Engineering Surface Ligands of Noble Metal Nanocatalysts in Tuning the Product Selectivity
Abstract
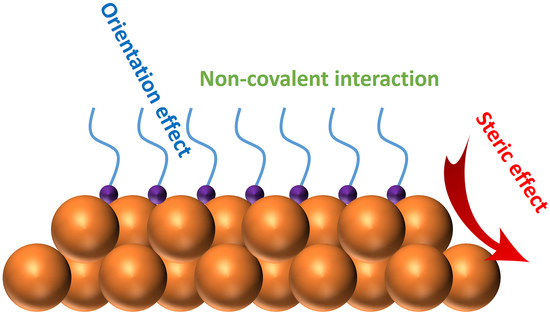
:1. Introduction
2. Steric Effect of Surface Ligands
3. Orientation Effect of Surface Ligands
4. Electronic Effect by Surface Ligands
5. Outlook
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haruta, M. Size- and support-dependency in the catalysis of gold. Catal. Today 1997, 36, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunoyama, H.; Sakurai, H.; Negishi, Y.; Tsukuda, T. Size-specific catalytic activity of polymer-stabilized gold nanoclusters for aerobic alcohol oxidation in water. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 9374–9375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, P.; Carthey, N.; Hutchings, G.J. Discovery, development, and commercialization of gold catalysts for acetylene hydrochlorination. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 14548–14557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philippot, K.; Serp, P. Concepts in nanocatalysis. In Nanomaterials in Catalysis, 1st ed.; Philippot, K., Serp, P., Eds.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co., KgaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2013; pp. 1–54. [Google Scholar]
- Jana, N.R.; Gearheart, L.; Murphy, C.J. Seeding growth for size control of 5–40 nm diameter gold nanoparticles. Langmuir 2001, 17, 6782–6786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Xia, Y. Shape-controlled synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles. Science 2002, 298, 2176–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Xia, Y. Shape-controlled synthesis of metal nanostructures: The case of palladium. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 3385–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lim, B.; Lee, E.P.; Xia, Y. Shape-controlled synthesis of platinum nanocrystals for catalytic and electrocatalytic applications. Nano Today 2009, 4, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohse, S.E.; Murphy, C.J. The quest for shape control: A history of gold nanorod synthesis. Chem. Mater. 2013, 25, 1250–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, R.; El-Sayed, M.A. Shape-dependent catalytic activity of platinum nanoparticles in colloidal solution. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 1343–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, N.; Zhou, Z.-Y.; Sun, S.-G.; Ding, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Synthesis of tetrahexahedral platinum nanocrystals with high-index facets and high electro-oxidation activity. Science 2007, 316, 732–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Jin, M.; Xiong, Y.; Lim, B.; Xia, Y. Shape-controlled synthesis of pd nanocrystals and their catalytic applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2012, 46, 1783–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, K.; Li, Y. Catalysis based on nanocrystals with well-defined facets. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 602–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiramatsu, H.; Osterloh, F.E. A simple large-scale synthesis of nearly monodisperse gold and silver nanoparticles with adjustable sizes and with exchangeable surfactants. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 2509–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumder, V.; Sun, S. Oleylamine-mediated synthesis of pd nanoparticles for catalytic formic acid oxidation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 4588–4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enustun, B.; Turkevich, J. Coagulation of colloidal gold. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1963, 85, 3317–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xia, H.; Ding, W.; Li, Y.; Shi, Q.; Wang, D.; Tao, X. Synthesis of monodisperse, quasi-spherical silver nanoparticles with sizes defined by the nature of silver precursors. Langmuir 2014, 30, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, J.C.; Estroff, L.A.; Kriebel, J.K.; Nuzzo, R.G.; Whitesides, G.M. Self-assembled monolayers of thiolates on metals as a form of nanotechnology. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 1103–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, M.N.; Jones, M.R.; Mirkin, C.A. The nature and implications of uniformity in the hierarchical organization of nanomaterials. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 11717–11725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, S.; Ishino, S.; Harada, T.; Okamoto, N.; Sakata, T.; Mori, H.; Kuwabata, S.; Torimoto, T.; Matsumura, M. Ligand-free platinum nanoparticles encapsulated in a hollow porous carbon shell as a highly active heterogeneous hydrogenation catalyst. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 118, 7221–7224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, C.; Tripkovic, D.; Sun, S.; Markovic, N.M.; Stamenkovic, V.R. Surfactant removal for colloidal nanoparticles from solution synthesis: The effect on catalytic performance. ACS Catal. 