Facile Fabrication and Characterization of Improved Proton Conducting Sulfonated Poly(Arylene Biphenylether Sulfone) Blocks Containing Fluorinated Hydrophobic Units for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Polymers
2.2.1. Synthesis of Sulfonated Poly(Arylene Biphenylehter Sulfone), Poly(Arylene Ether), and Poly(Arylene Biphenylether Sulfone)
2.2.2. Synthesis of Block Copolymers (PABES-PAE and SPABES-PAE)
2.3. Membrane Preparation
2.4. Chraterizations
2.5. Preparation of Membrane Electrode Assembly
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Structural Properties of SPABES-PAE Block Copolymers
3.2. Thermal Stabilities
3.3. Water Uptake, IEC, and Hydration Number Subsection
3.4. Dimensional Change and Mechanical Strength
3.5. Proton Conductivity and Activation Energy
3.6. Oxidative Stability and Single Cell Performance
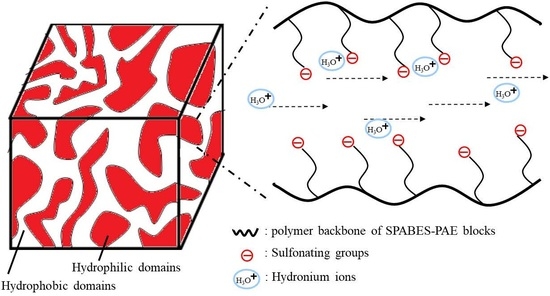
3.7. Morphology
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ren, X.; Gobrogge, E.A.; Beyer, F. States of water in thermally annealed recast Nafion® films and impact on fuel cell performance. ECS Trans. 2017, 80, 605–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makinouchi, T.; Tanaka, M.; Kawakami, H. Improvement in characteristics of a Nafion membrane by proton conductive nanofibers for fuel cell applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 530, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerres, J.A. Development of ionomer membranes for fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2001, 185, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, V.; Padmanaban, S.; Venkitusamy, K.; Selvamuthukumaran, R.; Blaabjerg, F.; Siano, P. Recent advances and challenges of fuel cell based power system architectures and control – A review. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2001, 185, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, K.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, T.H.; Yu, D.M.; Seo, D.W. Synthesis and properties of densely sulfonated polyketones (sPKs) with rigid backbone structure for PEM fuel cell application. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 2310–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Ni, J.; Xiang, X.; Wang, L.; Chem, Y. Synthesis and properties of reprocessable sulfonated polyimides cross-linked via acid stimulation for use as proton exchange membranes. J. Power Sources 2017, 337, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Long, S.; Zhang, G.; Yang, J. Poly(arylene sulfide sulfone) hybrid ultrafiltration membrane with TiO2-g-PAA nanoparticles: Preparation and antifouling performance. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2015, 55, 2829–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.S.; Kim, T.H.; Yoon, Y.J.; Kang, C.G.; Yu, D.M.; Lee, J.Y.; Hong, Y.T. Sulfonated poly(arylene sulfone) multiblock copolymers for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 459, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celso, F.; Mikhailenko, S.D.; Rodrigues, M.A.S.; Mauler, R.S.; Kaliaguine, S. Facile synthesis of polypyrrole functionalized nickel foam with catalytic activity comparable to Pt for the poly-generation of hydrogen and electricity. J. Power Sources 2016, 301, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mong, A.L.; Kim, D.J. Porous proton exchange membranes based on sulfonated poly (arylene ether ketone)/polylactide block copolymers for enhanced proton conductivity and dimensional stability. Solid State Ion. 2016, 290, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, X.; Zhuang, X.; Cheng, B.; Wang, W.; Kang, W.; Shi, L.; Li, H. Modification of Nafion membrane with biofunctional SiO2 nanofiber for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2017, 340, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.R.; Vinothkannan, M.; Yoo, D.J. Sulfonated-fluorinated copolymer blending membranes containing SPEEK for use as the electrolyte in polymer electrolyte fuel cells (PEFC). Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 4349–4365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Guo, R.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, M.B.; McGrath, J.E. Partly fluorinated poly(arylene ether ketone sulfone) hydrophilic–hydrophobic multiblock copolymers for fuel cell membranes. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 37, 6132–6139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamuku, S.; Weiber, E.A.; Jannash, P. Segmented tetrasulfonated copoly(arylene ether sulfone)s: Improving proton transport properties by extending the ionic sequence. ChemSusChem 2013, 6, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, A.R.; Vinothkannan, M.; Yoo, D.J. Sulfonated poly ether sulfone/heteropoly acid composite membranes as electrolytes for the improved power generation of proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Compos. Pt. B-Eng. 2018, 155, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.G.; Kim, A.R.; Nahm, K.S.; Yoo, D.J. High ion and lower molecular transportation of the poly vinylidene fluoride–hexa fluoro propylene hybrid membranes for the high temperature and lower humidity direct methanol fuel cell applications. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 5922–5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, P.; Shi, Q.; Li, S.; Gong, F.; Chen, X.; An, Z. Block poly(arylene ether sulfone) copolymers bearing quaterinized aromatic pendants: Synthesis, property and stability. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 26320–26332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.R.; Vinothkannan, M.; Yoo, D.J. Artificially designed, low humidifying organic–inorganic (SFBC-50/FSiO2) composite membrane for electrolyte applications of fuel cells. Compos. Pt. B-Eng. 2017, 130, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikami, T.; Miyataka, K.; Watanabe, M. Poly(arylene ether)s containing superacid groups as proton exchange membranes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 1714–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboki, J.; Jing, B.; Luo, S.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Guo, R. Highly proton conducting polyelectrolyte membranes with unusual water swelling behavior based on triptycene-containing poly(arylene ether sulfone) multiblock copolymers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 1173–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Chu, J.Y.; Kim, A.R.; Yoo, D.J. Enhanced performance of a sulfonated poly(arylene ether ketone) block copolymer bearing pendant sulfonic acid groups for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells operating at 80% relative humidity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 20835–20844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, T.W.; Sutradhar, S.C.; Ahmed, F.; Choi, K.; Yang, H.; Yoon, S.J.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, W.G. Synthesis and characterization of sulfonated mutiphenyl conjugated polyimide for PEMFC. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 49, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, C.; Wei, Y.; Hu, Q.; Liu, B.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Hu, W. Nanocystalline cellulose reinforced sulfonated fluorenyl-containing polyaryletherketones for proton exchange membranes. Solid State Ion. 2016, 297, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.Y.; Han, S.H. Sulfonated polySEPS/hydrophilic-SiO2 composite membranes for polymer electrolyte membranes (PEMs). J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 23, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Lee, S.Y.; Liu, Y.L.; Lee, Y.M.; Guiver, M.D. A new class of highly-conducting polymer electrolyte membranes: Aromatic ABA triblock copolymers. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 5346–5355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, A.R.; Vinothkannan, M.; Yoo, D.J. Sulfonated fluorinated multi-block copolymer hybrid containing sulfonated (poly ether ether ketone) and graphene oxide: A ternary hybrid membrane architecture for electrolyte applications in proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Energy Chem. 2018, 4, 1247–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, D.J.; Hyun, S.H.; Kim, A.R.; Kumar, G.G.; Nahm, K.S. Novel sulfonated poly(arylene biphenylsulfone ether) copolymers containing bisphenylsulfonyl biphenyl moiety: structural, thermal, electrochemical and morphological characteristics. Polym. Int. 2011, 60, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Hong, L.; Li, Y.; Zhao, L.; Wei, Y.; Zhao, C.; Na, H. Considerations of the effects of naphthalene moieties on the design of proton-conductive poly(arylene ether ketone) membranes for direct methanol fuel cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 24079–24088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, J.E.; Kim, B.H.; Noh, J.H.; Jung, J.W.; Kim, J.Y.; Jang, J.H.; Yoo, S.J.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, S.Y. Effect of the spirobiindane group in sulfonated poly(arylene ether sulfone) copolymer as electrode binder for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 47, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Jackson, A.B.; Kirk, N.J.; Mauritz, K.A.; Storey, R.F. Poly(arylene ether sulfone) statistical copolymers bearing perfluoroalkylsulfonic acid moieties. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhara, M.G.; Banerjee, S. Fluorinated high-performance polymers: Poly(arylene ether)s and aromatic polyimides containing trifluoromethyl groups. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 1022–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Zhang, Ke.; Liao, H.; Xiao, G.; Yao, Y.; Sun, G.; Yan, D. Trisulfonation approach: To improve the properties of poly(arylene thioether phosphine oxide)s based proton exchange membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 508, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, A.K.; Banerjee, S.; Komber, H.; Voit, B. Imidoaryl biphenol based new fluorinated sulfonated poly(arylene ether sulfone) copolymers and their proton exchange membrane properties. Solid State Ion. 2014, 254, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Li, G.; Yang, S.; Xiong, M.; Jin, J. Sulfonated poly(arylene ether sulfone) polymers containing 3,4-difluoro-phenyl moiety as proton exchange membranes. Solid State Ion. 2017, 300, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.D.T.; Yang, S.W.; Kim, D.J. Pendant dual sulfonated poly(arylene ether ketone) proton exchange membranes for fuel cell application. J. Power Sources 2016, 328, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Chen, J.C.; Wu, J.A.; Chen, K.H. Synthesis and properties of poly(ether sulfone)s with clustered sulfonic groups for PEMFC applications under various relative humidity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 9805–9814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Hickner, M.; Kim, Y.S.; Zawodzinski, T.A.; McGrath, J.E. Direct polymerization of sulfonated poly(arylene ether sulfone) random (statistical) copolymers: candidates for new proton exchange membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 197, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, M.; Kreuer, K.D.; Andersen, H.T.; Maier, J. Sulfonated poly(phenylene sulfone) polymers as hydrolytically and thermooxidatively stable proton conducting ionomers. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Tao, D.; Ni, J.; Xiang, X.; Gao, C.; Wang, L. Synthesis and properties of highly branched star-shaped sulfonated block polymers with sulfoalkyl pendant groups for use as proton exchange membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 497, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinothkannan, M.; Kim, A.R.; Kumar, G.G.; Yoon, J.M.; Yoo, D.J. Toward improved mechanical strength, oxidative stability and proton conductivity of an aligned quadratic hybrid (SPEEK/FPAPB/Fe3O4-FGO) membrane for application in high temperature and low humidity fuel cells. RSC Adv. 2017, 62, 39034–39048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.M.; Chen, S.Y.; Chen, D.Y.; Ye, Z.L. Sulfonated binaphthyl-containing poly(arylene ether ketone)s with rigid backbone and excellent film-forming capability for proton exchange membranes. Polymers 2018, 10, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilir, C.; Erdogan, T.; Odabas, S.; Unveren, E.E. Novel partially fluorinated graft block copolymer ionomer as potential proton exchange membrane material. Polymer 2016, 95, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Q.; Shen, Z.; Li, N. Novel anion exchange membranes based on quaternized diblock copolystyrene containing a fluorinated hydrophobic block. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 554, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinothkannan, M.; Kim, A.R.; Nahm, K.S.; Yoo, D.J. Ternary hybrid (SPEEK/SPVdF-HFP/GO) based membrane electrolyte for the applications of fuel cells: profile of improved mechanical strength, thermal stability and proton conductivity. RSC Adv. 2016, 110, 108851–108863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, K.A.; Kim, W.K.; Oh, K.H.; Choo, M.J.; Nam, K.W.; Park, J.K. Proton exchange membranes based on hydrophilic–hydrophobic multiblock copolymers using different hydrophobic oligomer. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2011, 36, 3956–3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.H.; Kwon, B.S.; Choi, S.W.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, D.H. Properties and morphology study of proton exchange membranes fabricated from the pendant sulfonated poly(arylene ether ketone) copolymers composed of hydrophobic and hydrophilic multi-blocks for fuel cell. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2015, 40, 16443–16456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Oshima, T.; Koizumi, S.; Rikukawa, M.; Szekely, N.; Radulescu, A.; Richter, D. Elucidation of the morphology of the hydrocarbon multi-block copolymer electrolyte membranes for proton exchange fuel cells. Polymer 2016, 86, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chauveau, E.; Marestin, C.; Mercier, R.; Espuche, E.; Morin, A. Ionic conducting membranes based on new sulfonated poly(arylene ether ketone)s for fuel cell applications. J. Polym. Sci. Pt. B-Polym. Phys. 2017, 55, 771–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Zhang, X.C.; Ma, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liu, X.B. Constructing continuous proton-conducting highways within sulfonated poly(arylene ether nitrile) composite membrane by incorporating amino-sulfo-bifunctionalized GO. Polymers 2018, 10, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Copolymer | Mn (kDa) | Mw (kDa) | Mz (kDa) | Mw/Mn (PDI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPABES-PAE (1:2) | 24.0 | 122.7 | 418.0 | 6.9 |
| SPABES-PAE (1:1) | 13.9 | 96.5 | 411.1 | 6.7 |
| SPABES-PAE (2:1) | 16.7 | 112.3 | 453.1 | 5.1 |
| Copolymer | TS (MPa) | YM (GPa) | EB (%) | Tg (℃) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPABES-PAE (1:2) | 40.3 | 0.48 | 17.9 | 177 |
| SPABES-PAE (1:1) | 36.8 | 0.36 | 18.1 | 184 |
| SPABES-PAE (2:1) | 28.9 | 0.33 | 19.1 | 188 |
| PABES-PAE (1:1) | 48.4 | 0.48 | 4.8 | 194 |
| Membrane | IEC (mequiv.·g−1) | Water Uptake (%) | Dimensional Stability (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 °C | 90 °C | 30 °C | 90 °C | ||
| SPABES-PAE (1:2) | 0.55 | 14 | 21 | 3.0 | 26.9 |
| SPABES-PAE (1:1) | 0.87 | 24 | 36 | 4.5 | 39.3 |
| SPABES-PAE (2:1) | 1.23 | 34 | 52 | 10.1 | 42.4 |
| Nafion 212 | 0.91 | 18 | 42 | 3.0 | 52.1 |
| Membrane | IEC (mequiv.·g−1) | Water uptake (%) at 90 °C | Proton conductivity (mS·cm−1) | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPABES-PAE (1:2) | 0.55 | 21.1 | 48.6 (90 °C) | this work |
| SPABES-PAE (1:1) | 0.87 | 36 | 81.9 (90 °C) | this work |
| SPABES-PAE (2:1) | 1.23 | 52.2 | 131.9 (90 °C) | this work |
| tsPTPO-100 | 1.65 | 72.1 | 96.4 (90 °C) | [32] |
| IBQSH-60 | 1.39 | 30.0 | 49.0 (80 °C) | [33] |
| SPAES-6FBPA-40 | 1.25 | 36.5 | 101.1 (90 °C) | [34] |
| B20V80-SDPA | 1.89 | 65.1 | 114.4 (90 °C) | [35] |
| Membrane | Hydration number a (H2O/SO3H) | Proton conductivity (mS·cm−1) b | Ea (kJ·mol−1) | Peak power density (mW·cm−2) c | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 °C | 90 °C | ||||
| SPABES-PAE (1:2) | 21.2 | 21.2 | 48.6 | 10.89 | 183.6 |
| SPABES-PAE (1:1) | 22.7 | 41.4 | 81.9 | 10.39 | 253.3 |
| SPABES-PAE (2:1) | 23.6 | 77.1 | 131.9 | 9.22 | 333.2 |
| Nafion 212 | 25.6 | 79.3 | 148.6 | 9.56 | 430.9 |
| Membrane | Scattering vector (qmax, nm−1) | Ion cluster size (nm) |
|---|---|---|
| SPABES-PAE (1:2) | 0.810 | 7.75 |
| SPABES-PAE (1:1) | 0.815 | 7.71 |
| SPABES-PAE (2:1) | 0.817 | 7.69 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, K.H.; Chu, J.Y.; Kim, A.R.; Yoo, D.J. Facile Fabrication and Characterization of Improved Proton Conducting Sulfonated Poly(Arylene Biphenylether Sulfone) Blocks Containing Fluorinated Hydrophobic Units for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Applications. Polymers 2018, 10, 1367. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10121367
Lee KH, Chu JY, Kim AR, Yoo DJ. Facile Fabrication and Characterization of Improved Proton Conducting Sulfonated Poly(Arylene Biphenylether Sulfone) Blocks Containing Fluorinated Hydrophobic Units for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Applications. Polymers. 2018; 10(12):1367. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10121367
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Kyu Ha, Ji Young Chu, Ae Rhan Kim, and Dong Jin Yoo. 2018. "Facile Fabrication and Characterization of Improved Proton Conducting Sulfonated Poly(Arylene Biphenylether Sulfone) Blocks Containing Fluorinated Hydrophobic Units for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Applications" Polymers 10, no. 12: 1367. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10121367
APA StyleLee, K. H., Chu, J. Y., Kim, A. R., & Yoo, D. J. (2018). Facile Fabrication and Characterization of Improved Proton Conducting Sulfonated Poly(Arylene Biphenylether Sulfone) Blocks Containing Fluorinated Hydrophobic Units for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Applications. Polymers, 10(12), 1367. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10121367