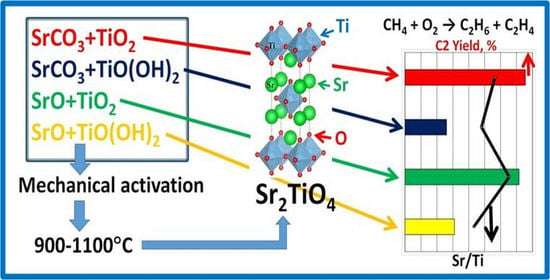
Sr2TiO4 Prepared Using Mechanochemical Activation: Influence of the Initial Compounds’ Nature on Formation, Structural and Catalytic Properties in Oxidative Coupling of Methane
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Study of MA Products by XRD and FT-IRS
2.2. Calcined Samples
2.2.1. Structural Properties
2.2.2. Surface Composition
2.2.3. Textural and Morphological Properties
2.2.4. Catalytic Activity
3. Experimental
3.1. Sr2TiO4 Preparation
3.2. Catalysts Characterization
3.3. Activity Tests
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gambo, Y.; Jalil, A.A.; Triwahyono, S.; Abdulrasheed, A.A. Recent advances and future prospect in catalysts for oxidative coupling of methane to ethylene: A review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 59, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galadima, A.; Muraza, O. Revisiting the oxidative coupling of methane to ethylene in the golden period of shale gas: A review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 37, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwach, P.; Pan, X.; Bao, X. Direct Conversion of Methane to Value-Added Chemicals over Heterogeneous Catalysts: Challenges and Prospects. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 8497–8520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexiadis, V.I.; Chaar, M.; van Veen, A.; Muhler, M.; Thybaut, J.W.; Marin, G.B. Quantitative screening of an extended oxidative coupling of methane catalyst library. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 199, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondratenko, E.V.; Schlüter, M.; Baerns, M.; Linke, D.; Holena, M. Developing catalytic materials for the oxidative coupling of methane through statistical analysis of literature data. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 1668–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, L.; Yamaguchi, D.; Wong, L.; Burke, N.; Chiang, K. The promoting effect of ceria on Li/MgO catalysts for the oxidative coupling of methane. Catal. Today 2011, 178, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thum, L.; Rudolph, M.; Schomäcker, R.; Wang, Y.; Tarasov, A.; Trunschke, A.; Schlögl, R. Activation in Oxidative Coupling of Methane on Calcium Oxide. J. Phys. Chem. 2018, 123, 8018–8026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sim, Y.; Kwon, D.; An, S.; Ha, J.-M.; Oh, T.-S.; Jung, J.C. Catalytic behavior of ABO3 perovskites in the oxidative coupling of methane. Mol. Catal. 2020, 489, 110925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Xi, R.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Fang, X.; Wang, X. Promoting the surface active sites of defect BaSnO3 perovskite with BaBr2 for the oxidative coupling of methane. Catal. Today 2021, 374, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Xi, R.; Xiao, Q.; Xu, X.; Liu, L.; Li, S.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Fang, X.; Wang, X. Design of strontium stannate perovskites with different fine structures for the oxidative coupling of methane (OCM): Interpreting the functions of surface oxygen anions, basic sites and the structure–reactivity relationship. J. Catal. 2022, 408, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Chen, Y.; Fu, X. Influence of surface composition of perovskite-type complex oxides on methane oxidative coupling. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 1993, 104, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.Y.; Li, W.Z.; Martin, G.A.; Mirodatos, C. Studies of CaTiO3 based catalysts for the oxidative coupling of methane. Appl. Catal. A. 1997, 158, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Fujimoto, K. Low Temperature Oxidative Coupling of Methane by Perovskite Oxide. Chem. Lett. 1994, 23, 1581–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Polo-Garzon, F.; Bao, Z.H.; Luo, S.; Moskowitz, B.M.; Tian, H.J.; Wu, Z.L. Impact of Surface Composition of SrTiO3 Catalysts for Oxidative Coupling of Methane. ChemCatChem 2019, 11, 2107–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabuffetti, F.A.; Stair, P.C.; Poeppelmeier, K.R. Synthesis-Dependent Surface Acidity and Structure of SrTiO3 nanoparticles solid-state reaction, molten salt, and sol-precipitation–hydrothermal treatment. J. Phys. Chem. 2010, 114, 11056–11067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Choi, J.