Phase Inversion-Induced Porous Polybenzimidazole Fuel Cell Membranes: An Efficient Architecture for High-Temperature Water-Free Proton Transport
Abstract
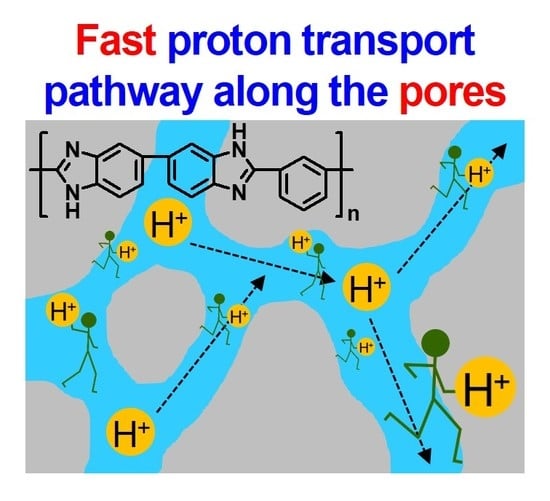
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of m-PBI
2.3. Preparation of Highly Porous m-PBI Membranes
2.4. Fabrication of PEM Fuel Cell MEA
2.5. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bose, S.; Kuila, T.; Nguyen, T.X.H.; Kim, N.H.; Lau, K.-T.; Lee, J.H. Polymer membranes for high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cell: Recent advances and challenges. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 813–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja Rafidah, R.S.; Rashmi, W.; Khalid, M.; Wong, W.Y.; Priyanka, J. Recent Progress in the Development of Aromatic Polymer-Based Proton Exchange Membranes for Fuel Cell Applications. Polymers 2020, 12, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; He, R.; Jensen, J.O.; Bjerrum, N.J. Approaches and Recent Development of Polymer Electrolyte Membranes for Fuel Cells Operating above 100 °C. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 4896–4915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chandan, A.; Hattenberger, M.; El-kharouf, A.; Du, S.; Dhir, A.; Self, V.; Pollet, B.G.; Ingram, A.; Bujalski, W. High temperature (HT) polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells (PEMFC)—A review. J. Power Sources 2013, 231, 264–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Seo, K.; Ghorpade, R.V.; Nam, K.H.; Han, H. High Temperature Anhydrous Proton Exchange Membranes Based on Chemically-Functionalized Titanium/Polybenzimidazole Composites for Fuel Cells. Mater. Lett. 2020, 263, 127167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeis, R. Materials and characterization techniques for high-temperature polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 68–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shao, Y.; Yin, G.; Wang, Z.; Gao, Y. Proton exchange membrane fuel cell from low temperature to high temperature: Material challenges. J. Power Sources 2007, 167, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, K.; Nam, K.H.; Han, H. Proton Transport in Aluminum-Substituted Mesoporous Silica Channel-Embedded High-Temperature Anhydrous Proton-Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, K.; Seo, J.; Nam, K.-H.; Han, H. Polybenzimidazole/inorganic composite membrane with advanced performance for high temperature polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. Polym. Compos. 2017, 38, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escorihuela, J.; Garcia-Bernabe, A.; Montero, A.; Sahuquillo, O.; Gimenez, E.; Compan, V. Ionic Liquid Composite Polybenzimidazol Membranes for High Temperature PEMFC Applications. Polymers 2019, 11, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosli, R.E.; Sulong, A.B.; Daud, W.R.W.; Zulkifley, M.A.; Husaini, T.; Rosli, M.I.; Majlan, E.H.; Haque, M.A. A review of high-temperature proton exchangemembrane fuel cell (HT-PEMFC) system. Int. J. hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 9293–9314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.A.; Sulong, A.B.; Loh, K.S.; Majlan, E.H.; Husaini, T.; Rosli, R.E. Acid doped polybenzimidazoles based membrane electrode assembly for high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cell: A review. Int. J. hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 9156–9179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya, S.S.; Zhou, F.; Liso, V.; Sahlin, S.L.; Vang, J.R.; Thomas, S.; Gao, X.; Jeppesen, C.; Kær, S.K. A comprehensive review of PBI-based high temperature PEM fuel cells. Int. J. hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 21310–21344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escorihuela, J.; Sahuquillo, O.; Garcia-Bernabe, A.; Gimenez, E.; Compan, V. Phosphoric Acid Doped Polybenzimidazole (PBI)/Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework Composite Membranes with Significantly Enhanced Proton Conductivity under Low Humidity Conditions. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uregen, N.; Pehlivanoglu, K.; Ozdemir, Y.; Devrim, Y. Development of polybenzimidazole/graphene oxide composite membranes for high temperature PEM fuel cells. Int. J. hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 2636–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Devi, N.; Srivastava, A.K.; Singh, R.K.; Song, S.-J.; Krishnan, N.N.; Konovalova, A.; Henkensmeier, D. High temperature polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells with Polybenzimidazole-Ce0.9Gd0.1P2O7 and polybenzimidazole-Ce0.9Gd0.1P2O7-graphite oxide composite electrolytes. J. Power Sources 2018, 401, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plackett, D.; Siu, A.; Li, Q.; Pan, C.; Jensen, J.O.; Nielson, S.F.; Permyakova, A.A.; Bjerrum, N.J. High-temperature proton exchange membranes based on polybenzimidazole and clay composites for fuel cells. J. Mem. Sci. 2011, 383, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooshyari, K.; Javanbakht, M.; Shabanikia, A.; Enhessari, M. Fabrication BaZrO3/PBI-based nanocomposite as a new proton conducting membrane for high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2015, 276, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mecerreyes, D.; Grande, H.; Miguel, O.; Ochoteco, E.; Marcilla, R.; Cantero, I. Porous Polybenzimidazole Membranes Doped with Phosphoric Acid: Highly Proton-Conducting Solid Electrolytes. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 604–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrin, H.; Jiang, G.; Lam, G.Y.Y.; Fowler, M.; Chen, Z. High performance porous polybenzimidazole membrane for alkaline fuel cells. Int. J. hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 18405–18415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barati, S.; Abdollahi, M.; Mehdipourghazi, M.; Khoshandam, B. High temperature proton exchange porous membranes based on polybenzimidazole/lignosulfonate blends: Preparation, morphology and physical and proton conductivity properties. Int. J. hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 30440–30453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sannigrahi, A.; Arunbabu, D.; Jana, T. Thermoreversible Gelation of Polybenzimidazole in Phosphoric Acid. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2006, 27, 1962–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sannigrahi, A.; Ghosh, S.; Maity, S.; Jana, T. Polybenzimidazole gel membrane for the use in fuel cell. Polymer 2011, 52, 4319–4330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.-H.; Jheng, L.-C.; Hsu, S.L.-C.; Wang, J.T.-W. Phosphoric acid-doped cross-linked porous polybenzimidazole membranes for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 15660–15665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Zhao, T.S.; An, L.; Zhao, G.; Yan, X.H. A high-performance sandwiched-porous polybenzimidazole membrane with enhanced alkaline retention for anion exchange membrane fuel cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 2768–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillen, G.R.; Pan, Y.; Li, M.; Hoek, E.M.V. Preparation and Characterization of Membranes Formed by Nonsolvent Induced Phase Separation: A Review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 3798–3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.-M.; Lai, J.-Y. Recent advances in preparation and morphology control of polymeric membranes formed by nonsolvent induced phase separation. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2013, 2, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulbricht, M. Advanced functional polymer membranes. Polymer 2006, 47, 2217–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valtcheva, I.B.; Marchetti, P.; Livingston, A.G. Crosslinked polybenzimidazole membranes for organic solvent nanofiltration (OSN): Analysis of crosslinking reaction mechanism and effects of reaction parameters. J. Mem. Sci. 2015, 493, 568–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, K.Y.; Xiao, Y.; Chung, T.-S. Chemically modified polybenzimidazole nanofiltration membrane for the separation of electrolytes and cephalexin. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2006, 61, 5807–5817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valtcheva, I.B.; Kumbharkar, S.C.; Kim, J.F.; Bhole, Y.; Livingston, A.G. Beyond polyimide: Crosslinked polybenzimidazole membranes for organic solvent nanofiltration (OSN) in harsh environments. J. Mem. Sci. 2014, 457, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Yu, S.; Liu, X.; Li, X. Porous polybenzimidazole membranes with excellent chemicalstability and ion conductivity for direct borohydride fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2015, 282, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, T.; David, O.; Gendel, Y.; Wessling, M. Porous poly (benzimidazole) membrane for all vanadium redox flow battery. J. Power Sources 2016, 312, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Ven, E.; Chairuna, A.; Merle, G.; Benito, S.P.; Borneman, Z.; Nijmeijer, K. Ionic liquid doped polybenzimidazole membranes for high temperature Proton Exchange Membrane fuel cell applications. J. Power Sources 2013, 222, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumbharkar, S.C.; Islam, M.N.; Potrekar, R.A.; Kharul, U.K. Variation in acid moiety of polybenzimidazoles: Investigation of physico-chemical properties towards their applicability as proton exchange and gas separation membrane materials. Polymer 2009, 50, 1403–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Jiang, H.; Gao, L.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; He, R. Fabrication of crosslinked polybenzimidazole membranes by trifunctional crosslinkers for high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Int. J. hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 3299–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aili, D.; Li, Q.; Christensen, E.; Jensen, J.O.; Bjerrum, N.J. Crosslinking of polybenzimidazole membranes by divinylsulfone post-treatment for high-temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cell applications. Polym. Int. 2011, 60, 1201–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-W.; Park, J.O.; Pak, C.; Choi, K.H.; Lee, J.-C.; Chang, H. Design and Synthesis of Cross-Linked Copolymer Membranes Based on Poly(benzoxazine) and Polybenzimidazole and Their Application to an Electrolyte Membrane for a High-Temperature PEM Fuel Cell. Polymers 2013, 5, 77–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kerres, J. Blended and Cross-Linked Ionomer membranes for Application in Membrane Fuel Cell. Fuel Cells 2005, 5, 230–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Hu, M.; Wang, L.; Wang, L. Synthesis and Properties of Phosphoric-Acid-Doped Polybenzimidazole with Hyperbranched Cross-Linkers Decorated with Imidazolium Groups as High-Temperature Proton Exchange Membranes. Polymers 2020, 15, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aili, D.; Cleemann, L.N.; Li, Q.; Jensen, J.O.; Christensen, E.; Bjerrum, N.J. Thermal curing of PBI membranes for high temperature PEM fuel cells. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 5444–5453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Søndergaard, T.; Cleemann, L.N.; Becker, H.; Aili, D.; Steenberg, T.; Hjuler, H.A.; Seerup, L.; Li, Q.; Jensen, J.O. Long-term durability of HT-PEM fuel cells based on thermally cross-linked polybenzimidazole. J. Power Sources 2017, 342, 570–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joseph, D.; Krishnan, N.N.; Henkensmeier, D.; Jang, J.H.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, H.-J.; Han, J.; Nam, S.W. Thermal crosslinking of PBI/sulfonated polysulfone based blend membranes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-G.; Lu, M.-I.; Chuang, H.-J. PVdF-HFP/P123 hybrid with mesopores: A new matrix for high-conducting, low-leakage porous polymer electrolyte. Polymer 2005, 46, 5929–5938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quartarone, E.; Magistris, A.; Mustarelli, P.; Grandi, S.; Carollo, A.; Zukowska, G.Z.; Garbarczyk, J.E.; Nowinski, J.L.; Gerbaldi, C.; Bodoardo, S. Pyridine-based PBI Composite Membranes for PEMFCs. Fuel Cells 2009, 9, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, H.; Liu, L.; Chang, Z.; Yuan, J. Organic/inorganic composite membranes based on polybenzimidazole and nano-SiO2. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 7536–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishel, K.J.; Gulledge, A.L.; Pingitore, A.T.; Hoffman, J.P.; Steckle, W.P., Jr.; Benicewicz, B.C. Solution Polymerization of Polybenzimidazole. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2016, 54, 1795–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galbiati, S.; Baricci, A.; Casalegno, A.; Marchesi, R. Degradation in phosphoric acid doped polymer fuel cells: A 6000 h parametric investigation. Int. J. hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 6469–6480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musto, P.; Karasz, F.E.; MacKnight, W.J. Fourier transform infra-red spectroscopy on the thermo-oxidative degradation of polybenzimidazole and of a polybenzimidazole/polyetherimide blend. Polymer 1993, 34, 2934–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, L.; Choe, E.W.; Benicewicz, B.C. Synthesis of Poly (2,2′- (1,4-phenylene) 5,5′-bibenzimidazole) (para-PBI) and Phosphoric Acid Doped Membrane for Fuel Cells. Fuel Cells 2009, 9, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.L.; Wainright, J.S.; Litt, M.H.; Savinell, R.F. Conductivity of PBI Membranes for High-Temperature Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2004, 151, A8–A16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuer, K.-D.; Rabenau, A.; Weppner, W. Vehicle Mechanism, A New Model for the Interpretation of the Conductivity of Fast Proton Conductors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1982, 21, 208–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escorihuela, J.; Garcia-Bernade, A.; Compan, V. A Deep Insight into Different Acidic Additives as Doping Agents for Enhancing Proton Conductivity on Polybenzimidazole Membranes. Polymers 2020, 12, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jheng, L.-C.; Hsu, S.L.-C.; Tsai, T.-Y.; Chang, W.J.-Y. A novel asymmetric polybenzimidazole membrane for high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Mater. Chem. 2014, 2, 4225–4233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jheng, L.-C.; Chang, W.J.-Y.; Hsu, S.L.-C.; Cheng, P.-Y. Durability of symmetrically and asymmetrically porous polybenzimidazole membranes for high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2016, 323, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.H.; Oh, K.; Ahn, S.; Kim, N.Y.; Byeon, A.; Park, H.-Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, H.S.; Yoo, S.J.; Jang, J.H.; et al. Investigation of electrolyte leaching in the performance degradation of phosphoric acid-doped polybenzimidazole membrane-basedf high temperature fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2017, 363, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Sample | Initial Thickness (μm) | Doped Thickness (μm) | Swelling Ratio (%) | Acid Doping Level (ADL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| m-PBI350-0 | 65 | 155 | 241 | 51.5 |
| m-PBI350-0.25 | 64 | 113 | 77.2 | 50.4 |
| m-PBI350-0.5 | 63 | 101 | 64.32 | 44.7 |
| m-PBI350-1 | 62 | 91 | 43.5 | 38.0 |
| m-PBI350-2 | 62 | 86 | 38.7 | 33.8 |
| m-PBI350-3 | 62 | 85 | 37.1 | 29.9 |
| m-PBI | 49 | 72 | 50.6 | 11.0 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.; Nam, K.-H.; Seo, K.; Kim, G.; Han, H. Phase Inversion-Induced Porous Polybenzimidazole Fuel Cell Membranes: An Efficient Architecture for High-Temperature Water-Free Proton Transport. Polymers 2020, 12, 1604. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12071604
Lee S, Nam K-H, Seo K, Kim G, Han H. Phase Inversion-Induced Porous Polybenzimidazole Fuel Cell Membranes: An Efficient Architecture for High-Temperature Water-Free Proton Transport. Polymers. 2020; 12(7):1604. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12071604
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Sangrae, Ki-Ho Nam, Kwangwon Seo, Gunhwi Kim, and Haksoo Han. 2020. "Phase Inversion-Induced Porous Polybenzimidazole Fuel Cell Membranes: An Efficient Architecture for High-Temperature Water-Free Proton Transport" Polymers 12, no. 7: 1604. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12071604
APA StyleLee, S., Nam, K. -H., Seo, K., Kim, G., & Han, H. (2020). Phase Inversion-Induced Porous Polybenzimidazole Fuel Cell Membranes: An Efficient Architecture for High-Temperature Water-Free Proton Transport. Polymers, 12(7), 1604. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12071604