The Preparation of Nano-SiO2/Dialdehyde Cellulose Hybrid Materials as a Novel Cross-Linking Agent for Collagen Solutions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of SiO2/DAC Hybrid Materials
2.3. Characterization of SiO2/DAC Hybrid Materials
2.3.1. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectra of SiO2/DAC
2.3.2. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) of SiO2/DAC
2.3.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA) of SiO2/DAC
2.4. Cross-Linking of Collagen with SiO2/DAC
2.5. Characterization of Cross-Linked Collagen
2.5.1. Sodium Dodecyl Sulphate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) of Collagens
2.5.2. FTIR of Collagens
2.5.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) of Collagens
2.5.4. Oscillatory Rheological Measurements of Collagens
2.5.5. Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FESEM) of Collagens
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of SiO2/DAC Hybrid Materials
3.2. FESEM of SiO2-DAC
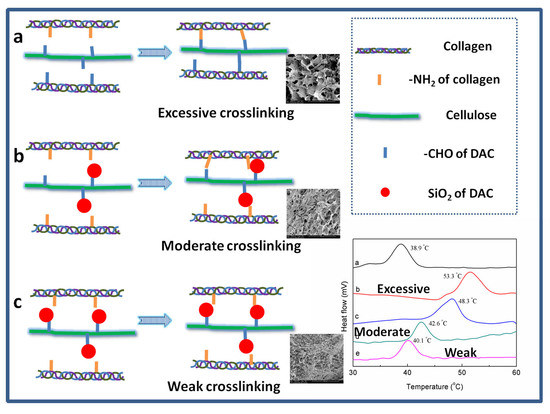
3.3. The Cross-Linking of Collagen Using SiO2/DAC Hybrid Materials as Modifiers
3.4. DSC Thermograms of Cross-Linked Collagens
3.5. Dynamic Rheology Tests of Cross-Linked Collagens
3.6. FESEM of Cross-Linked Collagens
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Patino, M.G.; Neiders, M.E.; Andreana, S.; Noble, B.; Cohen, R.E. Collagen: An overview. Implant Dent. 2002, 11, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, W.E.G.; Relkovic, D.; Ackermann, M.; Wang, S.; Neufurth, M.; Radicevic, A.P.; Ushijima, H.; Schröder, H.C.; Wang, X. Enhancement of Wound Healing in Normal and Diabetic Mice by Topical Application of Amorphous Polyphosphate. Superior Effect of a Host–Guest Composite Material Composed of Collagen (Host) and Polyphosphate (Guest). Polymers 2017, 9, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravamudhan, A.; Ramos, D.M.; Nip, J.; Kalajzic, I.; Kumbar, S.G. Micro-Nanostructures of Cellulose-Collagen for Critical Sized Bone Defect Healing. Macromol. Biosci. 2017, 18, 1700263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, C.N.; Bless, D.M.; Loftus, J.M. Role of injectable collagen in the treatment of glottic insufficiency: A study of 119 patients. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1992, 101, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toung, J.S.; Ogle, R.C.; Morgan, R.F.; Lindsey, W.H. Insulinlike Growth Factor 1– and 2–Augmented Collagen Gel Repair of Facial Osseous Defects. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1999, 125, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrlich, H. Chitin and collagen as universal and alternative templates in biomineralization. Int. Geol. Rev. 2010, 52, 661–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuq, B.; Gontard, N.; Guilbert, S. Proteins as agricultural polymers for packaging production. Cereal Chem. 1998, 75, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friess, W. Collagen–biomaterial for drug delivery1. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 1998, 45, 113–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinemann, S.; Heinemann, C.; Ehrlich, H.; Meyer, M.; Baltzer, H.; Worch, H.; Hanke, T. A novel biomimetic hybrid material made of silicified collagen: Perspectives for bone replacement. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2007, 9, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, H.; Wysokowski, M.; Żółtowskaaksamitowska, S.; Petrenko, I.; Jesionowski, T. Collagens of Poriferan Origin. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gough, J.E.; Scotchford, C.A.; Downes, S. Cytotoxicity of glutaraldehyde crosslinked collagen/poly (vinyl alcohol) films is by the mechanism of apoptosis. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2002, 61, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usha, R.; Ramasami, T. Effect of crosslinking agents (basic chromium sulfate and formaldehyde) on the thermal and thermomechanical stability of rat tail tendon collagen fibre. Thermochim. Acta 2000, 356, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rault, I.; Frei, V.; Herbage, D.; Abdul-Malak, N.; Huc, A. Evaluation of different chemical methods for cros-linking collagen gel, films and sponges. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1996, 7, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffel, D.L.S.; Hebling, J.; Scheffel, R.H.; Agee, K.A.; Cadenaro, M.; Turco, G.; Breschi, L.; Mazzoni, A.; de Souza Costa, C.A.; Pashley, D.H. Stabilization of dentin matrix after cross-linking treatments, in vitro. Dent. Mater. 2014, 30, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, H.; Murabayashi, S.; Mitamura, Y.; Taguchi, T. Characterization of alkali-treated collagen gels prepared by different crosslinkers. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2008, 19, 1297–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connell, D.W.; Birkinshaw, C.; O’Dwyer, T.F. Heavy metal adsorbents prepared from the modification of cellulose: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 6709–6724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.; Liu, R.; Huang, Y. Graft modification of cellulose: Methods, properties and applications. Polymer 2015, 70, A1–A16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wan, Y.; Li, L.; Liang, H.; Wang, J. Preparation and characterization of 2,3-dialdehyde bacterial cellulose for potential biodegradable tissue engineering scaffolds. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2009, 29, 1635–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanth, S.V.; Ramaraj, A.; Rao, J.R.; Nair, B.U. Stabilization of type I collagen using dialdehyde cellulose. Process Biochem. 2009, 44, 869–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, J.; Ding, C.; Liu, W.; Li, G. The rheological and structural properties of fish collagen cross-linked by N-hydroxysuccinimide activated adipic acid. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 30, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Li, L.; Shi, B.; He, Q.; Peng, B. Characteristics of leather tanned with nano-SiO2. J. Am. Leather Chem. Assoc. 2005, 100, 22–28. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, L.; Jiao, K.; Qi, Y.; Yiu, C.K.Y.; Ryou, H.; Arola, D.D.; Chen, J.; Breschi, L.; Pashley, D.H.; Tay, F.R. Infiltration of Silica Inside Fibrillar Collagen. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 123, 11892–11895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yang, J.; Ding, C.; Huang, L.; Chen, L. A novel strategy to fabricate water-soluble collagen using poly(γ-glutamic acid)-derivatives as dual-functional modifier. React. Funct. Polym. 2018, 122, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, A.; Kulkarni, M. Oxidation of cellulose under controlled conditions. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2002, 77, 25–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, U.-J.; Kuga, S. Thermal decomposition of dialdehyde cellulose and its nitrogen-containing derivatives. Thermochim. Acta 2001, 369, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of Structural Proteins during the Assembly of the Head of Bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Yang, Z.; Peng, Y.; Han, B.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, W. Preparation, characterization and feasibility study of dialdehyde carboxymethyl cellulose as a novel crosslinking reagent. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 137, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, U.-J.; Kuga, S.; Wada, M.; Okano, T.; Kondo, T. Periodate oxidation of crystalline cellulose. Biomacromolecules 2000, 1, 488–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowen, J.W.; Forziati, F.H.; Reeves, R.E. Spectrophotometric Evidence for the Absence of Free Aldehyde Groups in Periodate-oxidized Cellulose1. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1951, 73, 4484–4487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Zou, P.; Xiong, H.; Tang, H. Effect of nano-SiO2 on the performance of starch/polyvinyl alcohol blend films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 72, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ding, C.; Chen, L.; Huang, L. The preparation of cellulose/collagen composite films using 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate as a solvent. BioResources 2014, 9, 756–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshk, S.; Sameshima, K. Influence of lignosulfonate on crystal structure and productivity of bacterial cellulose in a static culture. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2006, 40, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, A.J.; Chavan, V.B. A study of crystallinity changes in oxidised celluloses. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1995, 49, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eglin, D.; Maalheem, S.; Livage, J.; Coradin, T. In vitro apatite forming ability of type I collagen hydrogels containing bioactive glass and silica sol-gel particles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2006, 17, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Wu, K.; Li, G. Interactions of collagen molecules in the presence of N-hydroxysuccinimide activated adipic acid (NHS-AA) as a crosslinking agent. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 49, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, C.; Zhang, M.; Li, G. Rheological properties of collagen/hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (COL/HPMC) blended solutions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, G. Non-isothermal kinetic analysis of the thermal denaturation of type I collagen in solution using isoconversional and multivariate non-linear regression methods. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 2233–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, D.G.; Rhee, W.; Reihanian, H.; Ksander, G.; Lee, R.; Braun, W.B.; Weiss, B.A.; Pharriss, B.B. Injectable cross-linked collagen with improved flow properties. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1989, 23, 931–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.-L.; Kaufman, L.J. Rheology and confocal reflectance microscopy as probes of mechanical properties and structure during collagen and collagen/hyaluronan self-assembly. Biophys. J. 2009, 96, 1566–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ruqaie, I.M.; Kasapis, S.; Abeysekera, R. Structural properties of pectin-gelatin gels. Part II: Effect of sucrose/glucose syrup. Carbohydr. Polym. 1997, 34, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, M.; Hellen, L.; Hirvonen, J.; Yliruusi, J. Rheological properties of creams with four different surfactant combinations-effect of storage time and conditions. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 221, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, B.; Yang, X.; Shi, R.; Zhang, M. The Preparation of Nano-SiO2/Dialdehyde Cellulose Hybrid Materials as a Novel Cross-Linking Agent for Collagen Solutions. Polymers 2018, 10, 550. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10050550
Ding C, Zhang Y, Yuan B, Yang X, Shi R, Zhang M. The Preparation of Nano-SiO2/Dialdehyde Cellulose Hybrid Materials as a Novel Cross-Linking Agent for Collagen Solutions. Polymers. 2018; 10(5):550. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10050550
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Cuicui, Yang Zhang, Binhan Yuan, Xiaodong Yang, Ronghui Shi, and Min Zhang. 2018. "The Preparation of Nano-SiO2/Dialdehyde Cellulose Hybrid Materials as a Novel Cross-Linking Agent for Collagen Solutions" Polymers 10, no. 5: 550. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10050550
APA StyleDing, C., Zhang, Y., Yuan, B., Yang, X., Shi, R., & Zhang, M. (2018). The Preparation of Nano-SiO2/Dialdehyde Cellulose Hybrid Materials as a Novel Cross-Linking Agent for Collagen Solutions. Polymers, 10(5), 550. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10050550