Computer-Aided Design of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Simultaneous Detection of Clenbuterol and Its Metabolites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Selection of Functional Monomer
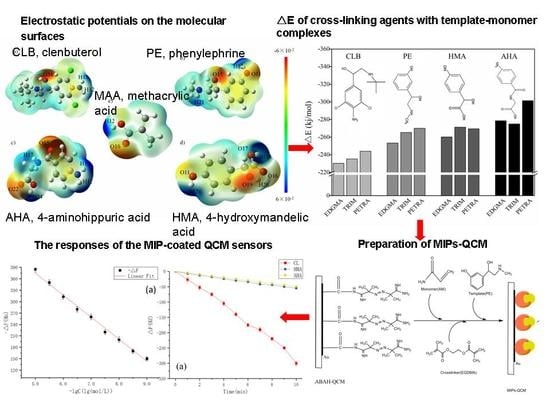
2.2. Analysis of Reaction Sites
2.3. Construction of Template-Monomer Complexes
2.4. AIM Topology Analysis
2.5. Cross-Linking Agent Screening
2.6. Selection of Solvent
2.7. Selectivity Examination by Computational Simulation
2.8. Preparation of MIP-QCM and Measurement of Sensors Response
2.8.1. Surface Cleaning of QCM Gold Electrode
2.8.2. Self-Assembled Monolayer (SAM) of QCM
2.8.3. Preparation of AIBN-QCM
2.8.4. In Situ Preparation of MIPs
2.8.5. MIP-QCM Performance Test
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Theoretical Selection of Functional Monomer
3.2. Theoretical Selection of Template Molecules and Determination of Functional Monomer Site of Action
3.3. Formation of the Template-Monomer Complexes
3.4. AIM Topology Analysis
3.5. Theoretical Selection of Crosslinker
3.6. Theoretical Selection of Solvent
3.7. Selectivity Simulation
3.8. Experimental Verification
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Blomgren, A.; Berggren, C.; Holmberg, A.; Larsson, F.; Sellergren, B.; Ensing, K. Extraction of clenbuterol from calf urine using a molecularly imprinted polymer followed by quantitation by high-performance liquid chromatography with UV detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 975, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.Y. Health hazards due to clenbuterol residues in food. J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol. 1999, 37, 517–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Qian, Y.; Deng, Y.; Song, W.; Liao, J.; Yang, M.; Lian, Y. Monitoring and analysis on internet public opinion of agro-products quality and safety in China, 2016. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2017, 62, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Nilghaz, A.; Choi, J.R.; Liu, X.; Lu, X. Rapid detection of clenbuterol in milk using microfluidic paper-based elisa. Food Chem. 2018, 246, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amendola, L.; Colamonici, C.; Rossi, F.; Botre, F. Determination of clenbuterol in human urine by GC–MS–MS–MS: Confirmation analysis in antidoping control. J. Chromatogr. B 2002, 773, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Yan, H.; Qiao, F.; Geng, Y. Determination of clenbuterol in porcine tissues using solid-phase extraction combined with ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction and HPLC–UV detection. J. Chromatogr. B 2011, 879, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanca, J.; Muñoz, P.; Morgado, M.; Méndez, N.; Aranda, A.; Reuvers, T.; Hooghuis, H. Determination of clenbuterol, ractopamine and zilpaterol in liver and urine by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 529, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Lei, C.; Zhang, S.; Bai, G.; Zhou, H.; Sun, M.; Fu, Q.; Chang, C. Determination of clenbuterol from pork samples using surface molecularly imprinted polymers as the selective sorbents for microextraction in packed syringe. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 91, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yang, W. Development of a label-free electrochemical immunosensor based on carbon nanotube for rapid determination of clenbuterol. Food Chem. 2009, 112, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirichai, S.; Khanatharana, P. Rapid analysis of clenbuterol, salbutamol, procaterol, and fenoterol in pharmaceuticals and human urine by capillary electrophoresis. Talanta 2008, 76, 1194–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Zhi, A.; Liu, Q.; Yang, J.; Jia, G.; Shervin, J.; Tang, L.; Hu, X.; Deng, R.; Xu, C. Rapid and sensitive detection of β-agonists using a portable fluorescence biosensor based on fluorescent nanosilica and a lateral flow test strip. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 50, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawaya, W.; Lone, K.; Husain, A.; Dashti, B.; Saeed, T. Screening for β-agonists in sheep urine and eyes by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in the state of Kuwait. Food Control 2000, 11, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Wei, Y. Development of an analytical method for the determination of β2-agonist residues in animal tissues by high-performance liquid chromatography with on-line electrogenerated [Cu (HIO6) 2] 5–luminol chemiluminescence detection. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 4949–4956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.-M.; Wei, S.-Y.; Liu, H.-L.; Fang, G.-Z.; Wang, S. Preparation and Evaluation of Core–Shell Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Solid-Phase Extraction and Determination of Sterigmatocystin in Food. Polymers 2017, 9, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Hu, H.; Zhong, W.; Zhang, M.; Ma, Y.; Guo, P.; Xin, M.; Yu, M.; Lin, H. Functionalization of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Microspheres for the Highly Selective Removal of Contaminants from Aqueous Solutions and the Analysis of Food-Grade Fish Samples. Polymers 2018, 10, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Huang, C.; Jiao, Y.; Chen, J. A Phenolphthalein-Dummy Template Molecularly Imprinted Polymer for Highly Selective Extraction and Clean-Up of Bisphenol A in Complex Biological, Environmental and Food Samples. Polymers 2018, 10, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xu, S.; Li, J. Recent advances in molecular imprinting technology: Current status, challenges and highlighted applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 2922–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitcombe, M.J.; Kirsch, N.; Nicholls, I.A. Molecular imprinting science and technology: A survey of the literature for the years 2004–2011. J. Mol. Recognit. 2014, 27, 297–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulff, G. Molecular imprinting in cross-linked materials with the aid of molecular templates—A way towards artificial antibodies. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1995, 34, 1812–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlatakis, G.; Andersson, L.I.; Müller, R.; Mosbach, K. Drug assay using antibody mimics made by molecular imprinting. Nature 1993, 361, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowen, T.; Karim, K.; Piletsky, S. Computational approaches in the design of synthetic receptors—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 936, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piletsky, S.A.; Karim, A.K.; Piletska, E.V.; Day, C.J.; Freebairn, K.W.; Legge, C.; Turner, A.P.F. Recognition of ephedrine enantiomers by molecularly imprinted polymers designed using a computational approach. Analyst 2001, 126, 1826–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadem, M.; Faridbod, F.; Norouzi, P.; Rahimi Foroushani, A.; Ganjali, M.R.; Shahtaheri, S.J.; Yarahmadi, R. Modification of carbon paste electrode based on molecularly imprinted polymer for electrochemical determination of diazinon in biological and environmental samples. Electroanalysis 2017, 29, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogány, P.; Razali, M.; Szekely, G. Experimental and theoretical investigation of the complexation of methacrylic acid and diisopropyl urea. Spectrochim. Acta A 2017, 170, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maouche, N.; Ktari, N.; Bakas, I.; Fourati, N.; Zerrouki, C.; Seydou, M.; Maurel, F.; Chehimi, M.M. A surface acoustic wave sensor functionalized with a polypyrrole molecularly imprinted polymer for selective dopamine detection. J. Mol. Recognit. 