Ti-Doped Pd-Au Catalysts for One-Pot Hydrogenation and Ring Opening of Furfural
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Catalytic Activity for FFR Hydrogenation
2.2. Catalytic Characterization
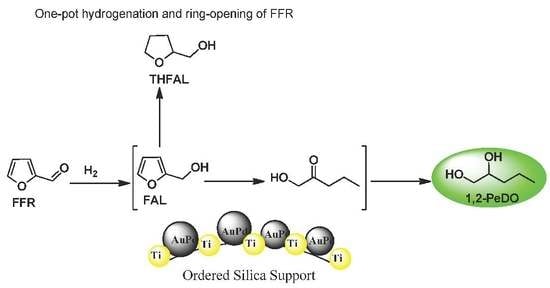
2.3. Plausible Reaction Pathway
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Catalyst Preparation
3.2.1. Synthesis of Silica Supports
3.2.2. Synthesis of Ti-HMS and Ti-SBA
3.2.3. Preparation of the PdxAuy Bimetallic Nanoparticles Supported on Mesoporous Silica
3.3. Catalyst Characterization
3.4. Catalytic Hydrogenation of Furfural
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chheda, J.; Huber, G.W.; Dumesic, J.A. Liquid-phase catalytic processing of biomass-derived oxygenated hydrocarbons to fuels and chemicals. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 7164–7183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corma, A.; Iborra, S.; Velty, A. Chemical routes for the transformation of biomass into chemicals. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2411–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernando, S.; Adhikari, S.; Chandrapal, C.; Murali, N. Current Status, Challenges, and Future Direction. Energy Fuels 2006, 20, 1727–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortright, R.D.; Davda, R.R.; Dumesic, J.A. Hydrogen from catalytic reforming of biomass-derived hydrocarbons in liquid water. Nature 2002, 418, 964–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodiansono, R.; Khairi, S.; Hara, T.; Ichikuni, N.; Shimazu, S. Highly efficient and selective hydrogenation of unsaturated carbonyl compounds using Ni–Sn alloy catalysts. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2012, 2, 2139–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Garcia, A.; Ortiz, M.; Martinez, R.; Ortiz, P.; Reguera, E. The condensation of furfural with urea. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2004, 19, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biradar, N.S.; Hengne, A.M.; Birajdar, S.N.; Niphadkar, P.S.; Joshi, P.N.; Rode, C.V. Single-Pot Formation of THFAL via Catalytic Hydrogenation of FFR over Pd/MFI Catalyst. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Date, N.S.; Hengne, A.M.; Haung, K.-W.; Chikate, R.C.; Rode, C.V. Single pot Selective hydrogenation of furfural to 2-methylfuran over carbon supported iridium catalysts. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 2027–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Date, N.S.; Biradar, N.S.; Chikate, R.C.; Rode, C.V. Effect of reduction Protocol of Pd Catalysts on Product Distribution in Furfural Hydrogenation. Chem. Sel. 2017, 2, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Ren, R.; Wang, Y.; Lu, G. Direct catalytic conversion of furfural to 1,5-pentanediol by hydrogenolysis of the furan ring under mild conditions over Pt/Co2AlO4 catalyst. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 3924–3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizugaki, T.; Yamakawa, T.; Nagatsu, Y.; Maeno, Z.; Mitsudome, T.; Jitsukawa, K.; Kaneda, K. Direct Transformation of furfural to 1,2-pentadiol using hydrotalcite-supported platinum nanoparticle catalyst. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 2243–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Wu, X.P.; Tong, T.; Shao, Z.J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Xia, Q.; Gong, X. The Critical Role of Water in the Ring Opening of Furfural Alcohol to 1,2-Pentanediol. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H.; Taniguchi, Y. Printing Method and Printed Products. JP Patent 201236121, 23 February 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Siegmeier, R.; Prescher, G.; Maurer, H.; Hering, G. Continuous Process for the Production of 1,2-Pentanediol. U.S. Patent 4,605,795, 12 August 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, O.; Koeckritz, A.; Kant, M.; Martin, A.; Schoening, A.; Armbruster, U.; Bartoszek, M.; Evert, S.; Lange, B.; Bienert, R.U.S. Method for Producing 1,2-Pentanediol. U.S. Patent 8,921,617, 30 December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Koso, S.; Furikado, I.; Shimao, A.; Miyazawa, T.; Kunimori, K.; Tomishige, K. Chemoselective hydrogenolysis of tetrahydrofurfuryl alcohol to 1,5-pentanediol. Chem. Commun. 