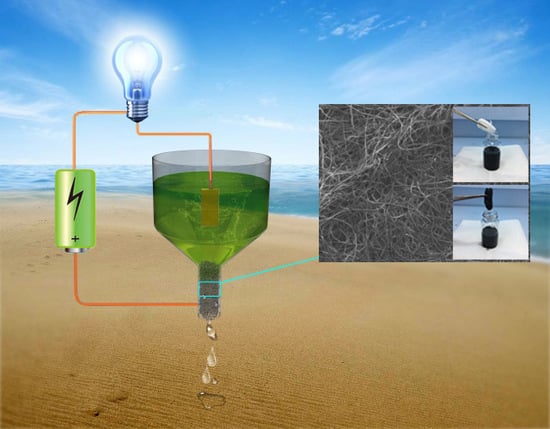
Conductive Cotton Filters for Affordable and Efficient Water Purification
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Fabrication of Conductive Cotton Filters
2.2. Electron Transfer
2.3. Performance of the Cotton Filter towards MO Removal
2.4. Performance of the Cotton Filter towards TC Removal
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Fabrication of Conductive Cotton Filter
3.3. Electrochemical Filtration Device
3.4. Characterizations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zodrow, K.R.; Li, Q.; Buono, R.M.; Chen, W.; Daigger, G.; Dueñas-Osorio, L.; Elimelech, M.; Huang, X.; Jiang, G.; Kim, J.-H.; et al. Advanced materials, technologies, and complex systems analyses: Emerging opportunities to enhance urban water security. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 10274–10281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, Y.; He, M.; Su, Y.; Zhao, X.; Elimelech, M.; Jiang, Z. Antifouling membranes for sustainable water purification: Strategies and mechanisms. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 5888–5924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madaeni, S.S.; Ghaemi, N.; Rajabi, H. 1—Advances in Polymeric Membranes for Water Treatment, in Advances in Membrane Technologies for Water Treatment; Woodhead Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 3–41. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Yang, G.; Shen, F.; Deng, S.; Zhang, X.; He, Y.; Hu, Y.; Chen, X. Fast and large-scale anodizing synthesis of pine-cone TiO2 for solar-driven photocatalysis. Catalysts 2017, 7, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, K.E.; Dionysiou, D.D. Advanced oxidation processes for water treatment. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 2112–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhao, R. Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) in wastewater treatment. Curr. Pollution Rep. 2015, 1, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, M.; Varghese, S.; Nair, S. Photocatalytic water treatment by titanium dioxide: Recent updates. Catalysts 2012, 2, 572–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.C.; Elabd, Y.A.; Jing, Y.; Chaplin, B.P.; Fang, L. Highly porous Ti4O7 reactive electrochemical water filtration membranes fabricated via electrospinning/electrospraying. AIChE J. 2016, 62, 508–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikehata, K.; Jodeiri Naghashkar, N.; Gamal El-Din, M. Degradation of aqueous pharmaceuticals by ozonation and advanced oxidation processes: A review. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2006, 28, 353–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-J.; Jang, A. Fouling characteristics of NOM during the ceramic membrane microfiltration process for water treatment. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 9034–9042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaplin, B.P. Critical review of electrochemical advanced oxidation processes for water treatment applications. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2014, 16, 1182–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anglada, Á.; Urtiaga, A.; Ortiz, I. Contributions of electrochemical oxidation to waste-water treatment: Fundamentals and review of applications. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2009, 84, 1747–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G. Electrochemical technologies in wastewater treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2004, 38, 11–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, V.N. Carbon nanotubes: Properties and application. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 2004, 43, 61–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Gerstandt, K.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; Hinds, B.J. Electrophoretically induced aqueous flow through single-walled carbon nanotube membranes. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Volder, M.F.L.; Tawfick, S.H.; Baughman, R.H.; Hart, A.J. Carbon nanotubes: Present and future commercial applications. Science 2013, 339, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Du, B.; Nasaruddin, R.R.; Chen, T.; Xie, J. Golden carbon nanotube membrane for continuous flow catalysis. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 2999–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zuo, K.; Vecitis, C.D. Titanium dioxide-coated carbon nanotube network filter for rapid and effective arsenic sorption. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 13871–13879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, G.; Zhang, Q.; Hao, Z.; Vecitis, C.D. Carbon nanotube membrane stack for flow-through sequential regenerative electro-Fenton. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Xie, J.; Ong, C.N.; Vecitis, C.D.; Zhou, Z. Electrochemical wastewater treatment with carbon nanotube filters coupled with in situ generated H2O2. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2015, 1, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, X.; Wei, J.; Wang, K.; Cao, A.; Zhu, H.; Jia, Y.; Shu, Q.; Wu, D. Carbon Nanotube Sponges. