Fabrication of Ti-Alloy Powder/Solid Composite with Uniaxial Anisotropy by Introducing Unidirectional Honeycomb Structure via Electron Beam Powder Bed Fusion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Densities and Microstructures of Specimens
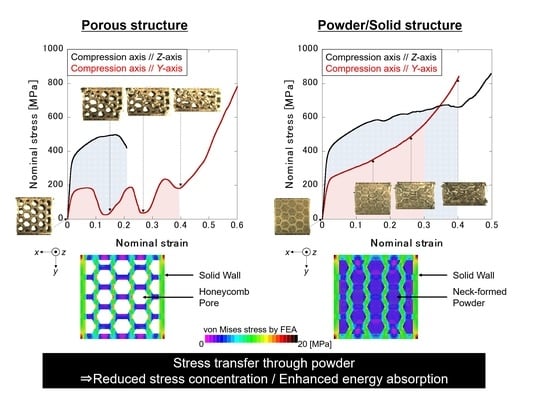
3.2. Deformation Behaviors and Mechanical Properties of the Products
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Powder/Solid Structuring on the Anisotropy Deformation Behavior of Porous Specimens with Unidirectional Honeycomb Pores
4.2. Influence of Honeycomb Pore Introduction and Powder/Solid Structuring on Anisotropy of Mechanical Properties
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weiner, S.; Traub, W. Bone structure from ångstroms to microns. FASEB J. 1992, 6, 879–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, T.; Kaibara, K.; Tabata, Y.; Nagata, N.; Enomoto, S.; Marukawa, E.; Umakoshi, Y. Unique alignment and texture of biological apatite crystallites in typical calcified tissues analyzed by micro-beam X-ray diffractometer system. Bone 2002, 31, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimoto, T.; Kawahara, K.; Matsugaki, A.; Kamioka, H.; Nakano, T. Quantitative evaluation of osteocyte morphology and bone anisotropic extracellular matrix in rat femur. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huiskes, R.; Weinans, H.; van Rietbergen, B. The relationship between stress shielding and bone resorption around total hip stems and the effects of flexible materials. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1992, 274, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noyama, Y.; Miura, T.; Ishimoto, T.; Itaya, T.; Niinomi, M.; Nakano, T. Bone loss and reduced bone quality of the human femur after total hip arthroplasty under stress-shielding effects by titanium-based implant. Mater. Trans. 2012, 53, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, J.; Dong, E.; Li, D.; Dong, S.; Zhang, C.; Wang, L. Anisotropy characteristics of microstructures for bone substitutes and porous implants with application of additive manufacturing in orthopaedic. Mater. Des. 2020, 191, 108608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimoto, T.; Hagihara, K.; Hisamoto, K.; Sun, S.-H.; Nakano, T. Crystallographic texture control of beta-type Ti–15Mo–5Zr–3Al alloy by selective laser melting for the development of novel implants with a biocompatible low Young’s modulus. Scr. Mater. 2017, 132, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeo, N.; Fukuda, H.; Matsugaki, A.; Inoue, T.; Serizawa, A.; Matsuzaka, T.; Ishimoto, T.; Ozasa, R.; Gokcekaya, O.; Nakano, T. 3D puzzle in cube pattern for anisotropic/isotropic mechanical control of structure fabricated by metal additive manufacturing. Crystals 2021, 11, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickels, L. AM and aerospace: An ideal combination. Met. Powder Rep. 2015, 70, 300–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Zou, J.; Li, S.; Jamshidi, P.; Abena, A.; Forsey, A.; Moat, R.J.; Essa, K.; Wang, M.; Zhou, K.; et al. Additive manufacturing of bio–inspired multi–scale hierarchically strengthened lattice structures. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2021, 167, 103764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeo, N.; Ishimoto, T.; Nakano, T. Novel powder/solid composites possessing low Young’s modulus and tunable energy absorption capacity, fabricated by electron beam melting, for biomedical applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 639, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soro, N.; Saintier, N.; Merzeau, J.; Veidt, M.; Dargusch, M.S. Quasi-static and fatigue properties of graded Ti–6Al–4V lattices produced by Laser Powder Bed Fusion (LPBF). Addit. Manuf. 2021, 37, 101653. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Li, X.; Jiang, Y.; Ling, M.; Nai, S.; Ding, J.; Wei, J. Electron beam melted heterogeneously porous micro lattices for metallic bone applications: Design and investigations of boundary and edge effects. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 36, 101566. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, L.; Ding, S.; Wen, C. Additive manufacturing technology for porous metal implant applications and triple minimal surface structures: A review. Bioact. Mater. 