Cobalt Oxide Catalysts in the Form of Thin Films Prepared by Magnetron Sputtering on Stainless-Steel Meshes: Performance in Ethanol Oxidation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characterization of the Catalysts
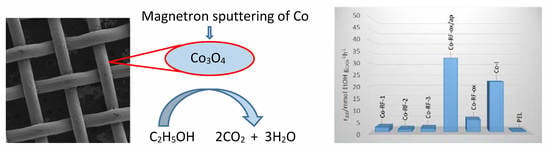
2.2. Catalytic Activity and Selectivity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Catalysts Preparation
4.2. Catalysts Characterization
4.3. Catalytic Tests
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duprez, D.; Cavani, F. Handbook of Advanced Methods and Processes in Oxidation Catalysis; Imperial College Press: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ojala, S.; Pitkaaho, S.; Laitinen, T.; Koivikko, N.N.; Brahmi, R.; Gaálová, J.; Matějová, L.; Kucherov, A.; Paivarinta, S.; Hirschmann, C.; et al. Catalysis in VOC abatement. Top. Catal. 2011, 54, 1224–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirátová, K.; Kovanda, F.; Balabánová, J.; Kšírová, P. Aluminum wire meshes coated with Co-Mn-Al and Co oxides as catalysts for deep ethanol oxidation. Catal. Today 2018, 304, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solsona, B.; Davies, T.E.; García, T.; Vázquez, I.; Dejoza, A.; Taylor, S.H. Total oxidation of propane using nanocrystalline cobalt oxide and supported cobalt oxide catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2008, 84, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, T.; Agouram, S.; Sanchez-Royo, J.F.; Murillo, R.; Maria Mastral, A.; Aranda, A.; Vazquez, I.; Dejoz, A.; Solsona, B. Deep oxidation of volatile organic compounds using ordered cobalt oxides prepared by a nanocasting route. Appl. Catal. A 2010, 386, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, L.C.; Chen, M.; Cao, Y.; He, H.Y.; Fan, K.N. Dry citrate-precursor synthesized nanocrystalline cobalt oxide as highly active catalyst for total oxidation of propane. J. Catal. 2009, 263, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Deng, J.; Zang, S.; Yang, H.; Guo, G.; Arandiyan, H.; Dai, H. Au–Pd/3DOM Co3O4: Highly active and stable nanocatalysts for toluene oxidation. J. Catal. 2015, 322, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Dai, H.; Deng, J.; Xie, S.; Han, W.; Tan, W.; Jiang, Y.; Au, C. Porous Cube-Aggregated Co3O4 Microsphere-Supported Gold Nanoparticles for Oxidation of Carbon Monoxide and Toluene. ChemSusChem 2014, 7, 1745–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, B.; Arandiyan, H.; Li, J. Comparison of the performance for oxidation of formaldehyde on nano- Co3O4, 2D-Co3O4, and 3D-Co3O4 catalysts. Appl. Catal. B 2013, 142, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovanda, F.; Jirátová, K.; Ludvíková, J.; Raabová, H. Co–Mn–Al mixed oxides on anodized aluminum supports and their use as catalysts in the total oxidation of ethanol. Appl. Catal. A 2013, 464–465, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twigg, M.V.; Webster, D.E. Structured Catalysts and Reactors, 2nd ed.; Cybulski, A., Moulijn, J.A., Eds.; Chemical Industries Series; Taylor and Francis: Abingdon-on-Thames, UK, 2006; Volume 110, p. 71. [Google Scholar]
- Sanz, O.; Banus, E.D.; Goya, A.; Larumbe, H.; Delgado, J.J.; Monzón, A.; Montes, M. Stacked wire-mesh monoliths for VOCs combustion: Effect of the mesh-opening in the catalytic performance. Catal. Today 2017, 296, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Xue, B.; Chen, M. Catalytic oxidation of VOCs over the structured bimetallic catalyst 0.1% Pt-0.75% CeO2/SSWM. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2015, 25, 167–170. [Google Scholar]
- Ahlstroem-Silverstand, A.F.; Odenbrand, C.U.I. Modelling catalytic combustion of carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons over catalytically active wire meshes. Chem. Eng. J. 1999, 73, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klyushina, A.; Pacultová, K.; Krejčová, S.; Słowik, G.; Jirátová, K.; Kovanda, F.; Ryczkowski, J.; Obalová, L. Advantages of stainless steel sieves as support for catalytic N2O decomposition over K-doped Co3O4. Catal. Today 2015, 257, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Río, L.; López, I.; Marbán, G. Stainless steel wire mesh-supported Co3O4 catalysts in the steam reforming of ethanol. Appl. Catal. B 2014, 150–151, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouotou, P.M.; Pan, G.F.; Weng, J.J.; Fan, S.B.; Tian, Z.Y. Stainless steel grid mesh-supported CVD made Co3O4 thin films for catalytic oxidation of VOCs of olefins type at low temperature. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 35, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlstroem-Silverstand, A.F.; Odenbrand, C.U.I. Thermally sprayed wire-mesh catalysts for the purification of flue gases from small-scale combustion of bio-fuel: Catalyst preparation and activity studies. Appl. Catal. A 1997, 153, 177–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Qui, W.; Qin, F.; Fang, H.; Hadjiev, V.G.; Litvinov, D.; Bao, J. Identification of Cobalt Oxides with Raman Scattering and Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 4511–4516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvořáková, M.; Perekrestov, R.; Kšírová, P.; Balabánová, J.; Jirátová, K.; Maixner, J.; Topka, P.; Rathouský, J.; Koštejn, M.; Čada, M.; et al. Preparation of cobalt oxide catalysts on stainless steel wire mesh by combination of magnetron sputtering and electrochemical deposition. Catal. Today 2019, 334, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perekrestov, R.; Spesyvyi, A.; Maixner, J.; Mašek, K.; Leiko, O.; Khalakhan, I.; Maňák, J.; Kšírová, P.; Hubička, Z.; Čada, M. The comparative study of electrical, optical and catalytic properties of Co3O4 thin nanocrystalline films prepared by reactive high-power impulse and radio frequency magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films 2019, 686, 137–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjiev, V.G.; Iliev, M.N.; Vergilov, I.V. The Raman spectra of Co3O4. J. Phys. Chem. Solid State Phys. 1988, 21, 199–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Z.; Jinwen, S.; Mao, S.S.; Liejin, G. Co3O4 quantum dots: Reverse micelle synthesis and visible-light-driven photocatalytic overall water splitting. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 2002–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.W.; Wang, C.B.; Chen, S.H. Characterization of cobalt oxides studied by FT-IR, Raman, TPR and TG-MS. Thermochim. Acta 2008, 473, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenglet, M.; Lopitaux, J.; Terrier, L.; Chartier, P.; Koenig, J.F.; Nkeng, P.; Poillerat, G. Initial Stages of Cobalt Oxidation by FTIR Spectroscopy. J. Phys. IV 1993, 3, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani-Moghadam, T.; Kompany, A.; Bagheri-Mohagheghi, M.M.; Abrishami, M.E. Cobalt spin states investigation of Ruddlesden-Popper La2−xSrxCoO4, using X-ray diffraction and infrared spectroscopy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 465, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sexton, B.A.; Hughes, A.E.; Turney, T.W. An XPS and TPR study of the reduction of promoted cobalt-kieselguhr Fischer-Tropsch catalysts. J. Catal. 1986, 97, 390–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Chen, Y.W. The mechanism of reduction of cobalt by hydrogen. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2004, 85, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnoldy, P.; Moulijn, J.A. Temperature-programmed reduction of CoO/Al2O3 catalysts. J. Catal. 1985, 93, 38–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirátová, K.; Mikulová, J.; Klempa, J.; Grygar, T.; Bastl, Z.; Kovanda, F. Modification of Co–Mn–Al mixed oxide with potassium and its effect on deep oxidation of VOC. Appl. Catal. A 2009, 361, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesinger, M.C.; Payne, B.P.; Grossvenor, A.O.; Lau, L.W.M.; Gerson, A.R. Resolving surface chemical states in XPS analysis of first row transition metals, oxides and hydroxides: Cr, Mn, Fe, Co and Ni. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 2717–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, T.E.; Garcia, T.; Solsona, B.; Taylor, S.H. Nanocrystalline cobalt oxide: A catalyst for selective alkane oxidation under ambient conditions. Chem. Commun. 