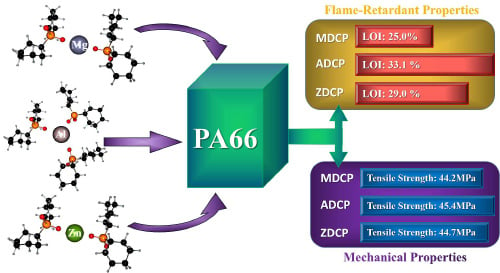
Comparative Study on the Flame-Retardant Properties and Mechanical Properties of PA66 with Different Dicyclohexyl Hypophosphite Acid Metal Salts
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experiment Reagents
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.2.1. Preparation of Dicyclohexyl Hypophosphite
2.2.2. Preparation of the Flame Retardant-PA66 Composite Materials
2.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis of Dicyclohexyl Hypophosphite
2.4. Flame-Retardant Property Test of Dicyclohexyl Hypophosphite on PA66
2.5. Mechanical Property Test of Dicyclohexyl Hypophosphite on PA66
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Flame-Retardant and Mechanical Properties of the PA66/ADPC Composites
3.2. Flame-Retardant and Mechanical Properties of the PA66/MDCP Composites
3.3. Flame-Retardant and Mechanical Properties of the PA66/ZDCP Composites
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marney, D.C.O.; Yang, W.; Russell, L.J.; Shen, S.Z.; Nguyen, T.; Yuan, Q.; Varley, R.; Li, S. Phosphorus intercalation of halloysite nanotubes for enhanced fire properties of polyamide 6. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2012, 23, 1564–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.L.; Wang, Y.Z.; Ban, D.M.; Yang, B.; Zhao, G.M. A Novel Phosphorus-Containing Polymer as a Highly Effective Flame Retardant. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2010, 289, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ruan, C.; Yang, R.; Wang, Y.Z. Phosphorus-containing thermotropic liquid crystalline polymers: A class of efficient polymeric flame retardants. Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levchik, S.V.; Levchik, G.F.; Camino, G.; Luigi, C.; Lesnikovich, A.I. Mechanism of action of phosphorus-based flame retardants in nylon 6. III. Ammonium polyphosphate/manganese dioxide. Fire Mater. 1996, 20, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levchik, G.F.; Levchik, S.V.; Lesnikovich, A.I. Mechanisms of action in flame retardant reinforced nylon 6. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1996, 54, 361–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, E. Phosphorus-based flame retardants for thermoplastics. Plast. Addit. Compd. 2007, 9, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, H.; Krause, W.; Sicken, M.; Weferling, N. Salts of dialkylphosphinic acids. CN ZL200410104691.6, 31 August 2005. Available online: http://www1.soopat.com/Patent/200410104691 (accessed on 1 November 2019).
- Weferling, N.; Schmitz, H.P.; Kolbe, G. Method for producing salts of dialkylphosphinic acids. CN ZL9881162.7, 17 January 2001. Available online: http://www1.soopat.com/Patent/98811622 (accessed on 1 November 2019).