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 617–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Xue, Y.; Zou, M.; Zhang, D.; Cao, A.; Duan, H. Direct oil recovery from saturated carbon nanotube sponges. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 12337–12343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoen, D.T.; Schoen, A.P.; Hu, L.; Kim, H.S.; Heilshorn, S.C.; Cui, Y. High speed water sterilization using one-dimensional nanostructures. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 3628–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arash, B.; Wang, Q.; Varadan, V.K. Mechanical properties of carbon nanotube/polymer composites. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makowski, T.; Kowalczyk, D.; Fortuniak, W.; Jeziorska, D.; Brzezinski, S.; Tracz, A. Superhydrophobic properties of cotton woven fabrics with conducting 3D networks of multiwall carbon nanotubes, MWCNTs. Cellulose 2014, 21, 4659–4670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasta, M.; La Mantia, F.; Hu, L.; Deshazer, H.D.; Cui, Y. Aqueous supercapacitors on conductive cotton. Nano Res. 2010, 3, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Sun, J.; Huang, Y.; Hu, H.; Jiang, R.; Gai, W.; Li, G.; Zhi, C. Polyurethane/Cotton/Carbon Nanotubes Core-Spun Yarn as High Reliability Stretchable Strain Sensor for Human Motion Detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 24837–24843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.F.; Rojas, E.; Bergey, D.M.; Johnson, A.T.; Yodh, A.G. High weight fraction surfactant solubilization of single-wall carbon nanotubes in water. Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Liu, J.; Mäder, E. Smart cellulose fibers coated with carbon nanotube networks. Fibers 2014, 2, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.J.; Mieno, T. Conductive cotton textile from safely functionalized carbon nanotubes. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Bertoldi, K.; Vecitis, C.D. Quantitative 2D electrooxidative carbon nanotube filter model: Insight into reactive sites. Carbon 2014, 80, 651–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Dustin Lee, J.H.; Xia, Q.; Ma, Y.; Yu, Y.; Lanry Yung, L.Y.; Xie, J.; Ong, C.N.; Vecitis, C.D.; Zhou, Z. A graphene-based electrochemical filter for water purification. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 16554–16562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecitis, C.D.; Gao, G.; Liu, H. Electrochemical carbon nanotube filter for adsorption, desorption, and oxidation of aqueous dyes and anions. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 3621–3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Pan, M.; Vecitis, C.D. Effect of the oxidation approach on carbon nanotube surface functional groups and electrooxidative filtration performance. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 7575–7582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, T.; Ong, C.N.; Vecitis, C.D. Degradation of the common aqueous antibiotic tetracycline using a carbon nanotube electrochemical filter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 7974–7980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avlonitis, S.A.; Kouroumbas, K.; Vlachakis, N. Energy consumption and membrane replacement cost for seawater RO desalination plants. Desalination 2003, 157, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Gerrity, D.; Lee, M.; Gamage, S.; Pisarenko, A.; Trenholm, R.A.; Canonica, S.; Snyder, S.A.; von Gunten, U. Organic contaminant abatement in reclaimed water by UV/H2O2 and a combined process consisting of O3/H2O2 followed by UV/H2O2: Prediction of abatement efficiency, energy consumption, and byproduct formation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 3809–3819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, S.; Yuan, H.; Childress, A.; He, Z. Energy consumption by recirculation: A missing parameter when evaluating forward osmosis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 6827–6829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Wu, M.; Zhao, G. Electrocatalytic oxidation of cellulose to gluconate on carbon aerogel supported gold nanoparticles anode in alkaline medium. Catalysts 2016, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, F.; Xia, Q.; Cheng, Q.; Huang, M.; Liu, Y. Conductive Cotton Filters for Affordable and Efficient Water Purification. Catalysts 2017, 7, 291. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7100291
Li F, Xia Q, Cheng Q, Huang M, Liu Y. Conductive Cotton Filters for Affordable and Efficient Water Purification. Catalysts. 2017; 7(10):291. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7100291
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Fang, Qin Xia, Qianxun Cheng, Mingzhi Huang, and Yanbiao Liu. 2017. "Conductive Cotton Filters for Affordable and Efficient Water Purification" Catalysts 7, no. 10: 291. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7100291
APA StyleLi, F., Xia, Q., Cheng, Q., Huang, M., & Liu, Y. (2017). Conductive Cotton Filters for Affordable and Efficient Water Purification. Catalysts, 7(10), 291. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7100291