Facile Fabrication of Multi-Structured SiO2@PVDF-HFP Nanofibrous Membranes for Enhanced Copper Ions Adsorption
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
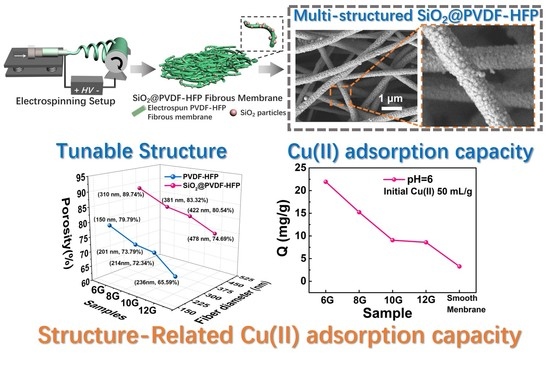
3.1. Fabrication and Morphology of Multi-Structured SiO2@PVDF-HFP Nanofibrous Membranes
3.2. Wettability Characterization
3.3. FTIR and XRD Analysis
3.4. Copper Ion (Cu(II)) Adsorption in Aqueous Solution
3.5. Adsorption Kinetics and Isotherms Simulation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Demirbas, A. Heavy metal adsorption onto agro-based waste materials: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 157, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.G.; Lei, X.J.; Xie, X.P.; Yu, B.; Cai, N.; Yu, F.Q. Adsorptive removal of Lead from water by the effective and reusable magnetic cellulose nanocomposite beads entrapping activated bentonite. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 151, 640–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.H.; Teng, T.T.; Omar, A.K.M. Removal of dyes and industrial dye wastes by magnesium chloride. Water Res. 2000, 34, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.K. A review on the adsorption of heavy metals by clay minerals, with special focus on the past decade. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 308, 438–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.-C.; Chen, J.-T.; Yang, H.-C.; Chen, J.-H.; Fang, C.-F. Ozone Decolorization of Mixed-Dye Solutions in a Gas-Induced Reactor. Water Environ. Res. 2001, 73, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Zhou, H.H.; Wu, W.Q.; Wei, S.D.; Yan, X.; Kuang, Y.F. Studies of heavy metal ion adsorption on Chitosan/Sulfydryl-functionalized graphene oxide composites. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 448, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.G.; Zeng, J.; Liu, S.L.; Zhang, L.N. An effective and recyclable adsorbent for theremoval of heavy metal ions from aqueous system: Magneticchitosan/cellulose microspheres. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 194, 403–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechtold, T.; Burtscher, E.; Turcanu, A. Cathodic decolourisation of textile waste water containing reactive dyes using a multi-cathode electrolyser. J. Chem. Technol. Biot. 2001, 76, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyuzhnyi, S.; Sklyar, V.; Mosolova, T.; Kucherenko, I.; Russkova, J.A.; Degtyaryova, N. Methanogenic biodegradation of aromatic amines. Water Sci. Technol. 2000, 42, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, A.; Misra, D.R. Contaminated Sewage Sludge Disposal as a Source of Heavy Metal Bioavailability to Native Plants. Natl. Acad. Sci. Lett. 2012, 35, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.Y.; Zhang, Y.M.; Ma, D.X.; Shi, Z.; Ma, S.Q. Mercury nano-trap for effective and efficient removal of mercury(II) from aqueous solution. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5537–5543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Shah, J.A.; Ashfaq, T.; Gardazi, S.M.; Tahir, A.A.; Pervez, A.; Haroon, H.; Mahmood, Q. Wastebiomass adsorbents for copper removal from industrial wastewater-are view. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 263, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujol, D.; Bartrolí, M.; Fiol, N.; Torre, F.D.L.; Villaescusa, I.; Poch, J. Modelling synergistic sorption of Cr (VI), Cu (II) and Ni (II) onto exhausted coffee wastes from binary mixtures Cr (VI)-Cu (II) and Cr (VI)-Ni (II). Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 230, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.E.; Abdelwahab, M.S.; Fathallah, E.M. Design of novel nanosorbents based on nano-magnetic iron oxide–bound-nano-silicon oxide-immobilized-triethylenetetramine for implementation in water treatment of heavy metals. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 223, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, D.; Lee, S.M. Novel hybrid materials in the remediation of ground waters contaminated with As (III) and As (V). Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 204, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.B.; Bai, R.B.; Chen, J.P. Aminated polyacrylonitrile fibers for lead and copper removal. Langmuir 2003, 19, 5058–5064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, K.; Haider, S.; Oh, T.