UV-Casting on Methacrylated PCL for the Production of a Peripheral Nerve Implant Containing an Array of Porous Aligned Microchannels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials: Synthesis and Characterization of Methacrylated Polycaprolactone
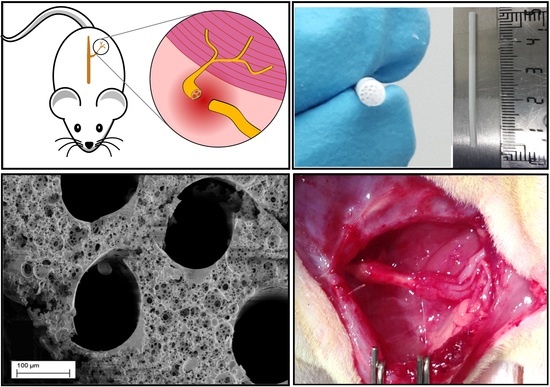
2.2. Sample Design and Characterization
2.2.1. Microfabrication of 3D Conduits
2.2.2. Porosity Creation
2.2.3. Micro Computed Tomography (MicroCT) of Nerve Guide Conduit
2.2.4. Mechanical Characterization of 3D Conduits
2.2.5. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC). Ageing Study of 3D Conduits
2.2.6. Biodegradation Analysis
2.3. In-Vitro Experiments and Analysis
2.3.1. Culture of Cell Lines
2.3.2. Cytotoxicity Analysis of 3D Conduits
2.3.3. In Vitro Analysis of PCLm Polymer Films
2.4. In Vivo Experiments and Analysis
2.4.1. In Vivo Nerve Model for Anatomical and Histological Analysis
2.4.2. In Vivo Analysis of the 3D Conduit in a 6 mm Gap Rat Sciatic Model
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physical Dimension of Rat Sciatic Nerve
3.2. Material and Manufactured 3D Porous Implant Characterization
3.3. Cytotoxicity and Biodegradability of 3D Conduits
3.4. In Vitro Analysis of PCLm Films
3.5. In Vivo Model for a 6 mm Gap in a Rat Sciatic Model
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martins, R.S.; Bastos, D.; Siqueira, M.G.; Heise, C.O.; Teixeira, M.J. Traumatic injuries of peripheral nerves: A review with emphasis on surgical indication. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 2013, 71, 811–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Phamornnak, C.; Hardy, J.; Blaker, J.; Cartmell, S. Electrical modification of aligned electrospun silk fibroin via interpenetrating polymer network of PEDOT:PSS for peripheral nerve regeneration. In Proceedings of the Termis EU2020, Manchester, UK, 26–29 May 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Rasulić, L. Peripheral nerve surgery: The road less traveled. Acta Neurochir. 2018, 160, 1587–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.Z. A Microfluidic Platform to Investigate the Mechanism by which GDNF Overexpression in Schwann Cells Causes Neuronal Axon Entrapment. Ph.D. Thesis, Washington Universiy, Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ronchi, G.; Morano, M.; Fregnan, F.; Pugliese, P.; Crosio, A.; Tos, P.; Geuna, S.; Haastert-Talini, K.; Gambarotta, G. The median nerve injury model in pre-clinical research—A critical review on benefits and limitations. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sedaghati, T.; Jell, G.; Seifalian, A.M. Nerve Regeneration and Bioengineering; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; ISBN 9780123985231. [Google Scholar]
- Pinho, A.C.; Fonseca, A.C.; Serra, A.C.; Santos, J.D.; Coelho, J.F.J. Peripheral Nerve Regeneration: Current Status and New Strategies Using Polymeric Materials. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2016, 5, 2732–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vijayavenkataraman, S. Nerve guide conduits for peripheral nerve injury repair: A review on design, materials and fabrication methods. Acta Biomater. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiono, V.; Tonda-Turo, C. Trends in the design of nerve guidance channels in peripheral nerve tissue engineering. Prog. Neurobiol. 2015, 131, 87–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, M.; Naghieh, S.; McInnes, A.D.; Schreyer, D.J.; Chen, X. Strategic Design and Fabrication of Nerve Guidance Conduits for Peripheral Nerve Regeneration. Biotechnol. J. 2018, 13, 1700635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, S.K.; Arumugam, M.; Chittoria, R. Outcome of human peripheral nerve repair interventions using conduits: A systematic review. J. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 396, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahriari, D. Degradable Microchannel Nerve Guidance Scaffolds for Central and Peripheral Nerve Repair- From Soft to Rigid. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, L.K.; Dhasmana, N.; Kamble, S.S.; Sharma, A.K. Frontiers in biomedical engineering: PHA Fabricated implants. In Microbial Factories; Kalia, V.C., Ed.; Springer India: New Delhi, India, 2015; pp. 91–102. ISBN 978-81-322-2594-2. [Google Scholar]