2015, 28, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazouz, Z.; Rahali, S.; Fourati, N.; Zerrouki, C.; Aloui, N.; Seydou, M.; Yaakoubi, N.; Chehimi, M.M.; Othmane, A.; Kalfat, R. Highly Selective Polypyrrole MIP-Based Gravimetric and Electrochemical Sensors for Picomolar Detection of Glyphosate. Sensors 2017, 17, 2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terracina, J.J.; Sharfstein, S.T.; Bergkvist, M. In silico characterization of enantioselective molecularly imprinted binding sites. J. Mol. Recognit. 2018, 31, e2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Yan, M.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y. A computational and experimental investigation of the interaction between the template molecule and the functional monomer used in the molecularly imprinted polymer. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 542, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashley, J.; Shukor, Y.; Tothill, I.E. The use of differential scanning fluorimetry in the rational design of plastic antibodies for protein targets. Analyst 2016, 141, 6463–6470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fish, W.P.; Ferreira, J.; Sheardy, R.D.; Snow, N.H.; O’Brien, T.P. Rational Design of an Imprinted Polymer: Maximizing Selectivity by Optimizing the Monomer–Template Ratio for a Cinchonidine MIP, Prior to Polymerization, Using Microcalorimetry. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Rel. Technol. 2005, 28, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Lv, R.; Xu, L. Electrochemical tolazoline sensor based on gold nanoparticles and imprinted poly-o-aminothiophenol film. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 4039–4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, F.; Zheng, J.; Qin, P.; Han, T.; Zhao, D. A novel quartz crystal microbalance sensor array based on molecular imprinted polymers for simultaneous detection of clenbuterol and its metabolites. Talanta 2017, 167, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisch, M.; Trucks, G.; Schlegel, H.; Scuseria, G.; Robb, M.; Cheeseman, J.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G. Gaussian 09, Revision D. 01; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Boys, S.F.; Bernardi, F.D. The calculation of small molecular interactions by the differences of separate total energies. Some procedures with reduced errors. Mol. Phys. 1970, 19, 553–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politzer, P.; Laurence, P.R.; Jayasuriya, K. Molecular electrostatic potentials: An effective tool for the elucidation of biochemical phenomena. Environ. Health Perspect. 1985, 61, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Politzer, P.; Murray, J.S. The fundamental nature and role of the electrostatic potential in atoms and molecules. Theor. Chem. Acc. 2002, 108, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, R.A. Nanomedicine, Volume I: Basic Capabilities; Landes Bioscience: Georgetown, TX, USA, 1999; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Jeffrey, G.A.; Jeffrey, G.A. An Introduction to Hydrogen Bonding; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997; Volume 12. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, T.; Chen, F. Multiwfn: A multifunctional wavefunction analyzer. J. Comput. Chem. 2012, 33, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, R.; Nguyen-Dang, T.T.; Tal, Y. A topological theory of molecular structure. Rep. Prog. Phys. 1981, 44, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bone, R.G.; Bader, R.F. Identifying and analyzing intermolecular bonding interactions in van der Waals molecules. J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 10892–10911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, R.F. A quantum theory of molecular structure and its applications. Chem. Rev. 1991, 91, 893–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempe, M.; Mosbach, K. Molecular imprinting used for chiral separations. J. Chromatogr. A 1995, 694, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Pal, S.; Krupadam, R.J. Computational strategies for understanding the nature of interaction in dioxin imprinted nanoporous trappers. J. Mol. Recognit. 