-J.; Park, S.-Y. Preparation of amidoxime-modified polyacrylonitrile (PAN-oxime) nanofibers and their applications to metal ions adsorption. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 322, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceylan, D.; Okay, O. Macroporous Polyisobutylene Gels: A Novel Tough Organogel with Superfast Responsivity. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 8742–8749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceylan, D.; Dogu, S.; Karacik, B.; Yakan, S.D.; Okay, O.S.; Okay, O. Evaluation of Butyl Rubber as Sorbent Material for the Removal of Oil and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons from Seawater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 3846–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.-M.; Moreau, J.P. Oil sorption behavior of various sorbents studied by sorption capacity measurement and environmental scanning electron microscopy. Microsc. Res. Tech. 1993, 25, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.L.; Wang, N.; Wu, J.; Cui, Z.M.; Jiang, L.; Zhao, Y. Bioinspired superwettability electrospun micro/nanofibers and their applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 1801114–1801135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, N.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, L. Electrospinning of multilevel structured functional micro-/nanofibers and their applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 7290–7305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhai, J. A Lotus-Leaf-like Superhydrophobic Surface: A Porous Microsphere/Nanofiber Composite Film Prepared by Electrohydrodynamics. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 116, 4438–4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, N.; Wang, L.; Dong, H.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, L. Electrospun porous structure fibrous film with high oil adsorption capacity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 3207–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöber, W.; Fink, A.; Bohn, E. Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micro size range. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1968, 26, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisson, K.; Zhang, C.; Farach-Carson, M.C.; Chase, D.B.; Rabolt, J.F. Fiber diameters control osteoblastic cell migration and differentiation in electrospun gelatin. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2010, 94A, 1312–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rnjak, J.; Li, Z.; Maitz, P.K.M.; Wise, S.G.; Weiss, A.S. Primary human dermal fibroblast interactions with open weave three-dimensional scaffolds prepared from synthetic human elastin. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 6469–6477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balguid, A.; Mol, A.; Marion, M.H.V.; Bank, R.A.; Bouten, C.V.C.; Baaijens, F.P.T. Tailoring fiber diameter in electrospun poly (-caprolactone) scaffolds for optimal cellular infiltration in cardiovascular tissue engineering. Tissue Eng. Part A 2009, 15, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichhorn, J.S.; Sampson, W.W. Statistical geometry of pores and statistics of porous nanofibrous assemblies. J. R. Soc. Interface 2005, 2, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rnjak-Kovacina, J.; Weiss, A.S. Increasing the pore size of electrospun Scaffolds. Tissue Eng. Part B 2011, 17, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, N.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, L. Simple synthesis of smart magnetically driven fibrous films for remote controllable oil removal. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 2625–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.X.; Wang, S.T.; Lin, L.; Chen, L.; Liu, M.J.; Feng, L.; Jiang, L. A Novel superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic hydrogel-coated mesh for oil/water separation. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 4270–4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deitzel, J.M.; Kleinmeyer, J.; Harris, D.; Tan, N.C.B. The effect of processing variables on the morphology of electrospun nanofibers and textiles. Polymer 2001, 42, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, D.Y.; Huang, Z.; Wang, X.F.; Yu, J.Y.; Ding, B. Continuous, Spontaneous, and Directional Water Transport in the Trilayered Fibrous Membranes for Functional Moisture Wicking Textiles. Small 2018, 14, 1801527–1801536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtar, N.M.; Lau, W.J.; Ismail, A.F.; Ng, B.C. Physicochemical study of polyvinylidene fluoride-Cloisite15A® composite membranes for membrane distillation application. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 63367–63379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gun’ko, V.M.; Voronin, E.F.; Pakhlov, E.M.; Zarko, V.I.; Turov, V.V.; Guzenko, N.V.; Leboda, R.; Chibowski, E. Features of fumed silica coverage with silanes having three or two groups reacting with the surface. Colloids Surf. A 2000, 166, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohkami, M.; Talaeipour, M. Investigation of the chemical structure of carboxylated and carboxymethylated fibers from waste paper via XRD and FTIR analysis. BioResources 2011, 6, 1988–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sagi, S.; Chandrasekar, R.; Zhang, L.F.; Hedin, N.E.; Fong, H. Preparation and characterization of electrospun SiO2 nanofibers. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2008, 8, 1528–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.-R.; Ju, D.-H.; Lee, W.-J.; Zhang, X.W.; Kotek, R. Electrospun hydrophilic fumed silica/polyacrylonitrile nanofiber-based composite electrolyte membranes. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 3630–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primeau, N.; Vautey, C.; Langlet, M. The effect of thermal annealing on aerosol-gel deposited SiO2, films: A FTIR deconvolution study. Thin Solid Films 1997, 310, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, Y.P.; Fei, X.L.; Sun, M.D.; Zhang, C.Q.; Li, Y.X.; Yang, Q.B.; Hong, X. Preparation of a durable superhydrophobic membrane by electrospinning poly (vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) mixed with epoxy-siloxane modified SiO2, nanoparticles: A possible route to superhydrophobic surfaces with low water sliding angle and high water contact angle. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 359, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, N.; Liang, Y.M.; Lan, S.; Liu, L.; Ji, G.J.; Gan, S.C.; Zou, H.F.; Xu, X.C. Uniform TiO2-SiO2 hollow nanospheres: Synthesis, characterization and enhanced adsorption-photodegradation of azo dyes and phenol. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 305, 562–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-J.; Ahn, C.H.; Lee, M.B.; Choi, M.-S. Characteristics of electrospun PVDF/SiO2, composite nanofiber membranes as polymer electrolyte. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2011, 127, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solarajan, A.K.; Murugadoss, V.; Angaiah, S. High performance electrospun PVdF-HFP/SiO2 nanocomposite membrane electrolyte for Li-ion capacitors. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 45177–45186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Wu, D.S.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, A.F.; Wei, Q.F.; Fong, H. Electrospun AOPAN/RC blend nanofiber membrane for efficient removal of heavy metal ions from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.M.; Tang, W.Z.; Luo, P.P.; Lyu, J.Q.; Chen, A.X.; Qiao, L.K.; Nover, D. Preparation of ureido-functionalized PVA/silica mesoporous fibre membranes via electrospinning for adsorption of Pb2+ and Cu2+ in wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 2526–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Lin, J.H.; Zhang, N.; Chen, L.Z.; Zhong, S.P.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.G.; Ling, Q.D. Preparation of MgAl-EDTA-LDH based electrospun nanofiber membrane and its adsorption properties of copper(II) from wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 345, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebru, K.A.; Das, C. Removal of Pb (II) and Cu (II) ions from wastewater using composite electrospun cellulose acetate/titanium oxide (TiO2) adsorbent. J. Water Process Eng. 2017, 16, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabourian, V.; Ebrahimi, A.; Naseri, F.; Irani, M.; Rahimi, A. Fabrication of chitosan/silica nanofibrous adsorbent functionalized with amine groups for the removal of Ni (II), Cu (II) and Pb (II) from aqueous solutions: Batch and column studies. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 40354–40365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, H.; Huang, M.T.; Yang, Y.; Li, Z.S.; Zhan, Y.F.; Chen, J.J.; Wu, Y.; Shi, X.W.; Deng, H.B.; Du, Y.M. Chitosan-rectorite nanospheres immobilized on polystyrene fibrous mats via alternate electrospraying/electrospinning techniques for copper ions adsorption. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 426, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.P.; Wang, L.H.; Dong, S.J.; Zhang, G.H.; Shi, X.J.; Xiang, C.H.; Li, L.L. Adsorption of hexavalent chromium by novel chitosan/poly(ethylene oxide)/permutit electrospun nanofibers. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 17740–17749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.H.; Wei, S.Y.; Gu, H.B.; Rapole, S.B.; Wang, Q.; Luo, Z.P.; Haldolaarachchige, N.; Young, D.P.; Guo, Z.H. One-Pot Synthesis of Magnetic Graphene Nanocomposites Decorated with Core@Double-shell Nanoparticles for Fast Chromium Removal. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.-B.; Wang, J.-N.; Wu, J.; Li, C.-J. “Flower-Like” PA6@Mg(OH)2, electrospun nanofibers with Cr (VI)-removal capacity. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 254, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.-F.; Zhang, N.; Wei, X.; Yang, J.-H.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z.-W. Blend-electrospun poly(vinylidene fluoride)/polydopamine membranes: Self-polymerization of dopamine and the excellent adsorption/separation abilities. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 14430–14443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanjale, S.; Birajdar, M.; Jog, J.; Neppalli, R.; Causin, V.; Karger-Kocsis, J.; Lee, J.; Panzade, P. Surface tailored PS/TiO2 composite nanofiber membranes for Copper removal from water. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 469, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, P.; Wen, J.J.; Hu, Y.Y.; Tan, X.J. Adsorption of Cu2+ and Cd2+ from aqueous solution by novel electrospun poly(vinyl alcohol)/graphene oxide nanofibers. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 79641–79650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluigia, A.; Rombaldoni, F.; Tonetti, C.; Jannoke, L. Study of Methylene Blue adsorption on keratin nanofibrous membranes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 268, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.; Losso, J.N.; Marshall, W.E.; Rao, R.M. Freundlich adsorption isotherms of agricultural by-product-based powdered activated carbons in a geosmin-water system. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 85, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Pseudo First Order Model | Pseudo Second Order Model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe(exp) (mg/g) | k1 | R2 | qe(cal) (mg/g) | k2 | R2 | qe(cal) (mg/g) |
| 9.9818 | −0.0322 | 0.98037 | 3.401 | 2.9064 | 0.99735 | 10.05025 |
| Langmuir Isothermal Models | Freundlich Isothermal Models | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KL | R2 | qm | KF | R2 | 1/n |
| 0.01238 | 0.92495 | 27.5634 | 1.09981 | 0.97377 | 0.55683 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pi, H.; Wang, R.; Ren, B.; Zhang, X.; Wu, J. Facile Fabrication of Multi-Structured SiO2@PVDF-HFP Nanofibrous Membranes for Enhanced Copper Ions Adsorption. Polymers 2018, 10, 1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10121385
Pi H, Wang R, Ren B, Zhang X, Wu J. Facile Fabrication of Multi-Structured SiO2@PVDF-HFP Nanofibrous Membranes for Enhanced Copper Ions Adsorption. Polymers. 2018; 10(12):1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10121385
Chicago/Turabian StylePi, Haohong, Rui Wang, Baona Ren, Xiuqin Zhang, and Jing Wu. 2018. "Facile Fabrication of Multi-Structured SiO2@PVDF-HFP Nanofibrous Membranes for Enhanced Copper Ions Adsorption" Polymers 10, no. 12: 1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10121385
APA StylePi, H., Wang, R., Ren, B., Zhang, X., & Wu, J. (2018). Facile Fabrication of Multi-Structured SiO2@PVDF-HFP Nanofibrous Membranes for Enhanced Copper Ions Adsorption. Polymers, 10(12), 1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10121385