2006, 32, 3417–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finocchio, E.; Willey, R.J.; Busca, G.; Lorenzelli, V. FTIR studies on the selective oxidation and combustion of light hydrocarbons at metal oxide surfaces. Part 3. Comparison of the oxidation of C3 organic compounds over Co3O4, MgCr2O4 and CuO. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1997, 93, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šolcová, O.; Matějová, L.; Topka, P.; Musilová, Z.; Schneider, P. Comparison of textural information from argon (87 K) and nitrogen (77 K) physisorption. J. Porous Mater. 2011, 18, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topka, P.; Jirátová, K.; Soukup, K.; Goliáš, J. Device for Measuring Specific Surface of Large Samples, Method of Measurement and Its Use. Patent Application PV 2019-380; Ústav Chemických Procesů, Prague, Czech Republic, 2019. [Google Scholar]







| Sample | Co3O4 Content/% | Weight a Loss/% | D b (Co3O4)/nm | FT-IR/νCo-O (cm−1) | TPR c/mmol H2·gCoOx−1 | TPR Tmax/°C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-RF-1 | 0.73 | 8 | 33.7 | 694; 649; 613; 555; 505 | 15.1 | 378 |
| Co-RF-2 | 0.79 | 12 | 32.5 | 694; 649; 613; 555; 505 | 15.2 | 360 |
| Co-RF-3 | 1.44 | 31 | 37.9 | 694; 655; 630; 613; 548 | 14.4 | 381 |
| Co-RF-ox/ap | 0.93 | 3 | 7.1 | 688; 653; 605; 547 | 14.0 | 266 d; 358 |
| Co-RF-ox | 0.75 | 3 | 21.9 | 688; 605; 547 | 14.7 | 367 |
| Co-I | 1.10 | 60 | 31.7 | 670; 547 | 14.6 | 262 d; 358; 554 |
| PEL | 97.0 | - | 75.3 | 660; 547 | 15.6 | 426 |
| Sample | Co | O | C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-RF-ox/ap | Fresh | 7.2 | 28.2 | 64.6 |
| Co-RF-ox/ap | Used | 7.8 | 29.7 | 62.4 |
| Co-RF-ox | Fresh | 3.2 | 24.2 | 72.6 |
| Co-RF-ox | Used | 4.2 | 21.2 | 74.6 |
| Sample | O 1s | Co 2p3/2 | O(529.5):Co | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BE, eV | 529.5 | 531.1–531.5 | 531.9–532.5 | 532.7–533.5 | 780.0 | 780.5 | |
| Co-RF-ox/ap | |||||||
| Fresh | 12.9 | 7.0 | 5.6 | 2.7 | 7.2 | 0 | 1.80 |
| Used | 14.4 | 6.5 | 5.4 | 3.5 | 7.9 | 0 | 1.83 |
| Co-RF-ox | |||||||
| Fresh | 6.0 | 6.9 | 7.9 | 3.4 | 3.2 | 0.04 | 1.85 |
| Used | 8.8 | 5.3 | 5.1 | 2.1 | 4.2 | 0 | 2.07 |
| Sample | Co3O4 Content/ wt.% | T50/ °C | T95CO2/°C | AcA a/ppm/°C | CO b/ppm/°C | X200/% | r200/ mmolEtOH gCo3O4−1 h−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-RF-1 | 0.73 | 291 | 364 | 500/325 | 110/356 | 2.1 | 2.1 |
| Co-RF-2 | 0.79 | 287 | 356 | 511/314 | 94/350 | 1.6 | 1.2 |
| Co-RF-3 | 1.44 | 285 | 351 | 512/314 | 78/357 | 3.2 | 1.6 |
| Co-RF-ox/ap | 0.93 | 216 | 244 | 433/223 | 12/234 | 43.0 | 32.4 |
| Co-RF-ox | 0.75 | 250 | 311 | 542/275 | 68/296 | 6.0 | 5.4 |
| Co-I | 1.10 | 212 | 265 | 454/240 | 62/255 | 36.6 | 22.1 |
| PEL | 97.0 | 210 | 399 c | 195/199 | 0/- | 39.4 | 0.29 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jirátová, K.; Perekrestov, R.; Dvořáková, M.; Balabánová, J.; Topka, P.; Koštejn, M.; Olejníček, J.; Čada, M.; Hubička, Z.; Kovanda, F. Cobalt Oxide Catalysts in the Form of Thin Films Prepared by Magnetron Sputtering on Stainless-Steel Meshes: Performance in Ethanol Oxidation. Catalysts 2019, 9, 806. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9100806
Jirátová K, Perekrestov R, Dvořáková M, Balabánová J, Topka P, Koštejn M, Olejníček J, Čada M, Hubička Z, Kovanda F. Cobalt Oxide Catalysts in the Form of Thin Films Prepared by Magnetron Sputtering on Stainless-Steel Meshes: Performance in Ethanol Oxidation. Catalysts. 2019; 9(10):806. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9100806
Chicago/Turabian StyleJirátová, Květa, Roman Perekrestov, Michaela Dvořáková, Jana Balabánová, Pavel Topka, Martin Koštejn, Jiří Olejníček, Martin Čada, Zdeněk Hubička, and František Kovanda. 2019. "Cobalt Oxide Catalysts in the Form of Thin Films Prepared by Magnetron Sputtering on Stainless-Steel Meshes: Performance in Ethanol Oxidation" Catalysts 9, no. 10: 806. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9100806
APA StyleJirátová, K., Perekrestov, R., Dvořáková, M., Balabánová, J., Topka, P., Koštejn, M., Olejníček, J., Čada, M., Hubička, Z., & Kovanda, F. (2019). Cobalt Oxide Catalysts in the Form of Thin Films Prepared by Magnetron Sputtering on Stainless-Steel Meshes: Performance in Ethanol Oxidation. Catalysts, 9(10), 806. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9100806