Effects of the Domain Wall Conductivity on the Domain Formation under AFM-Tip Voltages in Ion-Sliced LiNbO3 Films
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Results
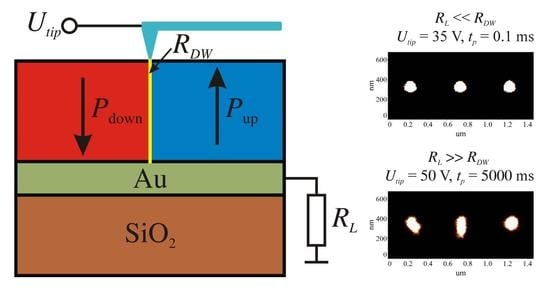
2.1. The Effects of RL Insertion on the Domain Formation
2.2. DWC Estimation Based on the Examination of Domain Patterns
3. Discussion
3.1. DWC Calculations
3.2. The DW Inclination Angle
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferroelectric Crystals for Photonic Applications; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 1–132.
- Cho, Y.; Fujimoto, K.; Hiranaga, Y.; Wagatsuma, Y.; Onoe, A.; Terabe, K.; Kitamura, K. Tbit/inch2 ferroelectric data storage based on scanning nonlinear dielectric microscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 81, 4401–4403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vul, B.M.; Guro, G.M.; Ivanchik, I.I. Encountering domains in ferroelectrics. Ferroelectrics 1973, 6, 29–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calleja, M.; Dove, M.T.; Salje, E.K.H. Trapping of oxygen vacancies on twin walls of CaTiO3: A computer simulation study. J. Physics Condens. Matter 2003, 15, 2301–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aird, A.; Salje, E.K.H. Sheet superconductivity in twin walls: Experimental evidence of. J. Physics Condens. Matter 1998, 10, L377–L380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, J.; Martin, L.W.; He, Q.; Zhan, Q.; Chu, Y.-H.; Rother, A.; Hawkridge, M.E.; Maksymovych, P.; Yu, P.; Gajek, M.; et al. Conduction at domain walls in oxide multiferroics. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Catalán, G.; Seidel, J.; Ramesh, R.; Scott, J.F. Domain wall nanoelectronics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2012, 84, 119–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bednyakov, P.S.; Sturman, B.I.; Sluka, T.; Tagantsev, A.K.; Yudin, P.V. Physics and applications of charged domain walls. NPJ Comput. Mater. 2018, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schröder, M.; Haußmann, A.; Thiessen, A.; Soergel, E.; Woike, T.; Eng, L.M. Conducting Domain Walls in Lithium Niobate Single Crystals. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 3936–3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonnissen, J.; Batuk, D.; Nataf, G.F.; Jones, L.; Abakumov, A.M.; Van Aert, S.; Schryvers, D.; Salje, E.K.H. Direct Observation of Ferroelectric Domain Walls in LiNbO3: Wall-Meanders, Kinks, and Local Electric Charges. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 7599–7604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolba, B.; Seidel, J.; Cazorla, C.; Godau, C.; Haußmann, A.; Eng, L.M. Resistor Network Modeling of Conductive Domain Walls in Lithium Niobate. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2018, 4, 1700242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godau, C.; Kampfe, T.; Thiessen, A.; Eng, L.M.; Haußmann, A. Enhancing the Domain Wall Conductivity in Lithium Niobate Single Crystals. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 4816–4824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volk, T.; Gainutdinov, R.V.; Zhang, H.H. Domain-wall conduction in AFM-written domain patterns in ion-sliced LiNbO3 films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 110, 132905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, C.S.; Herr, S.J.; Buse, K.; Sturman, B.; Soergel, E.; Razzaghi, C.; Breunig, I. Large and accessible conductivity of charged domain walls in lithium niobate. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Tan, Y.; McConville, J.P.V.; Ahmadi, Z.; Wang, B.; Conroy, M.; Moore, K.; Bangert, U.; Shield, J.E.; Chen, L.; et al. Electrical Tunability of Domain Wall Conductivity in LiNbO3 Thin Films. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1902890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poberaj, G.; Hu, H.; Sohler, W.; Gunter, P. Lithium niobate on insulator (LNOI) for micro-photonic devices. Laser Photon- Rev. 2012, 6, 488–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boes, A.; Corcoran, B.; Chang, L.; Bowers, J.; Mitchell, A. Status and Potential of Lithium Niobate on Insulator (LNOI) for Photonic Integrated Circuits. Laser Photon- Rev. 2018, 12, 1700256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusing, M.; Weigel, P.O.; Zhao, J.; Mookherjea, S. Toward 3D Integrated Photonics Including Lithium Niobate Thin Films: A Bridge Between Electronics, Radio Frequency, and Optical Technology. IEEE Nanotechnol. Mag. 2019, 13, 18–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaĭnutdinov, R.V.; Volk, T.; Zhang, H.H. Domain formation and polarization reversal under atomic force microscopy-tip voltages in ion-sliced LiNbO3 films on SiO2/LiNbO3 substrates. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 162903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk, T.; Gainutdinov, R.; Zhang, H. Domain Patterning in Ion-Sliced LiNbO3 Films by Atomic Force Microscopy. Crystals 2017, 7, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, G.-H.; Bai, Y.-H.; Cui, G.-X.; Li, C.; Qiu, X.-B.; Geng, D.-Q.; Wu, D.; Lu, Y.-Q. Ferroelectric domain inversion and its stability in lithium niobate thin film on insulator with different thicknesses. AIP Adv. 2016, 6, 075011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Slautin, B.N.; Turygin, A.; Greshnyakov, E.D.; Akhmatkhanov, A.R.; Zhu, H.; Shur, V.Y. Domain structure formation by local switching in the ion sliced lithium niobate thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2020, 116, 152904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kan, Y.; Bo, H.; Lu, X.; Xu, T.; Jin, Y.; Wu, X.; Huang, F.; Zhu, J. Decay properties of artificial two-domain structures in LiNbO3 crystals studied by scanning probe microscope. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 202903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofan, A.; Lilienblum, M.; Gaathon, O.; Sehrbrock, A.; Hoffmann, A.; Bakhru, S.; Bakhru, H.; Irsen, S.; Jr, R.M.O.; Soergel, E. Large-area regular nanodomain patterning in He-irradiated lithium niobate crystals. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 285309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ievlev, A.V.; Jesse, S.; Morozovska, A.N.; Strelcov, E.; Eliseev, E.A.; Pershin, Y.V.; Kumar, A.; Shur, V.Y.; Kalinin, S. Intermittency, quasiperiodicity and chaos in probe-induced ferroelectric domain switching. Nat. Phys. 2013, 10, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierolf, V.; Sandmann, C. Direct-write method for domain inversion patterns in LiNbO3. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 84, 3987–3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gainutdinov, R.; Volk, T. Effects of the Domain Wall Conductivity on the Domain Formation under AFM-Tip Voltages in Ion-Sliced LiNbO3 Films. Crystals 2020, 10, 1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10121160
Gainutdinov R, Volk T. Effects of the Domain Wall Conductivity on the Domain Formation under AFM-Tip Voltages in Ion-Sliced LiNbO3 Films. Crystals. 2020; 10(12):1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10121160
Chicago/Turabian StyleGainutdinov, Radmir, and Tatyana Volk. 2020. "Effects of the Domain Wall Conductivity on the Domain Formation under AFM-Tip Voltages in Ion-Sliced LiNbO3 Films" Crystals 10, no. 12: 1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10121160
APA StyleGainutdinov, R., & Volk, T. (2020). Effects of the Domain Wall Conductivity on the Domain Formation under AFM-Tip Voltages in Ion-Sliced LiNbO3 Films. Crystals, 10(12), 1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10121160