Synthesis of Activated Porous Carbon from Red Dragon Fruit Peel Waste for Highly Active Catalytic Reduction in Toxic Organic Dyes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. X-ray Diffraction
2.2. Raman Analysis
2.3. N2 Isotherms
2.4. Thermogravimetric Analysis
2.5. FT-IR Analysis
2.6. Structural Properties
2.7. Role of Chemical Activation
2.8. MgCl2 Activation
2.9. FeCl3 Activation
2.10. ZnCl2 Activation
2.11. Role of N-, B-, and P-Doping
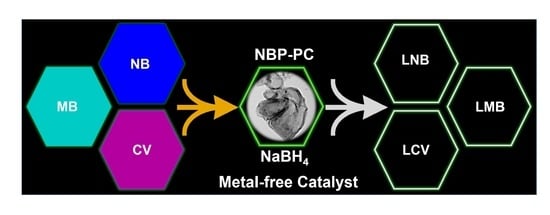
2.12. Reduction in Organic Dyes
2.13. Mechanism of Dye Reduction
2.14. Effect of Catalyst Dosage and Temperature
2.15. Simultaneous Reduction of Dyes
2.16. Stability and Reusability
2.17. Contaminated Water Treatment
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents
3.2. Material Characterization
3.3. Preparation of NBP-PC-M (M = Mg, Fe, and Zn)
3.4. Catalytic Reduction in Dyes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thomas, P.; Lai, C.W.; Johan, M.R.B. Recent developments in biomass-derived carbon as a potential sustainable material for supercapacitor-based energy storage and environmental applications. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2019, 140, 54–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manasa, P.; Lei, Z.J.; Ran, F. Biomass waste derived low cost activated carbon from Carchorus olitorius (Jute fiber) as sustainable and novel electrode material. J. Energy Storage 2020, 30, 101494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Huang, Y.; Chi, X.; Li, D.; Zhong, L.; Li, X.; Liu, C.; Peng, X. Biomass-based N doped carbon as metal-free catalyst for selective oxidation of d-xylose into d-xylonic acid. Green Energy Environ. 2022, 7, 1310–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, M.; Dun, R.; Su, Y.; He, L.; Ning, F.; Zhou, X.; Li, W. In situ self-doped biomass-derived porous carbon as an excellent oxygen reduction electrocatalyst for fuel cells and metal–air batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 14331–14343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Song, N.; Li, X. Biomass-derived renewable carbon materials for electrochemical energy storage. Mater. Res. Lett. 2017, 5, 69–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoang, A.T.; Nižetić, S.; Cheng, C.K.; Luque, R.; Thomas, S.; Banh, T.L.; Pham, V.V.; Nguyen, X.P. Heavy metal removal by biomass-derived carbon nanotubes as a greener environmental remediation: A comprehensive review. Chemosphere 2021, 287, 131959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manavalan, S.; Veerakumar, P.; Chen, S.-M.; Murugan, K.; Lin, K.-C. Binder-free modification of a glassy carbon electrode by using porous carbon for voltammetric determination of nitro isomers. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 8907–8918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, T.; Chen, L.; Mu, L.; Yuan, R.; Knoblauch, M.; Bao, F.S.; Shi, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhu, J. Green processing of plant biomass into mesoporous carbon as catalyst support. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 295, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerakumar, P.; Thanasekaran, P.; Subburaj, T.; Lin, K.-C. A metal-free carbon-based catalyst: An overview and directions for future research. J. Carbon Res. 2018, 4, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Z.; Cheng, M.; Ren, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, M. Treated activated carbon as a metal-free catalyst for effectively catalytic reduction of toxic hexavalent chromium. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 430, 128416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangraz, Y.; Heravi, M.M. Recent advances in metal-free heteroatom-doped carbon heterogonous catalysts. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 23725–23778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Shen, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Xia, K.; Yin, Z.; Zhang, Y. Biomass-derived carbon materials: Controllable preparation and versatile applications. Small 2021, 17, 2008079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johari, S. Johan, M.R. and Khaligh, N.G. An overview of metal-free sustainable nitrogen-based catalytic Knoevenagel condensation reaction. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2022, 20, 2164–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, P.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Xu, Z. Biomass-based activated carbon and activators: Preparation of activated carbon from corncob by chemical activation with biomass pyrolysis liquids. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 24064–24072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Xu, Z. The rational design of biomass-derived carbon materials towards next-generation energy storage: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 134, 110308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Chen, D.; Wang, S.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.; Liu, M. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by nitrogen-doped porous carbon for efficient degradation of organic pollutants in water: Performance and mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 280, 119791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, G.; Rehman, A.; Hussain, S.; Afzal, A.M.; Dastgeer, G.; Rehman, M.A.; Akhter, Z.; Al-Muhimeed, T.I.; AlObaid, A.A. Heteroatoms-doped hierarchical porous carbons: Multifunctional materials for effective methylene blue removal and cryogenic hydrogen storage. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 630, 127554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, W.; Badawi, A.K.; Rehan, Z.A.; Khan, A.M.; Khan, R.A.; Shah, F.; Ali, S.; Ismail, B. Enhanced visible light photocatalytic performance of Sr0.3(Ba, Mn)0.7ZrO3 perovskites anchored on graphene oxide. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 24979–24988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, A.H.; Saud Abdulhameed, A.; Wilson, L.D.; Syed-Hassan, S.S.A.; ALOthman, Z.A.; Rizwan Khan, M. High surface area and mesoporous activated carbon from KOH-activated dragon fruit peels for methylene blue dye adsorption: Optimization and mechanism study. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 32, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arampatzidou, A.C.; Deliyanni, E.A. Comparison of activation media and pyrolysis temperature for activated carbons development by pyrolysis of potato peels for effective adsorption of endocrine disruptor bisphenol-A. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 466, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaemsanit, S.; Matan, N.; Matan, N. Effect of peppermint oil on the shelf-life of dragon fruit during storage. Food Control 2018, 90, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandiyanto, A.B.D.; Maryanti, R.; Fiandini, M.; Ragadhita, R.; Usdiyana, D.; Anggraeni, S.; Arwa, W.R.; Sh. A.; Al-Obaidi, M. Synthesis of carbon microparticles from red dragon fruit (Hylocereus undatus) peel waste and their adsorption isotherm characteristics. Molekul 2020, 15, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandla, D.; Wu, X.; Zhang, F.; Wu, C.; Tan, D.Q. High-performance and high-voltage supercapacitors based on N-doped mesoporous activated carbon derived from dragon fruit peels. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 7615–7625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veerakumar, P.; Maiyalagan, T.; Raj, B.G.S.; Guruprasad, K.; Jiang, Z.; Lin, K.-C. Paper flower-derived porous carbons with high capacitance by chemical and physical activation for sustainable applications. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 2995–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rufford, T.E.; Hulicova-Jurcakova, D.; Zhu, Z.; Lu, G.Q. A comparative study of chemical treatment by FeCl3, MgCl2, and ZnCl2 on microstructure, surface chemistry, and double-layer capacitance of carbons from waste biomass. J. Mater. Res. 2010, 25, 1451–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedia, J.; Peñas-Garzón, M.; Gómez-Avilés, A.; Rodriguez, J.J.; Belver, C. Review on activated carbons by chemical activation with FeCl3. C 2020, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, F.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.