2012, 2, 1358–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahsar, K.R.; Schwartz, D.K.; Medlin, J.W. Selective hydrogenation of polyunsaturated fatty acids using alkanethiol self-assembled monolayer-coated Pd/Al2O3 catalysts. ACS Catal. 2013, 3, 2041–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Li, Y. Removal and utilization of capping agents in nanocatalysis. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoskamtorn, T.; Yamazoe, S.; Takahata, R.; Nishigaki, J.-I.; Thivasasith, A.; Limtrakul, J.; Tsukuda, T. Thiolate-mediated selectivity control in aerobic alcohol oxidation by porous carbon-supported Au25 clusters. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 3696–3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, B.; Yuan, X.; Asakura, H.; Tanaka, T.; Teramura, K.; Xie, J.; Yan, N. The support effect on the size and catalytic activity of thiolated Au25 nanoclusters as precatalysts. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 6325–6333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Yao, H.; Song, W.; Jin, L.; Mosa, I.M.; Rusling, J.F.; Suib, S.L.; He, J. Ligand-free noble metal nanocluster catalysts on carbon supports via “soft” nitriding. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 4718–4721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, H.; Liu, B.; Mosa, I.M.; Bist, I.; He, J.; Rusling, J.F. Electrocatalytic oxidation of alcohols, tripropylamine, and DNA with ligand-free gold nanoclusters on nitrided carbon. ChemElectroChem 2016, 3, 2100–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguchi, T.; Isozaki, K.; Miki, K. Enhanced catalytic activity of self-assembled-monolayer-capped gold nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 6462–6467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Wu, H.; Hua, Q.; Chang, S.; Huang, W. Enhancing catalytic selectivity of supported metal nanoparticles with capping ligands. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 2273–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Liu, S.; Zheng, N. C2H2 treatment as a facile method to boost the catalysis of Pd nanoparticulate catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 5583–5586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wan, X.-K.; Ren, L.; Su, H.; Li, G.; Malola, S.; Lin, S.; Tang, Z.; Häkkinen, H.; Teo, B.K.; et al. Atomically precise alkynyl-protected metal nanoclusters as a model catalyst: Observation of promoting effect of surface ligands on catalysis by metal nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 3278–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somorjai, G.A.; Kliewer, C.J. Reaction selectivity in heterogeneous catalysis. React. Kinet. Catal. Lett. 2009, 96, 191–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitford, D. Proteins: Structure and Function; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- García-Urdiales, E.; Lavandera, I.; Gotor, V. Concepts in biocatalysis. In Enzyme Catalysis in Organic Synthesis, 3rd ed.; Drauz, K., Gröger, H., May, O., Eds.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co., KgaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2012; pp. 43–66. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Xu, C.; Huang, X.; Ye, J.; Gu, L.; Li, G.; Tang, Z.; Wu, B.; Yang, H.; Zhao, Z. Interfacial electronic effects control the reaction selectivity of platinum catalysts. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoenbaum, C.A.; Schwartz, D.K.; Medlin, J.W. Controlling surface crowding on a pd catalyst with thiolate self-assembled monolayers. J. Catal. 2013, 303, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, S.H.; Schoenbaum, C.A.; Schwartz, D.K.; Medlin, J.W. Directing reaction pathways by catalyst active-site selection using self-assembled monolayers. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Huang, H.; Yang, J.; Zheng, N.; Fu, G. Selective hydrogenation of α,β-unsaturated aldehydes catalyzed by amine-capped platinum-cobalt nanocrystals. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 124, 3496–3499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.G.; Krylova, G.; Sumer, A.; Schwartz, M.M.; Bunel, E.E.; Marshall, C.L.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Lee, B.; Jellinek, J.; Shevchenko, E.V. Capping ligands as selectivity switchers in hydrogenation reactions. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 5382–5388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haruta, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Sano, H.; Yamada, N. Novel gold catalysts for the oxidation of carbon monoxide at a temperature far below 0 °C. Chem. Lett. 1987, 16, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landon, P.; Collier, P.J.; Papworth, A.J.; Kiely, C.J.; Hutchings, G.J. Direct formation of hydrogen peroxide from H2/O2 using a gold catalyst. Chem. Commun. 