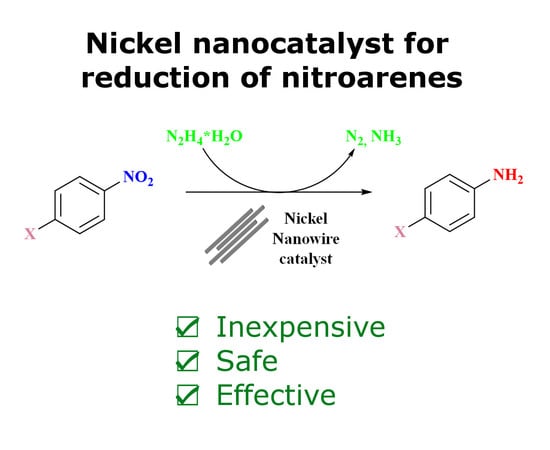
Nickel Nanowires: Synthesis, Characterization and Application as Effective Catalysts for the Reduction of Nitroarenes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Mechanism and Methodology of NiNW Synthesis
2.2. The Influence of Reaction Conditions on the Microstructure
2.2.1. Temperature
2.2.2. pH
2.2.3. NiNW Precursor Concentration
2.2.4. Alternative Reducing Agents
2.3. NW Composition
2.4. Catalytic Performance
3. Experimental
3.1. Materials and Methods
3.2. Catalytic Tests
3.2.1. General Procedure of Reduction of Nitroarenes
3.2.2. Large-Scale Reduction of 4-Nitrobenzoic Acid
3.2.3. Obtained Products
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lonjon, A.; Laffont, L.; Demont, P.; Dantras, E.; Lacabanne, C. New Highly Conductive Nickel Nanowire-Filled P(VDF-TrFE) Copolymer Nanocomposites: Elaboration and Structural Study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 12002–12006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamalakar, M.V.; Raychaudhuri, A.K. Low temperature electrical transport in ferromagnetic Ni nanowires. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 79, 205417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, M.N.; Yang, T.J.; Harutyunyan, S.R.; Chen, Y.Y.; Chen, C.D.; Lai, S.J. Electrical and thermal transport in single nickel nanowire. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 063101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razeeb, K.M.; Roy, S. Thermal diffusivity of nonfractal and fractal nickel nanowires. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 103, 084302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whitney, T.M.; Searson, P.C.; Jiang, J.S.; Chien, C.L. Fabrication and Magnetic Properties of Arrays of Metallic Nanowires. Science 1993, 261, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.W.; Chang, S.C.; Liu, R.S.; Hu, S.F.; Jan, N.T. Fabrication and magnetic properties of nickel nanowires. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2004, 282, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés, A.; Riveros, G.; Palma, J.L.; Denardin, J.C.; Marotti, R.E.; Dalchiele, E.A.; Gómez, H. Single-Crystal Growth of Nickel Nanowires: Influence of Deposition Conditions on Structural and Magnetic Properties. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2009, 9, 1992–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Chen, K.; Wang, M.; Li, H.; Chen, G.; Liu, J.; Xu, L.; Jian, Y.; Meng, C.; Zheng, X.; et al. Controllable synthesis of nickel nanowires and its application in high sensitivity, stretchable strain sensor for body motion sensing. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 4737–4745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samardak, A.S.; Sukovatitsina, E.V.; Ognev, A.V.; Chebotkevich, L.A.; Mahmoodi, R.; Peighambari, S.M.; Hosseini, M.G.; Nasirpouri, F. High-density nickel nanowire arrays for data storage applications. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2012, 345, 012011. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Pinheiro, P.C.; Sousa, C.T.; Araújo, J.P.; Guiomar, A.J.; Trindade, T. Functionalization of nickel nanowires with a fluorophore aiming at new probes for multimodal bioanalysis. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 410, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hong, X.B. Steam Reforming of Ethanol by a Nickel Nanowire Catalyst. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 651–653, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.; Wang, Y. Partial oxidation of methane to syngas catalyzed by a nickel nanowire catalyst. J. Nat. Gas Chem. 2009, 18, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Wang, D.; Diaz, L.A.; Botte, G.G. Nickel nanowires as effective catalysts for urea electro-oxidation. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 134, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aditya, T.; Pal, A.; Pal, T. Nitroarene reduction: A trusted model reaction to test nanoparticle catalysts. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 9410–9431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, G.; Sort, J.; Pleixats, R. Nickel Nanoparticles Stabilized by Trisimidazolium Salts: Synthesis, Characterization and Application as Recyclable Catalysts for the Reduction of Nitroarenes. ChemistrySelect 2018, 3, 8597–8603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanazzi, G.; Fiore, A.M.; Mali, M.; Rizzuti, A.; Leonelli, C.; Nacci, A.; Mastrorilli, P.; Dell’Anna, M.M. Polymer supported Nickel nanoparticles as recyclable catalyst for the reduction of nitroarenes to anilines in aqueous medium. Mol. Catal. 2018, 446, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.; Singha, R.K.; Sengupta, M.; Sasaki, T.; Pendem, C.; Bal, R. Surfactant-Induced Preparation of Highly Dispersed Ni-Nanoparticles Supported on Nanocrystalline ZrO2 for Chemoselective Reduction of Nitroarenes. ChemistrySelect 2018, 3, 1129–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Fu, J.; Muzzio, M.; Shen, T.; Su, D.; Zhu, J.; Sun, S. CuNi Nanoparticles Assembled on Graphene for Catalytic Methanolysis of Ammonia Borane and Hydrogenation of Nitro/Nitrile Compounds. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 1413–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornella, J.; Gómez-Bengoa, E.; Martin, R. Combined Experimental and Theoretical Study on the Reductive Cleavage of Inert C–O Bonds with Silanes: Ruling out a Classical Ni(0)/Ni(II) Catalytic Couple and Evidence for Ni(I) Intermediates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 1997–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasker, S.Z.; Standley, E.A.; Jamison, T.F. Recent advances in homogeneous nickel catalysis. Nature 2014, 509, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilke, G. Contributions to Organo-Nickel Chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1988, 27, 185–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burawoy, A.; Critchley, J.P. Electronic spectra of organic molecules and their interpretation—V: Effect of terminal groups containing multiple bonds on the K-bands of conjugated systems. Tetrahedron 1959, 5, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovar, R.F.; Armond, F.E. Ethynyl-Substituted Aromatic Ortho Diamines and Method of Synthesis. U.S. Patent US3,975,444, 19 May 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Suchy, M.; Winternitz, P.; Zeller, M. Heterocyclic Compounds. WO Patent WO1991000278, 27 June 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Butera, J.A.; Bagli, J.F. N-heteroaralkyl-substituted-1-aryloxy-2-propanolamina and propylamine derivatives possessing class III antiarrhythmic activity. WO Patent WO1991009023, 3 December 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Eluri, R.; Paul, B. Synthesis of nickel nanoparticles by hydrazine reduction: Mechanistic study and continuous flow synthesis. J. Nanopart. Res. 2012, 14, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Chen, Q.; Tang, Y.; Xiong, Y. Formation of one-dimensional nickel wires by chemical reduction of nickel ions under magnetic fields. Chem. Commun. 2007, 2844–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Xiang, W.; Liu, Y.; Hu, M.; Zhao, K. Synthesis of High-Aspect-Ratio Nickel Nanowires by Dropping Method. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, B.; Yan, H.; Chen, S.; Guan, Y.; Wu, G.; Jin, R.; Li, L. Stable and Controllable Synthesis of Silver Nanowires for Transparent Conducting Film. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samadaei, F.; Salami-Kalajahi, M.; Roghani-Mamaqani, H.; Banaei, M. A structural study on ethylenediamine- and poly(amidoamine)-functionalized graphene oxide: Simultaneous reduction, functionalization, and formation of 3D structure. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 71835–71843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Hussain, J.I.; Hashmi, A.A.; Al-Thabaiti, S.A. Preparation and characterization of silver nanoparticles using aniline. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S1506–S1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acke, F.; Skoglundh, M. Comparison between ammonia and propene as the reducing agent in the selective catalytic reduction of NO under lean conditions over Pt black. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 1999, 20, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Frett, B.; Li, H. Selective Reduction of Halogenated Nitroarenes with Hydrazine Hydrate in the Presence of Pd/C. Synlett 2014, 25, 1403–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oxley, P.; Adger, B.; Sasse, M.; Forth, M. N-Acetyl-N-phenylhydroxylamine via Catalytic Transfer Hydrogenation of Nitrobenzene using Hydrazine and Rhodium on Carbon. Org. Synth. 1989, 67, 187. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn, L. Catalytic Reduction with Hydrazine. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1951, 73, 1510–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Reaction Conditions | Product Parameters | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VNaOH [mL] | VN2H4 [mL] | VNiCl2 [mL] | CNiCl2 [M] | T [°C] | Yield [%] | Bundle Diameter [nm] |
| 70 | 20 | 10 | 0.1 | 80 | 33 | 655 ± 122 |
| 70 | 20 | 10 | 0.1 | 100 | 85 | 451 ± 87 |
| 70 | 20 | 10 | 0.1 | 120 | 97 | 335 ± 121 |
| Reaction Conditions | Product Parameters | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VNaOH [mL] | VN2H4 [mL] | VNiCl2 [mL] | CNiCl2 [M] | T [°C] | Yield [%] | Bundle Diameter [nm] |
| 35 | 20 | 10 | 0.1 | 100 | 51 | 426 ± 91 |
| 50 | 20 | 10 | 0.1 | 100 | 51 | 387 ± 65 |
| 100 | 20 | 10 | 0.1 | 100 | 68 | 306 ± 57 |
| Reaction Conditions | Product Parameters | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VNaOH [mL] | VN2H4 [mL] | VNiCl2 [mL] | CNiCl2 [M] | T [°C] | Yield [%] | Bundle Diameter [nm] |
| 175 | 50 | 5 | 0.5 | 100 | 77 | 498 ± 103 |
| 175 | 50 | 25 | 0.1 | 100 | 85 | 451 ± 87 |
| 175 | 50 | 50 | 0.050 | 100 | 95 | 363 ± 55 |
| 175 | 50 | 100 | 0.025 | 100 | 95 | 354 ± 65 |
| 175 | 50 | 250 | 0.010 | 100 | 88 | 316 ± 53 |
| Catalyst [%mol] | Equation of N2H4*H2O | Temp. [°C] | Time [h] | Yield [%] | Cost of Catalyst for Reduction of 1 mol of 4-bromonitrobenzene [$] | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pd/C 5% | 10.0 | 90 | 0.25 | 92 | 410 | [33] |
| Rh/C 5% | 1.0 | 40 | 3.0 | 90 | 290 | [34] |
| Pt/C 5% | 10.0 | 85 | 1.0 | 95 | 520 | [35] |
| NiNWs | 10.0 | 90 | 3.5 | 96 | 64 | This work |

| No. | [H] | Temp. [°C] | Yield [%] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | N2H4*H2O | 65 | 5 |
| 2 | N2H4*H2O | 75 | 30 |
| 3 | N2H4*H2O | 90 | 94 |
| 4 | N2H4*H2O | 100 | 92 |
| 5 | NaBH4 | 65 | 10 |
| 6 | NaBH4 | 75 | 15 |
| 7 | NaBH4 | 90 | 18 |
| 8 | NaBH4 | 100 | 18 |
| 9 | HCOOH | 65 | n.r. |
| 10 | HCOOH | 75 | n.r. |
| 11 | HCOOH | 90 | n.r. |
| 12 | HCOOH | 100 | 5 |
| 13 | HCOOH | 120 | 31 |
| 14 | NH4COOH | 65 | n.r. |
| 15 | NH4COOH | 75 | n.r. |
| 16 | NH4COOH | 90 | n.r. |
| 17 | NH4COOH | 100 | n.r |
| 18 | NH4COOH | 120 | n.r |

| No. | Substrate | Time [h] | Product | Yield [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  | 3.0 |  | 94 |
| 2 |  | 3.5 |  | 92 |
| 3 |  | 3.5 |  | 96 |
| 4 |  | 4.0 |  | 94 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wasiak, T.; Przypis, L.; Walczak, K.Z.; Janas, D. Nickel Nanowires: Synthesis, Characterization and Application as Effective Catalysts for the Reduction of Nitroarenes. Catalysts 2018, 8, 566. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8110566
Wasiak T, Przypis L, Walczak KZ, Janas D. Nickel Nanowires: Synthesis, Characterization and Application as Effective Catalysts for the Reduction of Nitroarenes. Catalysts. 2018; 8(11):566. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8110566
Chicago/Turabian StyleWasiak, Tomasz, Lukasz Przypis, Krzysztof Z. Walczak, and Dawid Janas. 2018. "Nickel Nanowires: Synthesis, Characterization and Application as Effective Catalysts for the Reduction of Nitroarenes" Catalysts 8, no. 11: 566. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8110566
APA StyleWasiak, T., Przypis, L., Walczak, K. Z., & Janas, D. (2018). Nickel Nanowires: Synthesis, Characterization and Application as Effective Catalysts for the Reduction of Nitroarenes. Catalysts, 8(11), 566. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8110566