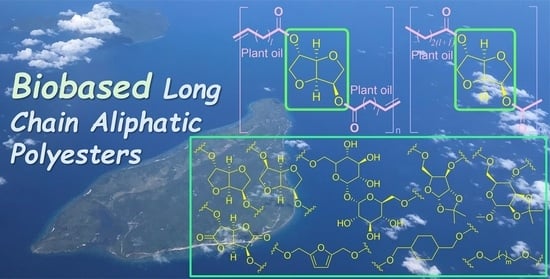
Acyclic Diene Metathesis (ADMET) Polymerization for the Synthesis of Chemically Recyclable Bio-Based Aliphatic Polyesters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Synthesis of Bio-Based Aliphatic Polyesters by ADMET Polymerization
2.1. Synthesis of Aliphatic Polyesters by ADMET Polymerization and Hydrogenation
2.2. Synthesis of High Molecular-Weight Polymers Exhibiting Tensile Properties beyond Polyethylene and Polypropylene
2.3. Chemical Recycling of Polyesters
3. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gandini, A. Polymers from renewable resources: A Challenge for the future of macromolecular materials. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 9491–9504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, M.A.R.; Metzger, J.O.; Schubert, U.S. Plant oil renewable resources as green alternatives in polymer science. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2007, 36, 1788–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Larock, R.C. Vegetable oil-based polymeric materials: Synthesis, properties, and applications. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 1893–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biermann, U.; Bornscheuer, U.; Meier, M.A.R.; Metzger, J.O.; Schäfer, H.J. Oils and fats as renewable raw materials in chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 3854–3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillmyer, M.A.; Tolman, W.B. Aliphatic polyester block polymers: Renewable, degradable, and sustainable. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 2390–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stempfle, F.; Ortmann, P.; Mecking, S. Long-chain aliphatic polymers to bridge the gap between semicrystalline polyolefins and traditional polycondensates. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 4597–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monomers and polymers from chemically modified plant oils and their fatty acids. In Polymers from Plant Oils, 2nd ed.; Gandini, A.; Lacerda, T.M. (Eds.) John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA; Scrivener Publishing LLC: Beverly, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 33–82. [Google Scholar]
- Nomura, K.; Awang, N.W.B. Synthesis of bio-based aliphatic polyesters from plant oils by efficient molecular catalysis: A selected survey from recent reports. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 5486–5505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häußler, M.; Eck, M.; Rothauer, D.; Mecking, S. Closed-loop recycling of polyethylene-like materials. Nature 2021, 590, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biermann, U.; Bornscheuer, U.T.; Feussner, I.; Meier, M.A.R.; Metzger, J.O. Fatty acids and their derivatives as renewable platform molecules for the chemical industry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 20144–20165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worch, J.C.; Dove, A.P. 100th Anniversary of macromolecular science viewpoint: Toward catalytic chemical recycling of waste (and future) plastics. ACS Macro Lett. 2020, 9, 1494–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishioka, R.; Kitakuni, E.; Ichikawa, Y. Aliphatic polyesters: “Bionolle”. In Biopolymers; Steinbüchel, A., Doi, Y., Eds.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2002; Volume 4, pp. 275–297. [Google Scholar]
- Korshak, W.V.; Vinogradova, S.V. Polyesters of 1,20-eicosanediol. Bull. Acad. Sci. USSR Div. Chem. Sci. 1953, 2, 995–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunn, C.W. The melting points of chain polymers. J. Polym. Sci. 1955, 16, 323–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, J.J.; Hillmyer, M.A.; Reineke, T.M. Isosorbide-based polymethacrylates. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Mahmud, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, J.; Shen, Z.; Liu, X. Bio-based amorphous polyesters with high Tg: Trade-off between rigid and flexible cyclic diols. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 6401–6411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, G.; Deutsch, J.; Martin, A.; Baumann, F.; Fridag, D.; Franke, R.; Kçckritz, A. α,ω-Functionalized C19 Monomers. ChemSusChem 2011, 4, 1052–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witt, T.; Häußler, M.; Kulpa, S.; Mecking, S. Chain multiplication of fatty acids to precise telechelic polyethylene. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 7589–7594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, N.; Köhnke, K.; Seidensticker, T. Selective product crystallization for concurrent product separation and catalyst recycling in the isomerizing methoxycarbonylation of methyl oleate. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 10633–10638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Rajput, B.S.; Chikkali, S.H. Refining plant oils and sugars to platform chemicals, monomers, and polymers. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 4255–4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyrębek, P.; Małecki, P.; Sytniczuk, A.; Kośnik, W.; Gawin, A.; Kostrzewa, J.; Kajetanowicz, A.; Grela, K. Looking for the noncyclic(amino)(alkyl)carbene ruthenium catalyst for ethenolysis of cthyl oleate: Selectivity is on target. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 18481–18488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sytniczuk, A.; Kajetanowicz, A.; Grela, K. “Inverted” cyclic(alkyl)(amino)carbene ligands allow olefin metathesis with ethylene at parts-per-billion catalyst loading. Chem. Catal. 2023, 3, 100713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawin, R.; Tracz, A.; Krajczy, P.; Kozakiewicz-Piekarz, A.; Martínez, J.P.; Trzaskowski, B. Inhibition of the decomposition pathways of ruthenium olefin metathesis catalysts: Development of highly efficient catalysts for ethenolysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 25010–25021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Vecchio, A.; Talcik, J.; Colombel-Rouen, S.; Lorkowski, J.; Serrato, M.R.; Roisnel, T.; Vanthuyne, N.; Bertrand, G.; Jazzar, R.; Mauduit, M. Highly robust and efficient Blechert-type cyclic(alkyl)(amino)carbene ruthenium complexes for olefin metathesis. ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 6195–6206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, M.E.; Long, T.E. Synthetic Methods in Step-Growth Polymers; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Le Fevere de Ten Hove, C.; Penelle, J.; Ivanov, D.A.; Jonas, A.M. Encoding crystal microstructure and chain folding in the chemical structure of synthetic polymers. Nat. Mater. 2004, 3, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menges, M.G.; Penelle, J.; Le Fevere de Ten Hove, C.; Jonas, A.M.; Schmidt-Rohr, K. Characterization of long-chain aliphatic polyesters: Crystalline and supramolecular structure of PE22,4 elucidated by X-ray scattering and nuclear magnetic resonance. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 8714–8725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roesle, P.; Stempfle, F.; Hess, S.K.; Zimmerer, J.; Río Bartulos, C.; Lepetit, B.; Eckert, A.; Kroth, P.G.; Mecking, S. Synthetic polyester from Algae oil. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 6800–6804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atallah, P.; Wagener, K.B.; Schulz, M.D. ADMET: The future revealed. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 4735–4741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pribyl, J.; Wagener, K.B.; Rojas, G. ADMET polymers: Synthesis, structure elucidation, and function. Mater. Chem. Front. 2021, 5, 14–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Abdellatif, M.M.; Nomura, K. Olefin metathesis polymerization: Some recent developments in the precise polymerizations for synthesis of advanced materials (by ROMP, ADMET). Tetrahedron 2018, 74, 619–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trnka, T.M.; Grubbs, R.H. The development of L2X2Ru=CHR olefin metathesis catalysts: An organometallic success story. Acc. Chem. Res. 2001, 34, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samojzowicz, C.; Bieniek, M.; Grela, K. Ruthenium-based olefin metathesis catalysts bearing N-heterocyclic carbene ligands. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 3708–3742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubbs, R.H.; Wenzel, A.G.; O’Leary, D.J.; Khosravi, E. (Eds.) Handbook of Metathesis, 2nd ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Vougioukalakis, G.; Grubbs, R.H. Ruthenium-based heterocyclic carbene-coordinated olefin metathesis catalysts. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 1746–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oskam, H.J.; Fox, H.H.; Yap, B.K.; McConville, H.D.; O’Dell, R.; Lichtenstein, J.B.; Schrock, R.R. Ligand variation in alkylidene complexes of the type Mo(CHR)(NR′)(OR″)2. J. Organomet. Chem. 1993, 459, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrock, R.R.; Hoveyda, A.H. Molybdenum and tungsten imido alkylidene complexes as efficient olefin-metathesis catalysts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 4592–4633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyashita, T.; Kunisawa, M.; Sueki, S.; Nomura, K. Synthesis of poly(arylene vinylene)s containing different end groups by combined acyclic diene metathesis polymerization with Wittig-type coupling. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 5288–5293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, K.; Wang, X.; Go, L.; Makino, R.; Matsumoto, Y.; Shimoyama, D.; Abdellatif, M.M.; Kadota, J.; Hirano, H.; Nomura, K. Synthesis of high molecular weight bio-based aliphatic polyesters exhibiting tensile properties beyond polyethylene. ACS Macro Lett. 2023, 12, 1403–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybak, A.; Meier, M.A.R. Acyclic diene metathesis with a monomer from renewable resources: Control of molecular weight and one-step preparation of block copolymers. ChemSusChem 2008, 1, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fokou, P.A.; Meier, M.A.R. Use of a renewable and degradable monomer to study the temperature-dependent olefin isomerization during ADMET polymerizations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 1664–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulman, M.; Grubbs, R.H. Ruthenium carbene-based olefin metathesis initiators: Catalyst decomposition and longevity. J. Org. Chem. 1999, 64, 7202–7207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehman, S.E.; Wagener, K.B. Comparison of the kinetics of acyclic diene metathesis promoted by Grubbs ruthenium olefin metathesis catalysts. Macromolecules 2001, 35, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, B. Catalysis at the interface of ruthenium carbene and ruthenium hydride chemistry: Organometallic aspects and applications to organic synthesis. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 2004, 1865–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.H.; Wenzel, A.G.; Salguero, T.T.; Day, M.W.; Grubbs, R.H. Decomposition of ruthenium olefin metathesis catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 7961–7968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higman, C.S.; Lanterna, A.E.; Marin, M.L.; Scaiano, J.C.; Fogg, D.E. Catalyst decomposition during olefin metathesis yields isomerization-active ruthenium nanoparticles. ChemCatChem 2016, 8, 2446–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawiczuk, M.; Marczyk, A.; Trzaskowski, B. Decomposition of ruthenium olefin metathesis catalyst. Catalysts 2020, 10, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokou, P.A.; Meier, M.A.R. Studying and suppressing olefin isomerization side reactions during ADMET polymerizations. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2010, 31, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trzaskowski, J.; Quinzler, D.; Bährle, C.; Mecking, S. Aliphatic long-chain C20 polyesters from olefin metathesis. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2011, 32, 1352–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stempfle, F.; Ortmann, P.; Mecking, S. Which polyesters can mimic polyethylene? Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2013, 34, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilela, C.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Meier, M.A.R. Plant oil-based long-chain C26 monomers and their polymers. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2012, 213, 2220–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stempfle, F.; Quinzler, D.; Heckler, I.; Mecking, S. Long-chain linear C19 and C23 monomers and polycondensates from unsaturated fatty acid esters. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 4159–4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roumanet, P.-J.; Jarroux, N.; Goujard, L.; Le Petit, J.; Raoul, Y.; Bennevault, V.; Guégan, P. Synthesis of linear polyesters from monomers based on 1,18-(Z)-octadec-9-enedioic acid and their biodegradability. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 16853–16860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, K.; Chaijaroen, P.; Abdellatif, M.M. Synthesis of bio-based long-chain polyesters by acyclic diene metathesis polymerization and tandem hydrogenation and depolymerization with ethylene. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 18301–18312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortmann, P.; Mecking, S. Long-spaced aliphatic polyesters. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 7213–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, M.; Abdellatif, M.M.; Nomura, K. Synthesis of semi-crystalline long chain aliphatic polyesters by ADMET copolymerization of dianhydro-D-glucityl bis(undec-10-enoate) with 1,9-decadiene and tandem hydrogenation. Catalysts 2021, 11, 1098–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccini, M.; Leak, D.J.; Chuck, C.J.; Buchard, A. Polymers from sugars and unsaturated fatty acids: ADMET polymerisation of monomers derived from d-xylose, d-mannose and castor oil. Polym. Chem. 2020, 11, 2681–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccini, M.; Lightfoot, J.; Castro, D.B.; Buchard, A. Xylose-Based Polyethers and Polyesters Via ADMET Polymerizationtoward Polyethylene-Like Materials. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 5870–5881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llevot, A.; Grau, E.; Carlotti, S.; Greliera, S.; Cramail, H. ADMET polymerization of bio-based biphenyl compounds. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 7693–7700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, D.; Samart, C.; Kongparakul, S.; Nomura, K. Synthesis of new polyesters by acyclic diene metathesis polymerization of bio-based α,ω-dienes prepared from eugenol and castor oil (undecenoate). RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 10245–10252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hibert, G.; Grau, E.; Pintori, D.; Lecommandoux, S.; Cramail, H. ADMET polymerization of α,ω-unsaturated glycolipids: Synthesis and physico-chemical properties of the resulting polymers. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 3731–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearouse, W.C.; Lillie, L.M.; Reineke, T.M.; Tolman, W.B. Sustainable Polyesters Derived from Glucose and Castor Oil: BuildingBlock Structure Impacts Properties. ACS Macro Lett. 2015, 4, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillie, L.M.W.; Tolman, B.T.; Reineke, M. Structure/property relationships in copolymers comprising renewable isosorbide, glucarodilactone, and 2,5-bis(hydroxymethyl)-furan subunits. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 3746–3754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebarbé, T.; Neqal, M.; Grau, E.; Alfos, C.; Cramail, H. Branched polyethylene mimicry by metathesis copolymerization of fatty acid-based α,ω-dienes. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 1755–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Lu, X.; Zhou, Q. Structures and Interactions of Ionic Liquids; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Lu, X.; Zhou, Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, S. Ionic Liquids. Physicochemical Properties; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Liu, X.; Dong, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S. Multiscale studies on ionic liquids. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 6636–6695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; He, H.; Wang, C.; Lu, Y.; Dong, K.; Huo, F.; Zhang, S. Insights into ionic liquids: From Z-bonds to quasi-liquids. JACS Au 2022, 2, 543–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Lu, X.; Zhou, Q.; Xu, J.; Xin, J.; Zhang, S. Efficient biomass pretreatment process based on the simple reuse of a low-viscosity ionic-liquid solvent system. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 12738–12750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zeng, J.; Lu, X.; Xin, J.; Zhang, S. High aluminum content beta zeolite as an active Lewis acid catalyst for γ-valerolactone decarboxylation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 11841–11848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amesho, K.T.T.; Lin, Y.-C.; Mohan, S.V.; Halder, S.; Ponnusamy, V.K.; Jhang, S.-R. Deep eutectic solvents in the transformation of biomass into biofuels and fine chemicals: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 21, 183–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, S.; Yao, X.; Kang, Y.; Xin, J.; Ibrahim, T.; Xu, J.; Lu, X. A Renewable co-solvent promoting the selective removal of lignin by increasing the total number of hydrogen bonds. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 6393–6403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simocko, C.; Yang, Y.; Swager, T.M.; Wagener, K.B. Metathesis step-growth polymerizations in ionic liquid. ACS Macro Lett. 2013, 2, 1061–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, D.; Autenrieth, B.; Buchmeiser, M.R. First acyclic diene metathesis polymerization under biphasic conditions using a dicationic ruthenium alkylidene: Access to high-molecular-weight polymers with very low ruthenium contamination. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2015, 36, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponkratov, D.O.; Shaplov, A.S.; Vygodskii, Y.S. Metathesis polymerization in ionic media. Polym. Sci. Ser. C 2019, 61, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weychardt, H.; Plenio, H. Acyclic diene metathesis polymerization of divinylarenes and divinylferrocenes with Grubbs-type olefin metathesis catalysts. Organometallics 2008, 27, 1479–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sydlik, S.A.; Delgado, P.A.; Inomata, S.; VanVeller, B.; Yang, Y.; Swager, T.M.; Wagener, K.B. Triptycene-containing polyetherolefins via acyclic diene metathesis polymerization. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2013, 51, 1695–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucero, J.M.; Romero, Z.; Moreno, A.; Huber, D.L.; Simocko, C. ADMET polymerization in affordable, commercially available, high boiling solvents. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, W.; Nomura, K. Synthesis of high molecular weight bio-based aliphatic polyesters by acyclic diene metathesis polymerization in ionic liquids. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 7222–7233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Chin, A.L.; Zhou, J.; Wang, H.; Tong, R. Resilient poly(α-hydroxy acids) with improved strength and ductility via scalable stereosequence-controlled polymerization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 16813–16823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, K.; Aoki, T.; Ohki, Y.; Kikkawa, S.; Yamazoe, S. Transesterification of methyl-10-undecenoate and poly(ethylene adipate) catalyzed by (cyclopentadienyl)titanium trichlorides as model chemical conversions of plant oils and acid-, base-free chemical recycling of aliphatic polyesters. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 12504–12509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohki, Y.; Ogiwara, Y.; Nomura, K. Depolymerization of polyesters by transesterification with ethanol using (cyclopentadienyl)titanium trichlorides. Catalysts 2023, 13, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Ru cat. | Temp. /°C | Nitrogen Purge 2 | Mn 3 | Mw/Mn 3 | Isomerization 4 /% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G2 | 60 | no | 5600 | 1.65 | 48 |
| G1 | 70 | no | 4400 | 1.57 | 3 |
| G2 | 70 | no | 6000 | 1.71 | 49 |
| G1 | 80 | no | 4750 | 1.56 | 4 |
| G2 | 80 | no | 6100 | 1.61 | 69 |
| G1 | 80 | yes | 6600 | 1.77 | 3 |
| G2 | 80 | yes | 8400 | 1.75 | 76 |
| G1 | 90 | no | 5450 | 1.69 | 3 |
| G2 | 90 | no | 6200 | 1.65 | 66 |
| G1 | 100 | no | 5000 | 1.61 | 42 5 |
| Monomer | Yield 2/% | Mn 3 | Mw/Mn 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| M2 | 93 | 39,200 | 1.95 |
| M24 | 86 | 37,500 | 1.91 |
| M6 | 92 | 26,000 | 1.95 |
| M7 | 89 | 33,400 | 2.30 |
| M7 4 | 87 | 34,900 | 1.82 |
| M8 | 94 | 38,800 | 3.38 |
| Monomer (μmol) | cat./mol% | Yield 2/% | Mn 3/g·mol−1 | Mw/Mn 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M2 (90.5) | 5.0 | 99 | 16,000 | 1.79 |
| M2 (90.5) | 2.5 | 90 | 25,100 | 1.43 |
| M2 (90.5) | 1.0 | 88 | 34,400 | 1.49 |
| M2 (272) | 1.0 | 88 | 46,100 | 2.08 |
| M2 (272) | 1.0 | 91 | 46,100 | 1.84 |
| M6 (272) | 1.0 | 87 | 34,800 | 1.87 |
| M19 (272) | 1.0 | 99 | 67,200 | 2.27 |
| M2 (272) | 0.5 | 90 | 48,700 | 2.04 |
| M2 (543) 4 | 0.5 | 91 | 49,400 | 2.47 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nomura, K.; Wang, X. Acyclic Diene Metathesis (ADMET) Polymerization for the Synthesis of Chemically Recyclable Bio-Based Aliphatic Polyesters. Catalysts 2024, 14, 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal14020097
Nomura K, Wang X. Acyclic Diene Metathesis (ADMET) Polymerization for the Synthesis of Chemically Recyclable Bio-Based Aliphatic Polyesters. Catalysts. 2024; 14(2):97. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal14020097
Chicago/Turabian StyleNomura, Kotohiro, and Xiuxiu Wang. 2024. "Acyclic Diene Metathesis (ADMET) Polymerization for the Synthesis of Chemically Recyclable Bio-Based Aliphatic Polyesters" Catalysts 14, no. 2: 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal14020097
APA StyleNomura, K., & Wang, X. (2024). Acyclic Diene Metathesis (ADMET) Polymerization for the Synthesis of Chemically Recyclable Bio-Based Aliphatic Polyesters. Catalysts, 14(2), 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal14020097