Size-Dependent Strong Metal–Support Interactions of Rutile TiO2-Supported Ni Catalysts for Hydrodeoxygenation of m-Cresol
Abstract
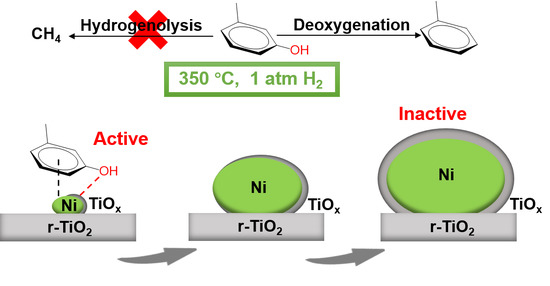
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Catalyst Characterization
2.2. Catalytic Performance
3. Experimental
3.1. Catalyst Preparation
3.2. Catalyst Characterization
3.3. Catalytic Activity Measurement
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anex, R.P.; Aden, A.; Kazi, F.K.; Fortman, J.; Swanson, R.M.; Wright, M.M.; Satrio, J.A.; Brown, R.C.; Daugaard, D.E.; Platon, A.; et al. Techno-economic comparison of biomass-to-transportation fuels via pyrolysis, gasification, and biochemical pathways. Fuel 2010, 89, S29–S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, R.; Singh, N.R. Synergistic routes to liquid fuel for a petroleum-deprived future. AIChE J. 2009, 55, 1898–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, H.; Karim, A.M.; Sun, J.; Wang, Y. Catalytic fast pyrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 7594–7623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Xu, Y.; Huber, G.W. High-throughput screening of monometallic catalysts for aqueous-phase hydrogenation of biomass-derived oxygenates. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2013, 140–141, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben, H.; Mu, W.; Deng, Y.; Ragauskas, A.J. Production of renewable gasoline from aqueous phase hydrogenation of lignin pyrolysis oil. Fuel 2013, 103, 1148–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Li, G.; Yang, F.; Wang, H.; Han, J.; Zhu, X.; Ge, Q. Competition and Cooperation of Hydrogenation and Deoxygenation Reactions during Hydrodeoxygenation of Phenol on Pt(111). J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 12249–12260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Ge, Q.; Zhu, X. Vapor phase hydrodeoxygenation of phenolic compounds on group 10 metal-based catalysts: Reaction mechanism and product selectivity control. Catal. Today 2021, 365, 143–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furimsky, E. Catalytic hydrodeoxygenation. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2000, 199, 147–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, A.; Holgado, J.P.; Gonzalez-delaCruz, V.M.; Habas, S.E.; Herranz, T.; Salmeron, M. In situ spectroscopic detection of SMSI effect in a Ni/CeO2 system: Hydrogen-induced burial and dig out of metallic nickel. Chem. Comm 2010, 46, 1097–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhou, F.; Wang, L.; Qi, X.; Shi, F.; Deng, Y. Low-temperature CO oxidation over supported Pt, Pd catalysts: Particular role of FeOx support for oxygen supply during reactions. J. Catal. 2010, 274, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deleitenburg, C.; Trovarelli, A. Metal-support interactions in Rh/CeO2, Rh/TiO2, and Rh/Nb2O5 catalysts as inferred from CO2 methanation activity. J. Catal. 1995, 156, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauster, S.J.; Fung, S.C.; Baker, R.T.K.; Horsley, J.A. Strong interactions in supported-metal catalysts. Science 1981, 211, 1121–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, D.; Wu, X.; Cui, B.; Guo, Y.; Wang, H.; Han, J.; Ge, Q.; Zhu, X. Ru0.05Ce0.95O2 Solid Solution Derived Ru Catalyst Enables Selective Hydrodeoxygenation of m-Cresol to Toluene. ChemCatChem 2021, 13, 4814–4823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertella, F.; Concepción, P.; Martínez, A. TiO2 polymorph dependent SMSI effect in Co-Ru/TiO2 catalysts and its relevance to Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. Catal. Today 2017, 289, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labich, S.; Taglauer, E.; Knözinger, H. Metal–support interactions on rhodium model catalysts. Top. Catal. 2000, 14, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Wagner, T.; Olliges, S.; Carstanjen, H.D. Metal-Oxide interfacial reactions: Encapsulation of Pd on TiO2 (110). J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.; Jin, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z. Study of high-temperature hydrogen reduced Pt0/TiO2 by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy combined with argon ion sputtering—Diffusion-encapsulation effect in relation to strong metal–support interaction. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 3991–3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauster, S.J.; Fung, S.C.; Garten, R.L. Strong metal-support interactions. Group 8 noble metals supported on titanium dioxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1978, 100, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, B.; Nikolla, E.; Medlin, J.W. Directing Reaction Pathways through Controlled Reactant Binding at Pd-TiO2 Interfaces. Angew. Chem. 2017, 23, 6694–6698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Kwon, O.; Lin, C.; Gorte, R.J. The effects of SMSI on m-Cresol hydrodeoxygenation over Pt/Nb2O5 and Pt/TiO2. J. Catal. 2021, 398, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wu, X.; Wang, H.; Han, J.; Ge, Q.; Zhu, X. Effect of Strong Metal-Support Interaction of Pt/TiO2 on Hydrodeoxygenation of m-Cresol. ChemistrySelect 2018, 3, 10364–10370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resende, K.A.; Noronha, F.B.; Hori, C.E. Hydrodeoxygenation of phenol over metal supported niobia catalysts. Renew. Energy 2020, 149, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Zhu, J.; Li, M.; Shan, Y.; He, M.; Song, C. TiO2-Modified Pd/SiO2 for Catalytic Hydrodeoxygenation of Guaiacol. Energy Fuel 2016, 30, 6671–6676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, C.; Zhou, X.; Goundie, B.; Ghampson, I.T.; Pollock, R.A.; Ross, Z.; Wheeler, M.C.; Meulenberg, R.W.; Austin, R.N.; Frederick, B.G. Effects of support identity and metal dispersion in supported ruthenium hydrodeoxygenation catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2014, 477, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Du, H.; Wei, B.; Zhu, J.; Li, M.; Shan, Y.; Shen, J.; Song, C. Hydrodeoxygenation of Guaiacol on Ru Catalysts: Influence of TiO2–ZrO2 Composite Oxide Supports. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 12070–12079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonyasuwat, S.; Omotoso, T.; Resasco, D.E.; Crossley, S.P. Conversion of Guaiacol over Supported Ru Catalysts. Catal. Lett. 2013, 143, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, G.; Yang, F.; Wang, H.; Han, J.; Ge, Q.; Zhu, X. Vapor phase hydrodeoxygenation and hydrogenation of m-cresol on silica supported Ni, Pd and Pt catalysts. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 135, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Kennedy, E.; Stockenhuber, M. Natural zeolite supported Ni catalysts for hydrodeoxygenation of anisole. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 4673–4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, R.; Xu, Y.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, P.; Wang, T. Synergistic effects of highly active Ni and acid site on the hydrodeoxygenation of syringol. Catal. Commun. 2017, 91, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, L.; de Souza, P.M.; Noronha, F.B.; An, W.; Sooknoi, T.; Resasco, D.E. Selective conversion of m-cresol to toluene over bimetallic Ni–Fe catalysts. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem 2014, 388–389, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Libretto, N.J.; Komarneni, M.R.; Zhou, W.; Miller, J.T.; Zhu, X.; Resasco, D.E. Enhancement of m-Cresol Hydrodeoxygenation Selectivity on Ni Catalysts by Surface Decoration of MoOx Species. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 7791–7800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortensen, P.M.; Grunwaldt, J.-D.; Jensen, P.A.; Jensen, A.D. Influence on nickel particle size on the hydrodeoxygenation of phenol over Ni/SiO2. Catal. Today 2016, 259, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, E.J.; Keane, M.A. Gas-phase hydrogenation/hydrogenolysis of phenol over supported nickel catalysts. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2000, 39, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yan, P.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, Z.C. Identification of electron-rich mononuclear Ni atoms on TiO2-A distinguished from Ni particles on TiO2-R in guaiacol hydrodeoxygenation pathways. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2021, 11, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yan, P.; Zhao, B.; Liu, K.; Kung, M.C.; Kung, H.H.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Z.C. Selective Hydrodeoxygenation of Guaiacol to Phenolics by Ni/Anatase TiO2 Catalyst Formed by Cross-Surface Migration of Ni and TiO2. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 3551–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Liu, D.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Han, J.; Ge, Q.; Zhu, X. Size dependence of vapor phase hydrodeoxygenation of m-cresol on Ni/SiO2 catalysts. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 1672–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Zhou, J.; Xia, Z.