Recent Advances on Nanofiber Fabrications: Unconventional State-of-the-Art Spinning Techniques
Abstract
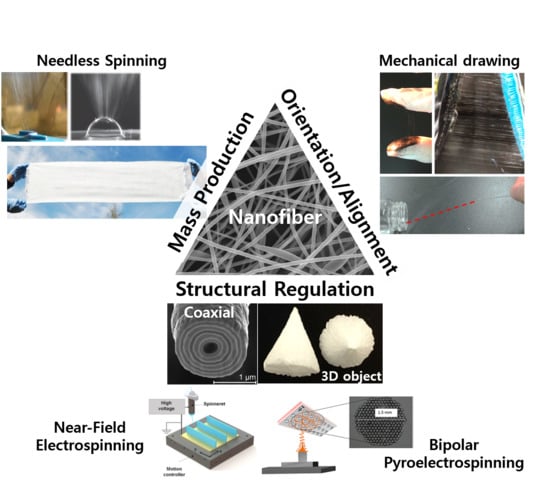
:1. Introduction
2. Needleless Spinning for Large Scale Production
2.1. Double-Ring Slit as Electrospinning Spinneret
2.2. Two-Level Coil Edge Electrospinning
2.3. Rotary Cone as Electrospinning Spinneret
2.4. Foam Based Needleless Electrospinning
3. The Use of Mechanical Force for Nanofiber Fabrication
3.1. Handspinning
3.2. Needle Spinning
3.3. Track Spinning
4. Structural and Architectural Regulations
4.1. Bipolar Pyroelectrospinning for the Formation of Nanofiber Arrays
4.2. Near-Field Electrospinning to Construct Nanoarchitecture
4.3. Sequential Metal Deposition for Multilayered Nanofiber
4.4. Transformation of 2D Nanofiber Mat to 3D Object
4.5. Yarn-Spinning
5. Closing Remarks and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, H.; Koo, J.M.; Sohn, D.; Kim, I.-S.; Im, S.S. High thermal stability and high tensile strength terpolyester nanofibers containing biobased monomer: Fabrication and characterization. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 40383–40388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kim, I.S. Nanofibers: Emerging Progress on Fabrication Using Mechanical Force and Recent Applications. Polym. Rev. 2018, 58, 688–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, D.-N.; Lee, H.; Choi, D.; Kang, C.-Y.; Im, S.S.; Kim, I.S. Fabrication of Two Polyester Nanofiber Types Containing the Biobased Monomer Isosorbide: Poly (Ethylene Glycol 1,4-Cyclohexane Dimethylene Isosorbide Terephthalate) and Poly (1,4-Cyclohexane Dimethylene Isosorbide Terephthalate). Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.; Kim, M.; Sohn, D.; Kim, S.H.; Oh, S.-G.; Im, S.S.; Kim, I.S. Electrospun tungsten trioxide nanofibers decorated with palladium oxide nanoparticles exhibiting enhanced photocatalytic activity. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 6108–6113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.; Xu, G.; Kharaghani, D.; Nishino, M.; Song, K.H.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, I.S. Electrospun tri-layered zein/PVP-GO/zein nanofiber mats for providing biphasic drug release profiles. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 531, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Phan, D.-N.; Kim, M.; Sohn, D.; Oh, S.-G.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, I.S. The Chemical Deposition Method for the Decoration of Palladium Particles on Carbon Nanofibers with Rapid Conductivity Changes. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, C.; Nagaishi, T.; Shi, J.; Lee, H.; Wong, P.Y.; Sui, J.; Hyodo, K.; Kim, I.S. Enhanced Wettability and Thermal Stability of a Novel Polyethylene Terephthalate-Based Poly(Vinylidene Fluoride) Nanofiber Hybrid Membrane for the Separator of Lithium-Ion Batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 26400–26406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, M.; West, J.L.; Fu, S. Preparation of temperature-response fibers with cholesteric liquid crystal dispersion. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 546, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.S.; Shambaugh, R.L. Vibration and stability in the melt blowing process. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1993, 32, 3100–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, H.-P.; Ren, X.-C.; Wang, P.; Yu, S.-H. Wet-spinning assembly of continuous, neat and macroscopic graphene fibers. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gogolewski, S.; Pennings, A.J. High-modulus fibres of nylon-6 prepared by a dry-spinning method. Polymer 1985, 26, 1394–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayleigh, L.X. On the equilibrium of liquid conducting masses charged with electricity. Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 1882, 14, 184–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Formhals, A. Process and Apparatus for Preparing Artificial Threads. U.S. Patent 1,975,504, 2 October 1934. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, G.I.; Dyke, M.D.V. Electrically driven jets. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A. Math. Phys. Sci. 1969, 313, 453–475. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.-M.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. A review on polymer nanofibers by electrospinning and their applications in nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 2223–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Nishino, M.; Sohn, D.