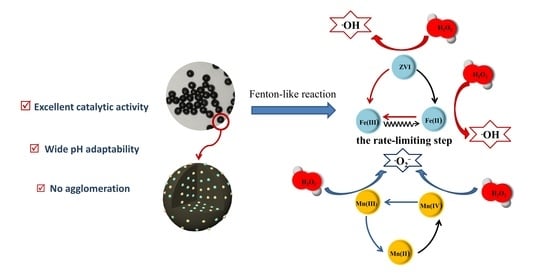
Spherical ZVI/Mn-C Bimetallic Catalysts for Efficient Fenton-like Reaction under Mild Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of Catalysts
2.2. Catalytic Activity
2.3. Mechanism Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of ZVI/Mn-C Spheres
3.3. Characterization
3.4. Other Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Babuponnusami, A.; Muthukumar, K. Advanced oxidation of phenol: A comparison between Fenton, electro-Fenton, sono-electro-Fenton and photo-electro-Fenton processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 183, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.P.; Sun, F. Application of Immobilized Microorganisms Technology for Wastewater Treatment. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Diffuse Pollution-Management Measures and Control Technique, Huainan, China, 27–29 October 2010; Anhui University of Science and Technology: Huainan, China, 2010; p. 359. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Zhang, W. An Optimized Method Using Light Enhanced Fenton to Treat Highly Toxic Phenol Wastewater. Asian J. Chem. 2013, 25, 4583–4587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgari, G.; Feradmal, J.; Poormohammadi, A.; Sadrnourmohamadi, M.; Akbari, S. Taguchi optimization for the removal of high concentrations of phenol from saline wastewater using electro-Fenton process. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 27331–27338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.Y.; Meng, L.K.; Zhao, Y.H. Adsorption of phenol from wastewater by organo-bentonite. Desalination Water Treat. 2014, 52, 3504–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, R.; Wang, F.C.; Yu, C.M.; Li, X.G. Research of advanced oxidation treatment of organic wastewater, 3rd. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Energy, Environment and Sustainable Development (EESD 2013), Shanghai, China, 12–13 November 2013; pp. 1621–1625. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, M.; Haritash, A.K. Degradation of amoxicillin by Fenton and Fenton-integrated hybrid oxidation processes. J. Environ. 2019, 7, 102886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues-Silva, F.; Lemos, C.R.; Naico, A.A.; Fachi, M.M.; do Amaral, B.; de Paula, V.C.S.; Rampon, D.S.; Beraldi-Magalhaes, F.; Prola, L.D.T.; Pontarolo, R.; et al. Study of isoniazid degradation by Fenton and photo-Fenton processes, by-products analysis and toxicity evaluation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2022, 425, 113671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulaksiz, E.; Kayan, B.; Gozmen, B.; Kalderis, D.; Oturan, N.; Oturan, M.A. Comparative degradation of 5-fluorouracil in aqueous solution by using H2O2-modified subcritical water, photocatalytic oxidation and electro-Fenton processes. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 111898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.Y.; Li, S.P.; Nguyen, T.T.; Gao, X.; Luo, S.Y.; Guo, M.H. Biochar loaded on MnFe2O4 as Fenton catalyst for Rhodamine B removal: Characterizations, catalytic performance, process optimization and mechanism. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 631, 127651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.W.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Zhang, Y.B. Sustainable Strategy for Enhancing Anaerobic Digestion of Waste Activated Sludge: Driving Dissimilatory Iron Reduction with Fenton Sludge. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 2220–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.H.; Cao, Y.J.; Wang, L.Z.; Li, S.L. A review on sustainable reuse applications of Fenton sludge during wastewater treatment. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2022, 16, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijide, J.; Dunlop, P.S.M.; Pazos, M.; Sanroman, M.A. Heterogeneous Electro-Fenton as “Green” Technology for Pharmaceutical Removal: A Review. Catalysts 2021, 11, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Jiang, M.; Zhao, G.S.; Wei, L.L.; Wang, S.N.; Zhao, Q.L. Treatment of leachate concentrate by electrocoagulation coupled with electro-Fenton-like process: Efficacy and mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 255, 117668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matira, E.M.; Chen, T.C.; Lu, M.C.; Dalida, M.L.P. Degradation of dimethyl sulfoxide through fluidized-bed Fenton process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 300, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimi, S.M.; Al-Musawi, T.J.; Arghavan, F.S.; Nasseh, N. Mechanism and efficiency of metronidazole removal via adsorption and heterogeneous Fenton reaction using FeNi3 nanoparticles. Desalination Water Treat. 