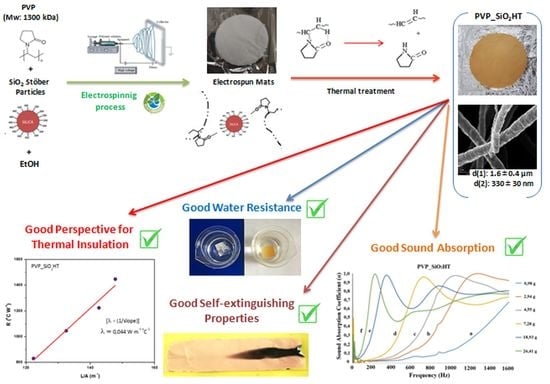
Water Resistant Self-Extinguishing Low Frequency Soundproofing Polyvinylpyrrolidone Based Electrospun Blankets
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of Electrospun Mats
- An ethanol solution (20 wt. %) of PVP (MW: 1,300,000 g mL−1)
- An ethanol suspension (40 wt. %) of silica particles
2.2.2. Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.2.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.2.4. Thermal Analysis
2.2.5. Dynamic Light Scattering
2.2.6. Fire Test Results
2.2.7. Water Resistance
2.2.8. Flow Resistivity
2.2.9. Sound Absorption Coefficient
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Silica Particles
3.2. Electrospun Mats Structure and Composition
- 2930 and 2850 cm−1 CH stretching
- 3460 cm−1 OH stretching
- 1650 cm−1 C = O symmetric stretching
- 1422 cm−1 CH2 in-plane bending
- 1286 cm−1 CN stretching
3.3. Water Resistance
3.4. Fire Test Results
- Extinguishing time: the time the specimen continues to flame after the burner flame is removed. It is required to be less than 15 s
- Drip extinguishing time: the time, in seconds, that any flaming material continues to flame after falling from the specimen to the floor of the chamber. It is required to be less than 5 s (for the 12 s test)
- Burn length: the distance from the original specimen edge to the farthest evidence of damage to the test specimen. It is required to be less than 203 mm (for the 12 s test)
3.5. Thermal Conductivity
3.6. Acoustic Properties
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Agarwal, S.; Greiner, A.; Wendorff, J.H. Functional materials by electrospinning of polymers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 963–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, N.; Kundu, S.C. Electrospinning: A fascinating fiber fabrication technique. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 325–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; Tian, M. Improved polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP)/graphite nanocomposites by solution compounding and spray drying. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2012, 23, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutledge, G.C.; Fridrikh, S.V. Formation of fibers by electrospinning. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 1384–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teo, W.E.; Ramakrishna, S. A review on electrospinning design and nanofibre assemblies. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, R89–R106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.M.; Zhang, Y.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. A review on polymer nanofibers by electrospinning and their applications in nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 2223–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huanga, A.; Penga, X.; Geng, L.; Zhang, L.; Huang, K.; Chen, B.; Gu, Z.; Kuang, T. Electrospun poly (butylene succinate)/cellulose nanocrystals bionanocomposite scaffolds for tissue engineering: Preparation, characterization and in vitro evaluation. Polym. Test. 2017, 302, 101–109. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, S.; Wendorff, J.H.; Greiner, A. Use of electrospinning technique for biomedical applications. Polymer 2008, 49, 5603–5621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sill, T.J.; Von Recum, H.A. Electrospinning applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1989–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanani, A.G.; Bahrami, S.H. Review on electrospun nanofibers scaffold and biomedical applications. Trends Biomater. Artif. Organs 2010, 24, 93–115. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, D.; Wang, R.; Tang, G.; Mou, Z.; Lei, J.; Han, J.; De Smedt, S.; Xiong, R.; Huang, C. Ecofriendly Electrospun Membranes Loaded with Visible-Light-Responding Nanoparticles for Multifunctional Usages: Highly Efficient Air Filtration, Dye Scavenging, and Bactericidal Activity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 12880–12889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lv, D.; Zhu, M.; Jiang, Z.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Xiong, R.; Huang, C. Green Electrospun Nanofibers and Their Application in Air Filtration. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2018, 303, 1800336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Han, J.; Wang, F.; Shao, W.; Xiong, R.