2009, 15, 2035–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, Y.; Tomishige, K. Production of 1,5-pentanediol from biomass via furfural and tetrahydrofurfuryl alcohol. Catal. Today 2012, 195, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bel’skii, I.F.; Shuikin, N.I.; Shostakovskii, V.M. Effect of carbonyl and alkoxycarbonyl groups on the hydrogenolysis of the furan ring under the conditions of vapor-phase hydrogenation. Bull. Acad. Sci. USSR 1962, 11, 1727–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winnick, C.N. Preparation of Glycols and Glycol Ethers. U.S. Patent 3,475,499, 28 October 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Hambrack, K.O.; Roberbson, J.A. Production of 1, 5-pentanediol from Furfural. U.S. Patent 2,768,979, 30 October 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Shokouhimehr, M. Magnetically separable and sustainable nanostructured catalysts for heterogeneous reduction of nitroaromatics. Catalysts 2015, 5, 534–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aejung, K.; Mahdi, S.; Shahrouz, A.; Shokouhimehr, M. Palladium nanocatalysts confined in mesoporous silica for heterogeneous reduction of nitroaromatics. Energy Environ. Focus 2015, 4, 18–23. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, C.; Kim, J.; Yoon, S.; Yang, E.; Kwak, J.; Lee, M.; An, K. Supported Pd nanoparticles catalysts with high activities and selectivities in liquid-phase furfural hydrogenation. Fuel 2018, 226, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ge, Y.; Guo, Y.; Chen, J. Selective hydrogenation of biomass-derived 5-hydroxymethylfurfural using palladium catalyst supported on mesoporous graphitic carbon nitride. J. Energy Chem. 2018, 27, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, W.; Yepez, A.; Romero, A.; Luque, R. Towards industrial furfural conversion: Selectivity and stability of palladium and platinum catalysts under flow regime. Catal. Today 2018, 308, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albilali, R.; Douthwaite, M.; He, Q.; Taylor, S. The selective hydrogenation of furfural over supported palladium nanoparticle catalysts prepared by sol-immobilisation: Effect of catalyst support and reaction conditions. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2018, 8, 252–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Dong, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, G.; Han, S.; Meng, X.; Zheng, A.; Xiao, F. Importance of zeolite wettability for selective hydrogenation of furfural over Pd@zeolite catalysts. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Jadeja, G.C.; Parikh, J. Synergim studies on alumina-supported copper-nickel catalysts towards furfural and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural hydrogenation. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2017, 426, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Li, D.; Tan, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, C.; Ma, L. Selective hydrodeoxygenation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural to 2,5-dimethylfuran on Ru-MoOx/C catalysts. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 16311–16318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, Y.; Takada, K.; Tamura, M.; Tomishige, K. Total hydrogenation of furfural and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural over supported Pd-Ir alloy catalyst. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 2718–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Amada, Y.; Tamura, M.; Nakagawa, Y.; Tomishige, K. One-pot selective conversion of furfural into 1,5-pentanediol over a Pd-added Ir-ReOx/SiO2 bifunctional catalyst. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Gao, L.; Wu, Y.; Yang, X.; Sheng, P.; Xiao, G. Short channeled Ni-Co/SBA-15 catalysts for highly selective hydrogenation of biomass-derived furfural to tetrahydrofurfurylalcohol. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 262, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, S.; Ikeda, N.; Ebitani, K. Selective hydrogenation of biomass-derived 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) to 2,5-dimethylfuran (DMF) under atmospheric hydrogen pressure over carbon supported PdAu bimetallic catalyst. Catal. Today 2014, 232, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, F.; Niu, X.; Zhu, Y. Efficient Production of the liquid fuel 2,5-dimethylfuran from 5-hydroxymethylfurfural in the absence of acid additive over bimetallic PdAu supported on Graphitized Carbon. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 6364–6373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Parola, V.; Testa, M.L.; Venezia, A.M. Pd and PdAu catalysts supported over 3-MPTES grafted HMS used in the HDS of thiophene. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 119, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chen, D.; Liao, S.; Song, H.; Li, Y.; Fu, Z.; Su, Y. High-performance Pd–Au bimetallic catalyst with mesoporous silica nanoparticles as support and its catalysis of cinnamaldehyde hydrogenation. J. Catal. 2012, 291, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottoni, C.A.; Da Silva, S.G.; De Souza, R.F.B.; Neto, A.O. Glycerol oxidation reaction using PdAu/C electrocatalysts. Ionics 2016, 22, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, T.J.; Lyman, S.D.; Motagamwala, A.H.; Mellmer, M.A.; Dumesic, J.A. Selective Hydrogenation of Unsaturated Carbon–Carbon Bonds in Aromatic-Containing Platform Molecules. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 2047–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testa, M.L.; Demailly, L.C.; La Parola, V.; Venezia, A.M.; Pinel, C. Effect of Au on Pd supported over HMS and Ti doped HMS as catalysts for the hydrogenation of levulinic acid to γ-valerolactone. Catal. Today 2015, 257, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, C.S.; Gorte, R.J. A study of surface defect of Si (511) by RHEED and LEED. Surf. Sci. 1985, 161, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Date, N.S.; Chikate, R.C.; Roh, H.S.; Rode, C.V. Bifunctional role of Pd/MMT-K 10 catalyst in direct transformation of furfural to 1,2-pentanediol. Catal. Today 2018, 309, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellmer, M.; Gallo, J.; Alonso, D.; Dumesic, J. Selective Production of Levulinic Acid from Furfuryl Alcohol in THF Solvent Systems over H-ZSM-5. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 3354–3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengne, A.M.; Kamble, S.B.; Rode, C.V. Single pot conversion of furfuryl alcohol to levulinic esters and γ-valerolactone in the presence of sulfonic acid functionalized ILs and metal catalysts. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 2540–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, G.; Li, N.; Wang, A.; Dong, W.; Wanga, X.; Conga, Y. Aqueous phase hydrogenation of levulinic acid to 1,4-pentanediol. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 1414–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, A.R. Solid State Chemistry and Its Applications; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Barzetti, T.; Selli, E.; Moscotti, D.; Forni, L. Pyridine and ammonia as probes for FTIR analysis of solid acid catalysts. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1996, 92, 1401–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, B.; Kobayashi, H.; Yu, T.; Wang, J.; Kim, M.J.; Li, Z.Y.; Rycemga, M.; Xia, Y. Synthesis of Pd−Au Bimetallic Nanocrystals via Controlled Overgrowth. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 2506–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santi, D.; Holl, T.; Calemma, V.; Weitkamp, J. High-performance ring-opening catalysts based on iridium-containing zeolite Beta in the hydroconversion of decalin. Appl. Catal. A Gener. 2013, 455, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miedziak, P.J.; Edwards, J.K.; Taylor, S.H.; Knight, D.W.; Tarbit, B.; Hutchings, G.J. Gold as a Catalyst for the Ring Opening of 2,5-Dimethylfuran. Catal. Lett. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testa, M.L.; Tummino, M.L.; Agostini, S.; Avetta, P.; Deganello, F.; Montoneri, E.; Magnacca, G.; Prevot, A.B. Synthesis, characterization and environmental application of silica grafted photoactive substances isolated from urban biowaste. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 47920–47927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirley, D.A. High-Resolution X-ray Photoemission Spectrum of the Valence Bands of Gold. Phys. Rev. B 1972, 5, 4709–4715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwood, P.M.A.; Briggs, D.; Seah, M.P. (Eds.) Practical Surface Analysis; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 181–185. [Google Scholar]