- Mendibil, X.; Ortiz, R.; Sáenz de Viteri, V.; Ugartemendia, J.M.; Sarasua, J.-R.; Quintana, I. High Throughput Manufacturing of Bio-Resorbable Micro-Porous Scaffolds Made of Poly(L-lactide-co-ε-caprolactone) by Micro-Extrusion for Soft Tissue Engineering Applications. Polymers 2019, 12, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basnett, P.; Nigmatullin, R.; Lukasiewicz, B.; Rodriguez, F.J.; Pacharra, S.; Mendibil, X.; Ortiz, R.; Quintana, I.; Merino, S.; Salber, J.; et al. Polyhydroxyalkanoates: A Family of Natural Polymers, for Medical Implant Development and Disease Modelling. In Proceedings of the Transactions of the Annual Meeting of the Society for Biomaterials and the Annual International Biomaterials Symposium, Seattle, WA, USA, 3–6 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Merino, S.; Quintana, I.; Márquez, M.C.; Mendibil, X.; Bazan, X.; Diez, R.; Roy, I.; Basnett, P.; Nigmatullin, R.; Lukasiewicz, B.; et al. Implantable Nerve Guidance Conduit for Nerve Repair. WO2019166087, 6 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, J.H.A.; Haycock, J.W. Next generation nerve guides: Materials, fabrication, growth factors, and cell delivery. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2012, 18, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Shi, R. Fabrication of patterned multi-walled poly-l-lactic acid conduits for nerve regeneration. J. Neurosci. Methods 2007, 165, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, A.; Tahilramani, M.; Bentley, J.T.; Gore, R.K.; Millard, D.C.; Mukhatyar, V.J.; Joseph, A.; Haque, A.S.; Stanley, G.B.; English, A.W.; et al. Microchannel-based regenerative scaffold for chronic peripheral nerve interfacing in amputees. Biomaterials 2015, 41, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pawelec, K.; Koffler, J.; Shahriari, D.; Galvan, A.R.; Tuszynski, M.; Sakamoto, J.S. Microstructure and in vivo characterization of multi-channel nerve guidance scaffolds. Biomed. Mater. 2018, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiura, T.; Tara, S.; Nakayama, H.; Kurobe, H.; Yi, T.; Lee, Y.U.; Lee, A.Y.; Breuer, C.K.; Shinoka, T. Novel Bioresorbable Vascular Graft With Sponge-Type Scaffold as a Small-Diameter Arterial Graft. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2016, 102, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, L.; Zhu, L.; Shi, X.; Xia, B.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, S.; Yang, Y.; Ma, T.; Cheng, P.; Luo, K.; et al. A compound scaffold with uniform longitudinally oriented guidance cues and a porous sheath promotes peripheral nerve regeneration in vivo. Acta Biomater. 2018, 68, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.J.; Fontaine, A.; Meng, X.; Park, D. Biomimetic nerve guidance conduit containing intraluminal microchannels with aligned nanofibers markedly facilitates in nerve regeneration. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2, 1403–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, M.D.; Bennett, J.M.; Waddell, R.L.; Doctor, J.S.; Marra, K.G. Multi-channeled biodegradable polymer/CultiSpher composite nerve guides. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, R.; Sherborne, C.; Paterson, T.; Green, N.H.; Reilly, G.C.; Claeyssens, F. Emulsion templated scaffolds with tunable mechanical properties for bone tissue engineering. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2016, 54, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aldemir Dikici, B.; Sherborne, C.; Reilly, G.C.; Claeyssens, F. Emulsion templated scaffolds manufactured from photocurable polycaprolactone. Polymer 2019, 175, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempsey, D.K.; Carranza, C.; Chawla, C.P.; Gray, P.; Eoh, J.H.; Cereceres, S.; Cosgriff-Hernandez, E.M. Comparative analysis of in vitro oxidative degradation of poly(carbonate urethanes) for biostability screening. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2014, 102, 3649–3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daud, M.F.B.; Pawar, K.C.; Claeyssens, F.; Ryan, A.J.; Haycock, J.W. An aligned 3D neuronal-glial co-culture model for peripheral nerve studies. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 5901–5913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaewkhaw, R.; Scutt, A.M.; Haycock, J.W. Integrated culture and purification of rat Schwann cells from freshly isolated adult tissue. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 1996–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewkhaw, R.; Scutt, A.M.; Haycock, J.W. Anatomical site influences the differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells for Schwann-cell phenotype and function. Glia 2011, 59, 734–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmalbruch, H. Fiber composition of the rat sciatic nerve. Anat. Rec. 1986, 215, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerri, F.; Salvatore, L.; Memon, D.; Martinelli Boneschi, F.; Madaghiele, M.; Brambilla, P.; Del Carro, U.; Taveggia, C.; Riva, N.; Trimarco, A.; et al. Peripheral nerve morphogenesis induced by scaffold micropatterning. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 4035–4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawelec, K.M.; Hix, J.; Shapiro, E.M.; Sakamoto, J. The mechanics of scaling-up multichannel scaffold technology for clinical nerve repair. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2019, 91, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokai, L.E.; Lin, Y.C.; Oyster, N.M.; Marra, K.G. Diffusion of soluble factors through degradable polymer nerve guides: Controlling manufacturing parameters. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 2540–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borschel, G.H.; Kia, K.F.; Kuzon, W.M.; Dennis, R.G. Mechanical properties of acellular peripheral nerve. J. Surg. Res. 2003, 114, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gordon, T. Electrical Stimulation to Enhance Axon Regeneration After Peripheral Nerve Injuries in Animal Models and Humans. Neurotherapeutics 2016, 13, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]















© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diez-Ahedo, R.; Mendibil, X.; Márquez-Posadas, M.C.; Quintana, I.; González, F.; Rodríguez, F.J.; Zilic, L.; Sherborne, C.; Glen, A.; Taylor, C.S.; et al. UV-Casting on Methacrylated PCL for the Production of a Peripheral Nerve Implant Containing an Array of Porous Aligned Microchannels. Polymers 2020, 12, 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040971
Diez-Ahedo R, Mendibil X, Márquez-Posadas MC, Quintana I, González F, Rodríguez FJ, Zilic L, Sherborne C, Glen A, Taylor CS, et al. UV-Casting on Methacrylated PCL for the Production of a Peripheral Nerve Implant Containing an Array of Porous Aligned Microchannels. Polymers. 2020; 12(4):971. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040971
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiez-Ahedo, Ruth, Xabier Mendibil, Mari Carmen Márquez-Posadas, Iban Quintana, Francisco González, Francisco Javier Rodríguez, Leyla Zilic, Colin Sherborne, Adam Glen, Caroline S. Taylor, and et al. 2020. "UV-Casting on Methacrylated PCL for the Production of a Peripheral Nerve Implant Containing an Array of Porous Aligned Microchannels" Polymers 12, no. 4: 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040971
APA StyleDiez-Ahedo, R., Mendibil, X., Márquez-Posadas, M. C., Quintana, I., González, F., Rodríguez, F. J., Zilic, L., Sherborne, C., Glen, A., Taylor, C. S., Claeyssens, F., Haycock, J. W., Schaafsma, W., González, E., Castro, B., & Merino, S. (2020). UV-Casting on Methacrylated PCL for the Production of a Peripheral Nerve Implant Containing an Array of Porous Aligned Microchannels. Polymers, 12(4), 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040971