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Xu, W.; Yan, P.; Liu, K.; Guo, X.; Zhang, Z.C. Anatase TiO2 Activated by Gold Nanoparticles for Selective Hydrodeoxygenation of Guaiacol to Phenolics. ACS Catal. 2016, 7, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omotoso, T.O.; Baek, B.; Grabow, L.C.; Crossley, S.P. Experimental and First-Principles Evidence for Interfacial Activity of Ru/TiO2 for the Direct Conversion of m-Cresol to Toluene. ChemCatChem 2017, 9, 2642–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.X.; Qian, K.; Jia, A.; Li, D.; Shi, L.; Hu, J.; Zhu, J.; Huang, W. Structure Sensitivity of Au-TiO2 Strong Metal-Support Interactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 12074–12081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.; Wang, H.; Han, J.; Ge, Q.; Zhu, X. Crystal-phase-depended strong metal-support interactions enhancing hydrodeoxygenation of m-cresol on Ni/TiO2 catalysts. J. Catal. 2022, 413, 880–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Wei, A.; Zhu, M.; Wu, X.; Wang, H.; Zhu, X.; Ge, Q. Tuning reverse water gas shift and methanation reactions during CO2 reduction on Ni catalysts via surface modification by MoOx. J CO2 Util 2021, 52, 101678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, V.N.; Laurenti, D.; Afanasiev, P.; Geantet, C. Hydrodeoxygenation of guaiacol with CoMo catalysts. Part I: Promoting effect of cobalt on HDO selectivity and activity. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2011, 101, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretto, L.; Glisenti, A. Surface acidity and basicity of a rutile powder. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 1181–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-Y.T.; Pacchioni, G. Role of Oxide Reducibility in the Deoxygenation of Phenol on Ruthenium Clusters Supported on the Anatase Titania (101) Surface. ChemCatChem 2016, 8, 2492–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| H2 Consumption | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | Total (mmol·g−1) | Ni (mmol·g−1) a | H2/Ni |
| 1Ni/r-TiO2 | 0.024 | 0.017 | 1.41 |
| 5Ni/r-TiO2 | 0.096 | 0.084 | 1.14 |
| 10Ni/r-TiO2 | 0.175 | 0.166 | 1.05 |
| Sample | Metal Ni dXRD a (nm) | Metal Ni dTEM b (nm) a | Metal Ni Dispersion b (%) | Metal Ni Dispersion c (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1Ni/r-TiO2 | — | 4.0 | 25 | 1.03 |
| 5Ni/r-TiO2 | 17.2 | 23.8 | 4.3 | 0.76 |
| 10Ni/r-TiO2 | 23.1 | 29.1 | 3.5 | 0.60 |
| Sample | Ni0/Ni2+ | Ti3+/Ti4+ |
|---|---|---|
| 1Ni/r-TiO2 | 0.09 | 0.03 |
| 5Ni/r-TiO2 | 0.17 | 0.04 |
| 10Ni/r-TiO2 | 0.22 | 0.06 |
| Catalyst | 1Ni/r-TiO2 | 5Ni/r-TiO2 | 10Ni/r-TiO2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| W/F | 6 | 4 | 3 |
| Conversion(%) | 97.75 | 99.25 | 95.2 |
| Selectivity(%) | |||
| Tol | 78.37 | 85.41 | 71.46 |
| DMB | 16.89 | 6.47 | 8.32 |
| Ben | 0.13 | 1.01 | 3.37 |
| Xylene | 0 | 0.05 | 0 |
| C14O | 2.20 | 1.58 | 4.60 |
| Ph | 0.07 | 0.26 | 1.30 |
| Xylenol | 2.05 | 3.63 | 8.63 |
| Iso-Cr | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.19 |
| MCHone | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MCHol | 0.04 | 0 | 0 |
| C2-C6 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.27 |
| CH4 | 0.02 | 0.23 | 1.01 |
| Reaction Rate (μmol·g−1·min−1) a | Turnover Frequency (min−1) a | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | m-cresol | Tol | Deoxygenation b | m-cresol | Tol | Deoxygenation b |
| 1Ni/r-TiO2 | 9.66 | 6.33 | 7.25 | 5.55 | 3.64 | 4.16 |
| 5Ni/r-TiO2 | 23.45 | 15.69 | 17.26 | 3.64 | 2.43 | 2.68 |
| 10Ni/r-TiO2 | 25.39 | 15.83 | 17.95 | 2.48 | 1.54 | 1.75 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, B.; Wang, H.; Ge, Q.; Zhu, X. Size-Dependent Strong Metal–Support Interactions of Rutile TiO2-Supported Ni Catalysts for Hydrodeoxygenation of m-Cresol. Catalysts 2022, 12, 955. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12090955
Cui B, Wang H, Ge Q, Zhu X. Size-Dependent Strong Metal–Support Interactions of Rutile TiO2-Supported Ni Catalysts for Hydrodeoxygenation of m-Cresol. Catalysts. 2022; 12(9):955. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12090955
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Beilei, Hua Wang, Qingfeng Ge, and Xinli Zhu. 2022. "Size-Dependent Strong Metal–Support Interactions of Rutile TiO2-Supported Ni Catalysts for Hydrodeoxygenation of m-Cresol" Catalysts 12, no. 9: 955. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12090955
APA StyleCui, B., Wang, H., Ge, Q., & Zhu, X. (2022). Size-Dependent Strong Metal–Support Interactions of Rutile TiO2-Supported Ni Catalysts for Hydrodeoxygenation of m-Cresol. Catalysts, 12(9), 955. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12090955