Design of γ-Alumina-Supported Phosphotungstic Acid-Palladium Bifunctional Catalyst for Catalytic Liquid-Phase Citral Hydrogenation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Bifunctional (Metal–Acid) Catalysts
2.3. Catalysts Characterization
2.4. Catalytic Reaction Study
2.4.1. Citronellal Cyclisation to Isopulegol
2.4.2. Synthesis of Menthols via Liquid-Phase Citral Hydrogenation
3. Results and Discussion
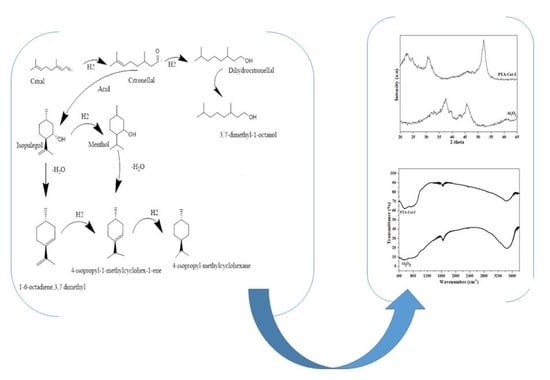
3.1. Catalysts Characterization
3.2. Reactions Study
3.2.1. Citronellal Cyclisation to Isopulegol
3.2.2. Citral Hydrogenation to Menthols
Metal-Supported Alumina Catalysts for Liquid-Phase Citral Hydrogenation
γ-Alumina-Supported Phosphotungstic Acid-Palladium Catalysts for Liquid-Phase Citral Hydrogenation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stassi, J.; Méndez, J.; Vilella, I.; De Miguel, S.; Zgolicz, P. Synthesis of PtSn nanoparticles on carbon materials by different preparation methods for selective catalytic hydrogenation of citral. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2020, 207, 1074–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borda, G.; Rojas, H.; Murcia, J.; Fierro, J.L.G.; Reyes, P.; Oportus, M. Hydrogenation of citral on Ir/SiO2 catalysts. Effect of the addition of Nb2O5 on surface and catalytic properties. React. Kinet. Catal. Lett. 2007, 92, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, P.; Rojas, H. Hydrogenation of citral over pt and pt-fe/sio2 catalysts. React. Kinet. Catal. Lett. 2006, 88, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, X.; Lafaye, G.; Especel, C.; Epron, F.; Qi, J.; Li, C.; Liang, C. Supported Co–Re Bimetallic Catalysts with Different Structures as Efficient Catalysts for Hydrogenation of Citral. ChemSusChem 2019, 12, 807–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Huang, C.; Chen, S.; Yu, B.; Xu, J.; Liu, Z. Pd nanoparticles immobilized on graphite oxide modified with a base: Highly efficient catalysts for selective hydrogenation of citral. Sci. China Chem. 2013, 56, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertens, P.; Verpoort, F.; Parvulescu, A.-N.; De Vos, D. Pt/H-beta zeolites as productive bifunctional catalysts for the one-step citronellal-to-menthol conversion. J. Catal. 2006, 243, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trasarti, A.F.; Marchi, A.J.; Apesteguía, C.R. Design of catalyst systems for the one-pot synthesis of menthols from citral. J. Catal. 2007, 247, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negoi, A.; Teinz, K.; Kemnitz, E.; Wuttke, S.; Parvulescu, V.; Coman, S. Bifunctional Nanoscopic Catalysts for the One-Pot Synthesis of (±)-Menthol from Citral. Top. Catal. 2012, 55, 680–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, E.; Virtanen, P.; Kordás, K.; Mikkola, J.-P. Alkaline modifiers as performance boosters in citral hydrogenation over supported ionic liquid catalysts (SILCAs). Catal. Today 2012, 196, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäki-Arvela, P.; Kumar, N.; Kubička, D.; Nasir, A.; Heikkilä, T.; Lehto, V.-P.; Sjöholm, R.; Salmi, T.; Murzin, D.Y. One-pot citral transformation to menthol over bifunctional micro- and mesoporous metal modified catalysts: Effect of catalyst support and metal. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2005, 240, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäki-Arvela, P.; Kumar, N.; Nieminen, V.; Sjöholm, R.; Salmi, T.; Murzin, D.Y. Cyclization of citronellal over zeolites and mesoporous materials for production of isopulegol. J. Catal. 2004, 225, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Rocha, K.A.; Robles-Dutenhefner, P.A.; Sousa, E.M.; Kozhevnikova, E.F.; Kozhevnikov, I.V.; Gusevskaya, E.V. Pd–heteropoly acid as a bifunctional heterogeneous catalyst for one-pot conversion of citronellal to menthol. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2007, 317, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H.; Yamada, S.; Itoh, H.; Hori, Y. A dual catalyst system provides the shortest pathway for L-menthol synthesis. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 1772–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirujano, F.; i Xamena, F.L.; Corma, A. MOFs as multifunctional catalysts: One-pot synthesis of menthol from citronellal over a bifunctional MIL-101 catalyst. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 4249–4254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negoi, A.; Wuttke, S.; Kemnitz, E.; Macovei, D.; Parvulescu, V.I.; Teodorescu, C.; Coman, S.M. One-Pot Synthesis of Menthol Catalyzed by a Highly Diastereoselective Au/MgF2 Catalyst. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 8134–8138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virtanen, P.; Karhu, H.; Toth, G.; Kordas, K.; Mikkola, J.-P. Towards one-pot synthesis of menthols from citral: Modifying supported ionic liquid catalysts (SILCAs) with Lewis and Brønsted acids. J. Catal. 2009, 263, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Jaenicke, S.; Chuah, G.K. Zr–Zeolite Beta: A New Heterogeneous Catalyst System for the Highly Selective Cascade Transformation of Citral to (±)-Menthol. Chem. A Eur. J. 2009, 15, 1991–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trasarti, A.F.; Marchi, A.J.; Apesteguıa, C. Highly selective synthesis of menthols from citral in a one-step process. J. Catal. 2004, 224, 484–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weingarten, R.; Tompsett, G.A.; Conner, W.C.; Huber, G.W. Design of solid acid catalysts for aqueous-phase dehydration of carbohydrates: The role of Lewis and Brønsted acid sites. J. Catal. 2011, 279, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corma, A.; Hamid, S.B.A.; Iborra, S.; Velty, A. Lewis and Brönsted basic active sites on solid catalysts and their role in the synthesis of monoglycerides. J. Catal. 2005, 234, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabeti, M.; Wan Daud, W.M.A.; Aroua, M.K. Activity of solid catalysts for biodiesel production: A review. Fuel Process. Technol. 2009, 90, 770–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, K.; Hölderich, W.F. Industrial application of solid acid–base catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 1999, 181, 399–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, G.D. Synergism of Clay and Heteropoly Acids as Nano-Catalysts for the Development of Green Processes with Potential Industrial Applications. Catal. Surv. Asia 2005, 9, 117–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.K.; Maitlo, G.; Korai, R.M.; Unar, I.N.; Shah, A.A.; Khan, H.A.; Shah, S.F.A.; Ismail, U.; Park, Y.H. Citronellal cyclisation to isopulegol over micro-mesoporous zsm-5 zeolite: Effects of desilication temperature on textural and catalytic properties. React. Kinet. Mech. Catal. 2019, 128, 507–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timofeeva, M.N. Acid catalysis by heteropoly acids. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2003, 256, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhorodwaj, S.K.; Dutta, D.K. Heteropoly acid supported modified Montmorillonite clay: An effective catalyst for the esterification of acetic acid with sec-butanol. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2010, 378, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, A.H.; Shafaq, N.; Umer, R. Supported solid and heteropoly acid catalysts for production of biodiesel. Catal. Rev. Sci. Eng. 2017, 59, 165–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farfan-Torres, E.M.; Sham, E.; Grange, P. Pillared clays: Preparation and characterization of zirconium pillared montmorillonite. Catal. Today 1992, 15, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming-li, C.; Yong-fu, Y.; Ji-zu, Y.; Ming-he, C. Preparation and properties of pillared montmorillonite by polyhydroxyl-aluminum-manganese cations. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mater. Sci. Ed. 2002, 17, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.K.; Park, S.; Khan, H.A.; Bhatti, U.H.; Kumar, P.; Bhutto, A.W.; Park, Y.H. Citronellal cyclisation over heteropoly acid supported on modified montmorillonite catalyst: Effects of acidity and pore structure on catalytic activity. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2018, 44, 2405–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flessner, U.; Jones, D.J.; Rozière, J.; Zajac, J.; Storaro, L.; Lenarda, M.; Pavan, M.; Jiménez-López, A.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E.; Trombetta, M.; et al. A study of the surface acidity of acid-treated montmorillonite clay catalysts. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2001, 168, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieseki, L.; Bertell, F.; Treichel, H.; Penha, F.G.; Pergher, S.B.C. Acid treatments of montmorillonite-rich clay for Fe removal using a factorial design method. Mater. Res. 2013, 16, 1122–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.M. Synthetic organic chemistry using pillared, cation-exchanged and acid-treated montmorillonite catalysts—A review. Appl. Clay Sci. 1987, 2, 309–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, T.; Parida, K.M.; Rao, S.B. Transition Metal Oxide Pillared Clay: 1. A Comparative Study of Textural and Acidic Properties of Fe(III) Pillared Montmorillonite and Pillared Acid Activated Montmorillonite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1996, 183, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolognini, M.; Cavani, F.; Cimini, M.; Pozzo, L.D.; Maselli, L.; Venerito, D.; Pizzoli, F.; Veronesi, G. An environmentally friendly synthesis of 2,4-dihydroxybenzophenone by the single-step O-mono-benzoylation of 1,3-dihydroxybenzene (resorcinol) and Fries rearrangement of intermediate resorcinol monobenzoate: The activity of acid-treated montmorillonite clay catalysts. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2004, 7, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Vyas, S.; Patel, A. Heteropolyacid supported onto neutral alumina: Characterization and esterification of 1° and 2° alcohol. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2004, 214, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, M.H.; Dummer, N.F.; Zhang, D.; Miedziak, P.; Davies, T.E.; Taylor, S.H.; Willock, D.J.; Knight, D.W.; Chadwick, D.; Hutchings, G.J. Rubidium- and caesium-doped silicotungstic acid catalysts supported on alumina for the catalytic dehydration of glycerol to acrolein. J. Catal. 2012, 286, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Conceição, L.R.V.; Reis, C.E.; de Lima, R.; Cortez, D.V.; de Castro, H.F. Keggin-structure heteropolyacid supported on alumina to be used in trans/esterification of high-acid feedstocks. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 23450–23458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Zhou, J.; Cen, K. Hydrodeoxygenation and hydrocracking of microalgae biodiesel to produce jet biofuel over H3PW12O40-Ni/hierarchical mesoporous zeolite Y catalyst. Fuel 2019, 245, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yang, J.; Sun, Y.; Li, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Hu, Y.H. Highly selective production of C5-C12 hydrocarbons over efficient Ru/heteropoly-acid catalysts. Fuel 2019, 244, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Hiraga, Y.; Qi, X.; Smith, R.L., Jr. Hydrogen gas-free processes for single-step preparation of transition-metal bifunctional catalysts and one-pot γ-valerolactone synthesis in supercritical CO2-ionic liquid systems. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2019, 147, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Zhang, L.; Kour, G.; Zhou, S.; Wang, S.; Yan, C.; Zhu, Z.; Du, A. Defective Graphene on Transition Metal Surface: Formation of Efficient Bifunctional Catalyst for Oxygen Evolution/Reduction Reactions in Alkaline Media. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 17410–17415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lear, T.; Marshall, R.; Gibson, E.K.; Schütt, T.; Klapötke, T.M.; Rupprechter, G.; Freund, H.-J.; Winfield, J.M.; Lennon, D. A model high surface area alumina-supported palladium catalyst. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2005, 7, 565–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.K.; Maitlo, G.; Shah, A.A.; Channa, I.A.; Kandhro, G.A.; Maitlo, H.A.; Bhatti, U.H.; Shah, A.; Memon, A.Q.; Jatoi, A.S.; et al. One pot menthol synthesis via hydrogenations of citral and citronellal over montmorillonite-supported Pd/Ni-heteropoly acid bifunctional catalysts. React. Kinet. Mech. Catal. 2019, 128, 917–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benesi, H. Acidity of catalyst surfaces. II. Amine titration using Hammett indicators. J. Phys. Chem. 1957, 61, 970–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emeis, C.A. Determination of Integrated Molar Extinction Coefficients for Infrared Absorption Bands of Pyridine Adsorbed on Solid Acid Catalysts. J. Catal. 1993, 141, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Vannice, M.A. Solvent effects in liquid-phase reactions: I. Activity and selectivity during citral hydrogenation on Pt/SiO2 and evaluation of mass transfer effects. J. Catal. 2006, 243, 108–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Vannice, M.A. Solvent effects in liquid-phase reactions II. Kinetic modeling for citral hydrogenation. J. Catal. 2006, 243, 131–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Davis, B.H. Alcohol dehydration: Mechanism of ether formation using an alumina catalyst. J. Catal. 1995, 157, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pines, H.; Haag, W.O. Alumina: Catalyst and Support. IX. 1 The Alumina Catalyzed Dehydration of Alcohols2, 3. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1961, 83, 2847–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudloff, E.v. A simple reagent for the specific dehydration of terpene alcohols. Can. J. Chem. 1961, 39, 1860–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plößer, J.; Lucas, M.; Claus, P. Highly selective menthol synthesis by one-pot transformation of citronellal using Ru/H-BEA catalysts. J. Catal. 2014, 320, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yongzhong, Z.; Yuntong, N.; Jaenicke, S.; Chuah, G.-K. Cyclisation of citronellal over zirconium zeolite beta—A highly diastereoselective catalyst to (±)-isopulegol. J. Catal. 2005, 229, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazachenko, A.S.; Vasilieva, N.Y.; Fetisova, O.Y.; Sychev, V.V.; Elsuf’ev, E.V.; Malyar, Y.N.; Issaoui, N.; Miroshnikova, A.V.; Borovkova, V.S.; Kazachenko, A.S.; et al. New reactions of betulin with sulfamic acid and ammonium sulfamate in the presence of solid catalysts. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2022, 4, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäki-Arvela, P.; Tiainen, L.P.; Neyestanaki, A.K.; Sjöholm, R.; Rantakylä, T.K.; Laine, E.; Salmi, T.; Murzin, D.Y. Liquid phase hydrogenation of citral: Suppression of side reactions. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2002, 237, 181–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Catalyst Type | BET (m2.g−1) a | VP (cm3.g−1) | dp (nm) | Acidity b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al2O3 | 136 | 0.248 | 7.2 | n.d |
| * PTA-Cat-I | 120 | 0.164 | 5.4 | 0.51 |
| Catalysts | Conversion a | Yield | Selectivity | Ds (±) Isopulegol | Others | K b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | min−1 | |
| Al2O3 | 12 | 2 | 16 | 2 | 10 | 0.003 |
| PTA-Cat-I | 95 | 92 | 97 | 87 | 3 | 0.044 |
| PMA-Cat-I | 89 | 83 | 93 | 84 | 6 | 0.037 |
| STA-Cat-I | 78 | 66 | 85 | 77 | 12 | 0.029 |
| SMA-Cat-I | 62 | 40 | 64 | 58 | 22 | 0.022 |
| Product Distribution Yield (%) a | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Catalysts | Conversion | MOL | CIT | IPOL | DHCIT | DMOL | Others | K b |
| (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | min−1 | |
| Cat-I | 100 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 95 | 2 | 2 | 0.050 |
| Cat-II | 98 | 0 | 63 | 0 | 25 | 3 | 7 | 0.042 |
| Cat-III | 92 | 0 | 75 | 0 | 11 | 0 | 6 | 0.037 |
| Cat-IV | 74 | 8 | 54 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 6 | 0.017 |
| Cat-V | 61 | 17 | 28 | 7 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 0.015 |
| Product Distribution Yield (%) a | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Catalysts | Conversion | MOL | CIT | IPOL | DHCIT | DMOL | Others | K b |
| (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | min−1 | |
| Cat-I | 100 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 95 | 2 | 2 | 0.050 |
| PTA-Cat-I | 100 | 45 | 2 | 4 | 25 | 6 | 18 | 0.038 |
| PMA-Cat-I | 100 | 27 | 23 | 10 | 21 | 1 | 18 | 0.032 |
| STA-Cat-I | 78 | 13 | 28 | 12 | 16 | 3 | 6 | 0.029 |
| SMA-Cat-I | 67 | 4 | 41 | 3 | 10 | 0 | 9 | 0.024 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shah, A.K.; Bukhari, S.N.-u.S.; Shah, A.A.; Jatoi, A.S.; Usto, M.A.; Hashmi, Z.; Shah, G.T.; Park, Y.H.; Choi, M.-S.; Iqbal, A.; et al. Design of γ-Alumina-Supported Phosphotungstic Acid-Palladium Bifunctional Catalyst for Catalytic Liquid-Phase Citral Hydrogenation. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1069. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12091069
Shah AK, Bukhari SN-uS, Shah AA, Jatoi AS, Usto MA, Hashmi Z, Shah GT, Park YH, Choi M-S, Iqbal A, et al. Design of γ-Alumina-Supported Phosphotungstic Acid-Palladium Bifunctional Catalyst for Catalytic Liquid-Phase Citral Hydrogenation. Catalysts. 2022; 12(9):1069. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12091069
Chicago/Turabian StyleShah, Abdul Karim, Syed Nizam-uddin Shah Bukhari, Ayaz Ali Shah, Abdul Sattar Jatoi, Muhammad Azam Usto, Zubair Hashmi, Ghulam Taswar Shah, Yeung Ho Park, Moo-Seok Choi, Arshad Iqbal, and et al. 2022. "Design of γ-Alumina-Supported Phosphotungstic Acid-Palladium Bifunctional Catalyst for Catalytic Liquid-Phase Citral Hydrogenation" Catalysts 12, no. 9: 1069. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12091069
APA StyleShah, A. K., Bukhari, S. N. -u. S., Shah, A. A., Jatoi, A. S., Usto, M. A., Hashmi, Z., Shah, G. T., Park, Y. H., Choi, M. -S., Iqbal, A., Seehar, T. H., & Raza, A. (2022). Design of γ-Alumina-Supported Phosphotungstic Acid-Palladium Bifunctional Catalyst for Catalytic Liquid-Phase Citral Hydrogenation. Catalysts, 12(9), 1069. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12091069