- Yang, L.; Han, X.Y.; Li, L.L.; Bi, C.L.; Tang, X.J.; Zhang, B.G. Synthesis of aluminium diethylphosphinate by gas-liquid free radical addition reaction under atmospheric pressure. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 194, 2237–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, U.; Schartel, B. Flame retardance mechanisms of aluminium phosphinate in combination with melamine cyanurate in glass-fibre-reinforced poly(1,4-butylene terephthalate). Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2008, 293, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, R.K.; Chen, L.; Chen, S.Y.; Long, J.W.; Wang, Y.Z. A novel flame-retardant acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene system based on aluminum isobutylphosphinate and red phosphorus: Flame retardance, thermal degradation and pyrolysis behavior. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 109, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Chen, L.; Lin, G.P.; Luo, Y.; Wang, Y.Z. Flame retardation of glass-fibre-reinforced polyamide 6 by a novel metal salt of alkylphosphinic acid. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2011, 96, 1538–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Wang, X.; Xing, W.Y.; Zhang, P.; Wang, B.B.; Hong, N.N.; Yang, W.; Hu, Y.; Song, L. Thermal Degradation and Flame Retardance of Biobased Polylactide Composites Based on Aluminum Hypophosphite. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 12009–12016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.G.; Su, Q.; Li, X.; Wang, B.; Tang, L.S. Flame retardancy of aluminium dipropyl phosphinate in nylon 6. Polym. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2014, 30, 108–112. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, B.; Chen, L.; Long, J.W.; Jian, R.K.; Wang, Y.Z. Synergistic effect between aluminum hypophosphite and alkyl-substituted phosphinate in flame-retarded polyamide 6. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 17162–17170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, L.; Yang, H.; Mu, K.J.; Tian, M.G. Study on synthesis process and properties of flame retardant of dicyclohexenyl aluminum hypophosphite at normal pressure. Polym. Bull. 2018, 3, 59–66. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, H.Y.; Yang, H.; Lu, J.L.; Mu, K.J.; Guo, Z.S. Pyrolysis dynamics of dicyclohexyl phosphonic acid aluminium flame retardant polyamide. Plast. Rubber Compos. 2019, 48, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lu, J.L.; Yang, H.Y.; Yang, H.; Lang, J.Y.; Zhang, Q.Q. Synergistic flame-retardant mechanism of dicyclohexenyl aluminum hypophosphite and nano-silica. Polymer 2019, 11, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- SAC. Plastics Combustion Performance Test Method Oxygen Index Method; GB/T 2406.1-2008; Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2008.
- Klatt, M.; Heitz, T.; Gareiss, B. Flame-Proof Thermoplastic Moulding Materials. U.S. Patent 6,306,941, 12 September 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Gosens, J.C.; Wit, D.G. Flame Retardant Polyester Compositions. U.S. Patent 3,873,496, 25 March 1975. [Google Scholar]
- SAC. Test Method for Plastic Burning Performance Horizontal Method and Vertical Method; GB/T 2408-2008; Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2008.
- SAC. Determination of Tensile Properties of Plastics; GB/T 1040.1-2006; Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2006.
- SAC. Determination of Bending Properties of Plastics; GB/T 9341-2008; Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2008.







| Sample | PA66 | Dicyclohexyl Aluminum Hypophosphite (ADCP) | Limiting Oxygen Index (LOI) | UL 94 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (wt %) | (wt %) | (%) | Dripping | Rating | |
