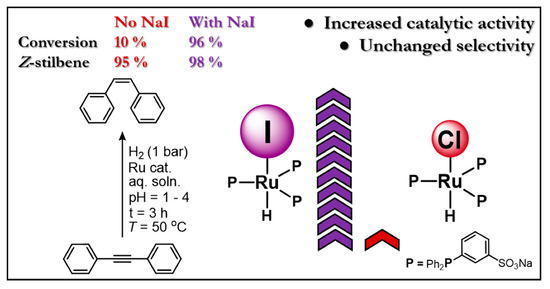
Effect of Iodide on the pH-Controlled Hydrogenations of Diphenylacetylene and Cinnamaldehyde Catalyzed by Ru(II)-Sulfonated Triphenylphosphine Complexes in Aqueous–Organic Biphasic Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kluwer, A.M.; Elsevier, C.J. Homogeneous Hydrogenation of Alkynes and Dienes. In Handbook of Homogeneous Hydrogenation; de Vries, J.G., Elsevier, C.J., Eds.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2007; Volume 1, pp. 375–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaloner, P.A.; Esteruelas, M.A.; Joó, F.; Oro, L.A. Homogeneous Hydrogenation; Kluwer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1994; pp. 5–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wienhöfer, G.; Westerhaus, F.Á.; Jagadeesh, R.V.; Junge, K.; Junge, H.; Beller, M. Selective iron-catalyzed transfer hydrogenation of terminal alkynes. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 4827–4829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swamy, K.C.K.; Reddy, A.S.; Sandeep, K.; Kalyani, A. Advances of chemoselective and/or stereoselective semihydrogenation of alkynes. Tetrahedron Lett. 2018, 50, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decker, D.; Drexler, H.-J.; Heller, D.; Beveries, T. Homogeneous catalytic transfer semihydrogenation of alkynes—An overview of hydrogen sources, catalysts and reaction mechanisms. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2020, 10, 6449–6463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Leng, X.; Huang, Z. An Amine-Assisted Ionic Monohydride Mechanism Enables Selective Alkyne cis-Semihydrogenation with Ethanol: From Elementary Steps to Catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 4824–4836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joó, F.; Kathó, Á. Two-Phase Aqueous Hydrogenations. In Handbook of Homogeneous Hydrogenation; de Vries, J.G., Elsevier, C.J., Eds.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2007; Volume 3, pp. 1327–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbe, M.; Budweg, S.; Papa, V.; Wei, Z.; Hornke, H.; Bachmann, S.; Scalone, M.; Spannenberg, A.; Jiao, H.; Junge, K. Chemoselective Semihydrogenation of Alkynes Catalyzed by Manganese(I)-PNP Pincer Complexes. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2020, 10, 3994–4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Both, N.F.; Spannenberg, A.; Junge, K.; Beller, M. Low-Valent Molybdenum PNP Pincer Complexes as Catalysts for the Semihydrogenation of Alkynes. Organometallics 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiel, N.O.; Teichert, J.F. Stereoselective alkyne semihydrogenations with an air-stable copper(I) catalyst. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 10660–10666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharma, D.M.; Gouda, C.; Gonnade, R.G.; Punji, B. Room temperature Z-selective hydrogenation of alkynes by hemilabile and non-innocent (NNN)Co(ii) catalysts. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2022, 12, 1843–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubar, V.; Sklyaruk, J.; Brzozowska, A.; Rueping, M. Chemoselective Hydrogenation of Alkynes to (Z)-Alkenes Using an Air-Stable Base Metal Catalyst. Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 5423–5428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekebergh, A.; Begon, R.; Kann, N. Ruthenium-Catalyzed E-Selective Alkyne Semihydrogenation with Alcohols as Hydrogen Donors. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 85, 2966–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yadav, S.; Dutta, I.; Saha, S.; Das, S.; Pati, S.K.; Choudhury, J.; Bera, J.K. An Annelated Mesoionic Carbene (MIC) Based Ru(II) Catalyst for Chemo- and Stereoselective Semihydrogenation of Internal and Terminal Alkynes. Organometallics 2020, 39, 3212–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetzer, M.N.A.; Tavakoli, G.; Klein, A.; Prechtl, M.H.G. Ruthenium-Catalyzed E-Selective Partial Hydrogenation of Alkynes under Transfer-Hydrogenation Conditions using Paraformaldehyde as Hydrogen Source. ChemCatChem 2021, 13, 1317–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, D.J.; Ferguson, M.J.; Turculet, L. (PSiP)Ni-Catalyzed (E)-Selective Semihydrogenation of Alkynes with Molecular Hydrogen. ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrar-Tobar, R.A.; Weber, S.; Csendes, Z.; Ammaturo, A.; Fleissner, S.; Hoffmann, H.; Veiros, L.F.; Kirchner, K. E-Selective Manganese-Catalyzed Semi hydrogenation of Alkynes with H2 Directly Employed or In Situ-Generated. ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 2253–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, R.; Chen, T.; Zhao, Y.; Qiu, R.; Zhou, Y.; Yin, S.; Wang, X.; Goto, M.; Han, L.B. Facile Regio- and Stereoselective Hydrometalation of Alkynes with a Combination of Carboxylic Acids and Group 10 Transition Metal Complexes: Selective Hydrogenation of Alkynes with Formic Acid. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 17037–17044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Shao, Z.; Luo, S.P.; Liu, Q. Ligand-Controlled Cobalt-Catalyzed Transfer Hydrogenation of Alkynes: Stereodivergent Synthesis of Z- and E-Alkenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 8588–8594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.; Pan, C.; Wang, W.; Ye, Z.; Cheng, J. Palladium-catalyzed reduction of alkynes employing HSiEt3: Stereoselective synthesis of trans- and cis-alkenes. Tetrahedron 2010, 66, 1399–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richmond, E.; Moran, J. Ligand Control of E/Z Selectivity in Nickel-Catalyzed Transfer Hydrogenative Alkyne Semireduction. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 6922–6929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Zhu, H.; Li, Y.; Peng, Q.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X. Dinuclear Cobalt Complex-Catalyzed Stereodivergent Semireduction of Alkynes: Switchable Selectivities Controlled by H2O. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 13696–13705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokmic, K.; Fout, A.R. Alkyne Semihydrogenation with a Well Defined Nonclassical Co-H2 Catalyst: A H2 Spin on Isomerization and E-selectivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 13700–13705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horváth, H.H.; Joó, F. Stereoselective homogeneous catalytic hydrogenation of disubstituted alkynes in aqueous-organic biphasic media. React. Kinet. Catal. Lett. 2005, 85, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.X.; Merola, J.S. Synthesis and Reaction Chemistry of Water-Soluble mer-(Me3P)3Ir(H)(H)Cl: Activation by Water of Alkyne Insertion into an Ir-H Bond. Organometallics 1993, 12, 3798–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bényei, A.; Joó, F. Organometallic catalysis in aqueous solutions: The biphasic transfer hydrogenation of aldehydes catalyzed by water-soluble phosphine complexes of ruthenium, rhodium and iridium. J. Mol. Catal. 1990, 58, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosselin, J.M.; Mercier, C.; Allmang, G.; Grass, F. Selective Hydrogenations of α,β-Unsaturated Aldehydes in Aqueous-Organic Two-Phase Solvent System Using Ruthenium or Rhodium Complexes of Sulfonated Phosphines. Organometallics 1991, 10, 2126–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Delgado, R.A.; Medina, M.; López-Linares, F.; Fuentes, A. The chemistry and catalytic properties of ruthenium and osmium compounds. Part 7. Regioselective hydrogenation of cinnamaldehyde (3-phenyl-2-propenal) catalyzed by Ru and Os triphenylphosphine complexes in homogeneous solution and by meta-sulfonatophenyl-diphenyldiphosphine (TPPMS) and tris-meta-sulfonato-phenylphosphine (TPPTS) derivatives in an aqueous biphasic system. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 1997, 116, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Linares, F.; Gonzalez, M.G.; Paez, D.E. The regioselective biphasic hydrogenation of trans-cinnaldehyde by meta sulfonatophenyl-diphenylphosphine (TPPMS) Ru(II) and Os(II) species. The influence of ionic strength, ligand tensoactivity and metal nature in the selective production of the unsaturated alcohol. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 1999, 145, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joó, F.; Kovács, J.; Bényei, A.C.; Kathó, Á. Solution pH: A Selectivity Switch in Aqueous Organometallic Catalysis—Hydrogenation of Unsaturated Aldehydes Catalyzed by Sulfonatophenylphosphane—Ru Complexes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1998, 37, 969–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joó, F.; Kovács, J.; Bényei, A.C.; Kathó, Á. The effects of pH on the molecular distribution of water soluble ruthenium(II) hydrides and its consequences on the selectivity of the catalytic hydrogenation of unsaturated aldehydes. Catal. Today 1998, 42, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp, G.; Horváth, H.; Laurenczy, G.; Szatmári, I.; Kathó, Á.; Joó, F. Classical and non-classical phosphine-Ru(II)-hydrides in aqueous solutions: Many, various, and useful. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fache, E.; Santini, C.; Senocq, F.; Basset, J.M. Homogeneous catalysis in water Part III. The catalytic hydrogenation of propionaldehyde with (RuCl2L2)2, RuHClL3, RuH(OAc)L3, RuH2L4, RuHlL3, RuCl2(CO)2L2 and [Ru(OAc)(CO)2L]2, (L = P(C6H4-mSO3Na)3. 3H2O): A kinetic investigation of the salt effect in water. J. Mol. Catal. 1992, 72, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fache, E.; Santini, C.; Senocq, F.; Basset, J.M. Homogeneous catalysis in water Part II. Synthesis and characterization of ruthenium water-soluble complexes. J. Mol. Catal. 1992, 72, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, J. Ions in Solution; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 1999; pp. 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, Z.; Joó, F.; Beck, M.T. Homogeneous Hydrogenations in Aqueous Solutions Catalyzed by Ruthenium-Phosphine Complexes. Inorg. Chim. Acta 1980, 42, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubas, G.J.; Burns, C.J.; Khaisha, G.R.K.; Van Der Sluys, L.S.; Kiss, G.; Hoff, C.D. Dihydrogen: A Better Ligand Than Water? IR and X-Ray Evidence for Aquo Coordination in W(CO)3(PR3)2(H2O), Thermodynamics of H2O versus η2-H2 Binding, and H2O/D2 Isotopic Exchange. Implications on the Biological Activation of Hydrogen. Organometallics 1992, 11, 3390–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joó, F.; Kovács, J.; Kathó, Á.; Bényei, A.C.; Decuir, T.; Darensbourg, D.J. (Meta-Sulfonatophenyl)diphenylphosphine sodium salt and its complexes with rhodium(I), ruthenium(II) and iridium(I). Inorg. Synth. 1998, 32, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagnou, K.; Lautens, M. Halide Effects in Transition Metal Catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 26–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kathó, Á.; Horváth, H.H.; Papp, G.; Joó, F. Effect of Iodide on the pH-Controlled Hydrogenations of Diphenylacetylene and Cinnamaldehyde Catalyzed by Ru(II)-Sulfonated Triphenylphosphine Complexes in Aqueous–Organic Biphasic Systems. Catalysts 2022, 12, 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12050518
Kathó Á, Horváth HH, Papp G, Joó F. Effect of Iodide on the pH-Controlled Hydrogenations of Diphenylacetylene and Cinnamaldehyde Catalyzed by Ru(II)-Sulfonated Triphenylphosphine Complexes in Aqueous–Organic Biphasic Systems. Catalysts. 2022; 12(5):518. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12050518
Chicago/Turabian StyleKathó, Ágnes, Henrietta H. Horváth, Gábor Papp, and Ferenc Joó. 2022. "Effect of Iodide on the pH-Controlled Hydrogenations of Diphenylacetylene and Cinnamaldehyde Catalyzed by Ru(II)-Sulfonated Triphenylphosphine Complexes in Aqueous–Organic Biphasic Systems" Catalysts 12, no. 5: 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12050518
APA StyleKathó, Á., Horváth, H. H., Papp, G., & Joó, F. (2022). Effect of Iodide on the pH-Controlled Hydrogenations of Diphenylacetylene and Cinnamaldehyde Catalyzed by Ru(II)-Sulfonated Triphenylphosphine Complexes in Aqueous–Organic Biphasic Systems. Catalysts, 12(5), 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12050518