2002, 2058–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Saltsburg, H.; Flytzani-Stephanopoulos, M. Active nonmetallic Au and Pt species on ceria-based water-gas shift catalysts. Science 2003, 301, 935–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, M.D.; Xu, Y.-J.; Jenkins, P.; McMorn, P.; Landon, P.; Enache, D.I.; Carley, A.F.; Attard, G.A.; Hutchings, G.J.; King, F. Tunable gold catalysts for selective hydrocarbon oxidation under mild conditions. Nature 2005, 437, 1132–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Zeng, C.; Jin, R. Thermally robust Au99(SPh)42 nanoclusters for chemoselective hydrogenation of nitrobenzaldehyde derivatives in water. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 3673–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ose, T.; Watanabe, K.; Mie, T.; Honma, M.; Watanabe, H.; Yao, M.; Oikawa, H.; Tanaka, I. Insight into a natural Diels–Alder reaction from the structure of macrophomate synthase. Nature 2003, 422, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Röthlisberger, D.; Khersonsky, O.; Wollacott, A.M.; Jiang, L.; DeChancie, J.; Betker, J.; Gallaher, J.L.; Althoff, E.A.; Zanghellini, A.; Dym, O. Kemp elimination catalysts by computational enzyme design. Nature 2008, 453, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, J.B.; Zanghellini, A.; Lovick, H.M.; Kiss, G.; Lambert, A.R.; Clair, J.L.S.; Gallaher, J.L.; Hilvert, D.; Gelb, M.H.; Stoddard, B.L. Computational design of an enzyme catalyst for a stereoselective bimolecular diels-alder reaction. Science 2010, 329, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahsar, K.R.; Schwartz, D.K.; Medlin, J.W. Control of metal catalyst selectivity through specific noncovalent molecular interactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 136, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, S.H.; Schoenbaum, C.A.; Schwartz, D.K.; Medlin, J.W. Effects of thiol modifiers on the kinetics of furfural hydrogenation over Pd catalysts. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 3123–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenbaum, C.A.; Schwartz, D.K.; Medlin, J.W. Controlling the surface environment of heterogeneous catalysts using self-assembled monolayers. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 1438–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaser, H.; Jalett, H.; Lottenbach, W.; Studer, M. Heterogeneous enantioselective hydrogenation of ethyl pyruvate catalyzed by cinchona-modified pt catalysts: Effect of modifier structure. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 12675–12682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, A.; Bürgi, T.; Baiker, A. Adsorption of cinchonidine on platinum: A DFT insight in the mechanism of enantioselective hydrogenation of activated ketones. J. Catal. 2004, 226, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diezi, S.; Ferri, D.; Vargas, A.; Mallat, T.; Baiker, A. The origin of chemo- and enantioselectivity in the hydrogenation of diketones on platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 4048–4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavoie, S.; Laliberté, M.-A.; Temprano, I.; McBreen, P.H. A generalized two-point H-bonding model for catalytic stereoselective hydrogenation of activated ketones on chirally modified platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 7588–7593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas, A.; Baiker, A. First principles study of the conformations of cinchonidine on a Pt(111) surface. J. Catal. 2006, 239, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallat, T.; Orglmeister, E.; Baiker, A. Asymmetric catalysis at chiral metal surfaces. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 4863–4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaera, F. Chiral modification of solid surfaces: A molecular view. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 16196–16203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaera, F. Regio-, stereo-, and enantioselectivity in hydrocarbon conversion on metal surfaces. Acc. Chem. Res. 2009, 42, 1152–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, N.; Hungerbühler, K.; Baiker, A. Asymmetric hydrogenation on chirally modified Pt: Origin of hydrogen in the N–H–O interaction between cinchonidine and ketone. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 19567–19569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bönnemann, H.; Braun, G.A. Enantioselective hydrogenations on platinum colloids. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1996, 35, 1992–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, M. Asymmetric hydrogenation of α-ketoesters over finely dispersed polymer-stabilized platinum clusters. Tetrahedron Lett. 1998, 39, 1941–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBlond, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Andrews, A.; Sun, Y.