active sites for deep desulfurization of fuels under mild conditions. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 7615–7622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Dai, W.L.; Sun, X.M.; Guan, N.J.; Li, L.D.; Hunger, M. A procedure for the preparation of Ti−Beta zeolites for catalytic epoxidation with hydrogen peroxide. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 2281–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krijnen, S.; Sánchez, P.; Jakobs, B.T.F.; Van Hooff, J.H.C. A controlled post−synthesis route to well−defined and active titanium Beta epoxidation catalysts. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 1999, 31, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.W.; Xu, H.; Zhu, Z.G.; Guan, Y.J.; Wu, P. Ultrafast synthesis of nanosized Ti−Beta via structural reconstruction method as efficient oxidation catalyst. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2019, 9, 1857–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.S.; Kanoh, H.; Abrams, L.; Kaneko, K. Mesoporemodified zeolites: Preparation, characterization, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 896–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.; Gao, X.H.; Yan, Z.F.; Mintova, S. Diffusion and catalyst efficiency in hierarchical zeolite catalysts. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 7, 1726–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerstens, D.; Smeyers, B.; Van Waeyenberg, J.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, J.; Sels, B.F. State of the art and perspectives of hierarchical zeolites: Practical overview of synthesis methods and use incatalysis. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2004690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.H.; Sun, M.H.; Wang, Z.; Yang, W.; Xie, Z.; Su, B.L. Hierarchically structured zeolites: From design to application. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 11194–11294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Q.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y.S.; Bi, C.Y.; Yang, X.; Sun, M.; Zhang, J.B.; Hao, Q.Q.; Chen, H.Y.; Ma, X.X. Hierarchical Ti−beta with a three−dimensional ordered mesoporosity for catalytic epoxidation of bulky cyclic olefins. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 10303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.C.; Hua, Z.L.; Ge, T.G.; Zhou, X.X.; Chen, L.S.; Zhu, Y.; Shi, J.L. Post−synthesis of hierarchically structured Ti−β zeolites and their epoxidation catalytic performance. Chinese. J. Catal. 2015, 36, 906–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, A.; Bludovsky, P.; Selzer, C.; Koch, U.; Giebeler, L.; Oswald, S.; Kaskel, S. Hierarchical Ti−beta obtained by simultaneous desilication and titanation as an efficient catalyst for cyclooctene epoxidation. ChemCatChem 2017, 9, 3860–3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordomsky, V.V.; Murzin, V.Y.; Monakhova, Y.V.; Zubavichus, Y.V.; Knyazeva, E.E.; Nesterenko, N.S.; Ivanova, I.I. Nature, strength and accessibility of acid sites in micro/mesoporous catalysts obtained by recrystallization of zeolite BEA. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2007, 105, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.J.; Qiu, Z.Y.; Han, J.; Chen, X.X.; Yu, J.H. Fluoride etching opens the access for bulky molecules to active sites in microporous Ti−Beta zeolite. Mater. Chem. Front. 2020, 4, 2982–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bregante, D.T.; Johnson, A.M.; Patel, A.Y.; Ayla, E.Z.; Cordon, M.J.; Bukowski, B.C.; Greeley, J.; Gounder, R.; Flaherty, D.W. Cooperative effects between hydrophilic pores and solvents: Catalytic consequences of hydrogen bonding on alkene epoxidation in zeolites. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 7302–7319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Li, G.; Su, R.M.; Lu, H.; Guo, H.C. Ti−sites environment−mediated hierarchical TS−1 catalyzing the solvent−free epoxidation: The remarkably promoting role of alcohol modification. Appl. Catal. A 2019, 582, 117108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnasamy, P.; Srinivas, D.; Knozinger, H. Active sites and reactive intermediates in titanium silicate molecular sieves. Adv. Catal. 2004, 48, 1–169. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Huang, D.D.; Li, C.G.; Ji, X.Y.; Jin, S.Q.; Feng, Z.C.; Xia, F.; Li, X.H.; Fan, F.T.; Li, C.; et al. Construction of unique six−coordinated titanium species with an organic ligand in titanosilicate and their unprecedented high efficiency for alkenes epoxidation. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 9010–9013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.B.; Liu, M.; Li, P.; Liu, Y.; Guo, X.W. Modification of micrometer−sized TS−1 with tetrapropylammonium hydroxide and its catalytic properties in hydroxylation of phenol and ammoxidation of methyl ethyl ketone. J. Fuel Chem. Technol. 2008, 36, 484–488. [Google Scholar]