2015, 28, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roux, B.; Simonson, T. Implicit solvent models. Biophys. Chem. 1999, 78, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marenich, A.V.; Cramer, C.J.; Truhlar, D.G. Universal Solvation Model Based on Solute Electron Density and on a Continuum Model of the Solvent Defined by the Bulk Dielectric Constant and Atomic Surface Tensions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 6378–6396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hariharan, P.C.; Pople, J.A. The influence of polarization functions on molecular orbital hydrogenation energies. Theor. Chim. Acta 1973, 28, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, I.A.; Andersson, H.S.; Golker, K.; Henschel, H.; Karlsson, B.C.; Olsson, G.D.; Rosengren, A.M.; Shoravi, S.; Suriyanarayanan, S.; Wiklander, J.G. Rational design of biomimetic molecularly imprinted materials: Theoretical and computational strategies for guiding nanoscale structured polymer development. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 400, 1771–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisch, M.J.; Pople, J.A.; Binkley, J.S. Self-consistent molecular orbital methods 25. Supplementary functions for Gaussian basis sets. J. Chem. Phys. 1984, 80, 3265–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, U.; Popelier, P.L. Characterization of CHO hydrogen bonds on the basis of the charge density. J. Phys. Chem. 1995, 99, 9747–9754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipkowski, P.; Grabowski, S.J.; Robinson, T.L.; Leszczynski, J. Properties of the C−H···H Dihydrogen Bond: An ab Initio and Topological Analysis. J. Phys. Chem. A 2004, 108, 10865–10872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozas, I.; Alkorta, I.; Elguero, J. Behavior of ylides containing N, O, and C atoms as hydrogen bond acceptors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 11154–11161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Type | Strong | Moderate | Weak |
|---|---|---|---|
| interaction type | strongly covalent | mostly electrostatic | electrostat/dispers |
| length of H…A (Å) | 1.2–1.5 | 1.5–2.2 | >2.2 |
| length of X…A (Å) | 2.2–2.5 | 2.5–3.2 | >3.2 |
| Template | Reactive Site | NPA Charge | Template | Reactive Site | NPA Charge |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLB | O34 | −0.781 | PE | O11 | −0.713 |
| H12 | 0.431 | O15 | −0.790 | ||
| H13 | 0.432 | H12 | 0.510 | ||
| N11 | −0.858 | H21 | 0.399 | ||
| N19 | −0.745 | N20 | −0.743 | ||
| HMA | O11 | −0.709 | AHA | O15 | −0.626 |
| O16 | −0.621 | O22 | −0.607 | ||
| O17 | −0.711 | H12 | 0.420 | ||
| O19 | −0.772 | H13 | 0.420 | ||
| H12 | 0.510 | H17 | 0.439 | ||
| H18 | 0.524 | H24 | 0.523 | ||
| H20 | 0.522 | N11 | −0.861 | ||
| N16 | −0.677 |
| Complex | △E (Kcal/mol) | Type | Length (a.u.) | Complex | △E (Kcal/mol) | Type | Length (a.u.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLB + 3MAA | −24.41008997 | C–O…H–O | 1.69824 | PE + 3MAA | −26.767172 | C=O…H–N | 2.40893 |
| C–H…O=C | 2.68041 | C–O…H–O | 1.75467 | ||||
| C=O…H–N | 2.19275 | C=O…H–O | 2.02096 | ||||
| O–H…CL–C(Ring) | 2.48079 | O–H…O–C(Ring) | 1.82306 | ||||
| HMA + 5MAA | −42.36144579 | C=O…H–O | 1.67043 | C(Ring)–H…O=C | 2.30929 | ||
| C=O…H–O | 1.56804 | C–O…H–O | 1.80407 | ||||
| C–O…H–O | 1.77916 | AHA + 5MAA | −47.047349 | C=O…H–O | 1.64880 | ||
| C=O…H–O | 2.09553 | C=O…H–O | 1.61433 | ||||
| O–H…O–C(Ring) | 1.98828 | C=O…H–O | 1.74762 | ||||
| C=O…H–O | 1.77762 | C=O…H–O | 1.74762 | ||||
| O–H…O–C(ring) | 1.84295 | C=O…H–O | 1.64637 | ||||
| C(Ring)–H…O=C | 2.51227 | N–H…O=C | 1.86144 | ||||
| C–O…H–O | 1.92005 | N–H…O=C | 2.11431 | ||||
| C–H…O=C | 2.40054 | C=O…H–O | 1.77100 | ||||
| C(Ring)–H…O=C | 2.54566 |
| Complex | H-bond Length (a.u.) | BCP | ρ(r) (a.u.) | ▽2ρ(r) (a.u.) | V(r) (a.u.) | H(r) (a.u.) | Energy Kcal/mol |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLB + 3MAA | 1.69824 | C–O…H–O | 0.043535397 | 0.127935635 | −0.032649256 | −0.000332674 | −10.24385917 |
