Temperature-Responsive Polymer Microgel-Gold Nanorods Composite Particles: Physicochemical Characterization and Cytocompatibility
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
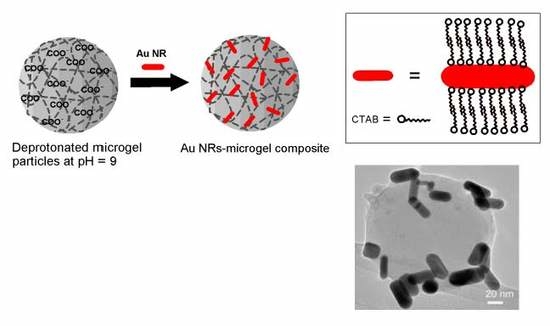
2.2. Experiment
2.3. Cell Viability Assay
2.4. Cell Hemolysis on Blood Agar
2.5. Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wei, M.; Gao, Y.; Li, X.; Serpe, M.J. Stimuli-responsive polymers and their applications. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 127–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Ravi, P.; Tam, K.C. pH-Responsive polymers: Synthesis, properties and applications. Soft Matter 2008, 4, 435–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong, L.E.; West, J.L. Thermally responsive polymer-nanoparticle composites for biomedical applications. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2011, 3, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.-C.; Hoffman, A.S. Synthesis and application of thermally reversible heterogels for drug delivery. J. Control. Release 1990, 13, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A. Preparation and characterization of N-isopropylacrylamide/acrylic acid copolymer core-shell microgel particles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 313, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, A.S. Stimuli-responsive polymers: Biomedical applications and challenges for clinical translation. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacEwan, S.R.; Chilkoti, A. Elastin-like polypeptides: Biomedical applications of tunable biopolymers. Pept. Sci. 2010, 94, 60–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, T.; Takenouchi, M.; Yamamoto, K.; Aoyagi, T. Coil-Globule Transition and/or Coacervation of Temperature and pH Dual-Responsive Carboxylated Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide). Polym. J. 2009, 41, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, E.; Wang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Li, G.; Ma, G. Covalent immobilization of trypsin onto thermo-sensitive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-acrylic acid) microspheres with high activity and stability. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sershen, S.R.; Westcott, S.L.; Halas, N.J.; West, J.L. Temperature-sensitive polymer–nanoshell composites for photothermally modulated drug delivery. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2000, 51, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Mei, Y.; Drechsler, M.; Ballauff, M. Thermosensitive Core-Shell Particles as Carriers for Ag Nanoparticles: Modulating the Catalytic Activity by a Phase Transition in Networks. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 813–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huff, T.B.; Tong, L.; Zhao, Y.; Hansen, M.N.; Cheng, J.-X.; Wei, A. Hyperthermic effects of gold nanorods on tumor cells. Nanomedicine (London) 2007, 2, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, T.; Dai, Z.; Mei, F.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, J.; Wu, W.; Xiao, X.; Jiang, C. Synthesis and optical properties of gold nanorods with controllable morphology. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2016, 28, 434002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nehl, C.L.; Liao, H.; Hafner, J.H. Optical Properties of Star-Shaped Gold Nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 683–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, T.; Shen, X.; Li, L.; Guan, Z.; Gao, N.; Yuan, P.; Yao, S.Q.; Xu, Q.-H.; Xu, G.Q. Gold nanorods as dual photo-sensitizing and imaging agents for two-photon photodynamic therapy. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 7712–7719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; He, Q.; Li, J. Smart core/shell nanocomposites: Intelligent polymers modified gold nanoparticles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 149, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-M.; Nguyen, S.T. Smart Nanoscale Drug Delivery Platforms from Stimuli-Responsive Polymers and Liposomes. Macroolecules 2013, 46, 9169–9180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contreras-Cáceres, R.; Sánchez-Iglesias, A.; Karg, M.; Pastoriza-Santos, I.; Pérez-Juste, J.; Pacifico, J.; Hellweg, T.; Fernández-Barbero, A.; Liz-Marzán, L.M. Encapsulation and Growth of Gold Nanoparticles in Thermoresponsive Microgels. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 1666–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budhlall, B.M.; Marquez, M.; Velev, O.D. Microwave, Photo- and Thermally Responsive PNIPAm-Gold Nanoparticle Microgels. Langmuir 2008, 24, 11959–11966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyer, C.; Whittaker, M.R.; Luzon, M.; Davis, T.P. Design and Synthesis of Dual Thermoresponsive and Antifouling Hybrid Polymer/Gold Nanoparticles. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 6917–6926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M.; Sanson, N.; Fava, D.; Kumacheva, E. Microgels Loaded with Gold Nanorods: Photothermally Triggered Volume Transitions under Physiological Conditions. Langmuir 2007, 23, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, M.; Lin, I.