Natural Silkworm Cocoon Composites with High Strength and Stiffness Constructed in Confined Cocooning Space
Abstract
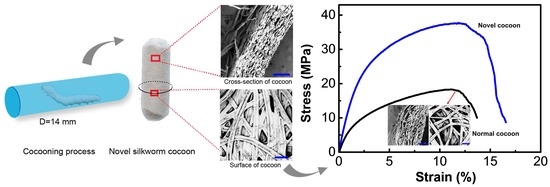
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fabrication of Normal and Modified Cocoons
2.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Observation
2.3. Sericin Concentration
2.4. Porosity of Cocoon Shell Specimens
2.5. Tensile Tests of Cocoons
2.6. Peel Tests of Cocoons
2.7. Theoretical Characterization Models for Porosity
2.8. Statistical Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphology and Microstructure
3.2. Sericin Content
3.3. Porosity of Cocoon Shells
3.4. Mechanical Properties of Cocoon Specimens
3.5. Interlaminar Peel Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, H.P.; Feng, X.Q.; Yu, S.W.; Cui, W.Z.; Zou, F.Z. Mechanical properties of silkworm cocoons. Polymer 2005, 46, 9192–9201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.P.; Feng, X.Q.; Cui, W.Z.; Zou, F.Z. Mechanical properties of silkworm cocoon pelades. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2007, 74, 1953–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Porter, D.; Vollrath, F. Silk cocoon (Bombyx mori): Multi-layer structure and mechanical properties. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 2620–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Porter, D.; Vollrath, F. Morphology and structure of silkworm cocoons. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2012, 32, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Porter, D.; Vollrath, F. Structure and physical properties of silkworm cocoons. J. R. Soc. Interface 2012, 9, 2299–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, F.; Hesselberg, T.; Porter, D.; Vollrath, F. The impact behaviour of silk cocoons. J. Exp. Biol. 2013, 216, 2648–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moriwaki, H.; Kitajima, S.; Kurashima, M.; Hagiwara, A.; Haraguchi, K.; Shirai, K.; Kanekatsu, R.; Kiguchi, K. Utilization of silkworm cocoon waste as a sorbent for the removal of oil from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 165, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tulachan, B.; Meena, S.K.; Rai, R.K.; Mallick, C.; Kusurkar, T.S.; Teotia, A.K.; Sethy, N.K.; Bhargava, K.; Bhattacharya, S.; Kumar, A.; et al. Electricity from the silk cocoon membrane. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, M.; Meena, S.K.; Kusurkar, T.S.; Singh, S.K.; Sethy, N.K.; Bhargava, K.; Sarkar, S.; Das, M. Carbondioxide gating in silk cocoon. Biointerphases 2012, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, J.; Rajkhowa, R.; Tsuzuki, T.; Millington, K.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X. Photoprotection by silk cocoons. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 3660–3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusurkar, T.S.; Gangwar, A.; Bawankar, M.; Mandal, A.; Dethe, D.; Thakur, A.K.; Singh, S.K.; Bhargava, K.; Khurana, S.; Sethy, N.K.; et al. A glowing antioxidant from Tasar silk cocoon. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 104563–104573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulachan, B.; Srivastava, S.; Kusurkar, T.S.; Sethy, N.K.; Bhargava, K.; Singh, S.K.; Philip, D.; Bajpai, A.; Das, M. The role of photo-electric properties of silk cocoon membrane in pupal metamorphosis: A natural solar cell. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Horrocks, N.P.; Vollrath, F.; Dicko, C. The silkmoth cocoon as humidity trap and waterproof barrier. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2013, 164, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Rajkhowa, R.; Li, J.; Liu, X.Y.; Wang, X.G. Silkworm cocoon as natural material and structure for thermal insulation. Mater. Des. 2013, 49, 842–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusurkar, T.S.; Tandon, I.; Sethy, N.K.; Bhargava, K.; Sarkar, S.; Singh, S.K.; Das, M. Fluorescent silk cocoon creating fluorescent diatom using a “Water glass-fluorophore ferry”. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blossman-Myer, B.; Burggren, W.W. The silk cocoon of the silkworm, Bombyx mori: Macro structure and its influence on transmural diffusion of oxygen and water vapor. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2010, 155, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, W.; Gao, X.; Meng, W.; Guan, J. Strain rate and anisotropic microstructure dependent mechanical behaviors of silkworm cocoon shells. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, J.; Zhu, W.; Liu, B.; Yang, K.; Vollrath, F.; Xu, J. Comparing the microstructure and mechanical properties of Bombyx mori and Antheraea pernyi cocoon composites. Acta Biomater. 2017, 47, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, D.U.; Vollrath, F. 6—Silk for sustainable composites. Nat. Fiber-Reinf. Biodegrad. Bioresorbable Polym. Compos. 2017, 91–109. [Google Scholar]
- Van Der Kloot, W.G.; Williams, C.M. Cocoon construction by the Cecropia silkworm, I. the role of the external environment. Behaviour 1953, 5, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Kloot, W.G.; Williams, C.M. Cocoon construction by the Cecropia silkworm II. the role of the internal environment. Behaviour 1953, 5, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Kloot, W.G.; Williams, C.M. Cocoon construction by the Cecropia silkworm III. the alteration of spinning behavior by chemical and surgical techniques. Behaviour 1954, 6, 233–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, M.; Morikawa, H.; Kato, H.; Iwasa, M. Analysis of the construction process of cocoon shape by Bombyx Mori. J. Seric. Sci. Jpn. 1997, 66, 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Kiyosawa, M.; Ito, E.; Shirai, K.; Kanekatsu, R.; Miura, M.; Kiguchi, K. Cocoon spinning behavior in the silkworm, Bombyx mori: Comparison of three strains constructing different cocoons in shape. Zool. Sci. 1999, 16, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lounibos, L. The cocoon spinning behaviour of the Chinese oak silkworm, Antheraea Pernyi. Anim. Behav. 1975, 23, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, M.; Hoshi, H.; Nishioka, T. Analysis of the spinning behaviour of silkworms. J. Seric. Sci. Jpn. 1990, 59, 118–126. [Google Scholar]
