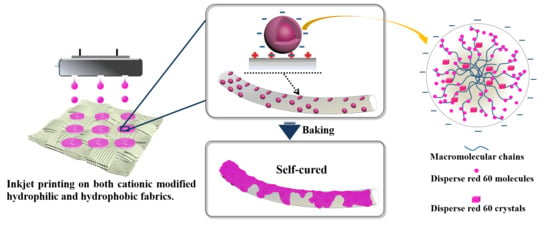
Inkjet Printable and Self-Curable Disperse Dyes/P(St-BA-MAA) Nanosphere Inks for Both Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Fabrics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of P(St-BA-MAA) Nanospheres
2.3. Preparation of DPN Inks
2.4. Droplet Formation Observation and Inkjet Printing
2.5. Sizes and Zeta Potentials of the Color Polymer Nanospheres
2.6. Observation by TEM
2.7. Observation by SEM
2.8. Dye Content Measurements
2.9. X-ray Diffraction Measurements (XRD)
2.10. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphology of the DPN
3.2. The Interaction between Disperse Dyes and P(St-BA-MAA) Nanospheres
3.3. The Stability of DPN Dispersions
3.4. Rheological Behavior and Droplet Formations
3.5. Self-Curing on Both Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Fabrics
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, H.; Fang, K.; Liu, X.; Cai, Y.; An, F. Effect of cotton cationization using copolymer nanospheres on ink-jet printing of different fabrics. Polymers 2018, 10, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaimouz, A.W.; Wardman, R.H.; Christie, R.M. The inkjet printing process for lyocell and cotton fibres. Part 1: The significance of pre-treatment chemicals and their relationship with colour strength, absorbed dye fixation and ink penetration. Dyes Pigments 2010, 84, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekaby, M.; Abd-El Thalouth, J.I.; Abd El-Salam Sh, H. Improving reactive ink jet printing via cationization of cellulosic linen fabric. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 98, 1371–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, J.H.; Bradbury, R.; Annable, T.; Yeates, S.G. Inkjet printable aqueous composite dye-Polymer nanoparticles. Dyes Pigments 2012, 95, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.J.; Lee, W.J.; Choi, J.H.; Kim, J.P. Synthesis and application of temporarily solubilised azo disperse dyes containing β-sulphatoethylsulphonyl group. Dyes Pigments 2005, 65, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Dong, X.; Yu, D.; He, J. Stabilization mechanisms of C.I. Disperse red 60 dispersions in the presence of its dye–polyether derivatives. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2012, 405, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Xue, M.; Zhang, Q.; Sheng, Q.; Liu, Y. Nanocolorants: A novel class of colorants, the preparation and performance characterization. Dyes Pigments 2008, 76, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-sayed, G.M.; Kamel, M.M.; Morsy, N.S.; Taher, F.A. Encapsulation of nano disperse red 60 via modified miniemulsion polymerization. I. Preparation and characterization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 125, 1318–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takasu, M.; Shiroya, T.; Takeshita, K.; Sakamoto, M.; Kawaguchi, H. Improvement of the storage stability and photostability of colored latex prepared by miniemulsion polymerization. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2004, 282, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polpanich, D.; Asawapirom, U.; Thiramanas, R.; Piyakulawat, P. Self-colored nanoparticles containing naphthalene-bisimide derivatives: Synthesis and protein adsorption study. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2011, 129, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.; Ren, B. A facile method for preparing colored nanospheres of poly(styrene-co-acrylic acid). Dyes Pigments 2014, 100, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgammal, M.; Schneider, R.; Gradzielski, M. Development of self-curable hybrid pigment inks by miniemulsion polymerization for inkjet printing of cotton fabrics. Dyes Pigments 2016, 133, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, B. Early (pre-DLVO) studies of particle aggregation. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 170, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benítez, E.I.; Genovese, D.B.; Lozano, J.E. Effect of ph and ionic strength on apple juice turbidity: Application of the extended dlvo theory. Food Hydrocoll. 2007, 21, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Hao, L.; Fang, K. Adsorption of cationic copolymer nanospheres onto cotton fibers investigated by a facile nephelometry. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 452, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, W.; Li, G.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y. Synthesis of P(St-MAA)-Fe3O4/PPy core–shell composite microspheres with conductivity and superparamagnetic behaviors. Synth. Met. 2011, 161, 1921–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Qiu, T.; Yuan, H.; Shi, W.; Li, X. Synthesis and characterization of novel Ag-polypyrrole@poly(styrene-co-methacrylic acid) nanocomposite particles. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 790–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.L.; Yasin, N.H.M.; Derek, C.J.C.; Lim, J.K. Harvesting of microalgal biomass using MF membrane: Kinetic model, CDE model and extended DLVO theory. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 446, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Cano, M.S.; Chauveteau, G.; Nieves, F.J.D.L. Colloidal stabilization of polystyrene particles by adsorption of nonionic surfactant. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 68, 3710–3713. [Google Scholar]