2021, 234, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.T.; Tu, C.H.; Lin, Y.S. Application of Graphene and Carbon Nanotubes on Carbon Felt Electrodes for the Electro-Fenton System. Materials 2019, 12, 1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oliveira, W.L.; Ferreira, M.A.; Mourao, H.; Pires, M.J.M.; Ferreira, V.; Gorgulho, H.F.; Cipriano, D.F.; Freitas, J.C.C.; Mastelaro, V.R.; Nascimento, O.R.; et al. Heterogeneous Fenton-like surface properties of oxygenated graphitic carbon nitride. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 587, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.C.; Pedroza, A.M.; Daza, C.E. Magnetic Fenton and Photo-Fenton-Like Catalysts Supported on Carbon Nanotubes for Wastewater Treatment. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, V.; Bingham, J.P.; Kan, E. Heterogeneous Fenton degradation of bisphenol A by carbon nanotube-supported Fe3O4. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 133, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bury, N.A.; Mumford, K.A.; Stevens, G.W. The electro-Fenton regeneration of Granular Activated Carbons: Degradation of organic contaminants and the relationship to the carbon surface. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.H.; Wu, X.F.; Li, S.D.; Tang, W.; Chen, Y.F. Magnetic porous Fe3O4/carbon octahedra derived from iron-based metal-organic framework as heterogeneous Fenton-like catalyst. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 436, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minella, M.; Bertinetti, S.; Hanna, K.; Minero, C.; Vione, D. Degradation of ibuprofen and phenol with a Fenton-like process triggered by zero-valent iron (ZVI-Fenton). Environ. Res. 2019, 179, 108750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos, N.O.; Teixeira, L.A.C.; Spadotto, J.C.; Campos, L.C. A simple ZVI-Fenton pre-oxidation using steel-nails for NOM degradation in water treatment. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 43, 102230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donadelli, J.A.; Caram, B.; Kalaboka, M.; Kapsi, M.; Sakkas, V.A.; Carlos, L.; Einschlag, F.S.G. Mechanisms of 4-phenylazophenol elimination in micro- and nano-ZVI assisted-Fenton systems. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.H.; Tang, C.L.; Zeng, H. Removing molybdate from water using a hybridized zero-valent iron/magnetite/Fe(II) treatment system. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 200, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, Z.X.; Belver, C.; Gao, G.L.; Guan, J.; Guo, Y.G.; Li, H.; Ma, J.; Bedia, J.; Wojtowicz, P. Comparison of the behavior of ZVI/carbon composites from both commercial origin and from spent Li-ion batteries and mill scale for the removal of ibuprofen in water. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 264, 110480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.F.; Dai, M.; Naz, I.; Hao, X.Y.; Wei, X.X.; Rong, R.; Peng, C.S.; Ali, I. Carbothermal reduction synthesis of zero-valent iron and its application as a persulfate activator for ciprofloxacin degradation. Sep. Purif.Technol. 2021, 275, 119201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Aneggi, E.; Goi, D.; Trovarelli, A. Bimetallic Cu/Fe Catalysts for Ibuprofen Mineralization. Catalysts 2021, 11, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.C.; Li, X.H.; Han, J.D.; Meng, F.S.; Jiang, J.Y.; Li, J.; Xu, C.L.; Li, Y. Mesoporous bimetallic Fe/Co as highly active heterogeneous Fenton catalyst for the degradation of tetracycline hydrochlorides. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.F.; Liu, W.P.; Ma, J.Q.; Wen, Y.Z.; Wu, Z.C. High catalytic activity of magnetic FeOx/NiOy/SBA-15: The role of Ni in the bimetallic oxides at the nanometer level. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 179, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oruc, Z.; Ergut, M.; Uzunoglu, D.; Ozer, A. Green synthesis of biomass-derived activated carbon/Fe-Zn bimetallic nanoparticles from lemon (Citrus limon (L.) Burm. f.) wastes for heterogeneous Fenton-like decolorization of Reactive Red 2. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, B.L.C.; Parpot, P.; Soares, O.