-C.; Whittaker, M.R.; Minchin, R.F.; Monteiro, M.J.; Toth, I. Cellular Uptake of Densely Packed Polymer Coatings on Gold Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, J.; Won, N.; Bang, J.; Jin, H.; Park, J.; Jung, S.; Jung, S.; Park, Y.; Kim, S. Surface engineering of inorganic nanoparticles for imaging and therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 622–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.; Kuang, H.; Xu, L.; Ding, L.; Xu, C.; Wang, L.; Kotov, N.A. Attomolar DNA detection with chiral nanorod assemblies. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Im, K.; Hwang, S.S.; Hur, J.; Nam, J.; Ahn, G.-O.; Hwang, S.S.; Kim, S.; Park, N. DNA hydrogel delivery vehicle for light-triggered and synergistic cancer therapy. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 9433–9437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordel, M.; Piela, K.; Kołkowski, R.; Koźlecki, T.; Buckle, M.; Samoć, M. End-to-end self-assembly of gold nanorods in isopropanol solution: Experimental and theoretical studies. J. Nanopart. Res. 2015, 17, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heitsch, A.T.; Smith, D.K.; Patel, R.N.; Ress, D.; Korgel, B.A. Multifunctional particles: Magnetic nanocrystals and gold nanorods coated with fluorescent dye-doped silica shells. J. Solid State Chem. 2008, 181, 1590–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Lopez, C.; Polavarapu, L.; Solis, D.M.; Taboada, J.M.; Obelleiro, F.; Contreras-Caceres, R.; Pastoriza-Santos, I.; Perez-Juste, J. Gold Nanorod-pNIPAM Hybrids with Reversible Plasmon Coupling: Synthesis, Modeling, and SERS Properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 12530–12538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkilany, A.M.; Nagaria, P.K.; Hexel, C.R.; Shaw, T.J.; Murphy, C.J.; Wyatt, M.D. Cellular Uptake and Cytotoxicity of Gold Nanorods: Molecular Origin of Cytotoxicity and Surface Effects. Small 2009, 5, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, J.; Wang, J.-H.; Liu, T.; Xie, Z.; Yu, X.-F.; Li, W. Surface chemistry but not aspect ratio mediates the biological toxicity of gold nanorods in vitro and in vivo. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, R.; Yang, J.; Choi, J.; Lim, E.-K.; Kim, E.; Suh, J.-S.; Huh, Y.-M.; Haam, S. Thiolated Dextran-Coated Gold Nanorods for Photothermal Ablation of Inflammatory Macrophages. Langmuir 2010, 26, 17520–17527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozlovskaya, V.; Kharlampieva, E.; Khanal, B.P.; Manna, P.; Zubarev, E.R.; Tsukruk, V.V. Ultrathin layer-by-layer hydrogels with incorporated gold nanorods as pH-sensitive optical materials. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 7474–7485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, R.; Zhou, Z.; Su, G.; Liu, L.; Guan, M.; Du, B.; Zhang, Q. Chitosan-coated Gold Nanorods for Cancer Therapy Combining Chemical and Photothermal Effects. Macromol. Biosci. 2014, 14, 1160–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawano, T.; Niidome, Y.; Mori, T.; Katayama, Y.; Niidome, T. PNIPAM Gel-Coated Gold Nanorods for Targeted Delivery Responding to a Near-Infrared Laser. Bioconjug. Chem. 2009, 20, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Alhoshan, M. Preparation and characterization of pH-responsive and thermoresponsive hybrid microgel particles with gold nanorods. J. Polym. Sci. A 2013, 51, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.J.; Gole, A.M.; Stone, J.W.; Sisco, P.N.; Alkilany, A.M.; Goldsmith, E.C.; Baxter, S.C. Gold Nanoparticles in Biology: Beyond Toxicity to Cellular Imaging. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 1721–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkilany, A.M.; Murphy, C.J. Toxicity and cellular uptake of gold nanoparticles: What we have learned so far? J. Nanopart. Res. 2010, 12, 2313–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkilany, A.M.; Shatanawi, A.; Kurtz, T.; Caldwell, R.B.; Caldwell, R.W. Toxicity and cellular uptake of gold nanorods in vascular endothelium and smooth muscles of isolated rat blood vessel: Importance of surface modification. Small 2012, 8, 1270–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabinski, C.; Schaeublin, N.; Wijaya, A.; D’Couto, H.; Baxamusa, S.H.; Hamad-Schifferli, K.; Hussain, S.M. Effect of Gold Nanorod Surface Chemistry on Cellular Response. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 2870–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebastian, V.; Lee, S.-K.; Zhou, C.; Kraus, M.F.; Fujimoto, J.G.; Jensen, K.F. One-step continuous synthesis of biocompatible gold nanorods for optical coherence tomography. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 6654–6656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; El-Toni, A.M.; Alrokayan, S.; Alsalhi, M.; Alhoshan, M.; Aldwayyan, A.S. Microwave-assisted synthesis of silver nanoparticles using poly-N-isopropylacrylamide/acrylic acid microgel particles. Colloids Surf. A 2011, 377, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikoobakht, B.; El-Sayed, M.A. Preparation and Growth Mechanism of Gold Nanorods (NRs) Using Seed-Mediated Growth Method. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 1957–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamed, M.; Akhtar, M.J.; Siddiqui, M.A.; Ahmad, J.; Musarrat, J.; Al-Khedhairy, A.A.; AlSalhi, M.S.; Alrokayan, S.A. Oxidative stress mediated apoptosis induced by nickel ferrite nanoparticles in cultured A549 cells. Toxicology 2011, 283, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coronado, R.; Pekerar, S.; Lorenzo, A.T.; Sabino, M.A. Characterization of thermo-sensitive hydrogels based on poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)/hyaluronic acid. Polym. Bull. 2011, 67, 101–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanks, C.T.; Wataha, J.C.; Sun, Z. In vitro models of biocompatibility: A review. Dent. Mater. 1996, 12, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Neretina, S.; El-Sayed, M.A. Gold Nanorods: From Synthesis and Properties to Biological and Biomedical Applications. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 4880–4910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiotani, A.; Akiyama, Y.; Kawano, T.; Niidome, Y.; Mori, T.; Katayama, Y.; Niidome, T. Active Accumulation of Gold Nanorods in Tumor in Response to Near-Infrared Laser Irradiation. Bioconjug. Chem. 2010, 21, 2049–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikoobakht, B.; El-Sayed, M.A. Evidence for Bilayer Assembly of Cationic Surfactants on the Surface of Gold Nanorods. Langmuir 2001, 17, 6368–6374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wróblewski, F.; Ladue, J.S. Lactic Dehydrogenase Activity in Blood. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1955, 90, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Jiang, X.; Ji, Y.; Bai, R.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, X.; Chen, C. Surface chemistry of gold nanorods: Origin of cell membrane damage and cytotoxicity. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 8384–8391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Jiang, X.; Ji, Y.; Wu, X.; Xu, L.; Qiu, Y.; Zhao, K.; Wei, T.; et al. Selective Targeting of Gold Nanorods at the Mitochondria of Cancer Cells: Implications for Cancer Therapy. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indrasekara, A.S.D.S.; Wadams, R.C.; Fabris, L. Ligand Exchange on Gold Nanorods: Going Back to the Future. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2014, 31, 819–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonov, A.P.; Zheng, J.; Clogston, J.D.; Stern, S.T.; Patri, A.K.; Wei, A. Detoxification of Gold Nanorods By Treatment With Polystyrenesulfonate. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 2481–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.R.K.; Rahman, M.A.; Wu, Y.; Han, T.; Peng, X.; Mackey, M.A.; Wang, D.; Shin, H.J.; Chen, Z.G.; Xiao, H.; et al. Efficacy, long-term toxicity, and mechanistic studies of gold nanorods photothermal therapy of cancer in xenograft mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E3110–E3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, D.; Li, Y.; Ahlemeyer, B.; Krieglstein, J.; Kissel, T. In vitro cytotoxicity testing of polycations: Influence of polymer structure on cell viability and hemolysis. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigderman, L.; Manna, P.; Zubarev, E.R. Quantitative Replacement of Cetyl Trimethylammonium Bromide by Cationic Thiol Ligands on the Surface of Gold Nanorods and Their Extremely Large Uptake by Cancer Cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 636–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, A.; Khan, T.H.; Ahamed, M.; El-Toni, A.M.; Aldalbahi, A.; Alam, J.; Ahamad, T. Temperature-Responsive Polymer Microgel-Gold Nanorods Composite Particles: Physicochemical Characterization and Cytocompatibility. Polymers 2018, 10, 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10010099
Khan A, Khan TH, Ahamed M, El-Toni AM, Aldalbahi A, Alam J, Ahamad T. Temperature-Responsive Polymer Microgel-Gold Nanorods Composite Particles: Physicochemical Characterization and Cytocompatibility. Polymers. 2018; 10(1):99. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10010099
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Aslam, Tajdar Husain Khan, Maqusood Ahamed, Ahmed Mohamed El-Toni, Ali Aldalbahi, Javed Alam, and Tansir Ahamad. 2018. "Temperature-Responsive Polymer Microgel-Gold Nanorods Composite Particles: Physicochemical Characterization and Cytocompatibility" Polymers 10, no. 1: 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10010099
APA StyleKhan, A., Khan, T. H., Ahamed, M., El-Toni, A. M., Aldalbahi, A., Alam, J., & Ahamad, T. (2018). Temperature-Responsive Polymer Microgel-Gold Nanorods Composite Particles: Physicochemical Characterization and Cytocompatibility. Polymers, 10(1), 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10010099