-N. Biomass-derived N-doped porous carbon: An efficient metal-free catalyst for methylation of amines with CO2. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 6252–6257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Song, X.; Yu, C.; Gui, J.; Qiu, J. Biomass-derived carbon nanospheres with turbostratic structure as metal-free catalysts for selective hydrogenation of o-chloronitrobenzene. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 7481–7485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Dai, L.; Lin, X.; Chen, J.F.; Zhang, J.; Feng, X.; Müllen, K.; Zhu, X.; Dai, S. Chemical approaches to carbon-based metal-free catalysts. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1804863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, S.; Zhang, H.; Clark, J.H.; Cao, F. A biomass-derived metal-free catalyst doped with phosphorus for highly efficient and selective oxidation of furfural into maleic acid. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 1370–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholipour, B.; Shojaei, S.; Rostamnia, S.; Naimi-Jamal, M.R.; Kim, D.; Kavetskyy, T.; Nouruzi, N.; Jang, H.W.; Varma, R.S.; Shokouhimehr, M. Metal-free nanostructured catalysts: Sustainable driving forces for organic transformations. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 6223–6272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Cui, L.; Peng, Z.; Wang, J.; Hu, Y.; Yu, A.; Wang, H.; Peng, P.; Li, F.-F. Eco-friendly synthesis of N, S co-doped hierarchical nanocarbon as a highly efficient metal-free catalyst for the reduction of nitroarenes. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 21764–21771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salahuddin, N.; Abdelwahab, M.A.; Akelah, A.; Elnagar, M. Adsorption of Congo red and crystal violet dyes onto cellulose extracted from Egyptian water hyacinth. Nat. Hazards 2021, 105, 1375–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, M.; Qamar, M.A.; Iqbal, S.; Aljazzar, S.O.; Iqbal, S.; Khan, H.; Abourehab, M.A.; Elkaeed, E.B.; Alharthi, A.I.; Awwad, N.S.; et al. Synergistic influences of doping techniques and well-defined heterointerface formation to improve the photocatalytic ability of the S-ZnO/GO nanocomposite. ChemistrySelect 2022, 7, e202201913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerakumar, P.; Chen, S.-M.; Madhu, R.; Veeramani, V.; Hung, C.-T.; Liu, S.-B. Nickel nanoparticle-decorated porous carbons for highly active catalytic reduction of organic dyes and sensitive detection of Hg(II) ions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 24810–24821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarwan, B.; Pare, B.; Acharya, A.D. Heterogeneous photocatalytic reduction of nile blue dye in aqueous BiOCl suspensions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 301, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerakumar, P.; Dhenadhayalan, N.; Lin, K.-C.; Liu, S.-B. Highly stable ruthenium nanoparticles on 3D mesoporous carbon: An excellent opportunity for reduction reactions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 23448–23457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerakumar, P.; Panneer Muthuselvam, I.; Thanasekaran, P.; Lin, K.-C. Low-cost palladium decorated on m-aminophenol-formaldehyde-derived porous carbon spheres for the enhanced catalytic reduction of organic dyes. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2018, 5, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Huang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Cai, J. Hierarchical porous carbons from biowaste: Hydrothermal carbonization and high-performance for rhodamine B adsorptive removal. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 330, 115580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qamar, M.A.; Shahid, S.; Javed, M.; Shariq, M.; Fadhali, M.M.; Madkhali, O.; Ali, S.K.; Syed, I.S.; Awaji, M.Y.; Shakir Khan, M.; et al. Accelerated decoloration of organic dyes from wastewater using ternary metal/g-C3N4/ZnO nanocomposites: An investigation of impact of g-C3N4 concentration and Ni and Mn doping. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, H.; Yu, H.; Yang, H.; Chen, T. Synthesis of lignin-derived nitrogen-doped carbon as a novel catalyst for 4-NP reduction evaluation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Baucom, J.; Wang, D.; Dai, L.; Chen, J.-F. Nitrogen-doped graphene foam as a metal-free catalyst for reduction reactions under a high gravity field. Engineering 2020, 6, 680–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ye, R.; Jian, P.; Liu, J. Pumpkin-derived N-doped porous carbon for enhanced liquid-phase reduction of 2-methyl-4-nitrophenol. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 606, 1758–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerakumar, P.; Salamalai, K.; Thanasekaran, P.; Lin, K.-C. Simple preparation of porous carbon-supported ruthenium: Propitious catalytic activity in the reduction of ferrocyanate(III) and a cationic dye. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 12609–12621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Deng, M. Eco-Friendly preparation of biomass-derived porous carbon and Its electrochemical properties. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 22689–22697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Xiao, X.; Gandla, D.; Liu, Z.; Tan, D.Q.; Ein-Eli, Y. Bio-derived carbon with tailored hierarchical pore structures and ultra-high specific surface area for superior and advanced supercapacitors. Nanomaterials 2021, 12, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasakin, O.; Dangbegnon, J.K.; Momodu, D.Y.; Madito, M.J.; Oyedotun, K.O.; Eleruja, M.A.; Manyala, N. Synthesis and characterization of porous carbon derived from activated banana peels with hierarchical porosity for improved electrochemical performance. Electrochimi. Acta 2018, 262, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, T.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, X.; Gao, Y.; Li, H. A facile and low-cost route to heteroatom doped porous carbon derived from Broussonetia Papyrifera bark with excellent supercapacitance and CO2 capture performance. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boudou, J.P.; Bégin, D.; Alain, E.; Furdin, G.; Marêché, J.F.; Albiniak, A. Effects of FeCl3 (intercalated or not in graphite) on the pyrolysis of coal or coal tar pitch. Fuel 1998, 77, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubir, M.H.M.; Zaini, M.A.A. Twigs-derived activated carbons via H3PO4/ZnCl2 composite activation for methylene blue and congo red dyes removal. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueiredo, J.L.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Freitas, M.M.A.; Órfão, J.J.M. Modification of the surface chemistry of activated carbons. Carbon 1999, 37, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaib, G.M.; El-Sikaily, A.; El Nemr, A.; Mohamed, A.E.-D.A.; Hassan, A.A. Preparation and characterization of highly surface area activated carbons followed type IV from marine red alga (Pterocladia capillacea) by zinc chloride activation. Biomass. Conv. Bioref. 2022, 12, 2253–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.A.; Puad, N.A.A.; Bello, O.S. Kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies of synthetic dye removal using pomegranate peel activated carbon prepared by microwave-induced KOH activation. Water Resour. Ind. 2014, 6, 18–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, X.Z.; Guan, W.; Ji, F.; Song, Z.; Zhao, Y. Production of biologically activated carbon from orange peel and landfill leachate subsequent treatment technology. J. Chem. 2014, 2014, 491912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dhelipan, M.; Arunchander, A.; Sahu, A.K.; Kalpana, D. Activated carbon from orange peels as supercapacitor electrode and catalyst support for oxygen reduction reaction in proton exchange membrane fuel cell. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2017, 21, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Wang, L.; Wu, M. Simultaneous removal of dye and heavy metal by banana peels derived hierarchically porous carbons. J. Taiwan Ins. Chem. Eng. 2018, 93, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsuka, Y.; Xu, C.; Kong, D.; Tsubouchi, N. Decomposition of ammonia with iron and calcium catalysts supported on coal chars. Fuel 2004, 83, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayiania, M.; Smith, M.; Hensley, A.J.R.; Scudiero, L.; McEwen, J.