A Computer Color-Matching Study of Reverse Micellar Dyeing of Wool with Reactive Dyes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of Calibration Curvex
2.3. Simulated Dyeing
2.4. Plot of Calibration Curves
2.5. Dye Recipe Prediction
2.6. The CIE L*a*b* Value Measurement
2.7. Levelness Measurement
3. Results
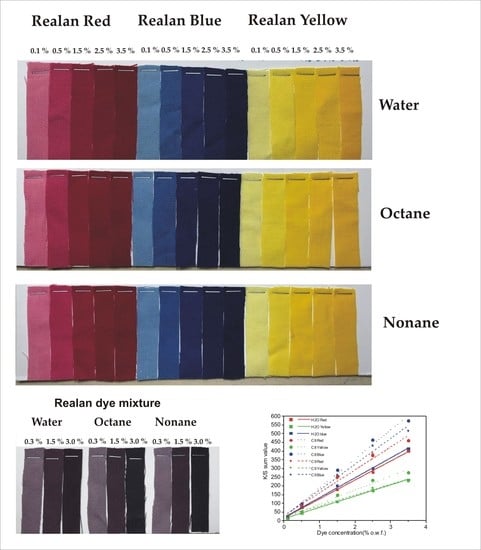
3.1. Reflectance Values of the Dyed Samples
3.2. CIE L*a*b* Values
3.3. Computer Color-Matching
3.3.1. Linearity of the Calibration Curves
3.3.2. CCM Results
3.4. Levelness
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Long, J.J.; Cui, C.-L.; Wang, L.; Xu, H.M.; Yu, Z.J.; Bi, X.P. Effect of treatment pressure on wool fiber in supercritical carbon dioxide fluid. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 43, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Gao, P.; Ma, H. The effect of tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine on the dyeing of wool fabrics with natural dyes. Dyes Pigment. 2014, 108, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, C.W.; Yuen, C.W.M.; Hung, O.N. Improving the pilling property of knitted wool fabric with atmospheric pressure plasma treatment. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 228 (Suppl. 1), S588–S592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, P.K.; Rastogi, D.; Jassal, M.; Agrawal, A.K. Effect of atmospheric pressure helium plasma on felting and low temperature dyeing of wool. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 124, 4289–4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christie, R.M. The Chemistry of Colour Application; Blackwell Science: Oxford, UK; Malden, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Broadbent, A.D. Basic Principles of Textile Coloration (Textile Coloration); Society of Dyers and Colorists: Bradford, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Wang, B.; Chen, J.; Ruan, X.; Yang, Y. Characterization of dimethyl sulfoxide-treated wool and enhancement of reactive wool dyeing in non-aqueous medium. Text. Res. J. 2016, 86, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.J.; Lewis, D.M.; Jia, B.H. Improved reactive dyeing of wool with novel trifunctional reactive dyes. Color. Technol. 2007, 123, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi-Kiakhani, M.; Safapour, S. Eco-friendly dyeing of treated wool fabrics with reactive dyes using chitosanpoly(propylene imine) dendreimer hybrid. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2015, 17, 1019–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jocić, D.; Julià, M.R.; Erra, P. Application of a chitosan/nonionic surfactant mixture to wool assessed by dyeing with a reactive dye. J. Soc. Dyers Colour. 1997, 113, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, M.S. Application of chitosan/nonionic surfactant mixture in reactive dyes for dyeing wool fabrics. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2001, 80, 2859–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; He, J.X.; Zhan, Y.Z. Research in the cold pad–batch dyeing process for wool pretreated by hydrogen peroxide. Color. Technol. 