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Rombi, E.; Fonseca, A.M.; Neves, I.C. Fenton-Type Bimetallic Catalysts for Degradation of Dyes in Aqueous Solutions. Catalysts 2021, 11, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Liu, M.; Li, K.; Han, Y.; Zuo, Y.; Chai, F.; Song, C.; Zhang, G.; Guo, X. Synthesis of Fe/M (M = Mn, Co, Ni) bimetallic metal organic frameworks and their catalytic activity for phenol degradation under mild conditions. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2017, 4, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, J.; Sun, S.P. Mn2+-mediated homogeneous Fenton-like reaction of Fe(III)-NTA complex for efficient degradation of organic contaminants under neutral conditions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 313, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Deng, Y.; Ai, J.; Li, L.; Liao, G.; Xu, S.; Wang, D.; Zhang, W. Fe/Mn loaded sludge-based carbon materials catalyzed oxidation for antibiotic degradation: Persulfate vs H2O2 as oxidant. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 263, 118409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peleyeju, M.G.; Mgedle, N.; Viljoen, E.L.; Scurrel, M.S.; Ray, S.C. Irradiation of Fe–Mn@SiO2 with microwave energy enhanced its Fenton-like catalytic activity for the degradation of methylene blue. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2021, 47, 4213–4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xin, C.; Shi, C.; Dong, A.; Wang, K. Simple Preparation of Spherical Activated Carbon with Mesoporous Structure from Phenolic Resol and Associated Catalytic Performance in Isobutane Dehydrogenation. Trans. Tianjin Univ. 2018, 24, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pani, S.; Singh, S.K.; Mohapatra, B.K. Synthesis and Characterization of MnO Nano-particles Using Thermal Plasma Technique. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2019, 72, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadzic, B.; Vasic, B.; Matovic, B.; Kuryliszyn-Kudelska, I.; Dobrowolski, W.; Romcevic, M.; Romcevic, N. Influence of laser-induced heating on MnO nanoparticles. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2018, 49, 817–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.J.; Han, P.X.; Gu, L.; Zhang, L.X.; Liu, Z.H.; Kong, Q.S.; Zhang, C.J.; Dong, S.M.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Yao, J.H.; et al. Synthesis of Nitrogen-Doped MnO/Graphene Nanosheets Hybrid Material for Lithium Ion Batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 658–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sewwandi, K.A.H.S.; Nitisoravut, R. Nano zero valent iron embedded on chitosan for enhancement of biohydrogen production in dark fermentation. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 392–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.P.; Li, X.Q.; Cao, J.; Zhang, W.X.; Wang, H.P. Characterization of zero-valent iron nanoparticles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 120, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Xu, J.; Zhang, M.; Lin, D. Re-recognizing micro locations of nanoscale zero-valent iron in biochar using C-TEM technique. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, B.K.; Shahi, A.K.; Gopal, R. Synthesis, optical properties and growth mechanism of MnO nano structures. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 283, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, Y.; Martínez, F.; Melero, J.A.; Fierro, J.L.G. Zero valent iron (ZVI) mediated Fenton degradation of industrial wastewater: Treatment performance and characterization of final composites. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 269, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, A.C.; Nanda, B.; Parida, K.M.; Rao, G.R. Fabrication of the Mesoporous Fe@MnO2NPs-MCM-41 Nanocomposite: An Efficient Photocatalyst for Rapid Degradation of Phenolic Compounds. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 14145–14159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.Q.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, Z.K.; Xu, H.; Wang, H.; Hu, K.; Yan, K. Remarkably enhanced sulfate radical-based photo-Fenton-like degradation of levofloxacin using the reduced mesoporous MnO@MnOx microspheres. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 379, 122340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xiao, B.; Liu, S.Q.; Meng, Z.D.; Chen, Z.G.; Zou, C.Y.; Liu, C.B.; Chen, F.; Zhou, X. Photo-Fenton degradation of ammonia via a manganese-iron double-active component catalyst of graphene-manganese ferrite under visible light. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 283, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niveditha, S.V.; Gandhimathi, R. Flyash augmented Fe3O4 as a heterogeneous catalyst for degradation of stabilized landfill leachate in Fenton process. Chemosphere 2020, 242, 125189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, S.; Keswani, M.; Brooks, B.; Fuerst, A.; Raghavan, S. A study of hydrogen peroxide decomposition in ammonia-peroxide mixtures (APM). Microelectron. Eng. 2013, 102, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Yang, M.X.; Yu, F.; Chen, J.H. Easy solid-phase synthesis of pH-insensitive heterogeneous CNTs/FeS Fenton-like catalyst for the removal of antibiotics from aqueous solution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 444, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.K.; Yao, Z.P.; Yang, M.; Wang, Y.J.; Xia, Q.X.; Jiang, Z.H. A Fe3O4/FeAl2O4 composite coating via plasma electrolytic oxidation on Q235 carbon steel for Fenton-like degradation of phenol. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 14927–14936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.L.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.G.; Yang, L.P.; Zhi, K.K.; Wang, L.L.; Zhang, L.T.; Guo, X.F. Unveiling the mechanism of electron transfer facilitated regeneration of active Fe2+ by nano-dispersed iron/graphene catalyst for phenol removal. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 26983–26991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, Q.X.; Jiang, Z.H.; Wang, J.K.; Yao, Z.P. A facile preparation of hierarchical dendritic zero-valent iron for Fenton-like degradation of phenol. Catal. Commun. 2017, 100, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.M.; Song, J.; Han, X. Schwertmannite as a new Fenton-like catalyst in the oxidation of phenol by H2O2. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 262, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.X.; Zhang, D.J.; Yao, Z.P.; Jiang, Z.H. Revealing the enhancing mechanisms of Fe-Cu bimetallic catalysts for the Fenton-like degradation of phenol. Chemosphere 2022, 289, 133195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.J.; Tian, P.F.; Zhang, X.M.; Yu, X.; Wu, T.; Xu, J.; Han, Y.F. The Generation of Hydroxyl Radicals by Hydrogen Peroxide Decomposition on FeOCl/SBA-15 Catalysts for Phenol Degradation. AlChE J. 2015, 61, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, J.K.; Yao, Z.P.; Chen, C.J.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, Z.H. Synthesis of the SO42−-Fe3O4/FeS coating catalyst on a TC4 titanium alloy for the enhanced Fenton-like degradation of phenol. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 1516–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, J.; Qi, J.; Wang, J.; Luo, R.; Shen, J.; Sun, X.; Han, W.; Wang, L. Yolk-shell Fe0@SiO2 nanoparticles as nanoreactors for fenton-like catalytic reaction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 13167–13173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panjwani, M.K.; Wang, Q.; Ma, Y.; Lin, Y.; Xiao, F.; Yang, S. High degradation efficiency of sulfamethazine with the dual-reaction-center Fe–Mn–SiO2 Fenton-like nanocatalyst in a wide pH range. Environ. Sci. Nano 2021, 8, 2204–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Chen, X.J.; Hao, M.J.; Xiao, F.; Yang, S.X. Oxygen vacancy enhancing the Fe2O3-CeO2 catalysts in Fenton-like reaction for the sulfamerazine degradation under O2 atmosphere. Chemosphere 2019, 228, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, M.A.; Puente Santiago, A.R.; Rodriguez, A.; Maturano-Rojas, V.; Alvarado-Tenorio, B.; Bernal, R.; Noveron, J.C. Biomass-derived ultrathin carbon-shell coated iron nanoparticles as high-performance tri-functional HER, ORR and Fenton-like catalysts. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 275, 124141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aramyan, S.M. Advances in Fenton and Fenton Based Oxidation Processes for Industrial Effluent Contaminants Control-A Review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Nat. Resour. 2017, 2, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, J.; Yang, X.; Men, B.; Wang, D. Interfacial mechanisms of heterogeneous Fenton reactions catalyzed by iron-based materials: A review. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 39, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosales, E.; Sanromán, M.