Error Analysis and Correction for Quantitative Phase Analysis Based on Rietveld-Internal Standard Method: Whether the Minor Phases Can Be Ignored?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Data Collection and Processing
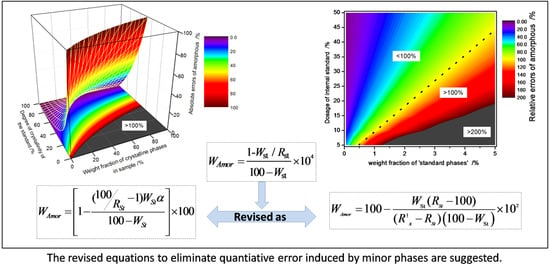
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Quantitative Error Induced by Minor Impurity Phase of Internal Standard
3.2. Quantitative Error Induced by Minor Standard Phase Present in Sample (SPS)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hull, A.W. A new method of chemical analysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1919, 41, 1168–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, L.; Klug, H.P. Basic aspects of X-ray absorption in quantitative diffraction analysis of powder mixtures. Powder Diffr. 1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, F.H. Quantitative interpretation of X-ray diffraction patterns of mixtures. II. Adiabatic principle of X-ray diffraction analysis of mixtures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1974, 7, 526–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeRoux, J.; Lennox, D.H.; Kay, K. Direct quantitative X-ray analysis by diffraction-absorption technique. Anal. Chem. 1953, 25, 740–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, F.H. Quantitative interpretation of X-ray diffraction patterns of mixtures. I. Matrix-flushing method for quantitative multicomponent analysis. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2010, 7, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zevin, L.S. A method of quantitative phase analysis without standards. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1977, 10, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popović, S.; Gržeta-Plenković, B. The doping method in quantitative X-ray diffraction phase analysis. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1983, 16, 505–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietveld, H.M.A. profile refinement method for nuclear and magnetic structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2010, 2, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bish, D.L.; Howard, S.A. Quantitative phase analysis using the Rietveld method. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1988, 21, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winburn, R.S.; Grier, D.G.; Mccarthy, G.J.; Peterson, R.B. Rietveld quantitative X-ray diffraction analysis of NIST fly ash standard reference materials. Powder Diffr. 2000, 15, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualtieri, A.; Artioli, G. Quantitative determination of chrysotile asbestos in bulk materials by combined Rietveld and RIR methods. Powder Diffr. 1995, 10, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snellings, R.; Salze, A.; Scrivener, K.L. Use of X-ray diffraction to quantify amorphous supplementary cementitious materials in anhydrous and hydrated blended cements. Cem. Concr. Res. 2014, 64, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Torre, A.G.; Bruque, S.; Aranda, M.A.G. Rietveld quantitative amorphous content analysis. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2001, 34, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, D.; Stabler, C.; Goetz-Neunhoeffer, F.; Dittrich, S.; Neubauer, J. Does Ordinary Portland Cement contain amorphous phase? A quantitative study using an external standard method. Powder Diffr. 2011, 26, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarlett, N.V.Y.; Madsen, I.C. Quantification of phases with partial or no known crystal structures. Powder Diffr. 2006, 21, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Pinazo, G.; Cuesta, A.M.; García-Maté, M.; Santacruz, I.; Losilla, E.R.; De la Torre, A.G.; León-Reina, L.; Aranda, M.A.G. Rietveld quantitativephaseanalysis of Yeelimite-containingcements. Cem. Concr. Res. 2012, 42, 960–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xu, W.; Yang, X.; Wu, J. Preparation of Portland cement with sugar filter mud as lime-based raw material. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 66, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Wang, P.; Liu, X. Influence of particle size distribution on accurate X-ray quantitative analysis of tetracalcium aluminoferrite. Adv. Cem. Res. 2015, 27, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, I.C.; Scarlett, N.V.Y.; Kern, A. Description and survey of methodologies for the determination of amorphous content via X-ray powder diffraction. Z. Kristallogr. Cryst. Mater. 2011, 12, 944–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, H.; Ermrich, M. Microabsorption Correction of X-Ray Intensities Diffracted by Multiphase Powder Specimens. Powder Diffr. 1989, 4, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westphal, T.; Füllmann, T.; Pöllmann, H. Rietveld quantification of amorphous portions with an internal standard—Mathematical consequences of the experimental approach. Powder Diffr. 2009, 24, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Liu, X.; De la Torre, A.G.; Lu, L.; Sobolev, K. Assessment of quantitative accuracy of Rietveld/XRD analysis of the crystalline and amorphous phases in fly ash. Anal. Method 2017, 9, 2415–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Torre, A.G.; Aranda, M.A.G. Accuracy in Rietveld quantitative phase analysis of Portland cements. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2003, 36, 1169–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.Q.; Liu, X.P.; Wu, J.G.; Wang, P. Rietveld quantification of γ-C2S conversion rate supported by synchrotron X-ray diffraction images. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 2013, 14, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guirado, F.; Galí, S. Quantitative Rietveld analysis of CAC clinker phases using synchrotron radiation. Cem. Concr. Res. 2006, 36, 2021–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León-Reina, L.; De la Torre, A.G.; Porras-Vázquez, J.M.; Cruz, M.; Ordonez, L.M.; Alcobé, X.; Gispert-Guirado, F.; Larrañaga-Varga, A.; Paul, M.; Fuellmann, T.; et al. Round robin on Rietveld quantitative phase analysis of Portland cements. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 906–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, A.C.; Von Dreele, R.B. General Structure Analysis System (GSAS); Los Alamos National Laboratory Report LAUR86-748; Los Alamos National Laboratory: Los Alamos, NM, USA, 2004.