2009, 125, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naebe, M.; Cookson, P.G.; Rippon, J.A.; Wang, X.G. Effects of leveling agent on the uptake of reactive dyes by untreated and plasma-treated wool. Text. Res. J. 2010, 80, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yan, H.; Mao, N. Functional modification with TiO2 nanoparticles and simultaneously dyeing of wool fibers in a one-pot hydrothermal process. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 2030–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z. Study of dyeing properties of wool fabrics treated with microwave. J. Text. Inst. 2016, 107, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendhe, P.; Arolkar, G.; Shukla, S.; Deshmukh, R. Low-temperature plasma processing for the enhancement of surface properties and dyeability of wool fabric. J. Appl. Sci. 2016, 133, 43097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Wei, X.C.; Long, J.J. Ecofriendly synthesis and application of special disperse reactive dyes in waterless coloration of wool with supercritical carbon dioxide. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 133, 746–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, J.I.N.R.; Genovez, M.C.; Hrdina, R. Controlling Exhaustion of Reactive Dyes on Wool by Microencapsulation with Liposomes. Text. Res. J. 1997, 67, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Zawahry, M.M.; El-Shami, S.; El-Mallah, M.H. Optimizing a wool dyeing process with reactive dye by liposome microencapsulation. Dyes Pigment. 2007, 74, 684–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussa, A.; El Ghali, A.; Ellouzi, S.; Sakli, F. Color and fastness study of wool dyeing in multiple reuse dye baths using acid and reactive dyestuffs in laboratory scale. J. Text. Inst. 2013, 104, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadbent, P.J.; Carr, C.M.; Rigout, M.; Kistamah, N.; Choolun, J.; Radhakeesoonb, C.L.; Uddinc, M.A. Investigation into the dyeing of wool with Lanasol and Remazol reactive dyes in seawater. Color. Technol. 2018, 134, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhavsar, P.S.; Zoccola, M.; Patrucco, A.; Montarsolo, A.; Mossotti, R.; Giansetti, M.; Rovero, G.; Maier, S.S.; Muresan, A.; Tonin, C. Superheated water hydrolyzed keratin: A new application as a foaming agent in foam dyeing of cotton and wool fabrics. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 9150–9159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeil, S.J.; McCall, R.A. Ultrasound for wool dyeing and finishing. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2011, 18, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanislav, A.; Fogorasi, M.; Stanescu, M.D.; Muntean, S.; Dochia, M. Ultrasound effect on dyeing wool fibers with two anthraquinone dyes. Fibers Polym. 2015, 16, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.M.; Bhagvandas, M. Sustainable ultrasound-assisted ultralow liquor ratio dyeing of wool textiles with an acid dye. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, J.S.; Davie, A.S.; Scammells, P.J.; Tucker, D.J. Lanasol dyes and wool fibres. Part I: Model studies on the mechanism of dye fixation in a mixed solvent system. Dyes Pigment. 1998, 39, 291–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, K.; Takagi, T.; Jun, J.H.; Ueda, M.; Lewis, D.M. Dyeing natural fibres in supercritical carbon dioxide using a nonionic surfactant reverse micellar system. Color. Technol. 