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, I.S. Control of the morphology of cellulose acetate nanofibers via electrospinning. Cellulose 2018, 25, 2829–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, N.; Kundu, S.C. Electrospinning: A fascinating fiber fabrication technique. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 325–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; An, S.; Kim, S.; Jeon, B.; Kim, M.; Kim, I.S. Readily Functionalizable and Stabilizable Polymeric Particles with Controlled Size and Morphology by Electrospray. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watanabe, K.; Kim, B.-S.; Enomoto, Y.; Kim, I.-S. Fabrication of Uniaxially Aligned Poly(propylene) Nanofibers via Handspinning. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2011, 296, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Parize, D.D.; Foschini, M.M.; de Oliveira, J.E.; Klamczynski, A.P.; Glenn, G.M.; Marconcini, J.M.; Mattoso, L.H.C. Solution blow spinning: Parameters optimization and effects on the properties of nanofibers from poly(lactic acid)/dimethyl carbonate solutions. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 4627–4638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Xu, G.; Fu, K.; Lee, H.; Zhang, X. Parameter study and characterization for polyacrylonitrile nanofibers fabricated via centrifugal spinning process. Eur. Polym. J. 2013, 49, 3834–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Jun, Y.; Qin, J.; Lee, S.-H. Electrospinning versus microfluidic spinning of functional fibers for biomedical applications. Biomaterials 2017, 114, 121–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; He, J.; Xu, L.; Yu, J. Bubble-electrospinning for fabricating nanofibers. Polymer 2009, 50, 5846–5850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.F.; Nuge, T.; Andriyana, A.; Ang, B.C.; Muhamad, F. Core–Shell Fibers: Design, Roles, and Controllable Release Strategies in Tissue Engineering and Drug Delivery. Polymers 2019, 11, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duan, G.; Greiner, A. Air-Blowing-Assisted Coaxial Electrospinning toward High Productivity of Core/Sheath and Hollow Fibers. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2019, 304, 1800669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Dong, R.-H.; Yan, X.; Yu, G.-F.; You, M.-H.; Ning, X.; Long, Y.-Z. Recent Advances in Needleless Electrospinning of Ultrathin Fibers: From Academia to Industrial Production. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2017, 302, 1700002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Jiang, J.; Chen, D.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, J.; Wang, X.; Li, W. Multinozzle high efficiency electrospinning with the constraint of sheath gas. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varabhas, J.S.; Chase, G.G.; Reneker, D.H. Electrospun nanofibers from a porous hollow tube. Polymer 2008, 49, 4226–4229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarin, A.L.; Zussman, E. Upward needleless electrospinning of multiple nanofibers. Polymer 2004, 45, 2977–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Niu, H.; Wang, X.; Lin, T. Needleless electrospinning of uniform nanofibers using spiral coil spinnerets. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 785920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Zhou, H.; Yan, G.; Wang, H.; Fu, S.; Zhao, X.; Shao, H.; Lin, T. Enhancement of Coil Electrospinning Using Two-Level Coil Structure. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 15473–15478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Duan, H.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, W.; Lan, W.; et al. Superhigh-Throughput Needleless Electrospinning Using a Rotary Cone as Spinneret. Small 2010, 6, 1612–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, U.; Niu, H.; Aslam, S.; Jabbar, A.; Rajput, A.W.; Lin, T. Needleless electrospinning using sprocket wheel disk spinneret. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 7567–7577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, J.-J.; Supaphol, P. Rotating-disk electrospinning: Needleless electrospinning of poly(caprolactone), poly(lactic acid) and poly(vinyl alcohol) nanofiber mats with controlled morphology. J. Polym. Res. 2018, 25, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Jiang, J.; Wang, X.; Li, W.; Zhong, W.; Guo, S. Self-cleaning threaded rod spinneret for high-efficiency needleless electrospinning. Appl. Phys. A 2018, 124, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holopainen, J.; Penttinen, T.; Santala, E.; Ritala, M. Needleless electrospinning with twisted wire spinneret. Nanotechnology 2014, 26, 025301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, T.; Weller, J.M.; Chan, C.K. Needleless Electrospinning for High Throughput Production of Li7La3Zr2O12 Solid Electrolyte Nanofibers. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 17399–17405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, W. Effect of experimental parameters on needleless electrospinning from a conical wire coil. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 123, 3703–3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Yu, H.; Jia, L.; Qin, X. High-throughput nanofiber produced by needleless electrospinning using a metal dish as the spinneret. Text. Res. J. 2018, 88, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, L.; Wu, S.; Shi, W.; Aldrich, A.L.; Kielian, T.; Carlson, M.A.; Sun, R.; Qin, X.; Duan, B. Large-Scale and Rapid Preparation of Nanofibrous Meshes and Their Application for Drug-Loaded Multilayer Mucoadhesive Patch Fabrication for Mouth Ulcer Treatment. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 28740–28751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; Niu, H.; Shao, H.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, H.; Lin, T. Curved convex slot: An effective needleless electrospinning spinneret. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 11749–11758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; Niu, H.; Zhao, X.; Shao, H.; Wang, H.; Zhou, H.; Lin, T. Improving Nanofiber Production and Application Performance by Electrospinning at Elevated Temperatures. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 12337–12343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoppey, N.M.; Bochinski, J.R.; Clarke, L.I.; Gorga, R.E. Edge electrospinning for high throughput production of quality nanofibers. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 345301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahan, I.; Wang, L.; Wang, X. Needleless Electrospinning from a Tube with an Embedded Wire Loop. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2019, 304, 1800588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, M.; Karenson, M.O.; Elabd, Y.A. High Production Rate of High Purity, High Fidelity Nafion Nanofibers via Needleless Electrospinning. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2019, 1, 2731–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Peng, H.; Li, X.; Streubel, P.N.; Liu, Y.; Duan, B. Effect of scaffold morphology and cell co-culture on tenogenic differentiation of HADMSC on centrifugal melt electrospun poly (L-lactic acid) fibrous meshes. Biofabrication 2017, 9, 044106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, L.; Qin, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, W.; Li, H. Efficient preparation of polymer nanofibers by needle roller electrospinning with low threshold voltage. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2019, 59, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Niu, H.; Wu, J.; Ke, Q.; Mo, X.; Lin, T. Needleless electrospinning of polystyrene fibers with an oriented surface line texture. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 473872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tripatanasuwan, S.; Reneker, D.H. Corona discharge from electrospinning jet of poly(ethylene oxide) solution. Polymer 2009, 50, 1835–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.E.; Moraes, E.A.; Costa, R.G.F.; Afonso, A.S.; Mattoso, L.H.C.; Orts, W.J.; Medeiros, E.S. Nano and submicrometric fibers of poly(D,L-lactide) obtained by solution blow spinning: Process and solution variables. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 122, 3396–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, R.M.d.C.; Menezes, R.R.; Oliveira, J.E.; de Medeiros, E.S. Production of submicrometric fibers of mullite by solution blow spinning (SBS). Mater. Lett. 2015, 149, 47–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha-Ray, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yarin, A.L.; Davis, S.C.; Pourdeyhimi, B. Solution Blowing of Soy Protein Fibers. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 2357–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha-Ray, S.; Yarin, A.L.; Pourdeyhimi, B. The production of 100/400nm inner/outer diameter carbon tubes by solution blowing and carbonization of core–shell nanofibers. Carbon 2010, 48, 3575–3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha-Ray, S.; Sinha-Ray, S.; Yarin, A.L.; Pourdeyhimi, B. Theoretical and experimental investigation of physical mechanisms responsible for polymer nanofiber formation in solution blowing. Polymer 2015, 56, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, E.S.; Glenn, G.M.; Klamczynski, A.P.; Orts, W.J.; Mattoso, L.H.C. Solution blow spinning: A new method to produce micro- and nanofibers from polymer solutions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 113, 2322–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liug, Y.; He, J.-H.; Xu, L.; Yu, J.-Y. The principle of bubble electrospinning and its experimental verification. J. Polym. Eng. 2008, 28, 55–66. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; He, J.-H. Bubble Electrospinning for Mass Production of Nanofibers. Int. J. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2007, 8, 393–396. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Ren, Z.F.; He, J.H. Bubble electrospinning method for preparation of aligned nanofibre mat. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2010, 26, 1309–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, R.; Cavaliere, S.; Jones, D.J.; Rozière, J. Electrospun nanofibre composite polymer electrolyte fuel cell and electrolysis membranes. Nano Energy 2016, 26, 729–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Snyder, J.D.; Elabd, Y.A. Nafion® nanofibers and their effect on polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell performance. J. Power Sources 2009, 186, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Richey, F.W.; Wujcik, K.H.; Elabd, Y.A. Ultra-low platinum loadings in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell electrodes fabricated via simultaneous electrospinning/electrospraying method. J. Power Sources 2014, 264, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Gwee, L.; Salas-de la Cruz, D.; Winey, K.I.; Elabd, Y.A. Super Proton Conductive High-Purity Nafion Nanofibers. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 3785–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Watanabe, K.; Kim, M.; Gopiraman, M.; Song, K.-H.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, I.S. Handspinning Enabled Highly Concentrated Carbon Nanotubes with Controlled Orientation in Nanofibers. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Inoue, Y.; Kim, M.; Ren, X.; Kim, I.S. Effective Formation of Well-Defined Polymeric Microfibers and Nanofibers with Exceptional Uniformity by Simple Mechanical Needle Spinning. Polymers 2018, 10, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jao, D.; Beachley, V.Z. Continuous Dual-Track Fabrication of Polymer Micro-/Nanofibers Based on Direct Drawing. ACS Macro Lett. 2019, 8, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokarev, A.; Asheghali, D.; Griffiths, I.M.; Trotsenko, O.; Gruzd, A.; Lin, X.; Stone, H.A.; Minko, S. Touch- and Brush-Spinning of Nanofibers. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 6526–6532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wunner, F.M.; Wille, M.-L.; Noonan, T.G.; Bas, O.; Dalton, P.D.; De-Juan-Pardo, E.M.; Hutmacher, D.W. Melt Electrospinning Writing of Highly Ordered Large Volume Scaffold Architectures. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1706570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; He, J.; Li, X.; Xu, F.; Li, D. Micro/nanoscale electrohydrodynamic printing: From 2D to 3D. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 15376–15388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ner, Y.; Asemota, C.; Olson, J.R.; Sotzing, G.A. Nanofiber Alignment on a Flexible Substrate: Hierarchical Order from Macro to Nano. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2009, 1, 2093–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, J.; Melchels, F.P.W.; Jeon, J.E.; van Bussel, E.M.; Kimpton, L.S.; Byrne, H.M.; Dhert, W.J.A.; Dalton, P.D.; Hutmacher, D.W.; Malda, J. Reinforcement of hydrogels using three-dimensionally printed microfibres. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Shin, H.J.; Cho, I.H.; Kang, Y.-M.; Kim, I.A.; Park, K.-D.; Shin, J.-W. Nanofiber alignment and direction of mechanical strain affect the ECM production of human ACL fibroblast. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 1261–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, B.M.; Mauck, R.L. The effect of nanofiber alignment on the maturation of engineered meniscus constructs. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 1967–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yin, Z.; Chen, X.; Chen, J.L.; Shen, W.L.; Hieu Nguyen, T.M.; Gao, L.; Ouyang, H.W. The regulation of tendon stem cell differentiation by the alignment of nanofibers. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 2163–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yao, Y. Nanofiber Alignment Mediates the Pattern of Single Cell Migration. Langmuir 2020, 36, 2129–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, J.; Lizu, M.; Stewart, M.; Zygula, K.; Lu, Y.; Chauhan, R.; Yan, X.; Guo, Z.; Wujcik, E.K.; Wei, S. Multifunctional Nanofibers towards Active Biomedical Therapeutics. Polymers 2015, 7, 186–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, H.; Li, H.; Ke, Q.; Chang, J. An Anisotropically and Heterogeneously Aligned Patterned Electrospun Scaffold with Tailored Mechanical Property and Improved Bioactivity for Vascular Tissue Engineering. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 8706–8718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Salim, A.; Ziaie, B. Selective Nanofiber Deposition through Field-Enhanced Electrospinning. Langmuir 2009, 25, 9648–9652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Dong, Z.; Wilson, S.; Clark, R.L. Template-assisted assembly of electrospun fibers. Polymer 2010, 51, 3244–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchko, C.J.; Chen, L.C.; Shen, Y.; Martin, D.C. Processing and microstructural characterization of porous biocompatible protein polymer thin films. Polymer 1999, 40, 7397–7407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Long, Y.-Z.; Chen, Z.-J.; Liu, S.-L.; Zhang, H.-D.; Zhang, J.-C.; Han, W.-P. Recent advances in flexible and stretchable electronic devices via electrospinning. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 1209–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rega, R.; Gennari, O.; Mecozzi, L.; Pagliarulo, V.; Bramanti, A.; Ferraro, P.; Grilli, S. Maskless Arrayed Nanofiber Mats by Bipolar Pyroelectrospinning. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 3382–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Chang, C.; Li, S.; Lin, L. Near-Field Electrospinning. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 839–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, S.H.; Kim, T.G.; Kim, H.C.; Yang, D.-Y.; Park, T.G. Development of dual scale scaffolds via direct polymer melt deposition and electrospinning for applications in tissue regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 1198–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, T.D.; Dalton, P.D.; Hutmacher, D.W. Direct Writing By Way of Melt Electrospinning. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 5651–5657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.; Kim, H.-Y. Toward Nanoscale Three-Dimensional Printing: Nanowalls Built of Electrospun Nanofibers. Langmuir 2014, 30, 1210–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-Y.; Lee, M.; Park, K.J.; Kim, S.; Mahadevan, L. Nanopottery: Coiling of Electrospun Polymer Nanofibers. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 2138–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.-S.; Kim, J.; Oh, J.M.; Park, S.; Cho, S.; Ko, H.; Cho, Y.-K. Near-Field Electrospinning for Three-Dimensional Stacked Nanoarchitectures with High Aspect Ratios. Nano Lett. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-W.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, S.S. Synthesis of SnO2–ZnO core–shell nanofibers via a novel two-step process and their gas sensing properties. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 465603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Pan, K.; He, Q.; Cao, B. Polyacrylonitrile/polypyrrole core/shell nanofiber mat for the removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 244, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.W.; An, S.; Lee, C.; Liou, M.; Yarin, A.L.; Yoon, S.S. Self-healing transparent core–shell nanofiber coatings for anti-corrosive protection. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 7045–7053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, A.; Sun, L.; Gong, X.; Russell, K.J.; Carter, D.J.D.; Gordon, R.G. Strong, Long, Electrically Conductive and Insulated Coaxial Nanocables. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2019, 1, 1717–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Yan, Z.; Jang, K.-I.; Huang, W.; Fu, H.; Kim, J.; Wei, Z.; Flavin, M.; McCracken, J.; Wang, R.; et al. Assembly of micro/nanomaterials into complex, three-dimensional architectures by compressive buckling. Science 2015, 347, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nan, K.; Luan, H.; Yan, Z.; Ning, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, A.; Wang, J.; Han, M.; Chang, M.; Li, K.; et al. Engineered Elastomer Substrates for Guided Assembly of Complex 3D Mesostructures by Spatially Nonuniform Compressive Buckling. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1604281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fu, H.; Nan, K.; Bai, W.; Huang, W.; Bai, K.; Lu, L.; Zhou, C.; Liu, Y.; Liu, F.; Wang, J.; et al. Morphable 3D mesostructures and microelectronic devices by multistable buckling mechanics. Nat. Mater. 2018, 17, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Carlson, M.A.; Teusink, M.J.; Wang, H.; MacEwan, M.R.; Xie, J. Expanding Two-Dimensional Electrospun Nanofiber Membranes in the Third Dimension By a Modified Gas-Foaming Technique. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 1, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Carlson, M.A.; Teusink, M.J.; MacEwan, M.R.; Gu, L.; Xie, J. Expanded 3D Nanofiber Scaffolds: Cell Penetration, Neovascularization, and Host Response. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2016, 5, 2993–3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Chen, S.; Wang, H.; Carlson, M.A.; Gombart, A.F.; Xie, J. CO2-expanded nanofiber scaffolds maintain activity of encapsulated bioactive materials and promote cellular infiltration and positive host response. Acta Biomater. 2018, 68, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, H.; McCarthy, A.; Yan, Z.; Kim, H.J.; Carlson, M.A.; Xia, Y.; Xie, J. Three-Dimensional Objects Consisting of Hierarchically Assembled Nanofibers with Controlled Alignments for Regenerative Medicine. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 2059–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Yamaguchi, K.; Nagaishi, T.; Murai, M.; Kim, M.; Wei, K.; Zhang, K.-Q.; Kim, I.S. Enhancement of mechanical properties of polymeric nanofibers by controlling crystallization behavior using a simple freezing/thawing process. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 43994–44000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chew, S.Y.; Hufnagel, T.C.; Lim, C.T.; Leong, K.W. Mechanical properties of single electrospun drug-encapsulated nanofibres. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 3880–3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-H.; Kim, S.-J.; Shin, H.; Koo, W.-T.; Jang, J.-S.; Kang, J.-Y.; Jeong, Y.J.; Kim, I.-D. High-Resolution, Fast, and Shape-Conformable Hydrogen Sensor Platform: Polymer Nanofiber Yarn Coupled with Nanograined Pd@Pt. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 6071–6082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Type | Spinneret | Polymer | Voltage (kV) | Productivity (g·h−1) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Needleless electrospinning | Secondary coil (T-coil) | PVA | 85 | ~9.72 | [31] |
| Double-ring slit | PVA | 30 | ~2.25 | [40] | |
| Twisted wire | PVP | 20 | ~1.023 | [37] | |
| Rotating-disk | PCL | 25 | ~10.611 | [34] | |
| Threaded rod | PEO | 60 | ~5.2 | [35] | |
| Rotating spiral wire coil | PVA | 60 | ~9.42 | [30] | |
| Curved convex slot | PVA | 70 | ~2 | [41] | |
| Foam | Nafion | 25 | ~9.73 | [45] | |
| Bowl edge | PEO | 16 | ~0.684 | [43] | |
| Rotating cone | PVP | 30 | ~600 | [32] | |
| Umbrella nozzle | PLLA | 30 | ~180 | [46] | |
| Curved slot with temperature elevation | PVA | 60 | ~1.98 | [42] | |
| Needle Roller | PVA | 40 | 12.8 | [47] | |
| Nozzle electrospinning | Multi-nozzle (19 nozzle) | PEO | 15 | ~0.712 | [27] |
| Coaxial with air-blowing | PAN(Core)/TPU(Shell) | 38 | ~3.6 | [25] | |
| Porous hollow tube (13 cm long, 20 holes) | PVP | 40–60 | 0.3–0.5 | [28] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, J.; Kim, M.; Lee, H. Recent Advances on Nanofiber Fabrications: Unconventional State-of-the-Art Spinning Techniques. Polymers 2020, 12, 1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12061386
Song J, Kim M, Lee H. Recent Advances on Nanofiber Fabrications: Unconventional State-of-the-Art Spinning Techniques. Polymers. 2020; 12(6):1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12061386
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Jinkyu, Myungwoong Kim, and Hoik Lee. 2020. "Recent Advances on Nanofiber Fabrications: Unconventional State-of-the-Art Spinning Techniques" Polymers 12, no. 6: 1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12061386
APA StyleSong, J., Kim, M., & Lee, H. (2020). Recent Advances on Nanofiber Fabrications: Unconventional State-of-the-Art Spinning Techniques. Polymers, 12(6), 1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12061386