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, H.; Yang, Y.; Samal, S.K.; Zhang, F.; et al. Green Electrospun Nanofibers Membranes for Effective Air Filtration. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2017, 302, 1600353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Sui, L.; Fang, H.; Ding, C.; Li, Z.; Jiang, S.; Hou, H. Superior mechanical enhancement of epoxy composites reinforced by polyimide nanofibers via a vacuum-assisted hot-pressing. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2019, 174, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, G.; Liu, S.; Jiang, S.; Hou, H. High-performance polyamide-imide films and electrospun aligned nanofibers from an amidecontaining Diamine. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 6719–6727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, W.S.; Asmatulu, R.; Yildirim, M.B. Acoustical Properties of Electrospun Fibers for Aircraft Interior Noise Reduction. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2012, 25, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.; Tan, S.; Yu, X.; Long, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, N.; Xu, J. Sound absorption behavior of electrospun polyacrylonitrile nanofibrous membranes. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2011, 29, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannace, G. Acoustic Properties of Nanofibers. Noise Vib. Worldw. 2014, 45, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, A. Handbook of Noise and Vibration Control, 6th ed.; Elsevier Advanced Technology: Oxford, UK, 1992; ISBN 978-1-85617-079-6. [Google Scholar]
- Crocker, M.J. Handbook of Noise and Vibration Control; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; ISBN 978-0-471-39599-7. [Google Scholar]
- Engel, Z. Notes on Sound Absorption Technology, K.U. INGARD. Arch. Acoust. 2014, 21, 115–117. [Google Scholar]
- Goines, L.; Hagler, L.C.S.M. Noise Pollution: A Modern Plague. South. Med. J. 2007, 100, 287–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahashabde, A.; Wolfe, P.; Ashok, A.; Dorbian, C.; He, Q.; Fan, A.; Lukachko, S.; Mozdzanowska, A.; Wollersheim, C.; Barrett, S.R.H.; et al. Assessing the environmental impacts of aircraft noise and emissions. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2011, 47, 15–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Li, X.Y. A review of acoustic dampers applied to combustion chambers in aerospace industry. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2015, 74, 114–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, C.M. Handbook of Acoustical Measurements and Noise Control, 3rd ed.; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1991; ISBN 978-0-07-026868-5. [Google Scholar]
- Arenas, J.P.; Crocker, M.J. Recent Trends in Porous Sound-Absorbing Materials. Sound Vib. 2010, 44, 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- Avossa, J.; Branda, F.; Marulo, F.; Petrone, G.; Guido, S.; Tomaiuolo, G.; Costantini, A. Light Electrospun Polyvinylpyrrolidone Blanket for Low Frequencies Sound Absorption. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2018, 36, 1368–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Del Sorbo, G.R.; Truda, G.; Bifulco, A.; Passaro, J.; Petrone, G.; Vitolo, B.; Ausanio, G.; Vergara, A.; Marulo, F.; Branda, F. Non Monotonous Effects of Noncovalently Functionalized Graphene Addition on the Structure and Sound Absorption Properties of Polyvinylpyrrolidone (1300 kDa) Electrospun Mats. Materials 2019, 12, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loría-Bastarrachea, M.I.; Herrera-Kao, W.; Cauich-Rodríguez, J.V.; Cervantes-Uc, J.M.; Vázquez-Torres, H.; Ávila-Ortega, A. A TG/FTIR study on the thermal degradation of poly(vinyl pyrrolidone). J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2011, 104, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsome, T.E.; Olesik, S.V. Electrospinning silica/polyvinylpyrrolidone composite nanofibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 40966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troitzsch, J. International Plastics Flammability Handbook: Principles-Regulations-Testing and Approval; Hanser: Munich, Germany, 1983; ISBN 978-3-446-13571-0. [Google Scholar]
- Mettler-Toledo International Inc. All Rights Simple Determination of the Thermal Conductivity of Polymers by DSC. Available online: https://www.mt.com/sg/en/home/supportive_content/matchar_apps/MatChar_UC226.html (accessed on 2 June 2019).
- Horner, A. Aircraft Materials Fire Test. Handbook; Office of Aviation Research: Washington, DC, USA, 2000.