2002, 118, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, K.; Jun, J.H.; Ueda, M. Dyeing of natural fibres from perfluoro-polyether reverse micelles in supercritical carbon dioxide. Color. Technol. 2003, 119, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, K.; Ueda, M. Dyeing of protein fiber in a reverse micellar system. Dyes Pigment. 2003, 58, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.; Bach, E.; Schollmeyer, E. The dyeing of natural fibres with reactive disperse dyes in supercritical carbon dioxide. Dyes Pigment. 2003, 56, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Kraan, M.; Fernandez Cid, M.V.; Woerlee, G.F.; Veugelers, W.J.T.; Witkamp, G.J. Dyeing of natural and synthetic textiles in supercritical carbon dioxide with disperse reactive dyes. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2007, 40, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, X.; Yan, J.; Zheng, L. An ecofriendly dyeing of wool with supercritical carbon dioxide fluid. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 143, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pileni, M. Reverse micelles as microreactors. J. Phys. Chem. 1993, 97, 6961–6973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyravi, A.; Gashti, M.P.; Hosseini, S.H. Chemical grafting of disperse dyes onto polyacrylonitrile: A novel method for coloration of fibers. Fibers Polym. 2014, 15, 2307–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gashti, M.P. New insight into compressive shrinkage finishing in a garment company: The effects on physical, mechanical and colorimetric properties of cotton woven fabrics. Fibers Polym. 2016, 17, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimia, I.; Gashti, M.P.; Sarafpour, M. Photocatalytic discoloration of denim using advanced oxidation process with H2O2/UV. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2018, 360, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimia, I.; Gashti, M.P. Extraction of polyphenolic dyes from henna, pomegranate rind, and Pterocarya fraxinifolia for nylon 6 dyeing. Color. Technol. 2016, 132, 162–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiumarsi, A.; Gashti, M.P.; Salehi, P.; Dayeni, M. Extraction of dyes from Delphinium Zalil flowers and dyeing silk yarns. J. Text. Inst. 2017, 108, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.M.; Lee, C.H.; Tang, A.Y.L.; Kan, C.W. Dyeing cotton in alkane solvent using polyethylene glycol-based reverse micelle as reactive dye carrier. Cellulose 2016, 23, 965–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, A.Y.L.; Lee, C.H.; Wang, Y.M.; Kan, C.W. Octane-assisted reverse micellar dyeing of cotton with reactive dyes. Polymers 2017, 9, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, A.Y.L.; Wang, Y.M.; Lee, C.H.; Kan, C.W. Computer color matching and levelness of PEG-based reverse micellar decamethyl cyclopentasiloxane (D5) solvent-assisted reactive dyeing on cotton fiber. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, A.Y.L.; Lee, C.H.; Wang, Y.M.; Kan, C.W. Dyeing properties of cotton with reactive dye in nonane nonaqueous reverse micelle system. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 2812–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, A.Y.L.; Lee, C.H.; Wang, Y.M.; Kan, C.W. Effect of hydrophilic-lipophilic balance (HLB) values of PEG-based non-ionic surfactant on reverse micellar dyeing of cotton fibre with reactive dyes in non-aqueous medium. Fibers Polym. 2018, 19, 894–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, A.Y.L.; Wang, Y.M.; Lee, C.H.; Kan, C.W. Comparison of computer colour matching of water-based and solvent-based reverse micellar dyeing of cotton fibre. Color. Technol. 2018, 134, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, J.H. Controlling Colourant Formulation in Total Colour Management in Textiles; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2006; pp. 136–159. [Google Scholar]
- Gulrajani, M. Colour Measurement: Principles, Advances and Industrial Applications; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Chong, C.; Li, S.; Yeung, K. An objective method for the assessment of levelness of dyed materials. J. Soc. Dyers Colour. 1992, 108, 528–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Wool-to-solvent weight ratio (w/v) | 1:10 |
| Surfactant-to-co-surfactant molar ratio | 1:8 |
| Surfactant-to-water molar ratio | 0.04:1 |
| Water-pool volume for dye (mL) | 0.5 |
| Dyeing time (min) | 50 |
| Dyeing temperature (°C) | 88 |
| Liquid Ratio 50:1, 98 °C | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dye | % of weight of wool fiber (% owf) | 0.1 | 0.5 | 1.5 | 2.5 | 3.5 |
| Salt (Na2SO4) | g/L | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| pH | 5 | 4.5 | 4.2 | 4 | 3.8 | |
| Solvent | Standard Sample | Red (%) | Yellow (%) | Blue (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | Sample 1 | 0.100 | 0.100 | 0.100 |
| Sample 2 | 0.500 | 0.500 | 0.500 | |
| Sample 3 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | |
| Octane | Sample 4 | 0.100 | 0.100 | 0.100 |
| Sample 5 | 0.500 | 0.500 | 0.500 | |
| Sample 6 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | |
| Nonane | Sample 7 | 0.100 | 0.100 | 0.100 |
| Sample 8 | 0.500 | 0.500 | 0.500 | |
| Sample 9 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Visual Appearance of Levelness | RUI |
|---|---|
| Excellent (unlevelness not detectable) | <0.2 |
| Good (noticeable unlevelness under close examination) | 0.2–0.49 |
| Poor (apparent unlevelness) | 0.5–1.0 |
| Bad (conspicuous unlevelness) | >1.0 |
| Solvent | Water | Octane | Nonane | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample (%) | L* | a* | b* | L* | a* | b* | L* | a* | b* |
| Red 0.1 | 61.337 | 31.254 | −1.043 | 59.61 | 35.431 | −0.864 | 60.768 | 33.315 | 0.030 |
| Red 0.5 | 47.070 | 45.574 | 1.972 | 46.484 | 48.976 | 1.939 | 46.213 | 49.451 | 2.772 |
| Red 1.5 | 38.009 | 49.965 | 6.687 | 35.454 | 52.490 | 9.185 | 35.691 | 51.966 | 8.551 |
| Red 2.5 | 33.238 | 49.285 | 9.580 | 31.108 | 50.184 | 12.679 | 33.507 | 53.042 | 16.384 |
| Red 3.5 | 29.518 | 47.711 | 12.063 | 28.775 | 48.130 | 15.538 | 28.382 | 47.09 | 15.652 |
| Yellow 0.1 | 79.059 | -5.516 | 35.130 | 80.338 | −5.813 | 36.958 | 80.371 | −6.052 | 38.364 |
| Yellow 0.5 | 76.850 | -2.476 | 61.000 | 77.565 | −2.974 | 65.359 | 76.918 | −1.931 | 65.065 |
| Yellow 1.5 | 74.322 | 3.117 | 78.398 | 74.937 | 3.941 | 84.543 | 74.800 | 4.522 | 84.212 |
