Degradation of Rhodamine B in Wastewater by Iron-Loaded Attapulgite Particle Heterogeneous Fenton Catalyst
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Catalyst Characterization
2.1.1. BET and EDS Analysis of Catalyst
2.1.2. SEM Analysis of Catalyst
2.2. Influence of Reaction Conditions on Degradation Performance
2.2.1. Influence of Different Reaction Systems on RhB Degradation
2.2.2. Influence of RhB Initial Concentration
2.2.3. Influence of Different H2O2 Concentrations
2.2.4. Influence of Different Catalyst Dosages
2.2.5. Influence of Initial pH Value
2.2.6. Influence of Temperature on Degradation of Rhodamine B
2.3. Study on Sustainability and Stability of the Granular Catalyst
2.4. Study on the Degradation Effect of Different Dyes by the Granular Catalyst
2.5. Dynamic Study on the Catalytic Degradation Process of the Granular Catalyst
2.5.1. Dynamic UV-VIS Spectra of RhB during the Reaction Process
2.5.2. Determination of Active Substances in the Reaction Process
2.5.3. Formation Rule of Hydroxyl Radical (•OH)
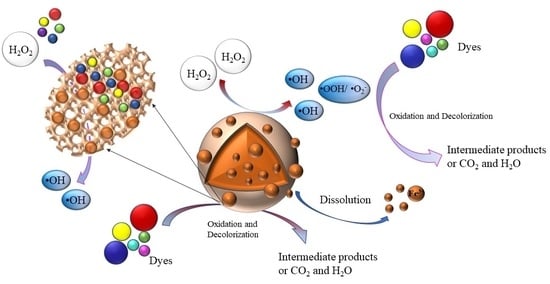
2.6. Speculation on the Mechanism of Catalytic Oxidation of RhB Dye by the Granular Catalyst
3. Experimental Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Materials
3.2. Preparation and Characterization of Catalyst
3.3. Instruments and Analytical Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosales, E.; Pazos, M.; Sanroman, M. Advances in the Electro-Fenton Process for Remediation of Recalcitrant Organic Compounds. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2012, 35, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ran, X.; Wu, X.; Zhang, D. Evaluation of electro-oxidation of biologically treated landfill leachate using response surface inversely proportional to the concentration of methodology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 188, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez-Sosa, D.R.; Castillo-Borges, E.R.; Mendez-Novelo, R.I.; Sauri-Riancho, M.R.; Barcelo-Quintal, M.; Marrufo-Gomez, J.M. Determination of organic compounds in landfill leachates treated by Fenton-Adsorption. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.; Bai, L.; Tan, Y.; Li, L.; Song, F.; Wang, Y. β-cyclodextrin-Crosslinked polymeric adsorbent for simultaneous removal and stepwise recovery of organic dyes and heavy metal ions: Fabrication, performance and mechanisms. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 372, 1007–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Chen, G.; Zeng, G.; Chen, A.; Huang, Z.; Shi, J.; Huang, T.; Peng, M.; Hu, L. Three-dimensional graphene supported catalysts for organic dyes degradation. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2018, 228, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, M.A.H.; Aziz, K.H.H.; Omer, K.M.; Salih, Y.M.; Mustafa, F.; Rahman, K.O.; Mohammad, Y. Degradation of aqueous organic dye pollutants by heterogeneous photo-assisted Fenton-like process using natural mineral activator: Parameter optimization and degradation kinetics. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 958, 012011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, T.S.; Thomas, M.; Natarajan, K.; Bajaj, H.C.; Tayade, R.J. Study on UV-LED/TiO2 process for degradation of Rhodamine B dye. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 169, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, S.; Li, M.; Wang, D.; Ju, X.; Fu, S. Cyano and acylamino group modification for tannery sludge bio-char: Enhancement of adsorption universality for dye pollutants. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tian, J.; Li, Y.; Sun, N.; Mi, S.; Xie, Y.; Chen, Z. Enhanced dyes adsorption from wastewater via Fe3O4 nanoparticles functionalized activated carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 373, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasana, M.M.; Hasan, M.N.; Awual, M.R.; Islam, M.M.; Shenashen, M.A.; Iqbal, J. Biodegradable natural carbohydrate polymeric sustainable adsorbents for efficient toxic dye removal from wastewater. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 319, 114356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhang, H.; Chen, L. A novel Pd decorated polydopamine-SiO2/PVA electrospun nanofiber membrane for highly efficient degradation of organic dyes and removal of organic chemicals and oils. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 275, 122937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, A.; Datta, D. Application of Amberlite XAD-7HP resin impregnated with Aliquat 336 for the removal of Reactive Blue-13 dye: Batch and fixed-bed column studies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel-Hassemer, M.E.; Carvalho-pinto, C.R.S.; Matias, W.G.; Lapolli, F.R. Removal of coloured compounds from textile industry effluents by UV/H2O2 advanced oxidation and toxicity evaluation. Environ. Technol. 2011, 32, 1867–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, K.H.H.; Mahyar, A.; Miessner, H.; Mueller, S.; Kalass, D.; Moeller, D.; Khorshid, I.M.; Rashid, M.A. Application of a planar falling fifilm reactor for decomposition and mineralization of methylene blue in the aqueous media via ozonation, Fenton, photocatalysis and non-thermal plasma: A comparative study. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 113, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, R.; Qazi, U.Y.; Kawasaki, S.I. Highly effificient decomposition of Remazol Brilliant Blue R using tubular reactor coated with thin layer of PdO. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 180, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanikya, P.; Nidheesh, P.V.; Babu, D.S.; Gopinath, A.; Kumar, M.S. Treatment of dyeing wastewater by combined sulfate radical based electrochemical advanced oxidation and electrocoagulation processes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 254, 117570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Yang, H.; Huang, J.W.; Tong, J.; Liu, X.Y.; Wang, Y.W.; Qiao, W.C.; Han, J.G. Theoretical and experimental insight into plasma-catalytic degradation of aqueous p-nitrophenol with graphene-ZnO nanoparticles. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 295, 121362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.W.; Huang, W.J.; Guo, H.; Puyang, C.D.; Han, J.G.; Li, Y.; Ruan, Y.X. Mechanism and process of sulfamethoxazole decomposition with persulfate activated by pulse dielectric barrier discharge plasma. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 287, 120540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Xu, X.; Fan, Y.; Xiao, C.; Ma, C. Pretreatment of water-based seed coating wastewater by combined coagulation and sponge-iron-catalyzed ozonation technology. Chemosphere 2018, 206, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.; Jing, X.; Ding, X.; Shen, Y.; Xu, S.; Miao, W. Synergistic effects of photocatalytic and electrocatalytic oxidation based on a three-dimensional electrode reactor toward degradation of dyes in wastewater. J. Alloy Compd. 2019, 809, 151749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Xu, Q.; Wei, R.; Ma, J.; Wang, Y. Mechanism and dynamic study of reactive red X-3B dye degradation by ultrasonic-assisted ozone oxidation process. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 38, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulca, O.; Palas, B.; Atalay, S.; Ersoz, G. Performance investigation of the hybrid methods of adsorption or catalytic wet air oxidation subsequent to electrocoagulation in treatment of real textile wastewater and kinetic modelling. J. Water Process. Eng. 2021, 40, 101821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreeja, P.H.; Sosamony, K.J. A Comparative Study of Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Photo-Fenton Process for Textile Wastewater Treatment. Procedia Technol. 2016, 24, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Tang, J. Fe-based Fenton-like catalysts for water treatment: Preparation, characterization and modification. Chemosphere 2021, 276, 130177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arimi, M.M. Modified natural zeolite as heterogeneous Fenton catalyst in treatment of recalcitrants in industrial effluent. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2017, 27, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Olono, J.T.; Infantes-Molina, A.; Vargas-Hernandez, D.; Dominguez-Talamantes, D.G.; Rodriguez-Castellon, E.; Herrera-Urbina, J.R.; Tanori-Cordova, J.C. A novel heterogeneous photo-Fenton Fe/Al2O3 catalyst for dye degradation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2021, 421, 113529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khataee, A.; Salahpour, F.; Fathinia, M.; Seyyedi, B.; Vahid, B. Iron rich laterite soil with mesoporous structure for heterogeneous Fenton-like degradation of an azo dye under visible light. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 26, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Miao, K.; Luo, X.; Guo, S.; Yuan, X.; Pei, F.; Qian, H.M.; Feng, G. Efficient Fenton-like treatment of high-concentration chlorophenol wastewater catalysed by Cu-Doped SBA-15 mesoporous silica. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 318, 128632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Guo, X.; Tang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, T. Magnetic Mn-Doped Fe3O4 hollow Microsphere/RGO heterogeneous Photo-Fenton Catalyst for high efficiency degradation of organic pollutant at neutral pH. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 238, 121893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Gou, L.; Tang, S.; Cheng, F.; Zhang, M.; Guo, M. Enhanced heterogeneous Fenton-like degradation of refractory organic contaminants over Cu doped (Mg,Ni)(Fe,Al)2O4 synthesized from laterite nickel ore. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 283, 111941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suligoj, A.; Ristic, A.; Drazic, G.; Pintar, A.; Logar, N.Z.; Tusar, N.N. Bimetal Cu-Mn porous silica-supported catalyst for Fenton-like degradation of organic dyes in wastewater at neutral pH. Catal. Today 2020, 358, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, R.; Kurosu, S.; Suzuki, M.; Kawase, Y. Hydroxyl radical generation by zero-valent iron/Cu (ZVI/Cu) bimetallic catalyst in wastewater treatment: Heterogeneous Fenton/Fenton-like reactions by Fenton reagents formed in-situ under oxic conditions. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 1537–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, R.G.L.; Mendes, H.M.; Bastos, S.L.; Dagostino, L.C.; Tronto, J.; Pulcinelli, S.H.; Santilli, C.V. Fenton-like degradation of methylene blue using Mg/Fe and MnMg/Fe layered double hydroxides as reusable catalysts. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 187, 105477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Kong, M. Simultaneous removal of ammonium and phosphate from eutrophic waters using natural calcium-rich attapulgite-based versatile adsorbent. Desalination 2014, 351, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, W.; Wang, A. Highly effective removal of Methylene Blue using functionalized attapulgite via hydrothermal process. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 33, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Shao, G.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, Z. CuO catalysts supported on attapulgite clay for low-temperature CO oxidation. Catal. Commun. 2008, 9, 2555–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, M.; Liang, T.; Yang, Z.; Yang, J.; Liu, S. Hydrogen Generation from Catalytic Steam Reforming of Acetic Acid by Ni/Attapulgite Catalysts. Catalysts 2016, 6, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, H.; Sun, K.; Li, Y.; Xu, X. Ultra-chemoselective hydrogenation of chloronitrobenzenes to chloroanilines over HCl-acidified attapulgite-supported platinum catalyst with high activity. Catal. Commun. 2009, 10, 1363–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmulski, M. pH-dependent surface charging and points of zero charge III Update. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 298, 730–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.; Gong, W.; Feng, D.; Xian, M.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, S.; Ge, Z.; Zhou, Y. Natural graphite tailings as heterogeneous Fenton catalysts for the decolorization of rhodamine B. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 197, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Lai, C.; Huang, F.; Cheng, M.; Zeng, G.; Huang, D.; Li, B.; Liu, S.; Zhang, M.; Qin, L.; et al. Degradation of naphthalene with magnetic bio-char activate hydrogen peroxide: Synergism of bio-char and Fe–Mn binary oxides. Water Res. 2019, 160, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Li, P.; Xie, T.; Wang, Y. Ultrasonic-enhanced Fenton-like degradation of bisphenol A using a bio-synthesized schwertmannite catalyst. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleveland, V.; Bingham, J.P.; Kan, E. Heterogeneous Fenton degradation of bisphenol A by carbon nanotube-supported Fe3O4. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 133, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, X.; Chen, H.; Zhai, Q. Iron-glutamate-silicotungstate ternary complex as highly active heterogeneous Fenton-like catalyst for 4-chlorophenol degradation. Chin. J. Catal. 2015, 36, 2203–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Lopez, C.; Martin-Pascual, J.; Martinez-Toledo, M.V.; Munio, M.M.; Hontoria, E.; Poyatos, J.M. Kinetic modelling of TOC removal by H2O2/UV, photo-Fenton and heterogeneous photocatalysis processes to treat dye-containing wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Te. 2015, 12, 3255–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rusevova, K.; Kopinke, F.D.; Georgi, A. Nano-sized magnetic iron oxides as catalysts for heterogeneous Fenton-like reactions-Influence of Fe (II)/Fe (III) ratio on catalytic performance. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 241, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Liu, F.; Shen, C.; Zhu, C.; Li, A. A green and energy-saving microwave-based method to prepare magnetic carbon beads for catalytic wet peroxide oxidation. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 215, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acisli, O.; Khataee, A.; Soltani, R.D.C.; Karaca, S. Ultrasound-assisted Fenton process using siderite nanoparticles prepared via planetary ball milling for removal of reactive yellow 81 in aqueous phase. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 35, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, A.; Al-Kindi, G.; Ghanim, D. Green synthesis of bentonite-supported iron nanoparticles as a heterogeneous Fenton-like catalyst: Kinetics of decolorization of reactive blue 238 dye. Water Sci. Eng. 2020, 13, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Cao, Y.; Wang, H. Copper-based catalyst from waste printed circuit boards for effective Fenton-like discoloration of Rhodamine B at neutral pH. Chemosphere 2019, 230, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krysa, J.; Mantzavinos, D.; Pichat, P.; Poulios, I. Advanced oxidation processes for water and wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 34799–34800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, P.; Huang, W.; Ji, Z.; Zhou, C.; Yuan, S. Mechanisms of hydroxyl radicals production from pyrite oxidation by hydrogen peroxide: Surface versus aqueous reactions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2018, 238, 394–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Hu, X.; Yue, P.; Qiao, S. Photo Fenton degradation of high concentration Orange II (2mM) using catalysts containing Fe: A comparative study. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 67, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemian, S. Fenton-like oxidation of malachite green solutions: Kinetic and thermodynamic study. J. Chem. 2013, 2013, 809318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Demirezen, D.A.; Yıldız, Y.S.; Yılmaz, D.D. Amoxicillin degradation using green synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles: Kinetics and mechanism analysis. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2019, 11, 100219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Wang, J.; Xiao, R.; Tafti, N.; Delaune, R.D.; Seo, D.C. Degradation of Orange G by Fenton-like reaction with Fe-impregnated biochar catalyst. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 249, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Guo, Y.; Shi, S.; Liu, E.; Li, T.; Wei, S.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Sun, G.; Zhao, Z. Efficient and stable iron-copper montmorillonite heterogeneous Fenton catalyst for removing Rhodamine B. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2021, 776, 138673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, M.D.L.; Pérez, U.M.G. Photocatalytic properties of BiVO 4 prepared by the co-precipitation method: Degradation of rhodamine B and possible reaction mechanisms under visible irradiation. Mater. Res. Bull. 2010, 45, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Hu, Q.; Du, X.; Xu, H.; Hao, L. Study on decolorization of Rhodamine B by raw coal fly ash catalyzed Fenton-like process under microwave irradiation. Adv. Powder Technol. 2019, 30, 2369–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulebd, H. Comparative study of the radical scavenging behavior of ascorbic acid, BHT, BHA and Trolox: Experimental and theoretical study. J. Mol. Struct. 2019, 1201, 127210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Zeng, X.; Lemley, A.T. Kinetics and mechanism of carbamazepine degradation by a modified Fenton-like reaction with ferric-nitrilotriacetate complexes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 252, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, N.; Sahoo, H.; Mohapatra, S. Decolourization of Methyl Orange using Fenton-like mesoporous Fe2O3-SiO2 composite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, H.; Yang, F.; Gao, Y.; Zhen, K.; Tang, X.; Zhang, P.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Sun, H. Efficient removal of pyrene by biochar supported iron oxide in heterogeneous Fenton-like reaction via radicals and high-valent iron-oxo species. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 265, 118518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Fang, J.; Huang, Y.; Wang, P.; Ma, J. Production of Hydroxyl Radical via the Activation of Hydrogen Peroxide by Hydroxylamine. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 10373–10379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Ma, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Fang, J.; Guan, Y.; Xie, P. Strong Enhancement on Fenton Oxidation by Addition of Hydroxylamine to Accelerate the Ferric and Ferrous Iron Cycles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 3925–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Song, S.; Ying, H.; Xu, L.; Chen, J. p-aminophenol degradation by ozonation combined with sonolysis: Operating conditions influence and mechanism. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2007, 14, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, R.; Qazi, U.Y.; Kawasaki, S.I. Efficient and Continuous Decomposition of Hydrogen Peroxide Using a Silica Capillary Coated with a Thin Palladium or Platinum Layer. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2015, 88, 976–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Zekker, I.; Zhang, B.L.; Hendi, A.H.; Ahmad, A.; Ahmad, S.; Zada, N. Review on Methylene Blue: Its Properties, Uses, Toxicity and Photodegradation. Water 2022, 2, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Ali, N.; Khan, I.; Zhang, B.L.; Sadiq, M. Heterogeneous photodegradation of industrial dyes: An insight to different mechanisms and rate affecting parameters. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Element | O | Mg | Al | Si | K | Ti | Fe | the Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight percentage (wt.%) | 54.44 | 2.3 | 4.9 | 24.42 | 1.21 | 0.63 | 12.09 | 100 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, P.; Dai, Z.; Lu, T.; Ru, X.; Ofori, M.A.; Yang, W.; Hou, J.; Jin, H. Degradation of Rhodamine B in Wastewater by Iron-Loaded Attapulgite Particle Heterogeneous Fenton Catalyst. Catalysts 2022, 12, 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12060669
Zhou P, Dai Z, Lu T, Ru X, Ofori MA, Yang W, Hou J, Jin H. Degradation of Rhodamine B in Wastewater by Iron-Loaded Attapulgite Particle Heterogeneous Fenton Catalyst. Catalysts. 2022; 12(6):669. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12060669
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Peiguo, Zongbiao Dai, Tianyu Lu, Xin Ru, Meshack Appiah Ofori, Wenjing Yang, Jiaxin Hou, and Hui Jin. 2022. "Degradation of Rhodamine B in Wastewater by Iron-Loaded Attapulgite Particle Heterogeneous Fenton Catalyst" Catalysts 12, no. 6: 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12060669
APA StyleZhou, P., Dai, Z., Lu, T., Ru, X., Ofori, M. A., Yang, W., Hou, J., & Jin, H. (2022). Degradation of Rhodamine B in Wastewater by Iron-Loaded Attapulgite Particle Heterogeneous Fenton Catalyst. Catalysts, 12(6), 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12060669