Aliphatic Polyester Nanofibers Functionalized with Cyclodextrins and Cyclodextrin-Guest Inclusion Complexes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Cyclodextrin Functionalized Aliphatic Polyester Nanofibers
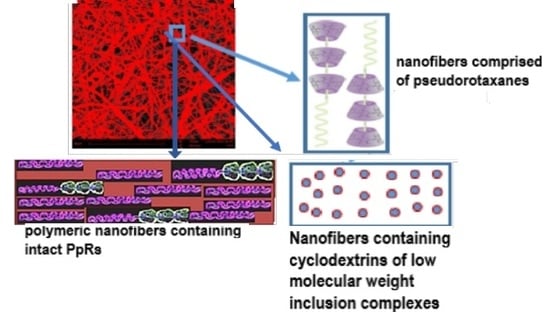
2.1. Poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) Nanofibers Functionalized with Cyclodextrins or Small Molecule Inclusion Complexes
2.2. PCL Nanofibers Functionalized with Cyclodextrin-Large Molecule Inclusion Complexes
2.3. Cyclodextrins or Inclusion Complex Functionalized Poly(lactic acid) Nanofibers
3. Future Outlook
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| A.a | Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans |
| AV | Aloe vera |
| BTEAC | Benzyl triethylammonium chloride salt |
| CA | Cinnamaldehyde |
| CDs | Cyclodextrins |
| CDI | N,N′-carbonyldiimidazole |
| CD-ICs | CD-inclusion complexes |
| CFM | Chloroform |
| CMFDA | 5-chloromethylfluoresceindiacetate |
| CEO | Cinnamon essential oil |
| CUR | Curcumin |
| DMA | Dynamic mechanical analyses |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| DMF | Dimethyl formamide |
| DPPH | 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl |
| DSC | Differential scanning calorimetry |
| E. coli | Escherichia coli |
| FITC | Fluorescein isothiocyanate |
| GA | Gallic acid |
| hADSCs | Human adipose-derived stem cells |
| HP-β-CD | 2-hydroxypropyl-β-CD |
| HPC | Hydroxypropyl cellulose |
| HPLC | High performance liquid chromatography |
| HCPT | Hydroxycamptothecin |
| HSF | Human skin fibroblasts |
| IC50 | Half maximal inhibitory concentration |
| MCF-7 | Michigan Cancer Foundation-7 |
| MgO | Magnesium oxide |
| NAP | Naproxen |
| OPN | Osteopontin |
| PCL | Poly(ε-caprolactone) |
| PDLA | Poly(d-lactic acid) |
| PELA | Poly(ethylene glycol)–poly(dl-lactic acid) |
| P.g | Porphyromonas gingivalis |
| PLCL | Poly(lactide-co-caprolactone) |
| PLLA | Poly(l-lactic acid) |
| PpR | Pseudorotaxanes |
| PLA | Poly lactic acid |
| RM-β-CD | Randomly methylated β-CD |
| S. aureus | Staphylococcus aureus |
| SAED | Selected area electron diffraction |
| SFS | Sulfisoxazole |
| α-TC | α-tocopherol |
| TGA | Thermogravimetric analyses |
| TR | Triclosan |
| WAXD | Wide angle-X-ray diffraction |
| WCA | Water contact angle |
| XPS | X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy |
References
- Kny, E.; Uyar, T.; Kny, E. Electrospun Materials for Tissue Engineering and Biomedical Applications; Kny, E., Uyar, T., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2017; pp. i–iii. [Google Scholar]
- Anu Bhushani, J.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Electrospinning and electrospraying techniques: Potential food based applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 38, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Huang, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, W.; Wang, C. Zinc Oxide Nanofiber Gas Sensors via Electrospinning. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2008, 91, 3817–3819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, G.; Vernekar, V.N.; Kuyinu, E.L.; Laurencin, C.T. Poly (lactic acid)-based biomaterials for orthopaedic regenerative engineering. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 247–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramakrishna, S.; Fujihara, K.; Teo, W.-E.; Yong, T.; Ma, Z.; Ramaseshan, R. Electrospun nanofibers: Solving global issues. Mater. Today 2006, 9, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muerza-Cascante, M.L.; Shokoohmand, A.; Khosrotehrani, K.; Haylock, D.; Dalton, P.D.; Hutmacher, D.W.; Loessner, D. Endosteal-like extracellular matrix expression on melt electrospun written scaffolds. Acta Biomater. 2017, 52, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes, A.C.; Gorzelanny, C.; Halter, N.; Schneider, S.W.; Chronakis, I.S. Hybrid electrospun chitosan-phospholipids nanofibers for transdermal drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 510, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodruff, M.A.; Hutmacher, D.W. The return of a forgotten polymer—Polycaprolactone in the 21st century. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 1217–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uyar, T.; El-Shafei, A.; Wang, X.; Hacaloglu, J.; Tonelli, A.E. The Solid Channel Structure Inclusion Complex Formed between Guest Styrene and Host γ-Cyclodextrin. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2006, 55, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyar, T.; Hunt, M.A.; Gracz, H.S.; Tonelli, A.E. Crystalline Cyclodextrin Inclusion Compounds Formed with Aromatic Guests: Guest-Dependent Stoichiometries and Hydration-Sensitive Crystal Structures. Cryst. Growth Des. 2006, 6, 1113–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, G.; Boy, R.; Gupta, B.S.; Tonelli, A.E. Analytical techniques for characterizing cyclodextrins and their inclusion complexes with large and small molecular weight guest molecules. Polym. Test. 2017, 62, 402–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonelli, A.E. Molecular Processing of Polymers with Cyclodextrins. In Inclusion Polymers; Wenz, G., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 55–77. [Google Scholar]
- Croft, A.P.; Bartsch, R.A. Synthesis of chemically modified cyclodextrins. Tetrahedron 1983, 39, 1417–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonelli, A.E. Restructuring polymers via nanoconfinement and subsequent release. Beil. J. Organ. Chem. 2012, 8, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, S.; Roy, M.N. Encapsulation of Vitamin C into β-Cyclodextrin for Advanced and Regulatory Release; Hamza, A.H., Vitamin, C., Eds.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatian, 2017; p. Ch. 07. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez-Lorenzo, C.; García-González, C.A.; Concheiro, A. Cyclodextrins as versatile building blocks for regenerative medicine. J. Control. Release 2017, 268, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Lorenzo, C.; Moya-Ortega, M.D.; Loftsson, T.; Concheiro, A.; Torres-Labandeira, J.J. Cyclodextrin-Based Hydrogels. In Cyclodextrins in Pharmaceutics, Cosmetics, and Biomedicine; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 297–321. [Google Scholar]
- Costoya, A.; Concheiro, A.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C. Electrospun Fibers of Cyclodextrins and Poly(cyclodextrins). Molecules 2017, 22, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftsson, T.; Moya-Ortega, M.D.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C.; Concheiro, A. Pharmacokinetics of cyclodextrins and drugs after oral and parenteral administration of drug/cyclodextrin complexes. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2016, 68, 544–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brackman, G.; Garcia-Fernandez, M.J.; Lenoir, J.; De Meyer, L.; Remon, J.-P.; De Beer, T.; Concheiro, A.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C.; Coenye, T. Dressings Loaded with Cyclodextrin–Hamamelitannin Complexes Increase Staphylococcus aureus Susceptibility Toward Antibiotics Both in Single as well as in Mixed Biofilm Communities. Macromol. Biosci. 2016, 16, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simoes, S.M.N.; Rey-Rico, A.; Concheiro, A.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C. Supramolecular cyclodextrin-based drug nanocarriers. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 6275–6289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simões, S.M.N.; Veiga, F.; Torres-Labandeira, J.J.; Ribeiro, A.C.F.; Concheiro, A.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C. Poloxamine-Cyclodextrin-Simvastatin Supramolecular Systems Promote Osteoblast Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Macromol. Biosci. 2013, 13, 723–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Concheiro, A.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C. Chemically cross-linked and grafted cyclodextrin hydrogels: From nanostructures to drug-eluting medical devices. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 1188–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malikmammadov, E.; Tanir, T.E.; Kiziltay, A.; Hasirci, V.; Hasirci, N. PCL and PCL-based materials in biomedical applications. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2017, 29, 863–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores, C.; Lopez, M.; Tabary, N.; Neut, C.; Chai, F.; Betbeder, D.; Herkt, C.; Cazaux, F.; Gaucher, V.; Martel, B.; et al. Preparation and characterization of novel chitosan and β-cyclodextrin polymer sponges for wound dressing applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 173, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabuchi, R.; Anraku, M.; Iohara, D.; Ishiguro, T.; Ifuku, S.; Nagae, T.; Uekama, K.; Okazaki, S.; Takeshita, K.; Otagiri, M.; et al. Surface-deacetylated chitin nanofibers reinforced with a sulfobutyl ether β-cyclodextrin gel loaded with prednisolone as potential therapy for inflammatory bowel disease. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 174, 1087–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.; Pan, Z.; Li, F.; Yu, J. Poly(butylene succinate-co-terephthalate) nanofibrous membrane composited with cyclodextrin polymer for superhydrophilic property. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 1378–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyar, T.; Balan, A.; Toppare, L.; Besenbacher, F. Electrospinning of cyclodextrin functionalized poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) nanofibers. Polymer 2009, 50, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamer, U.; Yusuf, N.; Jale, H.; Flemming, B. Electrospinning of functional poly(methyl methacrylate) nanofibers containing cyclodextrin-menthol inclusion complexes. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 125703. [Google Scholar]
- Uyar, T.; Havelund, R.; Nur, Y.; Balan, A.; Hacaloglu, J.; Toppare, L.; Besenbacherac, F.; Kingshotta, P. Cyclodextrin functionalized poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) electrospun nanofibers for organic vapors waste treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 365, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamer, U.; Rasmus, H.; Jale, H.; Xingfei, Z.; Flemming, B.; Peter, K. The formation and characterization of cyclodextrin functionalized polystyrene nanofibers produced by electrospinning. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 125605. [Google Scholar]
- Uyar, T.; Hacaloglu, J.; Besenbacher, F. Electrospun polystyrene fibers containing high temperature stable volatile fragrance/flavor facilitated by cyclodextrin inclusion complexes. React. Funct. Polym. 2009, 69, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyar, T.; Havelund, R.; Hacaloglu, J.; Besenbacher, F.; Kingshott, P. Functional Electrospun Polystyrene Nanofibers Incorporating α-, β-, and γ-Cyclodextrins: Comparison of Molecular Filter Performance. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 5121–5230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akçakoca Kumbasar, E.P.; Akduman, Ç.; Çay, A. Effects of β-cyclodextrin on selected properties of electrospun thermoplastic polyurethane nanofibres. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 104, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akduman, C.; Kumbasar, E.P.A.; Morsunbul, S. Electrospun nanofiber membranes for adsorption of dye molecules from textile wastewater. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 254, 102001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, N.A.; Burroughs, M.C.; Gracz, H.; Pritchard, C.Q.; Brozena, A.H.; Willoughby, J.; Khan, S.A. Cyclodextrin facilitated electrospun chitosan nanofibers. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 7131–7137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Yu, Z.; Cai, Z.; Yu, L.; Lv, Y. Voriconazole Composited Polyvinyl Alcohol/Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin Nanofibers for Ophthalmic Delivery. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, Q.; Lu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Lv, P.; Wei, Q. Preparation and characterization of electrospun polyvinyl alcoholstyrylpyridinium/β-cyclodextrin composite nanofibers: Release behavior and potential use for wound dressing. Fibers Polym. 2016, 17, 1835–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemma, S.M.; Scampicchio, M.; Mahon, P.J.; Sbarski, I.; Wang, J.; Kingshott, P. Controlled Release of Retinyl Acetate from β-Cyclodextrin Functionalized Poly(vinyl alcohol) Electrospun Nanofibers. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 3481–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayaci, F.; Uyar, T. Electrospun polyester/cyclodextrin nanofibers for entrapment of volatile organic compounds. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2014, 54, 2970–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyar, T.; Besenbacher, F. Electrospinning of cyclodextrin functionalized polyethylene oxide (PEO) nanofibers. Eur. Polym. J. 2009, 45, 1032–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, G.; Gupta, B.S.; Tonelli, A.E. Poly(ε-caprolactone) Nanowebs Functionalized with α- and γ-Cyclodextrins. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 4122–4133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanan, G.; Ormond, B.R.; Gupta, B.S.; Tonelli, A.E. Efficient wound odor removal by β-cyclodextrin functionalized poly (ε-caprolactone) nanofibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 42782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Allen, E.; Tonelli, A.E. Study of the inclusion compounds formed between α-cyclodextrin and high molecular weight poly(ethylene oxide) and poly(ε-caprolactone). Polymer 1998, 39, 4857–4865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Shuai, X.; Tonelli, A.E. Melting and Crystallization Behaviors of Biodegradable Polymers Enzymatically Coalesced from Their Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complexes. Biomacromolecules 2003, 4, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Mirau, P.A.; Tonelli, A.E. Dynamics of Isolated Polycaprolactone Chains in Their Inclusion Complexes with Cyclodextrins. Macromolecules 2001, 34, 3276–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusa, C.C.; Luca, C.; Tonelli, A.E. Polymer−Cyclodextrin Inclusion Compounds: Toward New Aspects of Their Inclusion Mechanism. Macromolecules 2001, 34, 1318–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, X.; Porbeni, F.E.; Wei, M.; Shin, I.D.; Tonelli, A.E. Formation of and Coalescence from the Inclusion Complex of a Biodegradable Block Copolymer and α-Cyclodextrin: A Novel Means To Modify the Phase Structure of Biodegradable Block Copolymers. Macromolecules 2001, 34, 7355–7361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, X.; Porbeni, F.E.; Wei, M.; Bullions, T.; Tonelli, A.E. Inclusion Complex Formation between α,γ-Cyclodextrins and a Triblock Copolymer and the Cyclodextrin-Type-Dependent Microphase Structures of Their Coalesced Samples. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 2401–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, B.R.; Tonelli, A.E. Constrained polymer chain behavior observed in their non-stoichiometric cyclodextrin inclusion complexes. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2012, 72, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.-C.; Kuo, S.-W.; Chang, F.-C. Synthesis of the Organic/Inorganic Hybrid Star Polymers and Their Inclusion Complexes with Cyclodextrins. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 3099–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Hill, M.A.; Hood, M.; Greeson, D.F., Jr.; Horton, J.R.; Orndorff, P.E.; Herndon, A.S.; Tonelli, A.E. Formation of antibiotic, biodegradable polymers by processing with Irgasan DP300R (triclosan) and its inclusion compound with β-cyclodextrin. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2001, 82, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Gerber, M.; Lu, J.; Tonelli, A.E. Formation of a flame retardant-cyclodextrin inclusion compound and its application as a flame retardant for poly(ethylene terephthalate). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2001, 71, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Taylor, H.; Gerber, M.; Orndorff, P.E.; Horton, J.R.; Tonelli, A. Formation of antibiotic, biodegradable/bioabsorbable polymers by processing with neomycin sulfate and its inclusion compound with β-cyclodextrin. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1999, 74, 937–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suk Whang, H.; Hunt, M.A.; Wrench, N.; Hockney, J.E.; Farin, C.E.; Tonelli, A.E. Nonoxynol-9-α-cyclodextrin inclusion compound and its application for the controlled release of nonoxynol-9 spermicide. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 106, 4104–4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonelli, A.E. Nanostructuring and functionalizing polymers with cyclodextrins. Polymer 2008, 49, 1725–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aytac, Z.; Uyar, T. Antioxidant activity and photostability of α-tocopherol/β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex encapsulated electrospun polycaprolactone nanofibers. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 79, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siafaka, P.; Üstündağ Okur, N.; Mone, M.; Giannakopoulou, S.; Er, S.; Pavlidou, E.; Karavas, E.; Bikiaris, D.N. Two Different Approaches for Oral Administration of Voriconazole Loaded Formulations: Electrospun Fibers versus β-Cyclodextrin Complexes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banik, A.; Gogoi, P.; Saikia, M.D. Interaction of naproxen with β-cyclodextrin and its derivatives/polymer: Experimental and molecular modeling studies. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2012, 72, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, J.; Vila-jato, J.L.; Otero, F.; Anguiano, S. Influence of Method of Preparation on Inclusion Complexes of Naproxen with Different Cyclodextrins. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 1991, 17, 943–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szafran, B.; Pawlaczyk, J. Preparation and characterization of the β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex with sulfafurazole. J. Incl. Phenom. Mol. Recognit. Chem. 1995, 23, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladys, G.; Claudia, G.; Marcela, L. The effect of pH and triethanolamine on sulfisoxazole complexation with hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2003, 20, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canbolat, M.F.; Celebioglu, A.; Uyar, T. Drug delivery system based on cyclodextrin-naproxen inclusion complex incorporated in electrospun polycaprolactone nanofibers. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 115, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, A.P.; Rocha, C.M.; Oliveira, M.F.; Gontijo, S.M.; Agudelo, R.R.; Sinisterra, R.D.; Cortés, M.E. Nanofibers containing tetracycline/β-cyclodextrin: Physico-chemical characterization and antimicrobial evaluation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 156, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, J.; Alves, G.; Oliveira, P.; Fortuna, A.; Falcão, A. Intranasal delivery of ciprofloxacin to rats: A topical approach using a thermoreversible in situ gel. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 97, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, S.; Chakraborti, C.K.; Mishra, S.C.; Naik, S. Ftir and Xrd Investigations of Some Fluoroquinolones. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 3, 165–170. [Google Scholar]
- Masoumi, S.; Amiri, S.; Bahrami, S.H. PCL-based nanofibers loaded with ciprofloxacin/cyclodextrin containers. J. Text. Inst. 2017, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aytac, Z.; Sen, H.S.; Durgun, E.; Uyar, T. Sulfisoxazole/cyclodextrin inclusion complex incorporated in electrospun hydroxypropyl cellulose nanofibers as drug delivery system. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 128, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrader, J.; Etschmann, M.M.W.; Sell, D.; Hilmer, J.-M.; Rabenhorst, J. Applied biocatalysis for the synthesis of natural flavour compounds—Current industrial processes and future prospects. Biotechnol. Lett. 2004, 26, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kourist, R.; Domínguez de María, P.; Bornscheuer, U.T. Enzymatic Synthesis of Optically Active Tertiary Alcohols: Expanding the Biocatalysis Toolbox. ChemBioChem 2008, 9, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, B. Very Large Scale Monoclonal Antibody Purification: The Case for Conventional Unit Operations. Biotechnol. Prog. 2007, 23, 995–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betancor, L.; Luckarift, H.R. Bioinspired enzyme encapsulation for biocatalysis. Trends Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleti, S.; Karaturi, H.; Subrahmanyam, C.V.S.; Narasu, M.L. Complexation and Characterization of -Amylase with Hydroxypropyl-Cyclodextrin. Int. J. Pharm. Phytopharmacol. Res. 2012, 1, 375–378. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Hwang, E.T.; Kim, B.C.; Lee, S.-M.; Sang, B.-I.; Choi, Y.S.; Kim, J.; Gu, M.B. Stable and continuous long-term enzymatic reaction using an enzyme–nanofiber composite. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 75, 1301–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canbolat, M.F.; Savas, H.B.; Gultekin, F. Improved catalytic activity by catalase immobilization using γ-cyclodextrin and electrospun PCL nanofibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canbolat, M.F.; Savas, H.B.; Gultekin, F. Enzymatic behavior of laccase following interaction with γ-CD and immobilization into PCL nanofibers. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 528, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, M.A.; Jung, D.W.; Shamsheer, M.; Uyar, T.; Tonelli, A.E. Polystyrenes in channels. Polymer 2004, 45, 1345–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyar, T.; Gracz, H.S.; Rusa, M.; Shin, I.D.; El-Shafei, A.; Tonelli, A.E. Polymerization of styrene in γ-cyclodextrin channels: Lightly rotaxanated polystyrenes with altered stereosequences. Polymer 2006, 47, 6948–6955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Tonelli, A.E. Compatiblization of Polymers via Coalescence from Their Common Cyclodextrin Inclusion Compounds. Macromolecules 2001, 34, 4061–4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Shin, I.D.; Urban, B.; Tonelli, A.E. Partial miscibility in a nylon-6/nylon-66 blend coalesced from their common α-cyclodextrin inclusion complex. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2004, 42, 1369–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusa, C.C.; Wei, M.; Shuai, X.; Bullions, T.A.; Wang, X.; Rusa, M.; Uyar, T.; Tonelli, A.E. Molecular mixing of incompatible polymers through formation of and coalescence from their common crystalline cyclodextrin inclusion compounds. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2004, 42, 4207–4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusa, C.C.; Wei, M.; Bullions, T.A.; Rusa, M.; Gomez, M.A.; Porbeni, F.E.; Gomez, M.A.; Porbeni, F.E.; Wang, X.; Shin, I.D.; et al. Controlling the Polymorphic Behaviors of Semicrystalline Polymers with Cyclodextrins. Cryst. Growth Des. 2004, 4, 1431–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porbeni, F.E.; Shin, I.D.; Shuai, X.; Wang, X.; White, J.L.; Jia, X.; Tonelli, A.E. Morphology and dynamics of the poly(ε-caprolactone)-b-poly(L-lactide) diblock copolymer and its inclusion compound with α-cyclodextrin: A solid-state 13C NMR study. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2005, 43, 2086–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusa, C.C.; Rusa, M.; Peet, J.; Uyar, T.; Fox, J.; Hunt, M.A.; Wang, X.; Balik, C.M.; Tonell, A.E. The Nano-threading of Polymers. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2006, 55, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusa, C.C.; Shuai, X.; Shin, I.D.; Bullions, T.A.; Wei, M.; Porbeni, F.E.; Lu, L.; Huang, L.; Fox, J.; Tonelli, A.E. Controlling the Behaviors of Biodegradable/Bioabsorbable Polymers with Cyclodextrins. J. Polym. Environ. 2004, 12, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, X.; Wei, M.; Porbeni, F.E.; Bullions, T.A.; Tonelli, A.E. Formation of and Coalescence from the Inclusion Complex of a Biodegradable block copolymer and α-cyclodextrin. 2: A novel way to regulate the biodegradation behavior of biodegradable block copolymers. Biomacromolecules 2002, 3, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, M.; Bullions, T.A.; Rusa, C.C.; Wang, X.; Tonelli, A.E. Unique morphological and thermal behaviors of reorganized poly(ethylene terephthalates). J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2004, 42, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, K.; Schmidt, B.; Kotek, R.; Tonelli, A. Reorganization of the chain packing between poly(ethylene isophthalate) chains via coalescence from their inclusion compound formed with γ-cyclodextrin. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 102, 6049–6053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedula, J.; Tonelli, A.E. Reorganization of poly(ethylene terephthalate) structures and conformations to alter properties. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2007, 45, 735–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, B.R.; Krishnaswamy, R.; Tonelli, A.E. Physical properties of poly(ε-caprolactone) coalesced from its α-cyclodextrin inclusion compound. Polymer 2011, 52, 4517–4527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.; Shin, K.-M.; Zhu, B.; Inoue, Y. Nucleation and Crystallization Behavior of Poly(butylene succinate) Induced by Its α-Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complex: Effect of Stoichiometry. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 2427–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, A.; Joyner, X.; Kotek, R.; Tonelli, A.E. Constrained/Directed Crystallization of Nylon-6. I. Nonstoichiometric Inclusion Compounds Formed with Cyclodextrins. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 8983–8991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonelli, A. Non-Stoichiometric Polymer-Cyclodextrin Inclusion Compounds: Constraints Placed on Un-Included Chain Portions Tethered at Both Ends and Their Relation to Polymer Brushes. Polymers 2014, 6, 2166–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.; Mori, T.; Pan, P.; Kai, W.; Zhu, B.; Inoue, Y. Crystallization behavior and mechanical properties of poly(ε-caprolactone)/cyclodextrin biodegradable composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 112, 2351–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, G.; Gupta, B.S.; Tonelli, A.E. Enhanced mechanical properties of poly (ε-caprolactone) nanofibers produced by the addition of non-stoichiometric inclusion complexes of poly (ε-caprolactone) and α-cyclodextrin. Polymer 2015, 76, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, G.; Aguda, R.; Hartman, M.; Chung, C.-C.; Boy, R.; Gupta, B.S.; Tonelli, A.E. Fabrication and Characterization of Poly(ε-caprolactone)/α-Cyclodextrin Pseudorotaxane Nanofibers. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanan, G.; Chung, C.-C.; Aguda, R.; Boy, R.; Hartman, M.; Mehraban, N.; Guptaa, B.S.; Tonelli, A.E. Correlation of the stoichiometries of poly(ε-caprolactone) and α-cyclodextrin pseudorotaxanes with their solution rheology and the molecular orientation, crystallite size, and thermomechanical properties of their nanofibers. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 111326–111336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, G.; Gupta, B.S.; Tonelli, A.E. Estimation of the poly (ε-caprolactone) [PCL] and α-cyclodextrin [α-CD] stoichiometric ratios in their inclusion complexes [ICs], and evaluation of porosity and fiber alignment in PCL nanofibers containing these ICs. Data Brief 2015, 5, 1048–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanan, G.; Boy, R.; Gupta, B.S.; Tonelli, A.E. Functional Nanofibers Containing Cyclodextrins. In Polysaccharide-Based Fibers and Composites: Chemical and Engineering Fundamentals and Industrial Applications; Lucia, L., Ayoub, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 29–62. [Google Scholar]
- Narayanan, G.; Bhattacharjee, M.; Nair, L.S.; Laurencin, C.T. Musculoskeletal Tissue Regeneration: The Role of the Stem Cells. Regen. Eng. Transl. Med. 2017, 3, 133–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, G.; Nair, L.S.; Laurencin, C.T. Regenerative Engineering of the Rotator Cuff of the Shoulder. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hein, C.D.; Liu, X.-M.; Wang, D. Click Chemistry, A Powerful Tool for Pharmaceutical Sciences. Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 2216–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, J.; Singh, A.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, L.; Elisseeff, J.H. Multifunctional aliphatic polyester nanofibers for tissue engineering. Biomatter 2012, 2, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oster, M.; Hébraud, A.; Gallet, S.; Lapp, A.; Pollet, E.; Avérous, L.; Schlatter, G. Star-Pseudopolyrotaxane Organized in Nanoplatelets for Poly(ε-caprolactone)-Based Nanofibrous Scaffolds with Enhanced Surface Reactivity. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2015, 36, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oster, M.; Schlatter, G.; Gallet, S.; Baati, R.; Pollet, E.; Gaillard, C.; Avérous, L.; Fajolles, C.; Hébraud, A. The study of the pseudo-polyrotaxane architecture as a route for mild surface functionalization by click chemistry of poly(ε-caprolactone)-based electrospun fibers. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 2181–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Qiu, C.; Narsimhan, G.; Jin, Z. Preparation and Characterization of Ternary Antimicrobial Films of β-Cyclodextrin/Allyl Isothiocyanate/Polylactic Acid for the Enhancement of Long-Term Controlled Release. Materials 2017, 10, 1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathi-Azarbayjani, A.; Chan, S.Y. Single and Multi-Layered Nanofibers for Rapid and Controlled Drug Delivery. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 58, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, C.; Li, X.; Luo, X.; Yang, Y.; Cui, W.; Zou, J.; Zhou, S. Release modulation and cytotoxicity of hydroxycamptothecin-loaded electrospun fibers with 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin inoculations. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 391, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudakaran, S.V.; Venugopal, J.R.; Vijayakumar, G.P.; Abisegapriyan, S.; Grace, A.N.; Ramakrishna, S. Sequel of MgO nanoparticles in PLACL nanofibers for anti-cancer therapy in synergy with curcumin/β-cyclodextrin. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 71, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aytac, Z.; Uyar, T. Core-shell nanofibers of curcumin/cyclodextrin inclusion complex and polylactic acid: Enhanced water solubility and slow release of curcumin. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 518, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liang, X.; Zhang, R.; Lan, W.; Qin, W. Fabrication of Electrospun Polylactic Acid/Cinnamaldehyde/β-Cyclodextrin Fibers as an Antimicrobial Wound Dressing. Polymers 2017, 9, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayaci, F.; Umu, O.C.O.; Tekinay, T.; Uyar, T. Antibacterial Electrospun Poly(lactic acid) (PLA) Nanofibrous Webs Incorporating Triclosan/Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complexes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 3901–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, P.; Zhu, D.-H.; Feng, K.; Liu, F.-J.; Lou, W.-Y.; Li, N.; Zong, M.-H.; Wu, H. Fabrication of electrospun polylactic acid nanofilm incorporating cinnamon essential oil/β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex for antimicrobial packaging. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 996–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aytac, Z.; Kusku, S.I.; Durgun, E.; Uyar, T. Encapsulation of gallic acid/cyclodextrin inclusion complex in electrospun polylactic acid nanofibers: Release behavior and antioxidant activity of gallic acid. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 63, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurarslan, A.; Joijode, A.; Shen, J.; Narayanan, G.; Antony, G.; Li, S.; Caydamli, Y.; Tonelli, A.E. Reorganizing Polymer Chains with Cyclodextrins. Polymers 2017, 9, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Narayanan, G.; Shen, J.; Boy, R.; Gupta, B.S.; Tonelli, A.E. Aliphatic Polyester Nanofibers Functionalized with Cyclodextrins and Cyclodextrin-Guest Inclusion Complexes. Polymers 2018, 10, 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10040428
Narayanan G, Shen J, Boy R, Gupta BS, Tonelli AE. Aliphatic Polyester Nanofibers Functionalized with Cyclodextrins and Cyclodextrin-Guest Inclusion Complexes. Polymers. 2018; 10(4):428. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10040428
Chicago/Turabian StyleNarayanan, Ganesh, Jialong Shen, Ramiz Boy, Bhupender S. Gupta, and Alan E. Tonelli. 2018. "Aliphatic Polyester Nanofibers Functionalized with Cyclodextrins and Cyclodextrin-Guest Inclusion Complexes" Polymers 10, no. 4: 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10040428
APA StyleNarayanan, G., Shen, J., Boy, R., Gupta, B. S., & Tonelli, A. E. (2018). Aliphatic Polyester Nanofibers Functionalized with Cyclodextrins and Cyclodextrin-Guest Inclusion Complexes. Polymers, 10(4), 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10040428