Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity of Titania by Co-Doping with Mo and W
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Photocatalysts Characterization
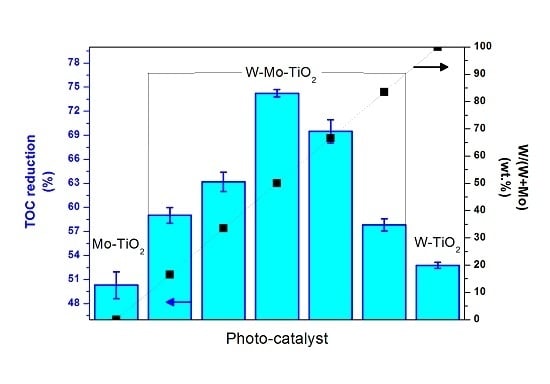
2.2. Photocatalytic Tests
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Preparation of Undoped, Doped and Co-Doped TiO2
3.3. Characterization of Photocatalysts
3.4. Photocatalytic activity and analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Finčur, N.L.; Krstić, J.B.; Šibul, F.S.; Šojić, D.V.; Despotović, V.N.; Banić, N.D.; Agbaba, J.R.; Abramović, B.F. Removal of alprazolam from aqueous solutions by heterogeneous photocatalysis: Influencing factors, intermediates, and products. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 307, 1105–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbruggen, S.W. TiO2 photocatalysis for the degradation of pollutants in gas phase: From morphological design to plasmonic enhancement. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2015, 24, 64–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linsebigler, A.L.; Lu, G.; Yates, J.T. Photocatalysis on TiO2 surfaces: Principles, mechanisms, and selected results. Chem. Rev. 1995, 95, 735–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujishima, A.; Zhang, X.; Tryk, D.A. TiO2 photocatalysis and related surface phenomena. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2008, 63, 515–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, M.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Tian, T.; Fang, P.; Zheng, F.; Zhao, X. Tuning the relative concentration ratio of bulk defects to surface defects in TiO2 nanocrystals leads to high photocatalytic efficiency. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 16414–16417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liqiang, J.; Honggang, F.; Baiqi, W.; Dejun, W.; Baifu, X.; Shudan, L.; Jiazhong, S. Effects of Sn dopant on the photoinduced charge property and photocatalytic activity of TiO2 nanoparticles. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2006, 62, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Yan, Z.; Xiao, T. Low-temperature solvothermal synthesis of visible-light-responsive S-doped TiO2 nanocrystal. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 4016–4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Sun, H.; Shan, Y. Preparation and characterization of mesoporous SBA-15 supported dye-sensitized TiO2 photocatalyst. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2005, 169, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, F. Enhanced photocatalytic activity of nitrogen-doped titania by deposited with gold. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 14689–14695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayati, M.R.; Golestani-Fard, F.; Moshfegh, A.Z. Photo-degradation of methelyne blue over V2O5–TiO2 nano-porous layers synthesized by micro arc oxidation. Catal. Lett. 2010, 134, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Jiang, Z.; Shi, H.; Xiao, T.; Yan, Z. Preparation of highly visible-light active N-doped TiO2 photocatalyst. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 5301–5309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilke, K.; Breuer, H.D. The influence of transition metal doping on the physical and photocatalytic properties of titania. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 1999, 121, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.; Termin, A.; Hoffmann, M.R. The role of metal ion dopants in quantum-sized TiO2: Correlation between photoreactivity and charge carrier recombination dynamics. J. Phys. Chem. 1994, 98, 13669–13679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrellan, C.R.; Salim, C.; Hinode, H. Photocatalytic activity of sol–gel derived TiO2 co-doped with iron and niobium. React. Kinet. Catal. Lett. 2009, 98, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Lai, H.; Yao, S.; Wang, S. Photocatalytic activity of Fe and Ce co-doped mesoporous TiO2 catalyst under UV and visible light. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2012, 59, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler-Illia, G.D.A.; Louis, A.; Sanchez, C. Synthesis and characterization of mesostructured titania-based materials through evaporation-induced self-assembly. Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 750–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ekabi, H.; Serpone, N. Kinetics studies in heterogeneous photocatalysis. I. Photocatalytic degradation of chlorinated phenols in aerated aqueous solutions over titania supported on a glass matrix. J. Phys. Chem. 1988, 92, 5726–5731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.; Kim, H.; Lee, G.Y.; Ahn, B.J. Catalytic hydrodechlorination reaction of chlorophenols by Pd nanoparticles supported on graphene. Res. Chem. Int. 2016, 42, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-García, C.; Heras, F.; Calvo, L.; Alonso-Morales, N.; Rodriguez, J.J.; Gilarranz, M.A. Platinum and N-doped carbon nanostructures as catalysts in hydrodechlorination reactions. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 238, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, S.R.; Kergaravat, S.V.; Pividori, M.I. Enzymatic electrochemical detection coupled to multivariate calibration for the determination of phenolic compounds in environmental samples. Talanta 2013, 106, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janda, V.; Svecova, M. By-products in drinking water disinfection. Chem. List 2000, 94, 905–908. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Zhao, Z.; Gao, F.; Wang, X.; Qiu, J. Mesoporous microspheres composed of carbon-coated TiO2 nanocrystals with exposed {001} facets for improved visible light photocatalytic activity. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 147, 958–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.T.; Siddiqa, A.; Siddiq, M.; Ali, S. Iron-doped titanium dioxide nanotubes: A study of electrical, optical, and magnetic properties. J. Nanopart. Res. 2011, 13, 6517–6525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, B.; Tian, B.; Zhang, J. Preparation of lanthanum and boron co-doped TiO2 by modified sol–gel method and study their photocatalytic activity. Catal. Today 2014, 224, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.-T.; Fan, W.-S.; Chen, W.-Y.; Lin, J.-Y. Adsorption and visible-light-derived photocatalytic kinetics of organic dye on Co-doped titania nanotubes prepared by hydrothermal synthesis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 67, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nešić, J.; Manojlović, D.D.; Anđelković, I.; Dojčinović, B.P.; Vulić, P.J.; Krstić, J.; Roglić, G.M. Preparation, characterization and photocatalytic activity of lanthanum and vanadium co-doped mesoporous TiO2 for azo-dye degradation. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2013, 378, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohsaka, T. Temperature dependence of the Raman spectrum in anatase TiO2. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1980, 48, 1661–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štengl, V.; Velická, J.; Maříková, M.; Grygar, T.M. New generation photocatalysts: how tungsten influences the nanostructure and photocatalytic activity of TiO2 in the UV and visible regions. ACS Appl. Mater. Int. 2011, 3, 4014–4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, L.; Chen, F. Properties of carbon and iron modified TiO2 photocatalyst synthesized at low temperature and photodegradation of acid orange 7 under visible light. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 4260–4268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaie, A.F.; Loghmani, M.H. La3+ and Zr4+ co-doped anatase nano TiO2 by sol-microwave method. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 157, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wu, Z.; Tian, F.; Ye, B.-C.; Tong, Y. Synthesis of N and La co-doped TiO2/AC photocatalyst by microwave irradiation for the photocatalytic degradation of naphthalene. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 676, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Jiang, H.; Zang, S.; Li, J.; Wang, Q. Gd, C., N and P quaternary doped anatase-TiO2 nano-photocatalyst for enhanced photocatalytic degradation of 4-chlorophenol under simulated sunlight irradiation. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 586, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubelka, P.; Munk, F. Ein beitrag zur optik der farbanstriche. Z. Tech. Phys. 1931, 12, 593–601. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez-Alejandre, A.; Ramírez, J.; Busca, G. The electronic structure of oxide-supported tungsten oxide catalysts as studied by UV spectroscopy. Catal. Lett. 1998, 56, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, B.