Á.; Dias-Ferreira, C. Green zero-valent iron nanoparticles synthesized using herbal extracts for degradation of dyes from wastewater. Desalination Water Treat. 2017, 92, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raman, C.D.; Kanmani, S. Textile dye degradation using nano zero valent iron: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 177, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Tang, J. Fe-based Fenton-like catalysts for water treatment: Catalytic mechanisms and applications. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 332, 115755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigg, T.; Taylor, W.; Weiss, J. The Rate Constant of the Reaction between Hydrogen Peroxide and Ferrous Ions. J. Chem. Phys. 1954, 22, 575–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Li, Y.; Ji, J.; Wong, F.-S.; Lu, X. Oxidation of 4-chlorophenol in a heterogeneous zero valent iron/H2O2 Fenton-like system: Kinetic, pathway and effect factors. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 62, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baral, S.; Lume-Pereira, C.; Janata, E.; Henglein, A. Chemistry of colloidal manganese dioxide. 2. Reaction with superoxide anion (O2−) and hydrogen peroxide (pulse radiolysis and stop flow studies). J. Phys. Chem. 1985, 89, 5779–5783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Sample | ZVI-C | ZVI/Mn-C-31 | ZVI/Mn-C-11 | ZVI/Mn-C-13 | Mn-C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical strength (N·bead−1) | 6.5 | 12.3 | 17.5 | 13.3 | 8.9 |
| Average pore diameter (nm) | 3.409 | 3.399 | 3.855 | 4.154 | 4.144 |
| Catalysts | Operating Conditions | Performance | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZVI/Mn-C-31 | [Catalyst] = 2 g/L; [H2O2] = 0.2 M; [phenol] = 1 g/L, pH = 7.0; room temperature | Phenol removal: 100% (10 min) COD removal: 64% (240 min) | this work |
| Fe/Mn-MOF-71 | [Catalyst]: 0.064 g/L; [H2O2]: 0.15 M; [Phenol]: 1 g/L; pH: 6.2; T: 35 °C | Phenol removal: 100% (120 min) COD removal: 43% (180 min) | [34] |
| Fe8O8(OH)4.5(SO4)1.75 | [Catalyst]: 1 g/L; [H2O2]: 14.70 mM; [Phenol]: 100 mg/L; pH: 3.0; room temperature | Phenol removal: 100% (30 min) TOC removal: 85% (300 min) | [56] |
| FeCu | [Catalyst]: 100 mg/L; [H2O2]: 6 M; [Phenol]: 35 mg/L; pH: 4.0; room temperature | Phenol removal: 100% (30 min) | [57] |
| Fe3O4/FeAl2O4 | PEO coating; [Catalyst]:35 mg/L; [H2O2]:6.0 mM; [Phenol]: 35 mg/L; pH: 4.0; T: 30 °C | Phenol removal: 100% (50 min) | [53] |
| Fe0/Fe3O4-RGO | [Catalyst]: 1 g/L; [H2O2]: 5.0 mM; [Phenol]: 50 mg/L; pH: 3.0; T: 25 °C | Phenol removal: 100% (30 min) | [54] |
| Dendritic Fe0 | [Catalyst]: 100 mg/L; [H2O2]: 6.0 mM; [Phenol]: 35 mg/L; pH: 4.0; T: 30 °C | Phenol removal: 90% (15 min) | [55] |
| FeOCl/SBA-15 | [Catalyst]: 200 mg/L; [H2O2]: 14.70 mM; [Phenol]: 100 mg/L; pH: 4.5; T: 40 °C | Phenol removal: 100% (15 min) | [58] |
| SO42−Fe3O4/FeS | TC4 coating; [Catalyst]: 20 g/L; [H2O2]: 6.0 mM; [Phenol]: 35 ppm; pH: 7.0; T: 30 °C | Phenol removal: 100% (3 min) | [59] |
| Fe0 @SiO2 | [Catalyst]: 1.08 g L−1; [H2O2]: 120 mM; [Phenol]: 100 ppm; pH: 5.6; T: 60 °C | Phenol removal: 99.9% (45 min); TOC removal: 81% (60 min) | [60] |
| Sample | c(Fe3+)/mol·L−1 | c(Mn2+)/mol·L−1 | c(Fe3+)/c(Mn2+) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZVI-C | 0.40 | 0 | - |
| ZVI/Mn-C-31 | 0.30 | 0.10 | 3:1 |
| ZVI/Mn-C-11 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 1:1 |
| ZVI/Mn-C-13 | 0.10 | 0.30 | 1:3 |
| Mn-C | 0 | 0.40 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, L.; Yu, X.; Wang, K.; Wang, X. Spherical ZVI/Mn-C Bimetallic Catalysts for Efficient Fenton-like Reaction under Mild Conditions. Catalysts 2022, 12, 444. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12040444
Qin L, Yu X, Wang K, Wang X. Spherical ZVI/Mn-C Bimetallic Catalysts for Efficient Fenton-like Reaction under Mild Conditions. Catalysts. 2022; 12(4):444. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12040444
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Lu, Xin Yu, Kang Wang, and Xitao Wang. 2022. "Spherical ZVI/Mn-C Bimetallic Catalysts for Efficient Fenton-like Reaction under Mild Conditions" Catalysts 12, no. 4: 444. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12040444
APA StyleQin, L., Yu, X., Wang, K., & Wang, X. (2022). Spherical ZVI/Mn-C Bimetallic Catalysts for Efficient Fenton-like Reaction under Mild Conditions. Catalysts, 12(4), 444. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12040444