- Will, G.; Bellotto, M.; Parrish, W.; Hart, M. Crystal structures of quartz and magnesium germanate by profile analysis of synchrotron-radiation high-resolution powder data. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1988, 21, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kihara, K.; Donnay, G. Anharmonic thermal vibrations in ZnO. Can. Mineral. 1985, 23, 647–654. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, P.; Cox, D.E.; Hastings, J.B. Rietveld refinement of Debye–Scherrer synchrotron X-ray data from Al2O3. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1987, 20, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finger, L.W.; Cox, D.E.; Jephcoat, A.P. A correction for powder diffraction peak asymmetry due to axial divergence. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1994, 27, 892–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brindley, G.W. The effect of grain or particle Size on X-ray reflections from mixed powders and alloys, considered in relation to the quantitative determination of crystalline substances by X-ray methods. Philos. Mag. 1977, 36, 347–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.C.; Matulis, C.E. Absorption contrast effects in the quantitative XRD analysis of powders by full multiphase profile refinement. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1991, 24, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Scanning Type Detector | Continuous Scanning |
|---|---|
| X’Celerator Detector | |
| Geometry | Reflection/flat sample |
| X-ray radiation/tube working conditions | CuKα1, 45 kV/40 mA |
| Primary Monochromator | Ge (111) |
| Anti-scatter slit/° | 1/2 |
| Soller slit (rad) | 0.04 |
| Divergence slit/° | 1/2 |
| Angular range, 2θ/° | 5–70 |
| Step width/° | 0.0167 |
| Measure time/h | 2 |
| Sample spinning speed (r.p.m) | 15 |
| Phases | Weighed/wt% | SiO2_ZnO_Glass | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Riet/wt%, Uncorrected | Riet/wt%, Microabsorption Corrected | ||
| SiO2 | 45.01 | 51.1 | 48.4 |
| ZnO | 44.67 | 48.9 | 51.6 |
| Glass | 10.32 | —— | —— |
| Phases | Weighed/wt% | SiO2_ZnO_Glass | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1Sta(SiO2)/wt% | 2Sta(ZnO)/wt% | ||
| SiO2 | 45.01 | Fixed | 41.90 |
| ZnO | 44.67 | 47.99 | Fixed |
| Glass | 10.32 | 7.00 | 13.43 |
| Cquartz | Density [g/cm3] | Refined Unit Cell Volume [cm3] | Total Mass Absorption Coefficient [cm2/g] | G Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 87.9 | 2.646 | 1.13 × 10−22 | 34.84 | 5.51 × 10−20 |
| Phases | Weighed/% | SiO2_ZnO_Glass |
|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | 45.01 | 44.16 |
| ZnO | 44.67 | 42.75 |
| Glass | 10.32 | 13.08 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, P.; Lu, L.; Liu, X.; De la Torre, A.G.; Cheng, X. Error Analysis and Correction for Quantitative Phase Analysis Based on Rietveld-Internal Standard Method: Whether the Minor Phases Can Be Ignored? Crystals 2018, 8, 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8030110
Zhao P, Lu L, Liu X, De la Torre AG, Cheng X. Error Analysis and Correction for Quantitative Phase Analysis Based on Rietveld-Internal Standard Method: Whether the Minor Phases Can Be Ignored? Crystals. 2018; 8(3):110. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8030110
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Piqi, Lingchao Lu, Xianping Liu, Angeles G. De la Torre, and Xin Cheng. 2018. "Error Analysis and Correction for Quantitative Phase Analysis Based on Rietveld-Internal Standard Method: Whether the Minor Phases Can Be Ignored?" Crystals 8, no. 3: 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8030110
APA StyleZhao, P., Lu, L., Liu, X., De la Torre, A. G., & Cheng, X. (2018). Error Analysis and Correction for Quantitative Phase Analysis Based on Rietveld-Internal Standard Method: Whether the Minor Phases Can Be Ignored? Crystals, 8(3), 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8030110