-W.; Jin Suh, D.; Lee, U.; Song, K.H.; Ha, J.-M. Low-temperature oxidative coupling of methane using alkaline earth metal oxide-supported perovskites. Catal. Today 2020, 352, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.M.; Yan, Q.J.; Fu, X.C. Oxidative coupling of methane over Sr−Ti, Sr−Sn perovskites and corresponding layered perovskites. React. Kinet. Catal. Lett. 1995, 54, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, D.V.; Isupova, L.A.; Gerasimov, E.Y.; Dovlitova, L.S.; Glazneva, T.S.; Prosvirin, I.P. Oxidative methane coupling over Mg, Al, Ca, Ba, Pb-promoted SrTiO3 and Sr2TiO4: Influence of surface composition and microstructure. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2014, 485, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, Y.A.; Sutormina, E.F.; Rudina, N.A.; Nartova, A.V.; Isupova, L.A. Effect of preparation route on Sr2TiO4 catalyst for the oxidative coupling of methane. Catal. Commun. 2018, 117, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruddlesden, S.N.; Popper, P. New compounds of the K2NIF4 type. Acta Crystallogr. 1957, 10, 538–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Kim, S.W.; Ohta, H.; Koumoto, K. Ruddlesden-Popper phases as thermoelectric oxides: Nb-doped SrO (SrTiO3) (n = 1,2). J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 100, 063717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorkh-Kaman-Zadeh, A.; Dashtbozorg, A. Facile chemical synthesis of nanosize structure of Sr2TiO4 for degradation of toxic dyes from aqueous solution. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 223, 921–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, B.S.; Do, J.Y.; Park, N.K.; Kang, M. Surface modification of layered perovskite Sr2TiO4 for improved CO2 photoreduction with H2O to CH4. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesić, Ž.; Lukić, I.; Zdujić, M.; Jovalekić, Č.; Veljković, V.; Skala, D. Assessment of CaTiO3, CaMnO3, CaZrO3 and Ca2Fe2O5 perovskites as heterogeneous base catalysts for biodiesel synthesis. Fuel Processing Technol. 2016, 143, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berbenni, V.; Marini, A.; Bruni, G. Effect of mechanical activation on the preparation of SrTiO3 and Sr2TiO4 ceramics from the solid state system SrCO3–TiO2. J. Alloy. Compd. 2001, 329, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hungrıa, T.; Hungrıa, A.-B.; Castro, A. Mechanosynthesis and mechanical activation processes to the preparation of the Sr2[Srn-1inO3n+1] Ruddlesden–Popper family. J. Solid State Chem. 2004, 177, 1559–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiss, B.G.; Richard, A.J.; Douglas, G.; Kojic, M.; Friščić, T.; Moores, A. Mechanochemical methods for the transfer of electrons and exchange of ions: Inorganic reactivity from nanoparticles to organometallics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 8279–8318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepelak, V.; Duvel, A.; Wilkening, M.; Beckerb, K.D.; Heitjans, P. Mechanochemical reactions and syntheses of oxide. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 7507–7520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balaz, P.; Achimovicova, M.; Balaz, M.; Billik, P.; Cherkezova-Zheleva, Z.; Criado, J.M.; Delogu, F.; Dutkova, E.; Gaffet, E.; Gotor, F.J.; et al. Hallmarks of mechanochemistry: From nanoparticles to technology. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 7571–7639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amrute, A.P.; De Bellis, J.; Felderhoff, M.; Schüth, F. Mechanochemical Synthesis of Catalytic Materials. Chem. Eur. J. 2021, 27, 6819–6847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba-Abbad, M.M.; Kadhum, A.A.H.; Mohamad, A.B.; Takriff, M.S.; Sopian, K. Synthesis and catalytic activity of TiO2 nanoparticles for photochemical oxidation of concentrated chlorophenols under direct solar radiation. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2012, 7, 4871–4888. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Chen, D.; Bai, L.; Shu, K. Hydrothermal Synthesis and Electrochemical Properties of TiO2 Nanotubes as an Anode Material for Lithium Ion Batteries. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2018, 13, 2118–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Toan, S.; Huang, L.; Fan, M.; Wang, Y.; Russell, A.G.; Luo, G.; Fe, W. TiO(OH)2—Highly effective catalysts for optimizing CO2 desorption kinetics reducing CO2 capture cost: A new pathway. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dutcher, B.; Fan, M.; Leonard, B. Use of multifunctional nanoporous TiO(OH)2 for catalytic NaHCO3 decomposition-eventually for Na2CO3/NaHCO3 based CO2 separation technology. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 80, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, G.M.; Wypych, F. A novel and facile synthesis route for obtaining highly urity free layered hydroxide sulfates: Gordaite and osakaite. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 143, 109723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgari-Fard, Z.; Sabet, M.; Salavati-Niasari, M. Synthesis and Characterization of Strontium Carbonate Nanostructures via Simple Hydrothermal Method. High Temp. Mater. Proc. 2016, 35, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Hu, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Liu, X.; He, Y.; Dong, F.; Fub, M.; Zhang, Z. One-step preparation of a novel SrCO3/g-C3N4 nano-composite and its application in selective adsorption of crystal violet. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 6315–6325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Márquez-Herrera, A.; Ovando-Medina, V.M.; Castillo-Reyes, B.E.; Zapata-Torres, M.; Meléndez-Lira, M.; González-Castañeda, J. Facile Synthesis of SrCO3-Sr(OH)2/PPy Nanocomposite with Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity under Visible Light. Materials 2016, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Granados-Correa, F.; Bonifacio-Martínez, J. Combustion synthesis process for the rapid preparation of high-purity SrO powders. Mater. Sci. -Pol. 2014, 32, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tabah, B.; Nagvenkar, A.P.; Perkas, N.; Gedanken, A. Solar-Heated Sustainable Biodiesel Production from Waste Cooking Oil Using a Sonochemically Deposited SrO Catalyst on Microporous Activated Carbon. Energy Fuels. 2017, 31, 6228–6239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Xu, L. New Insights into Sensitization Mechanism of the Doped Ce (IV) into Strontium Titanate. Materials 2018, 11, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grabowska, E.; Marchelek, M.; Klimczuk, T.; Lisowski, W.; Zaleska-Medynska, A. TiO2/SrTiO3 and SrTiO3 microspheres decorated with Rh, Ru or Pt nanoparticles: Highly UV–vis responsible photoactivity and mechanism. J. Catal. 2017, 350, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senna, M. A straight way toward phase pure complex oxides. J. Eur. Cer. Soc. 2005, 25, 1977–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senna, M. Grinding of mixture under mild condition for mechanochemical complexation. Int. J. Miner. Processing 1996, 187, 44–45. [Google Scholar]
- Avvakumov, E.G.; Karakchiev, L.G. Prospects for soft mechanochemical synthesis. Chem. Sustain. Dev. 2014, 22, 359–369. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Mi, Y.; Jiao, F.; Xu, X. Activating Layered Perovskite Compound Sr2TiO4 via La/N Codoping for Visible Light Photocatalytic Water Splitting. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 3209–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasquez, R.P. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy study of Sr and Ba compounds. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 1991, 56, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilleux, M.E.; Grahmann, C.R.; Fuenzalida, V.M. Hydrothermal Strontium Titanate Films on Titanium: An XPS and AES Depth-Profiling Study. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1994, 77, 1601–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Ji, S.; Shi, X.; Tang, J. Autothermal oxidative coupling of methane on the SrCO3/Sm2O3 catalysts. Catal. Commun. 