Magnetic Properties of Quasi-One-Dimensional Crystals Formed by Graphene Nanoclusters and Embedded Atoms of the Transition Metals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
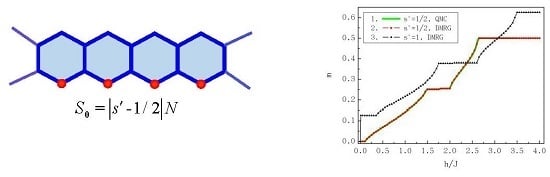
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Linear Spin Wave Approximation for Zigzag Nanoribbons
References
- Slota, M.; Keerthi, A.; Myers, W.K.; Tretyakov, E.; Baumgarten, M.; Ardavan, A.; Sadeghi, H.; Lambert, C.J.; Narita, A.; Müllen, K.; et al. Magnetic esge states and coherent manipulation of graphene nanoribbons. Nature 2018, 557, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salemi, L.; Lherbier, A.; Charlier, J.-C. Spin-dependent properties in zigzag graphene nanoribbons with phenul-edge defects. Phys. Rev. B 2018, 98, 214204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, R.; Kabanov, A.A.; Golov, A.A.; Proserpio, D.M. Homo Citans and Carbon Allotropes: For an Ethics of Citations. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 10962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Görne, A.L.; Dronskowski, R. Covalent bonding versus total energy: On the attainability of certain predicted low-energy carbon allotropes. Carbon 2019, 148, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samara Carbon Allotrope Database (SACADA). Available online: http://sacada.sctms.ru/ (accessed on 10 May 2019).
- Misurkin, I.A.; Ovchinnikov, A.A. The electronic structures and properties of polymeric molecules with conjugated bonds. Usp. Khim. 1977, 46, 1835–1870. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovchinnikov, A.A.; Shamovsky, I.L. The structure of the ferromagnetic phase of carbon. J. Mol. Struct. Theochem. 1991, 251, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchougréeff, A.L.; Hoffmann, R. Charge and Spin Density Waves in the Electronic Structure of Graphite. Application to Analysis of STM Images. J. Phys. Chem. 1992, 96, 8993–8998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, M.; Wakabayashi, K.; Nakada, K.; Kusakabe, K. Peculiar localized state at zigzag graphite edge. J. Phys. Soc. Jap. 1996, 65, 1920–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakabayashi, K.; Fujita, M.; Ajiki, H.; Sigrist, M. Electronic and magnetic properties of nanographite ribbons. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 59, 8271–8282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamashiro, A.; Shimoi, Y.; Harigaya, K.; Wakabayashi, K. Spin- and charge-polarized states in nanographene ribbons with zigzag edges. Phys. Rev. B 2003, 68, 193410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, Y.-W.; Cohen, M.L.; Louie, S.G. Energy gap in graphene nanoribbons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 2016803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieb, E.H. Two theorems on the Hubbard model. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1989, 62, 1201–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felder, H.; Meng, Z.Y.; Lang, T.C.; Assaad, F.F.; Wessel, S.; Honecker, A. Dynamical signatures of edge-state magnetism on graphene nanoribbons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 226401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hikihara, T.; Hu, X.; Lin, H.; Mou, C.-Y. Ground state properties of nanographite systems with zigzag edges. Phys. Rev. B 2003, 68, 035432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golor, M.; Lang, T.C.; Wessel, S. Quantum Monte Carlo studies of edge magnetism in chiral graphene nanoribbons. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 87, 155441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golor, M.; Wessel, S.; Schmidt, M.J. Quantum natire of edge magnetism in graphene. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 112, 046601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.; Lü, X.; Jiang, L.; Gao, W.; Zheng, Y. Structural, electronic and magnetic properties of transition-metal embedded zigzag-enged graphene nanoribbons. J. Phys. D 2013, 46, 375303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Li, J.; Li, S.-S. Antiferromagnetic-ferromagnetic transition in zigzag graphene nanoribbons indused by substitutional doping. Chin. Phys. 2018, 27, 117102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, M.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Sun, Q. Using carbon chains to mediate magnetic coupling in zigzag graphene nanoribbons. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 173106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Q.; Jena, P. Intinsic ferromagnetism in two-dimensional carbon structures: Triangular graphene nanoflakes linked by carbon chains. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.L.; Meng, S.; Kaxiras, E. Graphene nanoflakes with large spin. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulaevskii, L.N. Quasihomopolar electron levels in crystalls and molecules. Z. Eksp. Teor. Fiz. 1966, 51, 230–239. [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov, A.A. Multiplicity of the ground state of large alternant organic molecules with cojugated bonds (Do Organic Ferromagnetics Exist?). Theor. Chim. Acta 1978, 47, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, D.J.; Nelin, C.J.; Alexander, S.A. High-spin hydrocarbons. J. Chem. Phys. 1982, 77, 3101–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, D.J.; Alexander, S.A. Organic polyradicals, high-spin hydrocarbons, and organic ferromagnets. Stud. Phys. Theor. Chem. 1987, 51, 404–419. [Google Scholar]