-S.; Garcia-Perez, M. Deconvoluting the XPS spectra for nitrogen-doped chars: An analysis from first principles. Carbon 2020, 162, 528–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonkaya, Ö.; Ocakçı, Ş.; Toksoy, A.; Algi, M.P.; Algi, F. N-doped carbon nanomaterials as fluorescent pH and metal ion sensors for imaging. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2023, 292, 122412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, B.-N.; Du, H.L.; Hwang, J.-Y.; Jung, H.-G.; Sun, Y.-K. Improved electrochemical performance of boron doped carbon-coated lithium titanate as an anode material for sodium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 2802–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosas, J.M.; Ruiz-Rosas, R.; Rodríguez-Mirasol, J. Cordero, T. Kinetic study of the oxidation resistance of phosphorus-containing activated carbons. Carbon 2012, 50, 1523–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, K.; Pu, L. The performance of phosphorus (P)-doped activated carbon as a catalyst in air-cathode microbial fuel cells. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 170, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Zhu, Y.; Lei, H.; Wang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Huo, E.; Lin, X.; Zhang, Q.; Qian, M.; Mateo, W.; et al. P-dual-doped multilayer graphene as an efficient carbocatalyst for nitroarene reduction: A mechanistic study of metal-free catalysis. J. Catal. 2018, 359, 233–241. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, H.; Chen, S.; Bao, S.; Xing, F.; Jiang, B. Phosphorus-doped activated carbon catalyst for n-hexane dehydroaromatization reaction. Catal. Commun. 2021, 156, 106318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathiskumar, C.; Ramakrishnan, S.; Vinothkannan, M.; Rhan Kim, A.; Karthikeyan, S.; Yoo, D.J. Nitrogen-doped porous carbon derived from biomass used as trifunctional electrocatalyst toward oxygen reduction, oxygen evolution and hydrogen evolution reactions. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, M.; Lan, J.; Zhang, X.; Sui, G.; Yang, X. Porous carbon derived from Ailanthus altissima with unique honeycomb-like microstructure for high-performance supercapacitors. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 4281–4285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerakumar, P.; Sangili, A.; Manavalan, S.; Thanasekaran, P.; Lin, K.-C. Research progress on porous carbon supported metal/metal oxide nanomaterials for supercapacitor electrode applications. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 6347–6374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, G.; Xu, S.; Chao, J.; Fu, X.; Liao, W.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Cao, Y. Biomass-derived nitrogen-doped porous carbons activated by magnesium chloride as ultrahigh-performance supercapacitors. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 21756–21767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, D.; Chen, W.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Tian, D.; Deng, H.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, Z. Highly mesoporous activated carbon synthesized by pyrolysis of waste polyester textiles and MgCl2: Physiochemical characteristics and pore-forming mechanism. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 192, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Lu, G.; Wang, J.; Yu, J. Thermal decomposition mechanisms of MgCl2 6H2O and MgCl2 H2O. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 2011, 91, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Sun, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhang, T.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, D. Insights into the pyrolysis behavior and adsorption properties of activated carbon from waste cotton textiles by FeCl3-activation. Colloids Surf. A 2019, 582, 123934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, D.; Huang, Y.; Gu, S.; Chen, W. Understanding reactions and pore-forming mechanisms between waste cotton woven and FeCl3 during the synthesis of magnetic activated carbon. Chemosphere 2020, 241, 125120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazetta, A.L.; Pezoti, O.; Bedin, K.C.; Silva, T.L.; Paesano Junior, A.; Asefa, T.; Almeida, V.C. Magnetic activated carbon derived from biomass waste by concurrent synthesis: Efficient adsorbent for toxic dyes. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1058–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, V.T.; Jeong, T.-Y.; Lee, B.-H.; Jeon, C.-H. Variation of char structure during anthracite pyrolysis catalyzed by Fe2O3 and its influence on char combustion reactivity. Energy Fuels 2009, 23, 4547–4552. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, K.; Huang, Q.; Chi, Y.; Yan, J. Effect of ZnCl2-activated biochar on catalytic pyrolysis of mixed waste plastics for producing aromatic-enriched oil. Waste Manag. 2018, 81, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Hu, J.; Xiong, H.; Xiao, Y. Application and properties of microporous carbons activated by ZnCl2: Adsorption behavior and activation mechanism. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 9398–9407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lou, B.-S.; Veerakumar, P.; Chen, S.-M.; Veeramani, V.; Madhu, R.; Liu, S.-B. Ruthenium nanoparticles decorated curl-like porous carbons for high performance supercapacitors. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, R.; Li, L.; Liu, Z.; Lu, M.; Wang, C.; Li, H.; Ma, W.; Wang, S. Preparation and characterization of activated carbons from tobacco stem by chemical activation. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2017, 67, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Benzigar, M.R.; Talapaneni, S.N.; Joseph, S.; Ramadass, K.; Singh, G.; Scaranto, J.; Ravon, U.; Al-Bahily, K.; Vinu, A. Recent advances in functionalized micro and mesoporous carbon materials: Synthesis and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 2680–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharska, M.; Bulusheva, L.G.; Lisitsyn, A.S.; Beloshapkin, S.; Guo, Y.; Chuvilin, A.L.; Shlyakhova, E.V.; Podyacheva, O.Y.; Leahy, J.J.; Okotrub, A.V.; et al. Factors influencing the performance of Pd/C catalysts in the green production of hydrogen from formic acid. ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 720–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, R.; Miao, M.; Du, W.; Shi, J.; Liu, Y.; Hou, Z. Selective hydrogenation of C=C bond over N-doped reduced graphene oxides supported Pd catalyst. Appl. Catal. B 2016, 180, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qamar, M.A.; Javed, M.; Shahid, S. Designing and investigation of enhanced photocatalytic and antibacterial properties of 3d (Fe, Co, Ni, Mn and Cr) metal-doped zinc oxide nanoparticles. Opt. Mater. 2022, 126, 112211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serp, P.; Machado, B. Nanostructured Carbon Materials for Catalysis; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Zhao, J.; Han, D.; Li, X. One-step synthesis of B-doped mesoporous carbon as supports of Pd nanoparticles for liquid phase catalytic hydrodechlorination. Catal. Commun. 2017, 97, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quílez-Bermejo, J.; Morallón, E.; Cazorla-Amorós, D. Metal-free heteroatom-doped carbon-based catalysts for ORR: A critical assessment about the role of heteroatoms. Carbon 2020, 165, 434–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, Q.; Raza, R.; Shabbir, I.; Olabi, A.G. Heteroatom doped high porosity carbon nanomaterials as electrodes for energy storage in electrochemical capacitors: A review. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2019, 4, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriram, B.; Baby, J.N.; Hsu, Y.-F.; Wang, S.-F.; Benadict Joseph, X.; George, M.; Veerakumar, P.; Lin, K.C. MnCo2O4 microflowers anchored on P doped g C3N4 nanosheets as an electrocatalyst for voltammetric determination of the antibiotic drug sulfadiazine. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2021, 3, 3915–3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Dai, L. Carbon-based metal-free catalysts. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 16064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, S.; Bharagava, R.N. Exposure to crystal violet, its toxic, genotoxic and carcinogenic effects on environment and its degradation and detoxification for environmental safety. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2016, 237, 71–104. [Google Scholar]
