Numerical Simulation Study on the Front Shape and Thermal Stresses in Growing Multicrystalline Silicon Ingot: Process and Structural Design
Abstract
:1. Introduction
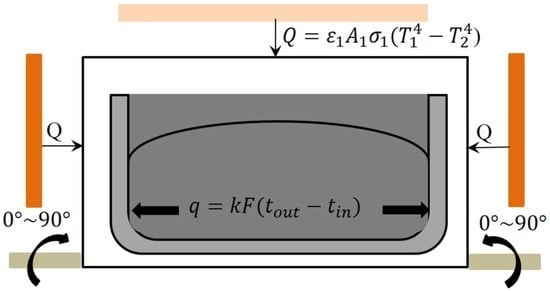
2. Physical Model
3. Effect of Power Ratio on Temperature and Thermal Stress Fields
3.1. Half State
3.2. End State
3.3. Discussion
4. Furnace Structure: The Effect of the Position of the Block under the Side Heater
4.1. Half State
4.2. End State
4.3. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems. Photovoltaics Report; Fraunhofer ISE: Freiburg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.F.; Huang, H.C.; Tsai, H.W.; Lan, A.; Chuck, C.; Lan, C.W. An enhanced cooling design in directional solidification for high quality multi-crystalline solar silicon. J. Cryst. Growth 2012, 340, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.J.; Nakano, S.; Liu, L.J.; Kakimoto, K. Study on thermal stress in a silicon ingot during a unidirectional solidification process. J. Cryst. Growth 2008, 310, 4330–4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, G.; Chen, D.; Yang, X.; Ma, W.; Luo, T.; Wei, K.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, G. Numerical simulation and experimental verification of vacuum directional solidification process for multicrystalline silicon. Vacuum 2015, 116, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K. Fundations of Materials Engineering, 2nd ed.; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Liao, S.H.; Chen, J.C.; Chen, C.H.; Huang, Y.H.; Yang, C.J.; Lin, H.W.; Nguyen, H.B. Effects of the hot zone design during the growth of large size multi-crystalline silicon ingots by the seeded directional solidification process. J. Cryst. Growth 2016, 452, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.G.; Dai, B. Optimization of power consumption on silicon directional solidification system by using numerical simulations. J. Cryst. Growth 2012, 354, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelian, C. Numerical modeling of carbon distribution and precipitation during directional solidification of photovoltaic silicon. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 145, 118775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cablea, M.; Zaidat, K.; Gagnoud, A.; Nouri, A.; Chichignoud, G.; Delannoy, Y. Multi-crystalline silicon solidification under controlled forced convection. J. Cryst. Growth 2015, 417, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.; Chen, X.H.; Zhang, F.; He, L.; Luo, Y.; Xiong, H.; Hu, Y.; Wang, F.; Song, B. Influence of modified bottom insulation on the seeded directional solidification process for high-performance multi-crystalline silicon. Vacuum 2020, 172, 108969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokland, E.S.A.; Heinze, V.; Meier, D.; Pätzold, O.; Stelter, M. Growth of multicrystalline silicon in a cone-shaped crucible. J. Cryst. Growth 2015, 416, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.K.; Lin, C.H.; Chen, C.Y. Numerical analysis of steady and transient processes in a directional solidification system. Multi-Scale Multi-Phys. Mech. 2016, 1, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhong, G.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Chen, W.; Huang, X. Upgrade of the hot zone for large-size high performance multi-crystalline silicon ingot casting. J. Cryst. Growth 2016, 441, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, M.; Nagarajan, S.G.; Ramasamy, P. Computational Study of Heat Transfer on Molten Silicon during Directional Solidification for Solar Cell Applications. Procedia Eng. 2015, 127, 1250–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, X.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, B.; Wang, C.; Xu, F. Thermal system design and optimization of an industrial silicon directional solidification system. J. Cryst. Growth 2011, 318, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trempa, C.R.M.; Jung, T.; Friedrich, J.; Müller, G. Modeling of incorporation of O, N, C and formation of related precipitates during directional solidification of silicon under consideration of variable processing parameters. J. Cryst. Growth 2010, 312, 878–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Liu, L.; Li, Z.; Shao, Y. Parameter study of traveling magnetic field for control of melt convection in directional solidification of crystalline silicon ingots. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2018, 71, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Qi, X.; Liu, L.; Zhou, G. Numerical study of melt flow under the influence of heater-generating magnetic field during directional solidification of silicon ingots. J. Cryst. Growth 2018, 484, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesavan, V.; Srinivasan, M.; Ramasamy, P. Numerical investigation of Directional Solidification process for improving multi-crystalline silicon ingot quality for photovoltaic applications. Mater. Lett. 2019, 241, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Stoddard, N.; Ma, R.H.; Clark, R. Bulk multicrystalline silicon growth for photovoltaic (PV) application. J. Cryst. Growth 2008, 310, 2178–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Lv, G.; Wang, Y.; Ma, W.; Yang, X.; Lei, Y. The influence of Marangoni effect on the growth quality of multi-crystalline silicon during the vacuum directional solidification process. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2019, 91, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karuppasamya, P.; Srinivasana, M.; Aravintha, K.; Ramasamya, P. Numerical Modelling on Modified Directional Solidification Process of Multi-crystalline Silicon Growth for Photovoltaic Applications. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 23014–23021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Silicon | Value | Value | |
| Liquid specific heat capacity (J/kg∙K) | 710 | Liquid thermal conductivity (W/m∙K) | 22 |
| Solid specific heat capacity (J/kg∙K) | 1000 | Solid thermal conductivity (W/m∙K) | 64 |
| Emissivity (W/m∙K) | 0.3 | Latent heat of fusion (J/kg) | 1.587 × 106 |
| Density of solid (kg/m3) | 2330 | Stress coefficient c11/c22/c33 | 1.653 × 1011 |
| Density of liquid in 1600 K (kg/m3) | 2520 | Stress coefficient c12/c13/c23 | 6.393 × 1010 |
| Phase change temperature (K) | 1687 | Stress coefficient c44 | 7.962 × 1010 |
| Crucible | Value | Value | |
| Specific heat capacity (J/kg∙K) | 740 | Thermal conductivity (W/m∙K) | 4.8 |
| Emissivity (W/m∙K) | 0.8 | ||
| Heater/graphite/cooler plate | Value | Value | |
| Specific heat capacity (J/kg∙K) | 740 | Thermal conductivity (W/m∙K) | 80 |
| Emissivity (W/m∙K) | 0.8 | ||
| Insulator | Value | ||
| Specific heat capacity (J/kg∙K) | 846 | Thermal conductivity (W/m∙K) | 0.4 |
| Emissivity (W/m∙K) | 0.8 |
| No. | Heating Power and Ratio * | Insulation Rising Velocity (m/s) |
|---|---|---|
| Case a | 26:26 kW, (1:1) | 2 × 10−6 |
| Case b | 17.3:34.7 kW, (1:2) | |
| Case c | 13:39 kW, (1:3) | |
| Case d | 10.4:41.6 kW, (1:4) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, C.; Liu, G.; Zhang, L.; Wang, G.; Hou, Y.; Li, Y. Numerical Simulation Study on the Front Shape and Thermal Stresses in Growing Multicrystalline Silicon Ingot: Process and Structural Design. Crystals 2020, 10, 1053. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10111053
Chen C, Liu G, Zhang L, Wang G, Hou Y, Li Y. Numerical Simulation Study on the Front Shape and Thermal Stresses in Growing Multicrystalline Silicon Ingot: Process and Structural Design. Crystals. 2020; 10(11):1053. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10111053
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Chengmin, Guangxia Liu, Lei Zhang, Guodong Wang, Yanjin Hou, and Yan Li. 2020. "Numerical Simulation Study on the Front Shape and Thermal Stresses in Growing Multicrystalline Silicon Ingot: Process and Structural Design" Crystals 10, no. 11: 1053. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10111053
APA StyleChen, C., Liu, G., Zhang, L., Wang, G., Hou, Y., & Li, Y. (2020). Numerical Simulation Study on the Front Shape and Thermal Stresses in Growing Multicrystalline Silicon Ingot: Process and Structural Design. Crystals, 10(11), 1053. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10111053