| PA66-0 | 100 | 0 | 21.5 ± 0.9 | Y | V-2 |
| PA66-1 | 95 | 5 | 24.0 ± 0.7 | Y | V-1 |
| PA66-2 | 90 | 10 | 28.0 ± 0.5 | N | V-0 |
| PA66-3 | 85 | 15 | 32.0 ± 0.9 | N | V-0 |
| PA66-4 | 80 | 20 | 33.1 ± 0.7 | N | V-0 |
| PA66-5 | 75 | 25 | 34.1 ± 0.8 | N | V-0 |
| Sample | Mechanical Properties | |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | Bending Strength (MPa) | |
| PA66-0 | 56.4 ± 0.6 | 53.4 ± 0.9 |
| PA66-1 | 55.2 ± 0.9 | 53.4 ± 0.5 |
| PA66-2 | 52.8 ± 0.7 | 54.1 ± 0.6 |
| PA66-3 | 49.6 ± 0.6 | 55.4 ± 0.8 |
| PA66-4 | 45.4 ± 0.5 | 56.8 ± 1.0 |
| PA66-5 | 40.5 ± 0.7 | 57.8 ± 0.8 |
| Sample | PA66 | Dicyclohexyl Magnesium Hypophosphite (MDCP) | LOI | UL 94 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (wt %) | (wt %) | (%) | Dripping | Rating | |
| PA66-0 | 100 | 0 | 21.5 ± 0.8 | Y | Burning |
| PA66-1 | 95 | 5 | 22.0 ± 0.9 | Y | Burning |
| PA66-2 | 90 | 10 | 23.0 ± 0.6 | Y | Burning |
| PA66-3 | 85 | 15 | 23.5 ± 0.5 | Y | V-2 |
| PA66-4 | 80 | 20 | 25.0 ± 0.8 | Y | V-2 |
| PA66-5 | 75 | 25 | 25.0 ± 0.7 | Y | V-2 |
| Sample | Mechanical Properties | |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | Bending Strength (MPa) | |
| PA66-0 | 56.4 ± 0.6 | 53.4 ± 0.8 |
| PA66-1 | 52.2 ± 0.8 | 53.8 ± 0.9 |
| PA66-2 | 50.8 ± 0.9 | 54.9 ± 0.7 |
| PA66-3 | 47.6 ± 0.7 | 55.9 ± 1.1 |
| PA66-4 | 44.2 ± 1.1 | 57.0 ± 0.9 |
| PA66-5 | 39.5 ± 0.9 | 58.2 ± 0.8 |
| Sample | PA66 | Dicyclohexyl Zinc Hypophosphite (ZDCP) | LOI | UL 94 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (wt %) | (wt %) | (%) | Dripping | Rating | |
| PA66-0 | 100 | 0 | 21.5 ± 0.7 | Y | Burning |
| PA66-1 | 95 | 5 | 23.0 ± 0.9 | Y | Burning |
| PA66-2 | 90 | 10 | 24.5 ± 0.8 | Y | V-2 |
| PA66-3 | 85 | 15 | 26.5 ± 0.9 | Y | V-1 |
| PA66-4 | 80 | 20 | 29.0 ± 0.9 | N | V-0 |
| PA66-5 | 75 | 25 | 30.5 ± 0.7 | N | V-0 |
| Sample | Mechanical Properties | |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | Bending Strength (MPa) | |
| PA66-0 | 56.4 ± 0.7 | 53.4 ± 0.9 |
| PA66-1 | 53.2 ± 0.6 | 53.6 ± 0.7 |
| PA66-2 | 50.8 ± 0.9 | 54.7 ± 0.6 |
| PA66-3 | 47.2 ± 0.9 | 55.9 ± 0.8 |
| PA66-4 | 44.7 ± 0.6 | 57.6 ± 0.9 |
| PA66-5 | 40.3 ± 0.8 | 58.9 ± 0.7 |
| Flame Retardant | Relative Molecular Mass (g/mol) | Number of Phosphorus Groups with the Same Mass M (mol) |
|---|---|---|
| ADCP | 745.062 | 3 M/745.062 |
| ZDCP | 544.110 | 2 M/544.110 |
| MDCP | 503.025 | 2 M/503.025 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Lu, J.; Yang, H.; Lang, J.; Yang, H. Comparative Study on the Flame-Retardant Properties and Mechanical Properties of PA66 with Different Dicyclohexyl Hypophosphite Acid Metal Salts. Polymers 2019, 11, 1956. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11121956
Zhang H, Lu J, Yang H, Lang J, Yang H. Comparative Study on the Flame-Retardant Properties and Mechanical Properties of PA66 with Different Dicyclohexyl Hypophosphite Acid Metal Salts. Polymers. 2019; 11(12):1956. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11121956
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Heng, Junliang Lu, Hongyan Yang, Jinyan Lang, and Heng Yang. 2019. "Comparative Study on the Flame-Retardant Properties and Mechanical Properties of PA66 with Different Dicyclohexyl Hypophosphite Acid Metal Salts" Polymers 11, no. 12: 1956. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11121956
APA StyleZhang, H., Lu, J., Yang, H., Lang, J., & Yang, H. (2019). Comparative Study on the Flame-Retardant Properties and Mechanical Properties of PA66 with Different Dicyclohexyl Hypophosphite Acid Metal Salts. Polymers, 11(12), 1956. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11121956