- Tozzola, G.; Mantegazza, M.A.; Ranghino, G.; Petrini, G.; Bordiga, S.; Ricchiardi, G.; Lamberti, C.; Zulian, R.; Zecchina, A. On the Structure of the Active Site of Ti−Silicalite in Reactions with Hydrogen Peroxide: A Vibrational and Computational Study. J. Catal. 1998, 179, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogier, J.P.; Millot, Y.; Man, P.P.; Méthivier, C.; Che, M.; Dzwigaj, S. Nature, Environment and Quantification of titanium species in TiSiBEA zeolites investigated by XRD, NMR, DR UV–Vis and XPS. Catal. Lett. 2009, 130, 588–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.K.; Wang, R.; Liu, W.; Chen, Z.; Liu, H.X.; Huang, X.; Tang, Z.M.; Liu, Y.M.; He, M.Y. Control of Ti active−site microenvironment in titanosilicate catalysts and its effect on oxidation pathways. Appl. Catal. A 2021, 610, 117953–117962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Xiong, G.; Zhou, J.C.; Liu, W.H.; Zhou, D.H.; Wang, G.R.; Wang, X.S.; Guo, H.C. Amorphous Ti species in titanium silicalite−1: Structural features, chemical properties, and inactivation with sulfosalt. J. Catal. 2012, 288, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xiong, G.; Xin, Q.; Liu, J.K.; Ying, P.L.; Feng, Z.C.; Li, J.; Yang, W.B.; Wang, Y.Z.; Wang, G.R.; et al. UV resonance raman spectroscopic identification of titanium atoms in the framework of TS−1 zeolite. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1999, 38, 2220–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bregante, D.T.; Flaherty, D.W. Impact of Specific Interactions among Reactive Surface Intermediates and Confined Water on Epoxidation Catalysis and Adsorption in Lewis Acid Zeolites. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 10951–10962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.Q.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, A.M.; Liu, Y.M.; Lin, L.F.; Wu, H.H.; Deng, F.; He, M.Y.; Wu, P. Post−synthesis, characterization and catalytic properties of fluorine−planted MWW−type titanosilicate. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 4930–4938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Song, W.C.; Dai, C.Y.; He, Y.P.; Wang, M.L.; Wang, X.S.; Guo, X.W. Modification of small−crystal titanium silicalite−1 with organic bases: Recrystallization and catalytic properties in the hydroxylation of phenol. Appl. Catal. A 2013, 453, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, X.; Han, Q.; Xu, L.J.; Zhang, S.Y.; Yuan, Y.Y.; Xu, L. Post−synthesis of hierarchical TS−1 and its unique catalytic performance in the direct hydroxylation of toluene. Appl. Catal. A 2020, 598, 117588–117596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.R.; Peng, X.X.; Zhang, W.F.; Lin, M.; Zhu, B.; Liao, W.L.; Guo, X.H.; Shu, X.T. Hierarchical TS−1 synthesized via the dissolution−recrystallization process: Influence of ammonium salts. Catal. Commun. 2017, 101, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levenspiel, O. Chemical Reaction Engineering, 3rd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]













| Sample | Bulk Si/Ti a | Surface Si/Ti b | SSA (m2 g−1) | Pore volume (cm3 g−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stotal c | Smicro | Sext d | Vtotal c | Vmicro d | Vmeso e | |||
| Ti−Beta | 28.1 | 102 | 610 | 451 | 159 | 0.80 | 0.18 | 0.62 |
| Re−Ti−Beta−0.20 | 26.6 | 57 | 613 | 439 | 174 | 0.89 | 0.18 | 0.71 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, H.; Peng, R.; Zhu, Z.; Xu, H.; He, M.; Wu, P. Highly Hydrophilic Ti−Beta Zeolite with Ti−Rich Exterior as Efficient Catalyst for Cyclohexene Epoxidation. Catalysts 2022, 12, 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12040434
Pan H, Peng R, Zhu Z, Xu H, He M, Wu P. Highly Hydrophilic Ti−Beta Zeolite with Ti−Rich Exterior as Efficient Catalyst for Cyclohexene Epoxidation. Catalysts. 2022; 12(4):434. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12040434
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Huang, Rusi Peng, Zhiguo Zhu, Hao Xu, Mingyuan He, and Peng Wu. 2022. "Highly Hydrophilic Ti−Beta Zeolite with Ti−Rich Exterior as Efficient Catalyst for Cyclohexene Epoxidation" Catalysts 12, no. 4: 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12040434
APA StylePan, H., Peng, R., Zhu, Z., Xu, H., He, M., & Wu, P. (2022). Highly Hydrophilic Ti−Beta Zeolite with Ti−Rich Exterior as Efficient Catalyst for Cyclohexene Epoxidation. Catalysts, 12(4), 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12040434