Improved Interlaminar Fracture Toughness and Electrical Conductivity of CFRPs with Non-Woven Carbon Tissue Interleaves Composed of Fibers with Different Lengths
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Work
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. NWCT Fabrication
2.3. Laminates Preparation
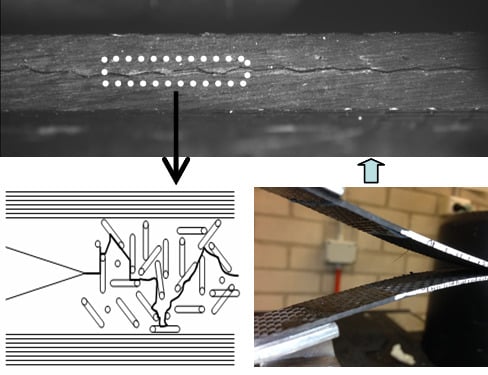
2.4. Experimental Procedure
2.5. Microstructure Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Fabrication of NWCT Made of the Chopped CFs with Different Length
3.2. The Distribution of Chopped Carbon Fibers in the Mid-Layer of Laminate
3.3. Mode-I Interlaminar Fracture Toughness of NWCT-Composites
3.4. Mode-II Interlaminar Fracture Toughness of NWCT-Composites
3.5. Flexural Properties of Short Chopped Carbon Fiber Reinforced Laminate
3.6. The Conductivity of the NWCT Modified Laminates
3.7. The Crack Propagation Path in the Mid-Layer
3.8. Toughening Mechanism Discussion
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The NWCT made of shorter carbon fibers (0.8 mm) perform better on Mode I interlaminar fracture toughness than those made of longer carbon fiber (4.3 mm), achieving a significant Mode I toughness increase. However, longer carbon fiber (4.3 mm) give more contribution to the Mode II interlaminar fracture toughness.
- (2)
- The electrical conductivity of composites interleaved by NWCT composed of shorter carbon fibers (0.8 mm) with high density of 7.8 mg/cm2 achieve an enhancement of 96% in the in-plane and 82% in the through-the-thickness direction, respectively, exhibiting the significant electrical conductivity improvement though the establishment of connected conductive network of SCFs in the mid-layer of laminate.
- (3)
- Microscopy analysis of the NWCT interleaving area in the laminate zone indicate that the shorter chopped carbon fibers are more easily to form into a 3D network with more fibers aligned along through-the-thickness direction compared with those longer ones, causing more effective fiber bridges induced by fiber pullout and matrix deformation during the crack propagation.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Argüelles, A.; Rocandio, C.; Rubiera, S.; Isabel, V.; Jaime, V. Influence of the Test Method on the Characterization of the Fatigue Delamination Behavior of a Composite Material under Mixed Mode I/II Fracture. Polymers 2019, 11, 1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, F.; Du, X.S.; Liu, H.Y.; Guo, W.G.; Mai, Y.W. Temperature effect on nano-rubber toughening in epoxy and epoxy/carbon fiber laminated composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 95, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, P.; Cui, Y.; Wu, G. Microstructure and Flexural Properties of Z-Pinned Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Aluminum Matrix Composites. Materials 2019, 12, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xuan, J.; Li, D.; Jiang, L. Fabrication, properties and failure of 3D stitched carbon/epoxy composites with no stitching fibers damage. Compos. Struct. 2019, 220, 602–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Liu, H.Y.; Xu, F.; Zeng, Y.; Mai, Y.W. Flame synthesis of carbon nanotubes onto carbon fiber woven fabric and improvement of interlaminar toughness of composite laminates. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2014, 101, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Liu, H.Y.; Du, X.S. An analytical model of interlaminar fracture of polymer composite reinforced by carbon fibres grafted with carbon nanotubes. Polymers 2018, 10, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, H.; Du, X.; Liu, H.Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Mai, Y.W. Delamination toughening of carbon fiber/epoxy laminates by hierarchical carbon nanotube-short carbon fiber interleaves. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 140, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, H.; Iijima, T.; Hu, N.; Liu, Y.; Wu, L.; Liu, F.; Arai, M. Investigation on mode-II interface fracture toughness of CFRP/Al laminates toughened by VGCF interleaves. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 1915–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, Y.; Xiang, D.; Zhao, C.; Wang, B.; Li, H.; Han, H. Simultaneous enhancement of electrical conductivity and interlaminar shear strength of CF/EP composites through MWCNTs doped thermoplastic polyurethane film interleaves. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beylergil, B.; Tanoğlu, M.; Aktaş, E. Enhancement of interlaminar fracture toughness of carbon fiber–epoxy composites using polyamide-6, 6 electrospun nanofibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 45244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, M.; Noro, Y.; Sugimoto, K.I.; Endo, M. Mode I and mode II interlaminar fracture toughness of CFRP laminates toughened by carbon nanofiber interlayer. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2008, 68, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, M.S.; Hu, X.Z. Delamination behaviour of carbon fibre/epoxy composite laminates with short fibre reinforcement. Scr. Mater. 1994, 30, 1467–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, M.S.; Hu, X.Z. Mode II delamination toughness of carbon-fiber/epoxy composites with chopped Kevlar fibre reinforcement. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1994, 52, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.Z.; Hu, X.Z.; Liu, J. Modelling of inter-laminar toughening from chopped Kevlar fibers. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2004, 64, 2165–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.Y.; Kim, S.C.; Jung, B. Interlaminar Fracture Toughness of Carbon Fiber/Epoxy Composites using Short Kevlar Fiber and/or Nylon-6 Powder Reinforcement. Polym. Adv. Technol. 1997, 8, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beylergil, B.; Tanoglu, M.; Aktas, E. Mode-I fracture toughness of carbon fiber/epoxy composites interleaved by aramid nonwoven veils. Steel Compos. Struct. 2019, 31, 113–123. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Wu, L.W.; Jiang, Q.; Tian, D.; Zhong, Z.; Wang, Y.; Fu, H.J. Improving interlaminar fracture toughness and impact performance of carbon fiber/epoxy laminated composite by using thermoplastic fibers. Molecules 2019, 24, 3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Ma, C.; Chen, G.; Dai, P. Interlaminar fracture toughness and conductivity of carbon fiber/epoxy resin composite laminate modified by carbon black-loaded polypropylene non-woven fabric interleaves. Compos. Struct. 2020, 234, 111649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.S.; Cheong, S.K. Interlaminar fracture toughness of CFRP laminates with silk fibers interleave. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2013, 27, 3651–3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Noguchi, H.; Kim, Y.B.; Cheong, S.K. Effect of interleaved non-woven carbon sissue on interlaminar fracture toughness of laminated composites. Part I-Mode II. J. Compos. Mater. 2002, 36, 2153–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Noguchi, H.; Kim, Y.B.; Cheong, S.K. Effect of interleaved non-woven carbon sissue on interlaminar fracture toughness of laminated composites Part II-Mode I. J. Compos. Mater. 2002, 36, 2169–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Noguchi, H.; Cheong, S.K. Tensile properties and fatigue characteristics of hybrid composites with non-woven carbon tissue. Int. J. Fatigue 2002, 24, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Noguchi, H.; Cheong, S.K. Static behavior characteristics of hybrid composites with nonwoven carbon tissue. J. Compos. Mater. 2003, 37, 233–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Lee, J.H.; Cheong, S.K.; Noguchi, H.A. Toughening and strengthening technique of hybrid composites with non-woven tissue. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2008, 207, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Aono, Y.; Noguchi, H.; Cheong, S.K. Damage mechanism of hybrid composites with nonwoven carbon tissue subjected to quasi-static indentation loads. J. Compos. Mater. 2003, 37, 333–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Kim, H.; Hang, S.; Cheong, S.K. Interlaminar fracture toughness of composite laminates with CNT-enhanced nonwoven carbon tissue interleave. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2012, 73, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Du, X.; Liu, H.Y.; Mai, Y.W.; Wang, X.J. Interlaminar toughening effects and mechanisms of non-woven carbon fiber tissue on CFRP laminates. Acta Mater. Compos. Sin. 2015, 32, 1784–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanakumar, K.; Farouk, N.; Arumugam, V. Effect of fiber orientation on mode-I delamination resistance of glass/epoxy laminates incorporated with milled glass fiber fillers. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2018, 199, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Huang, D.D.; Du, X.S. Improving the delamination resistance of carbon fiber/epoxy composites by brushing and abrading of the woven fabrics. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 158, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard Test Method for Mode I Interlaminar Fracture Toughness of Unidirectional Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Matrix Composites; ASTM D5528-13; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013.
- Davies, P. A Protocol for Interlaminar Fracture Testing of Composites; ESIS-Polymer and Composites Task Group: Delft, The Netherlands, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Standard Test Methods for Flexural Properties of Unreinforced and Reinforced Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materials; ASTM D790-10; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2010.
- Chen, C.; Li, Y.; Yu, T. Interlaminar toughening in flax fiber-reinforced composites interleaved with carbon nanotube buckypaper. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2014, 33, 1859–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Interleave | Test Method | Fracture Toughness Improvement 1 | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Interleave with NWCT tissues (15 mm) | DCB | 28% | [20] |
| Interleave with NWCT tissues (0.8mm) | DCB | 99% | This Work |
| Interleave with CNTs grafted NWCT tissues | DCB | 35% | [26] |
| Brushing and abrading carbon fibers | DCB | 83% | [29] |
| Interleave with CNTs bucky paper | DCB | 51% | [33] |
| Interleave with Carbon nanofibers | DCB | 50% | [11] |
| Interleave | Test Method | Fracture Toughness Improvement | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Interleave with NWCT tissues (15 mm) | ENF | 26–260% | [21] |
| Interleave with NWCT tissues (4.3 mm) | ENF | 105% | This Work |
| Interleave with CNTs grafted NWCT tissues | ENF | 246% | [26] |
| Interleave with Carbon nanofibers | ENF | 200–300% | [11] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, F.; Yang, B.; Feng, L.; Huang, D.; Xia, M. Improved Interlaminar Fracture Toughness and Electrical Conductivity of CFRPs with Non-Woven Carbon Tissue Interleaves Composed of Fibers with Different Lengths. Polymers 2020, 12, 803. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040803
Xu F, Yang B, Feng L, Huang D, Xia M. Improved Interlaminar Fracture Toughness and Electrical Conductivity of CFRPs with Non-Woven Carbon Tissue Interleaves Composed of Fibers with Different Lengths. Polymers. 2020; 12(4):803. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040803
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Feng, Bo Yang, Lijie Feng, Dedong Huang, and Min Xia. 2020. "Improved Interlaminar Fracture Toughness and Electrical Conductivity of CFRPs with Non-Woven Carbon Tissue Interleaves Composed of Fibers with Different Lengths" Polymers 12, no. 4: 803. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040803
APA StyleXu, F., Yang, B., Feng, L., Huang, D., & Xia, M. (2020). Improved Interlaminar Fracture Toughness and Electrical Conductivity of CFRPs with Non-Woven Carbon Tissue Interleaves Composed of Fibers with Different Lengths. Polymers, 12(4), 803. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040803