- Cheranovskii, V.O. Spin permutation tecnique in the theory of strongly correlated electron systems. In Valence Bond Theory; Cooper, D.L., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 699–727. [Google Scholar]
- Tchougréeff, A.L. Several Stories from Theoretical Chemistry with some Russian Flavor and Implications for Theorems of Chemistry, Vagueness of Its Concepts, Fuzziness of Its Definitions, Iconicity of Its Language, and Peculiarities of Its Nomenclature. Int. J. Quant. Chem. 2016, 116, 137–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plekhanov, E.A.; Tchougréeff, A.L. Resonating Valence Bonds in Chemistry and Solid State. In Handbook of Inorganic Chemistry; Dronskowski, R., Kikkawa, S., Stein, A., Eds.; Wiley Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Chapther 4; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- White, S.R. Density matrix formulation for quantum renormalization groups. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1992, 69, 2863–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandvik, A.W. Stochastic series expansion method with operator-loop update. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 59, R14157–R14160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lieb, E.H.; Mattis, D.C. Ordering energy levels of interacting spin systems. J. Math. Phys. 1962, 3, 749–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, D.J. Ground state features for Heisenberg models. J. Chem. Phys. 1982, 77, 3098–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieb, E.; Shoultz, T.; Mattis, D. Two soluble models of an antiferromagnetic chain. Ann. Phys. 1961, 16, 407–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovchinnikov, A.A.; Cheranovskii, V.O. On the excitation spectrum of alternant magnetic chains with odd number of atoms in elementary cell. Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 1982, 266, 838–840. [Google Scholar]
- Affleck, I.; Lieb, E.H. A proof of part of Haldane’s conjecture on spin chains. Lett. Math.Phys. 1986, 12, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, T.; Kawakami, N. Spin chain with periodic array of impurities. Phys. Rev. B 1997, 55, R14709–R14712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheranovskii, V.O.; Özkan, I. The ground state spin ordering and lowest energy excitations of a model organic ferrimagnet-polyallyl spin chain. J. Mag. Mag. Mater. 2001, 223, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasu, K. Periodic Kondo-Hubbard model for a quasi-one-dimensional organic ferromagnet m-polydiphenilcarbene: Cooperation between electron correlation and topological structure. Phys. Rev. B 1986, 33, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodenough, J.B. Magnetism and the Chemical Bond; Interscience-Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Slavin, V.V.; Krivchikov, A.A. Magnetic properties of the quantum Shastry–Sutherland model with spin S = ½. Low Temp. Phys. 2014, 40, 985–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovchinnikov, A.A.; Cheranovskii, V.O. Perturbation theory in the spin Hamiltonian methods. Theor. Exp. Chem. 1980, 16, 119–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheranovskii, V.O.; Ezerskaya, E.V.; Klein, D.J.; Kravchenko, A.A. Magnetic properties of model non-carbon nanotubes with macroscopic value of ground spin. J. Mag. Mag. Mater. 2011, 323, 1636–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheranovskii, V.O.; Slavin, V.V.; Ezerskaya, E.V.; Tchougréeff, A.L.; Dronskowski, R. Magnetic Properties of Quasi-One-Dimensional Crystals Formed by Graphene Nanoclusters and Embedded Atoms of the Transition Metals. Crystals 2019, 9, 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9050251
Cheranovskii VO, Slavin VV, Ezerskaya EV, Tchougréeff AL, Dronskowski R. Magnetic Properties of Quasi-One-Dimensional Crystals Formed by Graphene Nanoclusters and Embedded Atoms of the Transition Metals. Crystals. 2019; 9(5):251. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9050251
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheranovskii, Vladislav O., Viktor V. Slavin, Elena V. Ezerskaya, Andrei L. Tchougréeff, and Richard Dronskowski. 2019. "Magnetic Properties of Quasi-One-Dimensional Crystals Formed by Graphene Nanoclusters and Embedded Atoms of the Transition Metals" Crystals 9, no. 5: 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9050251
APA StyleCheranovskii, V. O., Slavin, V. V., Ezerskaya, E. V., Tchougréeff, A. L., & Dronskowski, R. (2019). Magnetic Properties of Quasi-One-Dimensional Crystals Formed by Graphene Nanoclusters and Embedded Atoms of the Transition Metals. Crystals, 9(5), 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9050251