- Jódarreyes, A.B.; Ortegavinuesa, J.L.; Martínrodríguez, A. Electrokinetic behavior and colloidal stability of polystyrene latex coated with ionic surfactants. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 297, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, Q.T.; de Sanoit, J.; Pierre, S.; Arnault, J.-C.; Bergonzo, P. Diamond electrodes for trace alpha pollutant sequestration via covalent grafting of nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA) ligand. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 136, 430–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendola, M.E.; Paul, T.; Strathmann, T.J.; Carbonaro, R.F. Investigation of the kinetics of aquation of the 1:2 complex between CrIII and nitrilotriacetic acid. Polyhedron 2009, 28, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, F.; Guillot, J.; Guyot, A. Study of poly(St/BA/MAA) copolymer latexes with bimodal particle size distribution. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2015, 9, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, Z.; Wu, M.; Li, T. Preparation and characterization of monodisperse magnetic poly(styrene butyl acrylate methacrylic acid) microspheres in the presence of a polar solvent. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 87, 1733–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xiao, H. Soap-free emulsion copolymerisation of styrene with cationic monomer: Effect of ethanol as a cosolvent. Polymer 2000, 41, 7023–7031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peymannia, M.; Soleimani-Gorgani, A.; Ghahari, M.; Najafi, F. Production of a stable and homogeneous colloid dispersion of nano coal 2 o 4 pigment for ceramic ink-jet ink. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 34, 3119–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Fang, K.J. Adsorption of cationic nanospheres on cotton fibers: The effect of emulsifiers used in the cationic emulsion polymerization. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2014, 292, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.; Xia, X.; Cai, Y.; Hao, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y. Blue core-shell nanospheres prepared by dyeing poly(styrene-co-methacrylic acid) dispersions. Color. Technol. 2015, 131, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.; Kanwal, F.; Ramay, S.; Atiq, S.; Rehman, R.; Ali, S.; Alzayed, N. Synthesis and characterization of BaTiO3/polypyrrole composites with exceptional dielectric behaviour. Polymers 2018, 10, 1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longyun, H.; Rui, W.; Yuetai, Z.; Kuanjun, F.; Yuqing, C. The enzymatic actions of cellulase on periodate oxidized cotton fabrics. Cellulose 2018, 25, 6759–6769. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, H.S.; Posey, J.C., Jr.; Singh, P. X-ray crystal structure of disperse red 167. Dyes Pigments 1992, 20, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.E.; Kim, H.J.; Han, M.R.; Su, Y.L.; Jo, W.J.; Lee, S.S.; Lee, J.S. Crystal structures of C.I. Disperse red 65 and C.I. Disperse red 73. Dyes Pigments 2009, 80, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.; Zhang, L.; Cai, Y.; Hao, L.; Liu, X. Hollow disperse dyes/copolymer composite nanospheres. Dyes Pigments 2017, 136, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guistina, R.A.; Santilli, D.; Bugner, D.E. Aqueous Pigment Dispersions Containing Sequestering Agents for Use as Ink Jet Printing Inks. U.S. Patent No. 5,611,847A, 18 March 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Güngör, G.L.; Kara, A.; Gardini, D.; Blosi, M.; Dondi, M.; Zanelli, C. Ink-jet printability of aqueous ceramic inks for digital decoration of ceramic tiles. Dyes Pigments 2016, 127, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergström, L. Shear thinning and shear thickening of concentrated ceramic suspensions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1998, 133, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoath, S.D.; Jung, S.; Hsiao, W.K.; Hutchings, I.M. How pedot: Pss solutions produce satellite-free inkjets. Org. Electron. 2012, 13, 3259–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.; Kim, D.; Moon, J. Influence of fluid physical properties on ink-jet printability. Langmuir ACS J. Surf. Colloids 2009, 25, 2629–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Yang, C.; Fang, K.; Cai, Y.; Hao, L. Removing the residual cellulase by graphene oxide to recycle the bio-polishing effluent for dyeing cotton fabrics. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 207, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, Y.; Fang, K.; Ren, Y.; Tang, Z.; Wang, R.; Chen, W.; Xie, R.; Shi, Z.; Hao, L. Inkjet Printable and Self-Curable Disperse Dyes/P(St-BA-MAA) Nanosphere Inks for Both Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Fabrics. Polymers 2018, 10, 1402. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10121402
Song Y, Fang K, Ren Y, Tang Z, Wang R, Chen W, Xie R, Shi Z, Hao L. Inkjet Printable and Self-Curable Disperse Dyes/P(St-BA-MAA) Nanosphere Inks for Both Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Fabrics. Polymers. 2018; 10(12):1402. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10121402
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Yawei, Kuanjun Fang, Yanfei Ren, Zhiyuan Tang, Rongqing Wang, Weichao Chen, Ruyi Xie, Zhen Shi, and Longyun Hao. 2018. "Inkjet Printable and Self-Curable Disperse Dyes/P(St-BA-MAA) Nanosphere Inks for Both Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Fabrics" Polymers 10, no. 12: 1402. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10121402
APA StyleSong, Y., Fang, K., Ren, Y., Tang, Z., Wang, R., Chen, W., Xie, R., Shi, Z., & Hao, L. (2018). Inkjet Printable and Self-Curable Disperse Dyes/P(St-BA-MAA) Nanosphere Inks for Both Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Fabrics. Polymers, 10(12), 1402. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10121402