| Yellow 2.5 | 73.081 | 7.676 | 86.107 | 73.450 | 7.847 | 91.897 | 73.174 | 8.393 | 88.616 |
| Yellow 3.5 | 70.665 | 14.771 | 90.549 | 71.927 | 11.824 | 93.782 | 71.920 | 11.288 | 90.928 |
| Blue 0.1 | 62.619 | −7.199 | −12.262 | 61.184 | −7.351 | −15.578 | 60.811 | −7.413 | −15.078 |
| Blue 0.5 | 43.906 | −5.392 | −22.837 | 40.789 | −5.312 | −24.752 | 40.515 | −5.380 | −24.244 |
| Blue 1.5 | 30.788 | −2.005 | −25.929 | 26.587 | −1.112 | −26.841 | 27.289 | −1.869 | −24.966 |
| Blue 2.5 | 25.727 | −0.193 | −25.902 | 20.334 | 1.545 | −24.503 | 20.67 | 0.629 | −21.704 |
| Blue 3.5 | 21.181 | 1.884 | −23.685 | 17.507 | 2.150 | −21.859 | 18.066 | 1.871 | −19.012 |
| Dyeing Medium | R2 Value |
|---|---|
| Water (red) | 0.998 |
| Water (yellow) | 0.999 |
| Water (blue) | 0.997 |
| Octane (red) | 0.976 |
| Octane (yellow) | 0.977 |
| Octane (blue) | 0.987 |
| Nonane (red) | 0.978 |
| Nonane (yellow) | 0.952 |
| Nonane (blue) | 0.980 |
| Formulae | Color | Water-Based Wool Dyeing | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 1 (0.3%) | Sample 2 (1.5%) | Sample 3 (3%) | ||
| Theoretical | Red | 0.100 | 0.500 | 1.000 |
| Yellow | 0.100 | 0.500 | 1.000 | |
| Blue | 0.100 | 0.500 | 1.000 | |
| CIE L*a*b* | Red | 0.108 | 0.477 | 1.021 |
| Yellow | 0.114 | 0.488 | 0.974 | |
| Blue | 0.095 | 0.554 | 1.081 | |
| CIE L*u*v* | Red | 0.108 | 0.477 | 1.021 |
| Yellow | 0.114 | 0.488 | 0.974 | |
| Blue | 0.095 | 0.554 | 1.081 | |
| ANLAB | Red | 0.108 | 0.477 | 1.021 |
| Yellow | 0.114 | 0.488 | 0.974 | |
| Blue | 0.095 | 0.554 | 1.081 | |
| Hunter lab | Red | 0.108 | 0.477 | 1.021 |
| Yellow | 0.114 | 0.488 | 0.974 | |
| Blue | 0.095 | 0.554 | 1.081 | |
| FMC2 | Red | 0.108 | 0.477 | 1.021 |
| Yellow | 0.114 | 0.488 | 0.974 | |
| Blue | 0.095 | 0.554 | 1.081 | |
| JPC79 | Red | 0.108 | 0.477 | 1.021 |
| Yellow | 0.114 | 0.488 | 0.974 | |
| Blue | 0.095 | 0.554 | 1.081 | |
| CMC 1.0 | Red | 0.108 | 0.477 | 1.021 |
| Yellow | 0.114 | 0.488 | 0.974 | |
| Blue | 0.095 | 0.554 | 1.081 | |
| BFD 1.0 | Red | 0.108 | 0.477 | 1.021 |
| Yellow | 0.114 | 0.488 | 0.974 | |
| Blue | 0.095 | 0.554 | 1.081 | |
| CIE94 1.0 | Red | 0.108 | 0.477 | 1.021 |
| Yellow | 0.114 | 0.488 | 0.974 | |
| Blue | 0.095 | 0.554 | 1.081 | |
| Formulae | Color | Octane Wool Dyeing | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 4 (0.3%) | Sample 5 (1.5%) | Sample 6 (3%) | ||
| Theoretical | Red | 0.100 | 0.500 | 1.000 |
| Yellow | 0.100 | 0.500 | 1.000 | |
| Blue | 0.100 | 0.500 | 1.000 | |
| CIE L*a*b* | Red | 0.080 | 0.543 | 1.144 |
| Yellow | 0.113 | 0.439 | 0.971 | |
| Blue | 0.105 | 0.459 | 0.959 | |
| CIE L*u*v* | Red | 0.080 | 0.543 | 1.144 |
| Yellow | 0.113 | 0.439 | 0.971 | |
| Blue | 0.105 | 0.459 | 0.959 | |
| ANLAB | Red | 0.080 | 0.543 | 1.144 |
| Yellow | 0.113 | 0.439 | 0.971 | |
| Blue | 0.105 | 0.459 | 0.959 | |
| Hunter lab | Red | 0.080 | 0.543 | 1.144 |
| Yellow | 0.113 | 0.439 | 0.971 | |
| Blue | 0.105 | 0.459 | 0.959 | |
| FMC2 | Red | 0.080 | 0.543 | 1.144 |
| Yellow | 0.113 | 0.439 | 0.971 | |
| Blue | 0.105 | 0.459 | 0.959 | |
| JPC79 | Red | 0.080 | 0.543 | 1.144 |
| Yellow | 0.113 | 0.439 | 0.971 | |
| Blue | 0.105 | 0.459 | 0.959 | |
| CMC 1.0 | Red | 0.080 | 0.543 | 1.144 |
| Yellow | 0.113 | 0.439 | 0.971 | |
| Blue | 0.105 | 0.459 | 0.959 | |
| BFD 1.0 | Red | 0.080 | 0.543 | 1.144 |