- Miura, M.; Morikawa, H.; Sugiura, A. Statistical analysis of body movement and shape of Bombyx mori in spinning behaviour. J. Seric. Sci. Jpn. 1995, 64, 237–245. [Google Scholar]
- Miura, M.; Morikawa, H.; Shimizu, T.; Mochizuki, S.; Kojima, T.; Iwasa, M.; Nakazawa, M. Analysis of the fixed direction of a silkworm body during cocoon construction. J. Seric. Sci. Jpn. 2000, 69, 207–214. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.M.R.; Miura, M.; Banno, Y.; Morikawa, H.; Chen, Y. 3D analysis of the spinning behavior of flossy cocoon mutants in the silkworm, Bombyx Mori. J. Insect Biotechnol. Seric. 2009, 78, 3139–3147. [Google Scholar]
- Miura, M.; Kuwako, N.; Nakamura, T.; Khan, M.M.R. Cocoon repair behavior of Bombyx mori silkworm. J. Insect Biotechnol. Seric. 2011, 79, 3085–3093. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Porter, D.; Vollrath, F. Silkworm cocoons inspire models for random fiber and particulate composites. Phys. Rev. E 2010, 82, 041911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Porter, D.; Vollrath, F. A nonwoven composite model based on silkworm cocoon (Bombyx mori). J. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2010, 4, 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Kaur, J.; Rajkhowa, R.; Li, J.L.; Liu, X.Y.; Wang, X.G. Mechanical properties and structure of silkworm cocoons: A comparative study of Bombyx mori, Antheraea assamensis, Antheraea pernyi and Antheraea mylitta silkworm cocoons. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 3206–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Rigueiro, J.; Viney, C.; Llorca, J.; Elices, M. Silkworm silk as an engineering material. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1998, 70, 2439–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Rigueiro, J.; Viney, C.; Llorca, J.; Elices, M. Mechanical properties of single-brin silkworm silk. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2000, 75, 1270–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Vollrath, F. Surprising strength of silkworm silk. Nature 2002, 418, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berardo, A.; Pantano, M.F.; Pugno, N.M. Slip knots and unfastening topologies enhance toughness without reducing strength of silk fibroin fibres. Interface Focus 2016, 6, 20150060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantano, M.F.; Berardo, A.; Pugno, N.M. Tightening slip knots in raw and degummed silk to increase toughness without losing strength. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 18222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, M.; Jian, M.; Zhang, Y. Feeding Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes or Graphene to Silkworms for Reinforced Silk Fibers. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 6695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Huang, H.; Chen, S.; Wang, W.; Dai, F.; Zhao, H. Characterization of silkworm larvae growth and properties of silk fibres after direct feeding of copper or silver nanoparticles. Mater. Des. 2017, 129, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Shao, H.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Y. Reinforced and ultraviolet resistant silks from silkworms fed with titanium dioxide nanoparticles. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2551–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Chen, L.; Du, L.; Shen, T.; Li, F.; Huang, L.; Li, Z.; Wu, D. Structure and properties of silkworm cocoon (Bombyx mori) treated by hot pressing. Mater. Des. 2017, 134, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kováčik, J. Correlation between shear modulus and porosity in porous materials. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 2001, 20, 1953–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phani, K.K.; Niyogi, S. Young’s modulus of porous brittle solids. J. Mater. Sci. 1987, 22, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papayianni, I.; Stefanidou, M. Strength–porosity relationships in lime–pozzolan mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2006, 20, 700–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, B.; Thygesen, A.; Lilholt, H. Plant fibre composites–porosity and stiffness. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 1057–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kováčik, J. Correlation between Young’s modulus and porosity in porous materials. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1999, 18, 1007–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, B.; Lilholt, H. Physical and mechanical properties of unidirectional plant fibre composites—An evaluation of the influence of porosity. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 1265–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, L.; Tong, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, Z.; Huang, H.; Zhao, H.; Dai, F. Natural Silkworm Cocoon Composites with High Strength and Stiffness Constructed in Confined Cocooning Space. Polymers 2018, 10, 1214. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10111214
Cheng L, Tong X, Li Z, Liu Z, Huang H, Zhao H, Dai F. Natural Silkworm Cocoon Composites with High Strength and Stiffness Constructed in Confined Cocooning Space. Polymers. 2018; 10(11):1214. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10111214
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Lan, Xiaoling Tong, Zhi Li, Zulan Liu, Huiming Huang, Hongping Zhao, and Fangyin Dai. 2018. "Natural Silkworm Cocoon Composites with High Strength and Stiffness Constructed in Confined Cocooning Space" Polymers 10, no. 11: 1214. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10111214
APA StyleCheng, L., Tong, X., Li, Z., Liu, Z., Huang, H., Zhao, H., & Dai, F. (2018). Natural Silkworm Cocoon Composites with High Strength and Stiffness Constructed in Confined Cocooning Space. Polymers, 10(11), 1214. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10111214