2019, 4, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobbert, F.S.L.; Lietaert, K.; Eftekhari, A.A.; Pouran, B.; Ahmadi, S.M.; Weinans, H.; Zadpoor, A.A. Additively manufactured metallic porous biomaterials based on minimal surfaces: A unique combination of topological, mechanical, and mass transport properties. Acta Biomater. 2017, 53, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, P.; Li, X.; Luo, S.; Ling, M.; Nai, S.; Ding, J.; Wei, J. Additively manufactured heterogeneously porous metallic bone with biostructural functions and bone-like mechanical properties. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 62, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugino, A.; Ohtsuki, C.; Tsuru, K.; Hayakawa, S.; Nakano, T.; Okazaki, Y.; Osaka, A. Effect of spatial design and thermal oxidation on apatite formation on Ti-15Zr-4Ta-4Nb alloy. Acta Biomater. 2008, 5, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsugaki, A.; Aramoto, G.; Nakano, T. The alignment of MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts on steps of slip traces introduced by dislocation motion. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 7327–7335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, Y.; Matsugaki, A.; Kawahara, K.; Ninomiya, T.; Sawada, H.; Nakano, T. Unique arrangement of bone matrix orthogonal to osteoblast alignment controlled by Tspan11-mediated focal adhesion assembly. Biomaterials 2019, 209, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Sin, W.J.; Nai, M.L.S.; Wei, J. Effects of processing parameters on surface roughness of additive manufactured Ti-6Al-4V via electron beam melting. Materials 2017, 10, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsugaki, A.; Aramoto, G.; Ninomiya, T.; Sawada, H.; Hata, S.; Nakano, T. Abnormal arrangement of a collagen/apatite extracellular matrix orthogonal to osteoblast alignment is constructed by a nanoscale periodic surface structure. Biomaterials 2015, 37, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, T.; Fujitani, W.; Ishimoto, T.; Lee, J.W.; Ikeo, N.; Fukuda, H.; Kuramoto, K. Formation of new bone with preferentially oriented biological apatite crystals using a novel cylindrical implant containing anisotropic open pores fabricated by the electron beam melting (EBM) method. ISIJ Int. 2011, 51, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakano, T.; Kan, T.; Ishimoto, T.; Ohashi, Y.; Fujitani, W.; Umakoshi, Y.; Hattori, T.; Higuchi, Y.; Tane, M.; Nakajima, H. Evaluation of bone quality near metallic implants with and without lotus-type pores for optimal biomaterial design. Mater. Trans. 2006, 2233–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeo, N.; Ishimoto, T.; Serizawa, A.; Nakano, T. Control of mechanical properties of three-dimensional Ti–6Al–4V products fabricated by electron beam melting with unidirectional elongated pores. Metall. Mater. Trans. A. 2014, 45, 4293–4301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, L.J.; Ashby, M.F. Cellular Solids—Structure and Properties, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Su, C.; Yu, H.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J.; Zeng, X. Controlling the tensile and fatigue properties of selective laser melted Ti–6Al–4V alloy by post treatment. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 857, 157552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaghmandfard, R.; Chalasani, D.; Odeshi, A.; Mohammadi, M. Activated slip and twin systems in electron beam melted Ti-6Al-4V subjected to elevated and high strain rate dynamic deformations. Mater. Charact. 2021, 172, 110866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, M.; Vijayan, S.; Nandwana, P.; Jinschek, J.R. The effect of beam scan strategies on microstructural variations in Ti–6Al–4V fabricated by electron beam powder bed fusion. Mater. Des. 2020, 196, 109165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bermani, S.; Blackmore, M.; Zhang, W.; Todd, I. The origin of microstructural diversity, texture, and mechanical properties in electron beam melted Ti6Al4V. Metal. Mater. Trans. A 2010, 41, 3422–3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, J.; Jiang, F.; Sun, X.; Chen, Z.; Tian, C.; Zhao, H. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V fabricated by electron beam melting. Crystals 2020, 10, 972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Sun, L.; Yang, P.; Fang, J.; Li, W. Energy absorption of additively manufactured functionally bi-graded thickness honeycombs subjected to axial loads. Thin-Walled Struct. 