| Yellow | 0.113 | 0.439 | 0.971 | |
| Blue | 0.105 | 0.459 | 0.959 | |
| CIE94 1.0 | Red | 0.080 | 0.543 | 1.144 |
| Yellow | 0.113 | 0.439 | 0.971 | |
| Blue | 0.105 | 0.459 | 0.959 | |
| Formulae | Color | Nonane Solvent-Assisted Dyeing | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 7 (0.3%) | Sample 8 (1.5%) | Sample 9 (3%) | ||
| Theoretical | Red | 0.100 | 0.500 | 1.000 |
| Yellow | 0.100 | 0.500 | 1.000 | |
| Blue | 0.100 | 0.500 | 1.000 | |
| CIE L*a*b* | Red | 0.086 | 0.530 | 1.107 |
| Yellow | 0.081 | 0.428 | 0.960 | |
| Blue | 0.097 | 0.464 | 0.952 | |
| CIE L*u*v* | Red | 0.086 | 0.530 | 1.107 |
| Yellow | 0.081 | 0.428 | 0.960 | |
| Blue | 0.097 | 0.464 | 0.952 | |
| ANLAB | Red | 0.086 | 0.530 | 1.107 |
| Yellow | 0.081 | 0.428 | 0.960 | |
| Blue | 0.097 | 0.464 | 0.952 | |
| Hunter lab | Red | 0.086 | 0.530 | 1.107 |
| Yellow | 0.081 | 0.428 | 0.960 | |
| Blue | 0.097 | 0.464 | 0.952 | |
| FMC2 | Red | 0.086 | 0.530 | 1.107 |
| Yellow | 0.081 | 0.428 | 0.960 | |
| Blue | 0.097 | 0.464 | 0.952 | |
| JPC79 | Red | 0.086 | 0.530 | 1.107 |
| Yellow | 0.081 | 0.428 | 0.960 | |
| Blue | 0.097 | 0.464 | 0.952 | |
| CMC 1.0 | Red | 0.086 | 0.530 | 1.107 |
| Yellow | 0.081 | 0.428 | 0.960 | |
| Blue | 0.097 | 0.464 | 0.952 | |
| BFD 1.0 | Red | 0.086 | 0.530 | 1.107 |
| Yellow | 0.081 | 0.428 | 0.960 | |
| Blue | 0.097 | 0.464 | 0.952 | |
| CIE94 1.0 | Red | 0.086 | 0.530 | 1.107 |
| Yellow | 0.081 | 0.428 | 0.960 | |
| Blue | 0.097 | 0.464 | 0.952 | |
| Percentage Difference (%) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Formulae | Color | Water-Based Dyeing (%) | Octane Dyeing (%) | Nonane Dyeing (%) | ||||||
| Sample1 (0.3%) | Sample2 (1.5%) | Sample3 (3%) | Sample4 (0.3%) | Sample5 (1.5%) | Sample6 (3%) | Sample7 (0.3%) | Sample8 (1.5%) | Sample9 (3%) | ||
| CIE L*a*b* | Red | ↑8.00 | ↓4.60 | ↑2.10 | ↓20.00 | ↑8.60 | ↑14.40 | ↓14.00 | ↑6.00 | ↑10.70 |
| Yellow | ↑14.00 | ↓2.40 | ↓2.70 | ↑13.00 | ↓12.20 | ↓2.90 | ↓19.00 | ↓14.40 | ↓4.00 | |
| Blue | ↓5.00 | ↑10.80 | ↑8.10 | ↑5.00 | ↓8.20 | ↓4.10 | ↓3.00 | ↓7.20 | ↓4.70 | |
| CIE L*u*v* | Red | ↑8.00 | ↓4.60 | ↑2.10 | ↓20.00 | ↑8.60 | ↑14.40 | ↓14.00 | ↑6.00 | ↑10.70 |
| Yellow | ↑14.00 | ↓2.40 | ↓2.70 | ↑13.00 | ↓12.20 | ↓2.90 | ↓19.00 | ↓14.40 | ↓4.00 | |
| Blue | ↓5.00 | ↑10.80 | ↑8.10 | ↑5.00 | ↓8.20 | ↓4.10 | ↓3.00 | ↓7.20 | ↓4.70 | |
| ANLAB | Red | ↑8.00 | ↓4.60 | ↑2.10 | ↓20.00 | ↑8.60 | ↑14.40 | ↓14.00 | ↑6.00 | ↑10.70 |
| Yellow | ↑14.00 | ↓2.40 | ↓2.70 | ↑13.00 | ↓12.20 | ↓2.90 | ↓19.00 | ↓14.40 | ↓4.00 | |
| Blue | ↓5.00 | ↑10.80 | ↑8.10 | ↑5.00 | ↓8.20 | ↓4.10 | ↓3.00 | ↓7.20 | ↓4.70 | |
| Hunter lab | Red | ↑8.00 | ↓4.60 | ↑2.10 | ↓20.00 | ↑8.60 | ↑14.40 | ↓14.00 | ↑6.00 | ↑10.70 |
| Yellow | ↑14.00 | ↓2.40 | ↓2.70 | ↑13.00 | ↓12.20 | ↓2.90 | ↓19.00 | ↓14.40 | ↓4.00 | |
| Blue | ↓5.00 | ↑10.80 | ↑8.10 | ↑5.00 | ↓8.20 | ↓4.10 | ↓3.00 | ↓7.20 | ↓4.70 | |
| FMC2 | Red | ↑8.00 | ↓4.60 | ↑2.10 | ↓20.00 | ↑8.60 | ↑14.40 | ↓14.00 | ↑6.00 | ↑10.70 |
| Yellow | ↑14.00 | ↓2.40 | ↓2.70 | ↑13.00 | ↓12.20 | ↓2.90 | ↓19.00 | ↓14.40 | ↓4.00 | |
| Blue | ↓5.00 | ↑10.80 | ↑8.10 | ↑5.00 | ↓8.20 | ↓4.10 | ↓3.00 | ↓7.20 | ↓4.70 | |
| JPC79 | Red | ↑8.00 | ↓4.60 | ↑2.10 | ↓20.00 | ↑8.60 | ↑14.40 | ↓14.00 | ↑6.00 | ↑10.70 |
