Performance Enhanced SAPO-34 Catalyst for Methanol to Olefins: Template Synthesis Using a CO2-Based Polyurea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterizations of Polyurea: 1H-NMR and MALDI-TOF-MS
2.2. Characterization of the Catalyst
2.2.1. Thermogravimetric Analysis and Powder X-ray Diffraction
2.2.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy and Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.2.3. Compositions and Textural Properties
2.2.4. Chemical Circumstances: Solid State NMR Spectroscopy
2.2.5. Acidic Properties: NH3-TPD Analysis
2.2.6. Influence of Polyurea as Mesoporogen
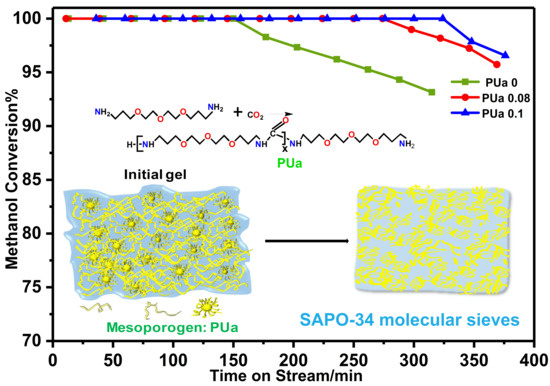
2.3. Catalytic Performance for MTO Reaction
3. Experimental
3.1. Materials
3.2. Measurement
3.3. Synthesis of CO2-Based Polyurea
3.4. Synthesis of SAPO-34 with Polyurea (PUa) as Structure Directing Reagent
3.5. Evaluation of Catalytic Performance
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tian, P.; Wei, Y.X.; Ye, M.; Liu, Z.M. Methanol to Olefins (MTO): From Fundamentals to Commercialization. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 1922–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.L.; Wang, C.M.; Dyballa, M.; Wu, G.J.; Guan, N.J.; Li, L.D.; Xie, Z.K.; Hunger, M. Understanding the Early Stages of the Methanol-to-Olefin Conversion on H-SAPO-34. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Wang, N.; Xi, D.; Yang, M.; Yu, J. Organosilane surfactant-directed synthesis of hierarchical porous SAPO-34 catalysts with excellent MTO performance. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 6502–6505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Moljord, K.; Holmen, A. A methanol to olefins review: Diffusion, coke formation and deactivation SAPO type catalysts. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2012, 164, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsbye, U.; Svelle, S.; Bjørgen, M.; Beato, P.; Janssens, T.V.W.; Joensen, F.; Bordiga, S.; Lillerud, K.P. Conversion of Methanol to Hydrocarbons: How Zeolite Cavity and Pore Size Controls Product Selectivity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 5810–5831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Liu, Z.; Gao, H.; Xie, Z. Synthesis and catalytic performances of hierarchical SAPO-34 monolith. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 3227–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.B.; Yang, M.; Qiao, Y.Y.; Li, J.Z.; Xiang, X.; Wu, P.F.; Wei, Y.X.; Xu, S.T.; Tian, P.; Liu, Z.M. A low-temperature approach to synthesize low-silica SAPO-34 nanocrystals and their application in the methanol-to-olefins (MTO) reaction. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 7569–7578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.M.; Wang, N.; Guo, G.Q.; Chen, X.X.; Yu, J.H. Synthesis of tri-level hierarchical SAPO-34 zeolite with intracrystalline micro-meso-macroporosity showing superior MTO performance. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 19783–19789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yi, X.F.; Xu, J.; Qi, G.D.; Gao, P.; Wang, W.Y.; Chu, Y.Y.; Wang, Q.; Feng, N.D.; Liu, X.L.; et al. Experimental Evidence on the Formation of Ethene through Carbocations in Methanol Conversion over H-ZSM-5 Zeolite. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 12061–12068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaripour, F.; Shariatinia, Z.; Sahebdelfar, S.; Irandoukht, A. Effect of boron incorporation on the structure, products selectivities and lifetime of H-ZSM-5 nanocatalyst designed for application in methanol-to-olefins (MTO) reaction. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2015, 203, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.Y.; Mueller, S.; Shi, H.; Haller, G.L.; Sanchez-Sanchez, M.; van Veen, A.C.; Lercher, J.A. On the impact of co-feeding aromatics and olefins for the methanol-to-olefins reaction on HZSM-5. J. Catal. 2014, 314, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.C.; Hofmann, J.P.; Mezari, B.; Kosinov, N.; Wu, L.L.; Qian, Q.Y.; Weckhuysen, B.M.; Asahina, S.; Ruiz-Martínez, J.; Hensen, E.J.M. Trimodal Porous Hierarchical SSZ-13 Zeolite with Improved Catalytic Performance in the Methanol-to-Olefins Reaction. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 2163–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.C.; Kosinov, N.; Kubarev, A.V.; Bolshakov, A.; Mezari, B.; Valastyan, I.; Hofmann, J.P.; Roeffaers, M.B.J.; Sarkadi-Pribόczki, E.; Hensen, E.J.M. Probing the Influence of SSZ-13 Zeolite Pore Hierarchy in Methanol-to-Olefins Catalysis by Using Nanometer Accuracy by Stochastic Chemical Reactions Fluorescence Microscopy and Positron Emission Profiling. ChemCatChem 2017, 9, 3470–3477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deimund, M.A.; Harrison, L.; Lunn, J.D.; Liu, Y.; Malek, A.; Shayib, R.; Davis, M.E. Effect of Heteroatom Concentration in SSZ-13 on the Methanol-to-Olefins Reaction. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lok, B.M.; Messina, C.A.; Patton, R.L.; Gajek, R.T.; Cannan, T.R.; Flanigen, E.M. Silicoalumino-phosphate molecular sieves: Another new class of microporous crystalline inorganic solids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1984, 106, 6092–6093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Inui, T. Effects of decrease in number of acid sites located on the external surface of Ni-SAPO-34 crystalline catalyst by the mechanochemical method. Catal. Lett. 1998, 53, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sastre, G.; Lewis, D.W.; Catlow, C.R.A. Modeling of Silicon Substitution in SAPO-5 and SAPO-34 Molecular Sieves. Acc. Chem. Res. 1997, 101, 5249–5262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadbakhsh, A.; Farhadi, F.; Khorasheh, F.; Sahebdelfar, S.; Asadi, M.; Feng, Y.Z. Effect of SAPO-34’s composition on its physico-chemical properties and deactivation in MTO process. Appl. Catal. A 2009, 364, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Li, H.; Zhao, S.; Guo, W.; Wang, R.; Ying, M. Characteristics and performance of SAPO-34 catalyst for methanol-to-olefin conversion. Appl. Catal. 1990, 64, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöcker, M. Methanol-to-hydrocarbons: Catalytic materials and their behavior. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 1999, 29, 3–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, I.M.; Mostad, H.; Akporiaye, D.; Wendelbo, R. Structural and chemical influences on the MTO reaction: A comparison of chabazite and SAPO-34 as MTO catalysts. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 1999, 29, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haw, J.F.; Song, W.; Marcus, D.M.; Nicholas, J.B. The mechanism of methanol to hydrocarbon catalysis. Acc. Chem. Res. 2003, 36, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arstad, B.; Kolboe, S. The reactivity of molecules trapped within the SAPO-34 cavities in the methanol-to-hydrocarbons reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 8137–8138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Grønvold, A.; Moljord, K.; Holmen, A. Methanol conversion to light olefins over SAPO-34: Reaction network and deactivation kinetics. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 4116–4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karger, J. Random walk through two-channel networks: A simple means to correlate the coefficients of anisotropic diffusion in ZSM-5 type zeolites. J. Phys. Chem. 1991, 14, 5558–5560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camara, L.; Rajagopal, K.; Aranda, D. The effects of pore structure on catalyst deactivation by coke formation. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 2001, 139, 61–68. [Google Scholar]
- Beyne, A.O.E.; Froment, G.F. A percolation approach for the modeling of deactivation of zeolite catalysts by coke formation: Diffusional limitations and finite rate of coke growth. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1993, 3, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahimi, M.; Gavalas, G.R.; Tsotsis, T.T. Statistical and continuum models of fluid-solid reactions in porous media. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1990, 6, 1443–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Rebo, H.P.; Holmen, A. Diffusion and deactivation during methanol conversion over SAPO-34: A percolation approach. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1999, 54, 3465–3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhong, B. Monte Carlo simulation of coke formation in zeolites. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 1998, 23, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahimi, M. Nonlinear transport processes in disordered media. AIChE J. 1993, 3, 369–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayagoitia, V.; Rojas, F.; Kornhauser, I.; Pérez-Aguilar, H. Modeling of porous media and surface structures: Their true essence as networks. Langmuir 1997, 5, 1327–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.; Wang, Q.; Jia, Z.; Ma, Y.; Cui, Y.; Muhammad, U.; Wang, Y.; Qian, W.; Wei, F. Equilibrium analysis of methylbenzene intermediates for a methanol-to-olefins process. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 5, 1297–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens, T.V.W. A new approach to the modeling of deactivation in the conversion of methanol on zeolite catalysts. J. Catal. 2009, 2, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.L.; Ma, Y.H.; Hou, Y.L.; Cui, Y.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, C.X.; Wang, Y.; Wei, F. Establishing a discrete Ising model for zeolite deactivation: Inspiration from the game of Go. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2017, 7, 2440–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Ramirez, J.; Christensen, C.H.; Egeblad, K.; Christensen, C.H.; Groen, J.C. Hierarchical zeolites: Enhanced utilisation of microporous crystals in catalysis by advances in materials design. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 2530–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Valla, J.; Garcia-Martinez, J. Realizing the Commercial Potential of Hierarchical Zeolites: New Opportunities in Catalytic Cracking. ChemCatChem 2014, 6, 46–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.X.; Xi, D.Y.; Sun, Q.M.; Wang, N.; Dai, Z.Y.; Fan, D.; Valtchev, V.; Yu, J.H. A top-down approach to hierarchical SAPO-34 zeolites with improved selectivity of olefin. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 234, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Wang, Y.Q.; Wang, Z.; Chen, H.B.; Wang, X.; Li, H.Y.; Sun, L.Y.; Fan, C.Y.; Zhang, X. Fabrication of hierarchical ZnSAPO-34 by alkali treatment with improved catalytic performance in the methanol-to-olefin reaction. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2018, 21, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, I.; Madsen, C.; Jacobsen, C.J.H. Confined space synthesis: A novel route to nanosized zeolites. Inorg. Chem. 2000, 39, 2279–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, C.J.H.; Madsen, C.; Janssens, T.V.W.; Jakobsen, H.J.; Skibsted, J. Zeolites by confined space synthesis—Characterization of the acid sites in nanosized ZSM-5 by ammonia desorption and Al-27/Si-29-MAS NMR spectroscopy. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2000, 39, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, F.; Paasch, S.; Brunner, E.; Kaskel, S. Carbon templated SAPO-34 with improved adsorption kinetics and catalytic performance in the MTO-reaction. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2012, 164, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yang, M.; Tian, P.; Xu, S.; Yang, Y.; Wang, D.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, Z. Dual template-directed synthesis of SAPO-34 nanosheet assemblies with improved stability in the methanol to olefins reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 5608–5616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egeblad, K.; Christensen, C.H.; Kustova, M.; Christensen, C.H. Templating mesoporous zeolites. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 946–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.S.; Wang, L.F.; Yin, C.Y.; Lin, K.F.; Yan, D.; Li, J.X.; Xu, R.R.; Su, D.S.; Schlögl, R.; Yokoi, T.; et al. Catalytic properties of hierarchical mesoporous zeolites templated with a mixture of small organic ammonium salts and mesoscale cationic polymers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 118, 3162–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanakaa, S.; Fukui, R.; Miyake, Y. Synthesis of ordered mesoporous silicoaluminophosphates by using LTA zeolite precursors dissolved under acidic conditions. Mater. Lett. 2013, 92, 259–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Sun, L.; Chen, C.L.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Z.W.; Wei, G.H.; Jiang, X.M. Polyethyleneimine templated synthesis of hierarchical SAPO-34 zeolites with uniform mesopores. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 46093–46096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Xiao, F.S. Mesoporous Zeolites: Preparation, Characterization, Applications; Garcia-Martinez, J., Li, K.H., Eds.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2015; pp. 199–226. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Q.W.; Zhou, Z.H.; He, L.N. Efficient, selective and sustainable catalysis of carbon dioxide. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 3707–3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, S.L.; Jiang, Y.J.; Cao, Y.Q.; Chen, F.; Chang, W.K.; Gao, Y.L. Influence of template content on selective synthesis of SAPO-18, SAPO-18/34 intergrowth and SAPO-34 molecular sieves used for methanol-to-olefins process. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 104985–104994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvaro-Muñoz, T.; Márquez-Álvarez, C.; Sastre, E. Use of different templates on SAPO-34 synthesis. Effect on the acidity and catalytic activity in the MTO reaction. Catal. Today 2012, 179, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvaro-Muñoz, T.; Márquez-Álvarez, C.; Sastre, E. Aluminium chloride: A new aluminum source to prepare SAPO-34 catalysts with enhanced stability in the MTO process. Appl. Catal. A 2014, 472, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bergh, J.; Gascon, J.; Kapteijn, F. Zeolites, Catalysis; Wiley-VCH GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2010; pp. 361–387. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, Y.; Koiwai, A.; Takeuchi, H.; Hyodo, S.; Noda, S. Multinuclear NMR studies on the thermal stability of SAPO-34. J. Catal. 1993, 143, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasha, D.; de Saldarriaga, L.S.; Saldarriaga, C.; Hathaway, P.E.; Cox, D.F.; Davis, M.E. Studies of Silicoaluminophosphates with the Sodalite Structure. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1988, 110, 2127–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fan, D.Q.; Yu, T.; Wang, J.Q.; Hao, T.; Hu, X.Q.; Shen, M.Q.; Li, W. Improvement of low-temperature hydrothermal stability of Cu/SAPO-34 catalysts by Cu2+ species. J. Catal. 2015, 322, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, S.L.; Gao, Y.L.; Cao, Y.Q.; Zhang, Q.; Chang, W.K.; Benziger, J.B. Enhanced methanol to Olefins Catalysis by Physical Mixtures of SAPO-34 Molecular and MgO. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 5572–5585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.C.; Deng, Z.Y.; Zhu, K.K.; Zhou, X.G. Insights into the growth of small-sized SAPO-34 crystals synthesized by a vapor-phase transport method. CrystEngComm 2015, 17, 3214–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.W.; Ding, J.J.; Jin, D.L.; Ye, G.H.; Zhu, K.K.; Zhou, X.G.; Yang, W.M.; Yuan, W.K. The tailored synthesis of nanosize SAPO-34 via time-controlled silicon release enabled by an organosilane precursor. Chem. Coummun. 2017, 53, 6132–6135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, Z.; Wu, C.Y.; Jiang, S.; Shi, R.H.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, F.Y. Synthesis of polyurethane-urea from double CO2-route oligomers. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 3614–3619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Sample Name | Molar Composition a | SBET b (m2/g) | Smicro c (m2/g) | Sext c (m2/g) | Vmicro c (cm3/g) | Vmeso d (cm3/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PUa0 | Al0.50P0.40Si0.09O2 | 641 | 631 | 10 | 0.28 | 0.04 |
| PUa0.08 | Al0.51P0.39Si0.09O2 | 606 | 584 | 22 | 0.27 | 0.22 |
| PUa0.1 | Al0.53P0.38Si0.08O2 | 555 | 506 | 49 | 0.25 | 0.31 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, Y.; Qin, J.; Xiao, M.; Wang, S.; Han, D.; Meng, Y. Performance Enhanced SAPO-34 Catalyst for Methanol to Olefins: Template Synthesis Using a CO2-Based Polyurea. Catalysts 2019, 9, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9010016
Yu Y, Qin J, Xiao M, Wang S, Han D, Meng Y. Performance Enhanced SAPO-34 Catalyst for Methanol to Olefins: Template Synthesis Using a CO2-Based Polyurea. Catalysts. 2019; 9(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9010016
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Yuehong, Jiaxiang Qin, Min Xiao, Shuanjin Wang, Dongmei Han, and Yuezhong Meng. 2019. "Performance Enhanced SAPO-34 Catalyst for Methanol to Olefins: Template Synthesis Using a CO2-Based Polyurea" Catalysts 9, no. 1: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9010016
APA StyleYu, Y., Qin, J., Xiao, M., Wang, S., Han, D., & Meng, Y. (2019). Performance Enhanced SAPO-34 Catalyst for Methanol to Olefins: Template Synthesis Using a CO2-Based Polyurea. Catalysts, 9(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9010016