| 2.19275 | N–H…O=C | 0.01507693 | 0.045642552 | −0.011384074 | 1.32821E-05 | −3.571807242 | |
| 2.48079 | O–H…CL–C(Ring) | 0.012694051 | 0.038173768 | −0.007446028 | 0.001048707 | −2.336226571 | |
| 2.16356 | N–H…O=C | 0.013996606 | 0.048719521 | −0.010914976 | 0.000632452 | −3.424625563 | |
| PE + 3MAA | 2.40893 | N–H…O=C | 0.009747326 | 0.03516367 | −0.007088061 | 0.000851428 | −2.22391283 |
| 1.75467 | C–O…H–O | 0.039957715 | 0.109973591 | −0.029138968 | −0.000822785 | −9.142489513 | |
| 2.02096 | C=O…H–O | 0.023316164 | 0.069012021 | −0.018481353 | −0.000614174 | −5.798612246 | |
| 1.82306 | O–H…O–C(Ring) | 0.03203572 | 0.096666388 | −0.02385453 | 0.000156034 | −7.484472015 | |
| 2.30929 | C(Ring)–H…O=C | 0.013204826 | 0.039189977 | −0.009323669 | 0.000236913 | −2.925345378 | |
| 1.80407 | C–O…H–O | 0.033958284 | 0.098802002 | −0.024766909 | −3.32041E-05 | −7.770735288 | |
| AHA + 5MAA | 1.64880 | C=O…H–O | 0.049287466 | 0.139181341 | −0.037615209 | −0.001409937 | −11.8019506 |
| 1.61433 | C=O…H–O | 0.053882161 | 0.146874063 | −0.042683048 | −0.002982266 | −13.3920091 | |
| 1.74762 | C=O…H–O | 0.038615681 | 0.112801746 | −0.028256176 | −2.78698E-05 | −8.865509525 | |
| 1.74762 | C=O…H–O | 0.049922233 | 0.139027425 | −0.03838753 | −0.001815337 | −12.04426994 | |
| 1.64637 | C=O…H–O | 0.031355728 | 0.089591298 | −0.023029819 | −0.000315997 | −7.225715144 | |
| 1.86144 | N–H…O=C | 0.010611115 | 0.039224958 | −0.008058956 | 0.000873642 | −2.528535829 | |
| 2.11431 | N–H…O=C | 0.016231044 | 0.052271763 | −0.012528486 | 0.000269727 | −3.930871974 | |
| 1.77100 | C=O…H–O | 0.034097227 | 0.109044945 | −0.024677559 | 0.001291839 | −7.74270143 | |
| HMA + 5MAA | 1.67043 | C=O…H–O | 0.046441973 | 0.134085029 | −0.034848649 | −0.000663696 | −10.9339293 |
| 1.56804 | C=O…H–O | 0.060896745 | 0.153953802 | −0.05136232 | −0.006436935 | −16.11517194 | |
| 1.77916 | C-O…H–O | 0.036416615 | 0.10657766 | −0.026942346 | −0.000148965 | −8.453288886 | |
| 2.09553 | C=O…H–O | 0.020289963 | 0.061744074 | −0.016108194 | −0.000336087 | −5.054022243 | |
| 1.98828 | O-H…O–C(Ring) | 0.023371537 | 0.065811757 | −0.017801058 | −0.000674059 | −5.585166537 | |
| 1.77762 | C=O…H–O | 0.038597233 | 0.110446154 | −0.029301292 | −0.000844877 | −9.193419389 | |
| 1.84295 | O–H…O–C(Ring) | 0.030576225 | 0.089785381 | −0.022241089 | 0.000102628 | −6.97824731 | |
| 2.51227 | C(Ring)–H…O=C | 0.008593919 | 0.028551998 | −0.005604602 | 0.000766699 | −1.758470634 | |
| 1.92005 | C–O…H–O | 0.024679618 | 0.073704853 | −0.018155766 | 0.000135224 | −5.696457753 | |
| 2.40054 | C–H…O=C | 0.011004729 | 0.034475186 | −0.007524568 | 0.000547114 | −2.360868924 | |
| 2.54566 | C(Ring)–H…O=C | 0.007706916 | 0.027055854 | −0.005051907 | 0.000856028 | −1.585059833 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, B.; Fan, X.; Zhao, D. Computer-Aided Design of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Simultaneous Detection of Clenbuterol and Its Metabolites. Polymers 2019, 11, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11010017
Zhang B, Fan X, Zhao D. Computer-Aided Design of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Simultaneous Detection of Clenbuterol and Its Metabolites. Polymers. 2019; 11(1):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11010017
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Bingcheng, Xin Fan, and Dayun Zhao. 2019. "Computer-Aided Design of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Simultaneous Detection of Clenbuterol and Its Metabolites" Polymers 11, no. 1: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11010017
APA StyleZhang, B., Fan, X., & Zhao, D. (2019). Computer-Aided Design of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Simultaneous Detection of Clenbuterol and Its Metabolites. Polymers, 11(1), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11010017