| Yellow | ↑14.00 | ↓2.40 | ↓2.70 | ↑13.00 | ↓12.20 | ↓2.90 | ↓19.00 | ↓14.40 | ↓4.00 | |
| Blue | ↓5.00 | ↑10.80 | ↑8.10 | ↑5.00 | ↓8.20 | ↓4.10 | ↓3.00 | ↓7.20 | ↓4.70 | |
| CMC 1.0 | Red | ↑8.00 | ↓4.60 | ↑2.10 | ↓20.00 | ↑8.60 | ↑14.40 | ↓14.00 | ↑6.00 | ↑10.70 |
| Yellow | ↑14.00 | ↓2.40 | ↓2.70 | ↑13.00 | ↓12.20 | ↓2.90 | ↓19.00 | ↓14.40 | ↓4.00 | |
| Blue | ↓5.00 | ↑10.80 | ↑8.10 | ↑5.00 | ↓8.20 | ↓4.10 | ↓3.00 | ↓7.20 | ↓4.70 | |
| BFD 1.0 | Red | ↑8.00 | ↓4.60 | ↑2.10 | ↓20.00 | ↑8.60 | ↑14.40 | ↓14.00 | ↑6.00 | ↑10.70 |
| Yellow | ↑14.00 | ↓2.40 | ↓2.70 | ↑13.00 | ↓12.20 | ↓2.90 | ↓19.00 | ↓14.40 | ↓4.00 | |
| Blue | ↓5.00 | ↑10.80 | ↑8.10 | ↑5.00 | ↓8.20 | ↓4.10 | ↓3.00 | ↓7.20 | ↓4.70 | |
| CIE94 1.0 | Red | ↑8.00 | ↓4.60 | ↑2.10 | ↓20.00 | ↑8.60 | ↑14.40 | ↓14.00 | ↑6.00 | ↑10.70 |
| Yellow | ↑14.00 | ↓2.40 | ↓2.70 | ↑13.00 | ↓12.20 | ↓2.90 | ↓19.00 | ↓14.40 | ↓4.00 | |
| Blue | ↓5.00 | ↑10.80 | ↑8.10 | ↑5.00 | ↓8.20 | ↓4.10 | ↓3.00 | ↓7.20 | ↓4.70 | |
| Sample | Water | Octane | Nonane | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RUI | Visual | RUI | Visual | RUI | Visual | |
| Red 0.1% | 0.40 | Good | 0.45 | Good | 0.26 | Good |
| Red 0.5% | 0.24 | Good | 0.48 | Good | 0.20 | Good |
| Red 1.5% | 0.13 | Excellent | 0.20 | Good | 0.43 | Good |
| Red 2.5% | 0.14 | Excellent | 0.13 | Excellent | 0.14 | Excellent |
| Red 3.5% | 0.09 | Excellent | 0.44 | Excellent | 0.30 | Good |
| Yellow 0.1% | 0.09 | Excellent | 0.04 | Excellent | 0.05 | Excellent |
| Yellow 0.5% | 0.06 | Excellent | 0.05 | Excellent | 0.12 | Excellent |
| Yellow 1.5% | 0.10 | Excellent | 0.13 | Excellent | 0.04 | Excellent |
| Yellow 2.5% | 0.09 | Excellent | 0.15 | Excellent | 0.08 | Excellent |
| Yellow 3.5% | 0.05 | Excellent | 0.13 | Excellent | 0.05 | Excellent |
| Blue 0.1% | 0.22 | Good | 0.12 | Excellent | 0.31 | Good |
| Blue 0.5% | 0.16 | Excellent | 0.45 | Good | 0.42 | Good |
| Blue 1.5% | 0.46 | Good | 0.17 | Excellent | 0.11 | Excellent |
| Blue 2.5% | 0.08 | Excellent | 0.14 | Excellent | 0.34 | Good |
| Blue 3.5% | 0.08 | Excellent | 0.07 | Excellent | 0.08 | Excellent |
| Mixture 0.3% | 0.19 | Excellent | 0.28 | Excellent | 0.20 | Good |
| Mixture 1.5% | 0.34 | Good | 0.22 | Excellent | 0.29 | Good |
| Mixture 3.0% | 0.08 | Excellent | 0.14 | Excellent | 0.18 | Excellent |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Tang, Y.-l.; Lee, C.-h.; Kan, C.-W. A Computer Color-Matching Study of Reverse Micellar Dyeing of Wool with Reactive Dyes. Polymers 2019, 11, 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11010132
Wang Y, Tang Y-l, Lee C-h, Kan C-W. A Computer Color-Matching Study of Reverse Micellar Dyeing of Wool with Reactive Dyes. Polymers. 2019; 11(1):132. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11010132
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yanming, Yiu-lun Tang, Cheng-hao Lee, and Chi-Wai Kan. 2019. "A Computer Color-Matching Study of Reverse Micellar Dyeing of Wool with Reactive Dyes" Polymers 11, no. 1: 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11010132
APA StyleWang, Y., Tang, Y. -l., Lee, C. -h., & Kan, C. -W. (2019). A Computer Color-Matching Study of Reverse Micellar Dyeing of Wool with Reactive Dyes. Polymers, 11(1), 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11010132