| Sample | Conv. (%) | Selectivity | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FAL | THF | THFAL | 2-MF | 2MTHF | 1,2-PeDO | 1,4-PeDO | ||
| 4PdC 1 | >99 | - | 27 | 8 | 18 | 40 | - | 7 |
| 4PdHMS | 97 | 31 | 4 | 31 | - | - | 24 | 10 |
| 1Pd3AuHMS | 94 | 47 | 4 | 31 | 1 | - | 13 | 4 |
| 3Pd1AuHMS | 98 | 22 | 2 | 33 | 2 | 3 | 29 | 9 |
| 2Pd2AuHMS | 42 | 86 | - | 8 | - | - | 6 | - |
| 2Pd2AuSBA | 100 | 5 | 11 | 30 | 9 | 12 | 21 | 12 |
| 2Pd2AuTiHMS | 93 | 29 | 1 | 26 | 4 | - | 32 | 8 |
| 2Pd2AuTiSBA | 97 | 19 | 6 | 18 | 3 | 1 | 40 | 13 |
| 4AuHMS | 40 | 72 | - | 2 | 4 | 1 | 17 | 4 |
| Entry | Sample | P (psi) | Conv. (%) | Selectivity (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FAL | THFAL | 2-MF | 1,2-PeDO | 1,4-PeDO | ||||
| 1 | 2Pd2Au TiSBA | 750 | 95 | 40 | 8 | - | 48 | 3 |
| 2 | 500 | 95 | 42 | 6 | 1 | 49 | 2 | |
| 3 | 300 | 93 | 26 | 7 | 7 | 59 | - | |
| 4 | 100 | 89 | 30 | 10 | 2 | 58 | 1 | |
| 5 | 2Pd2Au TiHMS | 750 | 94 | 28 | 9 | 9 | 46 | 2 |
| 6 | 500 | 89 | 35 | 8 | 3 | 50 | 3 | |
| 7 | 300 | 88 | 33 | 10 | 5 | 51 | - | |
| 8 | 100 | 69 | 46 | 15 | 8 | 31 | - | |
| 9 | 2Pd2Au SBA | 300 | 91 | 42 | 26 | 6 | 24 | 2 |
| 10 | 100 | 79 | 52 | 24 | 5 | 18 | 1 | |
| 11 | 2Pd2Au HMS | 300 | 84 | 70 | 12 | 6 | 12 | - |
| 12 | 100 | 76 | 72 | 16 | 2 | 10 | - | |
| Sample | Pore to Pore Distance * (L, nm) | Surface Area ** (m2 g−1) | Pore Volume ** (cm3 g−1) | Pore Diameter ** (d, nm) | Wall Thickness *** (τ, nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HMS | 3.2 | 890 | 1.5 | 2.4 | 0.8 |
| TiHMS | 3.9 | 740 | 1.2 | 2.4 | 1.5 |
| SBA | 9.4 | 840 | 0.9 | 6.2 | 3.2 |
| TiSBA | 9.4 | 516 | 0.9 | 5.5 | 4.1 |
| Sample | PdO (nm) | Au (nm) | Pd-Au (Composition) | Pd-Au (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4Pd HMS | - | - | - | - |
| 1Pd3Au HMS | 15 | 14 | - | - |
| 3Pd1Au HMS | Traces | Traces | - | - |
| 2Pd2Au HMS | 8.5 | - | Pd15Au85 | 15 |
| Pd50Au50 | 13 | |||
| 2Pd2Au SBA | 8 | - | Pd15Au85 | 10 |
| Pd50Au50 | 9 | |||
| 2Pd2AuTiHMS | 17 | 18 | Pd40Au60 | 10 |
| 2Pd2Au TiSBA | 4 | 9 | Pd57Au43 | 5 |
| Sample | Pd3d5/2 eV | Au4f7/2 eV | Pd/(Si + Ti) | Au/(Si + Ti) | Au/Pd | Ti/Si |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2Pd2Au HMS | 334.9 (84%) 336.7 (16%) | 83.8 | 0.01 | 0.004 | 0.4 | - |
| 2Pd2AuTiHMS fresh | 334.7 (53%) 336.6 (47%) | 83.6 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.7 | 0.2 |
| 2Pd2AuTiHMS Spent | 334.8 (100%) | 83.2 | 0.007 | 0.009 | 1.2 | 0.01 |
| 2Pd2Au SBA | 336.0 (25%) 337.7 (75%) | - | 0.007 | - | - | - |
| 2Pd2Au TiSBA Fresh | 335.9 (49%) 337.7 (51%) | 83.4 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| 2Pd2Au TiSBA Spent | 334.2 (75%) 336.4 (27%) | 83.0 | 0.03 | 0.009 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Date, N.S.; La Parola, V.; Rode, C.V.; Testa, M.L. Ti-Doped Pd-Au Catalysts for One-Pot Hydrogenation and Ring Opening of Furfural. Catalysts 2018, 8, 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8060252
Date NS, La Parola V, Rode CV, Testa ML. Ti-Doped Pd-Au Catalysts for One-Pot Hydrogenation and Ring Opening of Furfural. Catalysts. 2018; 8(6):252. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8060252
Chicago/Turabian StyleDate, Nandan Shreehari, Valeria La Parola, Chandrashekhar Vasant Rode, and Maria Luisa Testa. 2018. "Ti-Doped Pd-Au Catalysts for One-Pot Hydrogenation and Ring Opening of Furfural" Catalysts 8, no. 6: 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8060252
APA StyleDate, N. S., La Parola, V., Rode, C. V., & Testa, M. L. (2018). Ti-Doped Pd-Au Catalysts for One-Pot Hydrogenation and Ring Opening of Furfural. Catalysts, 8(6), 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8060252