2019, 164, 107810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lee, P.D.; Singh, R.; Wu, G.; Lindley, T.C. Micro-CT characterization of structural features and deformation behavior of fly ash/aluminum syntactic foam. Acta Mater. 2009, 57, 3003–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, Q.; Patil, D.; Le, T.; Eppley, T.; Salti, Z.; Goss, D.; Grishin, A.; Bhate, D. An examination of the low strain rate sensitivity of additively manufactured polymer, composite and metallic honeycomb structures. Materials 2019, 12, 3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baranowski, P.; Płatek, P.; Antolak-Dudka, A.; Sarzyński, M.; Kucewicz, M.; Durejko, T.; Małachowski, J.; Janiszewski, J.; Czujko, T. Deformation of honeycomb cellular structures manufactured with Laser Engineered Net Shaping (LENS) technology under quasi-static loading: Experimental testing and simulation. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 25, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonyongmaneerat, Y. Mechanical properties of partially sintered materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 452–453, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tan, Y.H.; Wang, P.; Su, X.; Jean, H.; Herng, T.S.; Ding, J. Metallic microlattice and epoxy interpenetrating phase composites: Experimental and simulation studies on superior mechanical properties and their mechanisms. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2020, 135, 105934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeo, N.; Ishimoto, T.; Hiramoto, N.; Fukuda, H.; Ogisu, H.; Araki, Y.; Nakano, T. Solid/powder clad Ti-6Al-4V alloy with low Young’s modulus and high toughness fabricated by electron beam melting. Mater. Trans. 2015, 56, 755–758. [Google Scholar]
- Nakano, T.; Ishimoto, T. Powder-based additive manufacturing for development of tailor-made implants for orthopedic applications. KONA 2015, 32, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tilton, M.; Lewis, G.S.; Wee, H.B.; Armstrong, A.; Hast, M.W.; Manogharan, G. Additive manufacturing of fracture fixation implants: Design, material characterization, biomechanical modeling and experimentation. Addit. Manufact. 2020, 33, 101137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Compressive Axis | Porous Specimen | Composite Specimen | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z-Direction | Y-Direction | Z-Direction | Y-Direction | |
| Young’s modulus [GPa] | 41.9 ± 9.3 | 28.9 ± 1.1 | 50.5 ± 3.9 | 38.1 ± 2.9 |
| 0.2% Proof stress [MPa] | 326 ± 8 | 120 ± 13 | 368 ± 13 | 210 ± 20 |
| Plateau stress [MPa] | - | - | 629 ± 12 | 455 ± 26 |
| Densification strain | - | - | 0.40 ± 0.02 | 0.29 ± 0.00 |
| Toughness [MPa] | 85.8 ± 6.2 | 16.0 ± 1.8 | 231 ± 8 | 101 ± 12 |
| Specific energy absorption [J/g] | 19.4 ± 1.4 | 3.6 ± 0.4 | 52.1 ± 1.8 | 22.8 ± 0.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ikeo, N.; Matsumi, T.; Ishimoto, T.; Ozasa, R.; Matsugaki, A.; Matsuzaka, T.; Gokcekaya, O.; Takigawa, Y.; Nakano, T. Fabrication of Ti-Alloy Powder/Solid Composite with Uniaxial Anisotropy by Introducing Unidirectional Honeycomb Structure via Electron Beam Powder Bed Fusion. Crystals 2021, 11, 1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11091074
Ikeo N, Matsumi T, Ishimoto T, Ozasa R, Matsugaki A, Matsuzaka T, Gokcekaya O, Takigawa Y, Nakano T. Fabrication of Ti-Alloy Powder/Solid Composite with Uniaxial Anisotropy by Introducing Unidirectional Honeycomb Structure via Electron Beam Powder Bed Fusion. Crystals. 2021; 11(9):1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11091074
Chicago/Turabian StyleIkeo, Naoko, Tatsuya Matsumi, Takuya Ishimoto, Ryosuke Ozasa, Aira Matsugaki, Tadaaki Matsuzaka, Ozkan Gokcekaya, Yorinobu Takigawa, and Takayoshi Nakano. 2021. "Fabrication of Ti-Alloy Powder/Solid Composite with Uniaxial Anisotropy by Introducing Unidirectional Honeycomb Structure via Electron Beam Powder Bed Fusion" Crystals 11, no. 9: 1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11091074
APA StyleIkeo, N., Matsumi, T., Ishimoto, T., Ozasa, R., Matsugaki, A., Matsuzaka, T., Gokcekaya, O., Takigawa, Y., & Nakano, T. (2021). Fabrication of Ti-Alloy Powder/Solid Composite with Uniaxial Anisotropy by Introducing Unidirectional Honeycomb Structure via Electron Beam Powder Bed Fusion. Crystals, 11(9), 1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11091074