2009, 10, 807–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Sun, X.; Feifei, B.; He, H. Sol-gel Preparation of Photocatalytic Porous Strontium Titanate using PEG4000 as the Template. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. -Asia 2012, 2, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasquez, R.P. SrSO4 by XPS. Surf. Sci. Spectra 1992, 1, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Choi, J.W.; Suh, D.J.; Song, K.H.; Ham, H.C.; Ha, J.M. Combined experimental and density functional theory (DFT) studies on the catalyst design for the oxidative coupling of methane. J. Catal. 2019, 375, 478–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| Sample/ T °C | Initial Compounds | Phase Composition/ Content,% | Lattice Parameters *, Å | Crystallite size, nm | Specific Surface Area, m2/g | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | b | c | |||||
| MA-1 900 1100 | SrCO3 + TiO2 | Sr2TiO4 (27.1) SrTiO3 (26.4) Sr4Ti3O10 (11) SrCO3 (35.5) Sr2TiO4 (100) | 3.8786 | 3.8786 | 12.593 | 120 | 3 1.2 |
| MA-2 900 °C 1100 °C | SrCO3 + TiO(OH)2 | Sr2TiO4 (92.5) Sr4Ti3O10 SrTiO3 SrCO3 Sr2TiO4 (100) | 3.8850 3.8756 | 3.8850 3.8756 | 12.580 12.561 | 120 120 | 1.7 1 |
| MA-3 900 °C 1100 °C | SrO + TiO2 | Sr2TiO4 (40) SrTiO3 (57) Sr4Ti3O10 Sr2TiO4 (40) SrTiO3 (56) Sr4Ti3O10 | 3.8735 3.9049 3.8856 | 3.8735 3.8856 | 12.653 12.647 | 50 | 1.9 1.4 |
| MA-4 900 °C 1100 °C | SrO + TiO(OH)2 | Sr2TiO4 (70) SrTiO3 (14) Sr4Ti3O10 (16) Sr2TiO4 (68) SrTiO3 (14) Sr4Ti3O10 (18) | 3.8861 3.8862 | 3.8861 3.8862 | 12.549 12.564 | 50 120 | 1.6 1.3 |
| Sample | Sr/Ti | Op/Ti | Oo/Ti | Oh | Oo/Op | EOp | EOo | EOOH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MA-1(1100) | 2.5 | 3.2 | 4.6 | 0.086 | 1.4 | 529.8 | 531.1 | 533.5 |
| MA-2 1,2(1100) | 2.1 | 3.1 | 3.3 | 0.1 | 1.1 | 529.2 | 531.4 | 533.8 |
| MA-3(1100) | 2.9 | 3.6 | 6.1 | 0.2 | 1.9 | 528.7 | 531.0 | 533.4 |
| MA-4 1,3(1100) | 1.9 | 3.2 | 3.2 | 0.1 | 1.0 | 529.1 | 531.4 | 533.8 |
| Catalyst | Reaction Conditions | Methane Conversion, % | C2 selectivity(S)/ Yield(Y),% | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CaTiO3 SrTiO3 BaTiO3 | 700 °C, CH4/O2 = 3, GHSV = 10,000 h−1 | 13 24 19 | 2/ 12/ 36/ | [16] |
| SrTiO3 SrTi0.8Sn0.2 O3 SrTi0.8Nd0.2 O3 | 800 °C, CH4/O2 = 3, GHSV = 10,000 h−1 | 32.5 30.8 30.5 | 48.9/ 52.1/ 54.4/ | [52] |
| SrZrO3 | 775 °C, CH4/O2 = 3, GHSV = 10,000 h−1 | 30.7 | 45.4/ | [8] |
| Sr2TiO4 | 850 °C, CH4/O2 = 4, GHSV = 75,000 h−1 | 19.8 | 59.6/11.8 | [19] |
| SrTiO3 Sr2 TiO4 Sr2 Ti0.9 Mg0.1O4 | 850 °C, CH4/O2 = 4, GHSV = 75,000 h−1 | - | 65.9/12.8 68.5/17.3 71.2/18.2 | [18] |
| Sr2TiO4 (MA-1) Sr2TiO4 (MA-3) | 850 °C, CH4/O2 = 4, GHSV = 75,000 h−1 | 24.1 | 62.7/15.1 | This work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pavlova, S.; Ivanova, Y.; Tsybulya, S.; Chesalov, Y.; Nartova, A.; Suprun, E.; Isupova, L. Sr2TiO4 Prepared Using Mechanochemical Activation: Influence of the Initial Compounds’ Nature on Formation, Structural and Catalytic Properties in Oxidative Coupling of Methane. Catalysts 2022, 12, 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12090929
Pavlova S, Ivanova Y, Tsybulya S, Chesalov Y, Nartova A, Suprun E, Isupova L. Sr2TiO4 Prepared Using Mechanochemical Activation: Influence of the Initial Compounds’ Nature on Formation, Structural and Catalytic Properties in Oxidative Coupling of Methane. Catalysts. 2022; 12(9):929. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12090929
Chicago/Turabian StylePavlova, Svetlana, Yulia Ivanova, Sergey Tsybulya, Yurii Chesalov, Anna Nartova, Evgenii Suprun, and Lyubov Isupova. 2022. "Sr2TiO4 Prepared Using Mechanochemical Activation: Influence of the Initial Compounds’ Nature on Formation, Structural and Catalytic Properties in Oxidative Coupling of Methane" Catalysts 12, no. 9: 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12090929
APA StylePavlova, S., Ivanova, Y., Tsybulya, S., Chesalov, Y., Nartova, A., Suprun, E., & Isupova, L. (2022). Sr2TiO4 Prepared Using Mechanochemical Activation: Influence of the Initial Compounds’ Nature on Formation, Structural and Catalytic Properties in Oxidative Coupling of Methane. Catalysts, 12(9), 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12090929