-K. Highly enantioselective heterogeneously catalyzed hydrogenation of α-ketoesters under mild conditions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 4920–4921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demers-Carpentier, V.; Rasmussen, A.M.; Goubert, G.; Ferrighi, L.; Dong, Y.; Lemay, J.-C.; Masini, F.; Zeng, Y.; Hammer, B.; McBreen, P.H. Stereodirection of an α-ketoester at sub-molecular sites on chirally modified Pt(111): Heterogeneous asymmetric catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 9999–10002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meemken, F.; Hungerbühler, K.; Baiker, A. Monitoring surface processes during heterogeneous asymmetric hydrogenation of ketones on a chirally modified platinum catalyst by operando spectroscopy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 8640–8644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansat, S.; Gómez, M.; Philippot, K.; Muller, G.; Guiu, E.; Claver, C.; Castillón, S.; Chaudret, B. A case for enantioselective allylic alkylation catalyzed by palladium nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 1592–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, E.; Liu, J.H.; Alayoglu, S.; Marcus, M.A.; Fakra, S.C.; Toste, F.D.; Somorjai, G.A. Asymmetric catalysis at the mesoscale: Gold nanoclusters embedded in chiral self-assembled monolayer as heterogeneous catalyst for asymmetric reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 3881–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, E.; Liu, J.H.-C.; Toste, F.D.; Somorjai, G.A. Control of selectivity in heterogeneous catalysis by tuning nanoparticle properties and reactor residence time. Nat. Chem. 2012, 4, 947–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäfer, C.; Mhadgut, S.C.; Kugyela, N.; Török, M.; Török, B. Proline-induced enantioselective heterogeneous catalytic hydrogenation of isophorone on basic polymer-supported Pd catalysts. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Sham, T. Tuning the electronic behavior of Au nanoparticles with capping molecules. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 81, 736–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunoyama, H.; Ichikuni, N.; Sakurai, H.; Tsukuda, T. Effect of electronic structures of Au clusters stabilized by poly(N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone) on aerobic oxidation catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 7086–7093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, S.; Qu, J.; Tedsree, K.; Gong, X.Q.; Tsang, S.C.E. Prominent electronic and geometric modifications of palladium nanoparticles by polymer stabilizers for hydrogen production under ambient conditions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 11275–11278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Zheng, N. Surface and interface control of noble metal nanocrystals for catalytic and electrocatalytic applications. Nano Today 2013, 8, 168–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, S.T.; O’Brien, M.; Oetter, B.; Corpuz, A.; Richards, R.M.; Schwartz, D.K.; Medlin, J.W. Controlled selectivity for palladium catalysts using self-assembled monolayers. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.; Kim, D.; Hong, D.; Yu, Y.; Xu, J.; Lin, S.; Wen, X.; Nichols, E.M.; Jeong, K.; Reimer, J.A.; et al. A molecular surface functionalization approach to tuning nanoparticle electrocatalysts for carbon dioxide reduction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 8120–8125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Jiang, D.; Mann, A.K.P.; Mullins, D.R.; Qiao, Z.-A.; Allard, L.F.; Zeng, C.; Jin, R.; Overbury, S.H. Thiolate ligands as a double-edged sword for Co oxidation on CeO2 supported Au25(SCH2CH2Ph)18 nanoclusters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 6111–6122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, L.; Liu, B.; Duay, S.S.; He, J. Engineering Surface Ligands of Noble Metal Nanocatalysts in Tuning the Product Selectivity. Catalysts 2017, 7, 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7020044
Jin L, Liu B, Duay SS, He J. Engineering Surface Ligands of Noble Metal Nanocatalysts in Tuning the Product Selectivity. Catalysts. 2017; 7(2):44. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7020044
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Lei, Ben Liu, Searle S. Duay, and Jie He. 2017. "Engineering Surface Ligands of Noble Metal Nanocatalysts in Tuning the Product Selectivity" Catalysts 7, no. 2: 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7020044
APA StyleJin, L., Liu, B., Duay, S. S., & He, J. (2017). Engineering Surface Ligands of Noble Metal Nanocatalysts in Tuning the Product Selectivity. Catalysts, 7(2), 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7020044