- Duggan, P.J.; Johnson, A.A.; Rogers, R.L. Chemical reaction hazards associated with the use of sodium borohydride. In Chemical Engineers Symposium Series; Hemsphere Publishing Corporation: New York, NY, USA, 1994; Volume 134, p. 553. [Google Scholar]
- Saka, C. Highly active and durable hydrogen release in NaBH4 methanolysis reaction with sulphur and phosphorus-doped metal-free microalgal carbon nanoparticles. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 292, 120165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, V.; Henary, M. Nile red and Nile blue: Applications and syntheses of structural analogues. Chem. Euro J. 2016, 22, 13764–13782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Li, J.; Ye, R.; Yan, X.; Wang, L.; Jian, P. Versatile bifunctional nitrogen-doped porous carbon derived from biomass in catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol and oxidation of styrene. Chin. J. Catal. 2020, 41, 1217–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerakumar, P.; Jeyapragasam, T.; Surabhi; Salamalai, K.; Maiyalagan, T.; Lin, K.C. Functionalized mesoporous carbon nanostructures for efficient removal of Eriochrome black-T from aqueous solution. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2019, 64, 1305–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Sample | Stotal (m2 g−1) a | Smicro (m2 g−1) b | Smeso (m2 g−1) b | Vtot (cm3 g−1) a | Vmicro (cm3 g−1) b | DP (nm) c | ID/IG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NBP-PC-Mg | 851.4 | 368.3 | 483.1 | 0.433 | 0.12 | 2.6 | 0.96 |
| NBP-PC-Fe | 877.5 | 289.2 | 588.3 | 0.454 | 0.13 | 2.3 | 0.94 |
| NBP-PC-Zn | 1000.8 | 487.4 | 513.4 | 0.632 | 0.20 | 5.0 | 1.03 |
| Entry | Catalyst | Catalyst (mg) | Time (min) | kapp (min−1) | K (min−1 mg−1) b | TOF (min−1) c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | − | 1.0 | 30 | − | − | − |
| 2 | DFC | 2.0 | 30 | 0.0103 | 0.0103 | 3.3 × 10−4 |
| 3 | PC-Zn | 1.0 | 30 | 0.0255 | 0.0255 | 6.6 × 10−4 |
| 4 | N-PC-Zn | 1.0 | 30 | 0.0483 | 0.0483 | 6.6 × 10−4 |
| 5 | B-PC-Zn | 1.0 | 30 | 0.0462 | 0.0462 | 6.6 × 10−4 |
| 6 | P-PC-Zn | 1.0 | 30 | 0.0397 | 0.0397 | 6.6 × 10−4 |
| 7 | NB-PC-Zn | 1.0 | 30 | 0.0565 | 0.0565 | 6.6 × 10−4 |
| 8 | BP-PC-Zn | 1.0 | 30 | 0.0544 | 0.0544 | 6.6 × 10−4 |
| 9 | NP-PC-Zn | 1.0 | 30 | 0.0498 | 0.0498 | 6.6 × 10−4 |
| 10 | NBP-PC-Mg | 1.0 | 22.2 | 0.1614 | 0.1614 | 9.0 × 10−4 |
| 11 | NBP-PC-Fe | 1.0 | 25.5 | 0.1460 | 0.1460 | 7.9 × 10−4 |
| 12 | NBP-PC-Zn | 0.2 | 12.0 | 0.0685 | 0.3425 | 8.3 × 10−3 |
| 13 | NBP-PC-Zn | 0.4 | 12.0 | 0.1398 | 0.3495 | 4.1 × 10−3 |
| 14 | NBP-PC-Zn | 0.6 | 12.0 | 0.2473 | 0.4122 | 2.7 × 10−4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Veerakumar, P.; Hung, S.-T.; Hung, P.-Q.; Vishnu Priya, V. Synthesis of Activated Porous Carbon from Red Dragon Fruit Peel Waste for Highly Active Catalytic Reduction in Toxic Organic Dyes. Catalysts 2023, 13, 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13020449
Veerakumar P, Hung S-T, Hung P-Q, Vishnu Priya V. Synthesis of Activated Porous Carbon from Red Dragon Fruit Peel Waste for Highly Active Catalytic Reduction in Toxic Organic Dyes. Catalysts. 2023; 13(2):449. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13020449
Chicago/Turabian StyleVeerakumar, Pitchaimani, Shih-Tung Hung, Pei-Qi Hung, and Veeraraghavan Vishnu Priya. 2023. "Synthesis of Activated Porous Carbon from Red Dragon Fruit Peel Waste for Highly Active Catalytic Reduction in Toxic Organic Dyes" Catalysts 13, no. 2: 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13020449
APA StyleVeerakumar, P., Hung, S. -T., Hung, P. -Q., & Vishnu Priya, V. (2023). Synthesis of Activated Porous Carbon from Red Dragon Fruit Peel Waste for Highly Active Catalytic Reduction in Toxic Organic Dyes. Catalysts, 13(2), 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13020449