- Rhim, J.W. Physical and mechanical properties of water resistant sodium alginate films. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 37, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannace, G. Sound Absorption of Materials Obtained from the Shredding of Worn Tyres. Build. Acoust. 2014, 21, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.Y.; Blaser, D.A. Transfer function method of measuring in-duct acoustic properties. I. Theory. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1980, 68, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koruk, H. An assessment of the performance of impedance tube method. Noise Control. Eng. J. 2014, 62, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinker, C.; Scherer, G. Sol-Gel Science: The Physics and Chemistry of Sol-Gel Processing; Academic Press Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 1990; ISBN 0-12-134970-5. [Google Scholar]
- Branda, F. The Sol-Gel Route to Nanocomposites. In Advances in Nanocomposites—Synthesis, Characterization and Industrial Applications; Reddy, B., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011; ISBN 978-953-307-165-7. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Bogatyrev, V.M.; Borisenko, N.V.; Pokrovskii, V.A. Thermal Degradation of Polyvinylpyrrolidone on the Surface of Pyrogenic Silica. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2001, 74, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toki, M.; Chow, T.Y.; Ohnaka, T.; Samura, H.; Saegusa, T. Structure of poly(vinylpyrrolidone)-silica hybrid. Polym. Bull. 1992, 29, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peniche, C.; Zaldívar, D.; Pazos, M.; Páz, S.; Bulay, A.; Román, J.S. Study of the thermal degradation of poly(N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone) by thermogravimetry–FTIR. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1993, 50, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Yu, D.; Wei, J. Thermal conductivity determination of small polymer samples by differential scanning calorimetry. Polym. Test. 2007, 26, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manville, J. OEM Insulations Division. www.jm.com. Available online: https://www.tricityinsulation.com/cms/wp-content/uploads/2010/11/Microlite-Blankets1.pdf (accessed on 2 June 2019).
















| Fiber Diameter [μm] | Apparent Density ρ [g/cm3] | Density ρs [g/cm3] | Porosity [%] | Flow Resistivity [kPa (s/m2)] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVP | 1.6 ± 0.4 | 0.063 | 1.06 | 94 | 440 |
| PVP_SiO2NT | 1.6 ± 0.4 0.33 ± 0.03 | 0.071 | 2.08 | 97 | 783 |
| PVP_SiO2HT | 1.6 ± 0.4 0.33 ± 0.03 | 0.042 | 2.12 | 98 | 289 |
| I T 2 (s) | E T 3 (s) | Burn Length (mm) | D E T 4 (s) | M F T 5 (°C) | Coupon Size (cm3) | Weight (g) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 1 | 12 | 0 | 57.1 | No Drip | 843 | 7.5 × 0.1 × 20 | 1.3 |
| Sample 2 | 12 | 0 | 70.3 | No Drip | 843 | 7.5 × 0.1 × 20 | 1.2 |
| Sample 3 | 12 | 0 | 50.8 | No Drip | 843 | 7.5 × 0.1 × 20 | 1.1 |
| Results 1 | / | 0 | 59.4 ± 206 | No Drip | / | / | / |
| Specific Optical Density (-) | Coupon Size (cm3) | Weight (g) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 1 | 33.2 | 7.3 × 0.5 × 7.3 | 1.1 |
| Sample 2 | 32.8 | 7.3 × 0.5 × 7.3 | 1.2 |
| Sample 3 | 30.9 | 7.3 × 0.5 × 7.3 | 1.3 |
| Results 1 | 32.3 ± 3.02 | / | / |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Passaro, J.; Russo, P.; Bifulco, A.; De Martino, M.T.; Granata, V.; Vitolo, B.; Iannace, G.; Vecchione, A.; Marulo, F.; Branda, F. Water Resistant Self-Extinguishing Low Frequency Soundproofing Polyvinylpyrrolidone Based Electrospun Blankets. Polymers 2019, 11, 1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11071205
Passaro J, Russo P, Bifulco A, De Martino MT, Granata V, Vitolo B, Iannace G, Vecchione A, Marulo F, Branda F. Water Resistant Self-Extinguishing Low Frequency Soundproofing Polyvinylpyrrolidone Based Electrospun Blankets. Polymers. 2019; 11(7):1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11071205
Chicago/Turabian StylePassaro, Jessica, Paolo Russo, Aurelio Bifulco, Maria Teresa De Martino, Veronica Granata, Bonaventura Vitolo, Gino Iannace, Antonio Vecchione, Francesco Marulo, and Francesco Branda. 2019. "Water Resistant Self-Extinguishing Low Frequency Soundproofing Polyvinylpyrrolidone Based Electrospun Blankets" Polymers 11, no. 7: 1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11071205
APA StylePassaro, J., Russo, P., Bifulco, A., De Martino, M. T., Granata, V., Vitolo, B., Iannace, G., Vecchione, A., Marulo, F., & Branda, F. (2019). Water Resistant Self-Extinguishing Low Frequency Soundproofing Polyvinylpyrrolidone Based Electrospun Blankets. Polymers, 11(7), 1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11071205