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, B. Visible-light-driven photocatalyst of La–N-codoped TiO2 nano-photocatalyst: Fabrication and its enhanced photocatalytic performance and mechanism. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 25, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, L.J.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Liu, Q.J. Synthesis and properties of (Yb, N)-TiO2 photocatalyst for degradation of methylene blue (MB) under visible light irradiation. Mater. Res. Bull. 2015, 70, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.; Berk, D. Characterization and mechanistic study of Mo+6 and V+5 codoped TiO2 as a photocatalyst. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2014, 294, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Xu, S.; Shen, F. Preparation and characterization of TiO2 photocatalysts co-doped with iron (III) and lanthanum for the degradation of organic pollutants. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 7671–7677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, C.; Wu, F.; Zou, B.; Zhao, M.; Wang, J.; Feng, C. Photodegradation of rhodamine B under visible light by bimetal codoped TiO2 nanocrystals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Bai, L.N.; Sun, H.M.; Jiang, Q.; Lian, J.S. Structure and photocatalytic property of Mo-doped TiO2 nanoparticles. Powder Technol. 2013, 244, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.-Y.; Yan, B.-X.; Shen, J. Enhancement of photoelectric and photocatalytic activities: Mo doped TiO2 thin films deposited by sputtering. Thin Solid Films 2012, 522, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tae Kwon, Y.; Yong Song, K.; In Lee, W.; Jin Choi, G.; Rag Do, Y. Photocatalytic behavior of WO3-loaded TiO2 in an oxidation reaction. J. Catal. 2000, 191, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Park, Y.; Kim, W.; Choi, W. Surface modification of TiO2 photocatalyst for environmental applications. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2013, 15, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Wang, H.; Li, H. Enhancing the photocatalytic degradation of salicylic acid by using molecular imprinted S-doped TiO2 under simulated solar light. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 8863–8867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Mukhopadhyay, M.; Murthy, Z.V.P. Rate parameter estimation for 4-chlorophenol degradation by UV and organic oxidants. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2012, 18, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Wang, E.; Chen, Y.; Yang, W.; Yao, J.; Cao, Y. Doping mode, band structure and photocatalytic mechanism of B–N-codoped TiO2. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 7335–7342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, X.; Yin, Z.; Wei, L. Visible light responsive N-F-codoped TiO2 photocatalysts for the degradation of 4-chlorophenol. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 1919–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neville, E.M.; Mattle, M.J.; Loughrey, D.; Rajesh, B.; Rahman, M.; MacElroy, J.M.D.; Sullivan, J.A.; Thampi, K.R. Carbon-Doped TiO2 and Carbon, Tungsten-Codoped TiO2 through Sol–Gel Processes in the Presence of Melamine Borate: Reflections through Photocatalysis. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 16511–16521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamaila, S.; Sajjad, A.K.L.; Chen, F.; Zhang, J. Synthesis and characterization of mesoporous-TiO2 with enhanced photocatalytic activity for the degradation of chloro-phenol. Mater. Res. Bull. 2010, 45, 1375–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theurich, J.; Lindner, M.; Bahnemann, D.W. Photocatalytic degradation of 4-chlorophenol in aerated aqueous titanium dioxide suspensions: A kinetic and mechanistic study. Langmuir 1996, 12, 6368–6376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaya, U.I.; Abdullah, A.H.; Zainal, Z.; Hussein, M.Z. Photocatalytic treatment of 4-chlorophenol in aqueous ZnO suspensions: Intermediates, influence of dosage and inorganic anions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipczynska-Kochany, E.; Kochany, J.; Bolton, J.R. Electron paramagnetic resonance spin trapping detection of short-lived radical intermediates in the direct photolysis of 4-chlorophenol in aerated aqueous solution. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 1991, 62, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozan, G.S.; Kambur, A. Removal of 4-chlorophenol from wastewater: Preparation, characterization and photocatalytic activity of alkaline earth oxide doped TiO2. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2013, 129, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| Sample | Average Crystallite Size (nm) | Lattice Distortion (ε) | Lattice Parameters | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a (nm) | c (nm) | V (nm3) | |||
| TiO2 | 8.6 | 0.0183 | 0.377 | 0.931 | 0.132 |
| DM2 | 8.6 | 0.0183 | 0.378 | 0.933 | 0.133 |
| DW0.3M1.7 | 7.7 | 0.0207 | 0.378 | 0.982 | 0.140 |
| DW0.7M1.3 | 6.6 | 0.0238 | 0.378 | 0.943 | 0.135 |
| DW1M1 | 8.3 | 0.0191 | 0.379 | 0.937 | 0.134 |
| DW1.3M0.7 | 7.3 | 0.0216 | 0.378 | 0.947 | 0.136 |
| DW1.7M0.3 | 7.1 | 0.0224 | 0.379 | 0.959 | 0.138 |
| DW2 | 8.1 | 0.0195 | 0.379 | 0.933 | 0.134 |
| Catalyst | Specific Surface Area (m2/g) | Average Pore Diameter (nm) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| TiO2 | 144 | 6.1 | 0.328 |
| DM2 | 161 | 6.1 | 0.354 |
| DW0.3M1.7 | 181 | 5.6 | 0.362 |
| DW0.7M1.3 | 191 | 5.6 | 0.365 |
| DW1M1 | 172 | 6.6 | 0.391 |
| DW1.3M0.7 | 185 | 5.6 | 0.352 |
| DW1.7M0.3 | 188 | 5.6 | 0.352 |
| DW2 | 160 | 4.6 | 0.307 |
| Sample | Band Gap (eV) | Wavelength (nm) |
|---|---|---|
| TiO2 | 3.16 | 392 |
| DM2 | 2.74 | 452 |
| DW0.3M1.7 | 2.78 | 446 |
| DW0.7M1.3 | 2.80 | 443 |
| DW1M1 | 2.87 | 432 |
| DW1.3M0.7 | 2.90 | 428 |
| DW1.7M0.3 | 3.01 | 412 |
| DW2 | 3.08 | 403 |
| Catalyst | 4CP Degradation (%) | k × 102 (min−1) | t1/2 (min) | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DM2 | 76 | 1.31 | 52.8 | 0.97 |
| DW0.3M1.7 | 86 | 1.98 | 34.9 | 0.99 |
| DW0.7M1.3 | 93 | 2.75 | 25.2 | 0.99 |
| DW1M1 | 97 | 3.49 | 19.9 | 0.99 |
| DW1.3M0.7 | 93 | 2.73 | 25.4 | 0.99 |
| DW1.7M0.3 | 92 | 2.51 | 27.6 | 0.99 |
| DW2 | 75 | 1.26 | 54.9 | 0.95 |
| TiO2 | 67 | 1.04 | 66.8 | 0.90 |
| Degussa P25 | 51 | 0.67 | 102.9 | 0.97 |
| Photo-Catalyst | [4CP]0 × 105 (mol/L) | Radiation | 4CP Degradation (%) | 4CP Mineralization (%) | k × 102 (min−1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W-Mo-TiO2 | 15.56 | UV | 97 (100 min) | 74 (100 min) | 3.49 | - |
| B-N-TiO2 | 5.00 | UV | 98 (120 min) | - | 3.41 | [46] |
| N-F-TiO2 | 7.78 | VL | 72 (300 min) | - | - | [47] |
| C-W-TiO2 | 50.00 | VL | - | 57 (300 min) | - | [48] |
| Intermediate Compound ID | Name | Molecular Structure |
|---|---|---|
| HQ | Hydroquinone 1,4-benzenediol 1,4-dihydroxybenzene |  |
| BQ | Benzoquinone 1,4-benzoquinone p-benzoquinone Quinone |  |
| 4CC | 4-chlorocatechol 4-chloro-1,2-benzenediol |  |
| BT | 1,2,4-benzenetriol Hydroxyhydroquinone |  |
| DHB | 1,2-dihydroxybenzene 1,2-benzenediol Catechol Pyrocatechol |  |
| P | Phenol Hydroxybenzene |  |
| 4CR | 4-chlororesorcinol 1,3-dihydroxy-4-chlorobenzene |  |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Avilés-García, O.; Espino-Valencia, J.; Romero-Romero, R.; Rico-Cerda, J.L.; Arroyo-Albiter, M.; Solís-Casados, D.A.; Natividad-Rangel, R. Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity of Titania by Co-Doping with Mo and W. Catalysts 2018, 8, 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8120631
Avilés-García O, Espino-Valencia J, Romero-Romero R, Rico-Cerda JL, Arroyo-Albiter M, Solís-Casados DA, Natividad-Rangel R. Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity of Titania by Co-Doping with Mo and W. Catalysts. 2018; 8(12):631. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8120631
Chicago/Turabian StyleAvilés-García, Osmín, Jaime Espino-Valencia, Rubí Romero-Romero, José Luis Rico-Cerda, Manuel Arroyo-Albiter, Dora Alicia Solís-Casados, and Reyna Natividad-Rangel. 2018. "Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity of Titania by Co-Doping with Mo and W" Catalysts 8, no. 12: 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8120631
APA StyleAvilés-García, O., Espino-Valencia, J., Romero-Romero, R., Rico-Cerda, J. L., Arroyo-Albiter, M., Solís-Casados, D. A., & Natividad-Rangel, R. (2018). Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity of Titania by Co-Doping with Mo and W. Catalysts, 8(12), 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8120631