Relationship between Photoelasticity of Polyurethane and Dielectric Anisotropy of Diisocyanate, and Application of High-Photoelasticity Polyurethane to Tactile Sensor for Robot Hands
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. History and Purpose of This Study
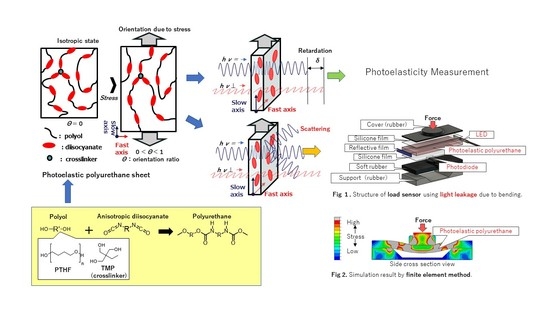
1.2. Mechanism Undelying Photoelasticity
1.3. Previous Study of Photoelastic Polyurethane
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Polyurethane Synthesis
2.1.1. Crude Materials
2.1.2. Preparation of Polyurethanes
2.1.2.1. AR-2 Synthesis
2.1.2.2. AR-1 and AR-3 Synthesis
2.1.2.3. AL-1 Synthesis
2.2. Method of Polyurethane Evaluation
2.2.1. Photoelasticity Measurement Method
2.2.2. Measurement of Glass Transition Temperature
2.2.3. Density Measurement
2.3. Calculation of Polarizability of Polyurethanes
2.3.1. Molecular Structure Used in Calculations and Structural Optimization
2.3.2. Polarizability Calculation and Definition of Anisotropy
2.4. Assembly of Bending Device
2.4.1. Assembly of Bending Elasticity Measurement Device
2.4.2. Assembly of Light-Leakage-Type Load Sensor
2.4.3. Constant-Speed Loading Test of Sensors
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Polyurethanes
3.1.1. Photoelasticity and Young’s Modulus
3.1.2. Dynamic Viscoelasticity Measurement
3.1.3. Complex Photoelasticity
3.1.4. Polarizability Anisotropy of Diisocyanate and Origin of Photoelasticity
3.2. Characterization of Sensor
3.2.1. Observation of Light Leakage and Finite Element Simulation
3.2.2. Light-Leakage-Type Load Sensor
3.3. Comparison with Other Grip Sensors
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B

Appendix C

References
- Ren, Z.; Xie, H.; Ju, Y. Quantification of Photoelastic Fringe Orders Using Polarized Light Camera and Continuous Loading. Opt. Laser Eng. 2020, 134, 106263–106270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, K.E.; Kollmer, J.E. Photoelastic Force Measurements in Granular Materials. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2017, 88, 51808–51830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scafidi, M.; Pitarresi, G.; Toscano, A.; Petrucci, G.; Alessi, S.; Ajovalasit, A. Review of Photoelastic Image Analysis Applied to Structural Birefringent Materials: Glass and Polymers. Opt. Eng. 2015, 54, 81206–81213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woina, M. Polymer Material in Practical Uses of Photoelasticity. Opt. Eng. 1995, 34, 3427–3432. [Google Scholar]
- Ham, S.; Kown, T. Photoelastic Observation of Toughness-Dominant Hydraulic Fracture Propagation Across an Orthogonal Discontinuity in Soft, Viscoelastic Layered Formations. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2020, 134, 104438–104452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelfar, M.; Tavangar, R.; Horandghadim, N.; Khalil-Allafi, J. Evaluation Superelastic and Shape Memory Effects Using the Photostress Technique. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 24, 101156–101164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.L.; Sawada, D.; Kurokawa, T.; Kakugo, A.; Yang, W.; Fukuhara, H.; Gong, J.P. Strain-Induced Molecular Reorientation and Birefringence Reversion of a Robust, Anisotropic Double-network Hydrogel. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 3542–3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mott, P.H.; Roland, C.M. Birefringence of Rubber during Creep and Recovery. Macromolecules 1996, 29, 8492–8496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubey, V.N.; Crowder, R.M. A Dynamic Tactile Sensor on Photoelastic Effect. Sens. Actuators A 2006, 128, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costanzo, M.; De Maria, G.; Natale, C. Two-fingered In-hand Object Handling Based on Force/Tactile Feedback. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2020, 36, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moisio, S.; Leon, B.; Korkealaakso, P.; Morales, A. Model of Tactile Sensors using Soft Contacts and Its Application in Robot Grasping Simulation. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2013, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agarwal, P.; Zhou, W.; Roy, R.; Chang, S.; Liu, X. Photoelastic Birefringence of Copolymers with Non-planar Structure. Polymer 2019, 164, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seif, S.; Cakmak, M. Stress-Optical Behavior of Poly (m-xylylenediamine adipamide) (NylonMXD6): Influence of Molecular Weight. Polymer 2010, 51, 3762–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, B.B.; Mclean, R.S.; Brill, D.J.; Londono, D.J. Morphology and Orientation During the Deformation of Segmented Elastomers Studied with Small-Angle X-ray Scattering and Atomic Force Microscopy. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2002, 40, 1727–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebisawa, M.; Otani, Y.; Umeda, N. Mechanical Characterization Measurement of Polymer Material under Stress by Birefringence Microscope. Opt. Rev. 2007, 14, 310–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilavsky, M.; Sedlakova, Z.; Plestil, J.; Valentova, H.; Nedbal, J. Chemical Clusters in Polyurethane Networks. SAXS, Photoelastic and Dynamic Mechanical Behavior of Networks from Poly(oxypropylene)diol, Diisocyanate, and Trimethylpropane Prepared One-Stage and Two-Stage Process. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B Phys. 2005, 44, 909–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanford, R.J. A General Method for Determining Mixed-Mode Stress Intensity Factors from Isochromatic Fringe Patterns. Eng. Fract. Mech. 1979, 11, 621–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osaki, K.; Takatori, E.; Ueda, M.; Kurata, M.; Kotaka, T.; Ohnuma, H. Birefringence of a Block Copolymer Solution in The Stress-Relaxation Process. Macromolecules 1989, 22, 2457–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curgul, S.; Yilgor, I.; Yilgor, E.; Erman, B.; Cakmak, M. Effect of Chemical Composition on Large Deformation Mechanooptical Properties of High Thermoplastic Poly (urethane urea)s. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 8676–8685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwawaki, H.; Urakawa, O.; Inoue, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Matsumiya, Y. Pheo-Optical and Dielectric Study on Dynamics of Bottlebrush-Like Polymacromonomer Contsisting of A Polyisoprene Main Chain and Polystyrene Side Chains. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 7096–7106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amimori, I.; Priezjev, N.; Pelcovits, R.A.; Crawford, G.P. Optomechanical Properties of Stretched Polymer Dispersed Liquid Crystal Films for Scattering Polarizer Applications. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 93, 3248–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jagt, H.; Dirix, Y.; Hikmet, R.; Bastiaansen, C. Linear Polarizers Based on Oriented Polymer Blends. Adv. Mater. 1998, 10, 934–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuzzo, D.; Kulkarni, C.; Zhao, B.; Smolinsky, E.; Tassinari, F.; Meskers, S.C.J.; Naaman, R.; Meijer, E.W.; Friend, R.H. High Circular Polarization of Electroluminescence Achieved via Self-Assembly of a Light-Emitting Chiral Conjugated Polymer into Multidomain Cholesteric Films. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 12713–12722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, T.; Liu, T.; He, H.; Wu, J.; Ma, H. Distinguishing Anisotropy Orientations Originated from Scattering and Birefringence of Turbid Media Using Mueller Matrix Derived Parameters. Opt. Lett. 2018, 43, 4092–4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsuzuka, M.; Yamasaki, S.; Tajitsu, Y. Patent: US20180022861. Photoelastic polyurethane Resin, Detection Member, Robot, and Method for Producing Photoelastic Polyurethane Resin. U.S. Patent 10,626,213, 21 April 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, Y.; Zhu, M.; Kim, H.; Wada, A.; Mitsuzuka, M.; Tajitsu, Y.; Kawamura, S. Development of a Pneumatically Driven Flexible Finger with Feedback Control of a Polyurethane Bend Sensor. Int. Conf. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2018, 5952–5957. [Google Scholar]
- Nye, J. Physical Properties of Crystals; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Tsujiki, M.; Kowa, H.; Muraki, K.; Umeda, N.; Tajitsu, Y. Measurement of Pockels Effect in Piezoelectric Chiral Polymer Film. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 44, 7115–7118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukiji, M.; Kowa, H.; Muraki, K.; Umeda, N.; Imoto, K.; Kanasaki, M.; Tahara, K.; Morii, K.; Tajitsu, Y. Measurement System for Very Small Photoelastic Constant of Polymer Films. Macromol. Symp. 2006, 242, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olszewski, A.; Kosmela, P.; Mielewzyk-Gryn, A.; Piszczk, L. Bio-Based Polyurethane Composites and Hybrid Composites Containing a New Type of Bio-Polyol and Addition of Natural and Synthetic Fibers. Materials 2020, 13, 2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmawati, R.; Nozaki, S.; Kojio, K.; Takahara, A.; Shinohara, N.; Yamasaki, S. Microphase-Separated Structure and Mechanical Properties of Cycloaliphatic Diisocyanate-based Thiourethane Elastomer. Polym. J. 2019, 51, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Shou, T.; Guo, M.; Wang, R.; Wang, J.; Tian, H.; Qin, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, L. Fabrication of New Thermoplastic polyurethane Elastomers with High Heat Resistance for 3D printing Derived from 3,3-Dimethyl-4,4′-diphenyl Diisocyanate. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 10476–10482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangadharan, R.P.; Krishnan, S.S. Experimental and Computational Study on Molecular Structure and Vibrational Analysis of Hydroxybenzopyridine Using DFT Method. Asian J. Chem. 2014, 26, 4571–4581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guennec, M.L.; Evain, K.; Illien, B. Calculation of Static Mean Polarisability and Polarisability Anisotropy. Statistical Comparison with the Results of Gases and Influence of the Geometrical Parameters. J. Mol. Struct. 2001, 542, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caillie, C.V.; Amos, R.D. Static and Dynamic Polarizabilities, Cauchy Coefficients and Their Anisotropies: An Evaluation of DFT Functionals. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2000, 328, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Cieplak, P.; Luo, R.; Duan, Y. Development of Polarizable Gaussian Model for Molecular Mechanical Calculations 1: Atomic Polarizability Parameterization to Reproduce ab initio Anisotropy. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2019, 15, 1146–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hickey, A.L.; Rowley, C.N. Benchmarking Quantum Chemical Method for the Calculation of Molecular Dipole Moments and Polarizabilities. J. Phys. Chem. A 2014, 118, 3678–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terui, Y.; Ando, S. Coefficients of Molecular Packing and Intrinsic Birefringence of Aromatic Polyimides Estimated Using Refractive Indices and Molecular Polarizabilities. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2004, 42, 2354–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Lenick, A.J. Refractive Index Modification with Silicone Polymers. Personal Care, 6 November 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, T.; Kuwada, S.; Ryu, D. Effect of Strain-Induced Birefringence of Polymers. Polym. J. 1998, 30, 929–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prasad, D.; Nath, V. Design of CMOS Difference Amplifier Circuit for Sigma Delta ADC for Aerospace Applications. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information, Communication, Instrumentation and Control, Indore, India, 17–19 August 2017. Paper ID 239. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, H.; Xiong, B.; Poselt, E.; Eling, B.; Men, Y. Destruction and Reorganization of Physically Cross-Linked Network of Thermoplastic Polyurethane Depending on Its Grass Transition Temperature. Appl. Polym. Mater. 2019, 1, 3074–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugar, J.A.; Childs, C.M.; Huang, C.; Haider, K.W.; Washburn, N.R. Elucidating the Physicochemical Basis of the Grass Transition Temperature in Linear Polyurethane Elastomers with Machine Learning. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 9722–9733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtita, H.; Tagaya, A.; Koike, Y. Preparation of Zero-Birefringence Polymer Doped with a Birefringent Crystal and Analysis of Its Characteristics. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 8342–8348. [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa, R.; Tagaya, A.; Iwata, S.; Koike, Y. Polarization-Maintaining Mechanism of a Birefringence-Reduced Plastic Optical Fiber Fabricated Using Poly (methy methacrylate/bezyl methacrylate) Copolymer. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 7946–7952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoda, K.; Tada, Y.; Asada, M. Internal Representation of Slip Finger with Vision and Tactile Sensors. In Proceedings of the 2002 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems 2002, Lausanne, Switzerland, 30 September–4 October 2002; pp. 111–115. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz, A.; Maggiali, M.; Natale, L.; Bonino, B.; Metta, G. A Tactile Sensor for the Fingertips of the Humanoid Robot iCub. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems 2010, Taipei, Taiwan, 18–22 October 2010; pp. 2212–2217. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, J.; Aspinall, P.; Santos, V.J.; Posner, J.D. Measuring Dynamic Shear Force and Vibration with a Bioinspired Tactile Sensor Skin. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 3544–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomo, T.P.; Schmitz, A.; Wong, W.K.; Kristanto, H.; Somlor, S.; Hwang, J.; Jamone, L.; Sugano, S. Covering a Robot Fingertip with uSkin: A Soft Electronic Skin with Distributed 3-Axis Force Sensitive Elements for Robot Hands. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomo, T.P.; Regoli, M.; Schmitz, A.; Natale, L.; Kristanto, H.; Somlor, S.; Jamone, L.; Metta, G.; Sugano, S. A New Silicone Structure for uSkin—A Soft, Distributed, Digital 3-Axis Skin Sensor and Its Integration on the Humanoid Robot iCub. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 2584–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruebele, A.; Roberge, J.; Zerbe, A.; Ruotolo, W.; Huh, T.M.; Cutkosky, M.R. A Stretchable Capacitive Sensor Skin for Exploring Cluttered Environments. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 1750–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagahama, S.; Migita, K.; Sugano, S. Soft Magnetic Powdery Sensor for Tactile Sensing. Sensors 2019, 19, 2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Song, Y.; Miao, L.; Chen, X.; Su, Z.; Zhang, H. Hybrid Porous Micro Structured Finger Skin Inspired Self-Powered Electronic Skin System for Pressure Sensing and Sliding Detection. Nano Energy 2018, 51, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Abbreviation | Chemical Name | CAS No. | Supplier |
|---|---|---|---|
| TODI | 3,3’-Dimethyl-4,4’-biphenylene diisocyanate | 91-97-4 | Nippon Soda |
| MDI | 4,4’-methylenediphenyl diisocyanate | 101-68-8 | Mitsui Chemicals |
| 1,3-XDI | 1,3-Bis(isocyanatomethyl)benzene | 3634-83-1 | Mitsui Chemicals |
| H12-MDI | Dicyclohexylmethane 4,4’-diisocyanate | 5124-30-1 | Tokyo Chemical Industry |
| PDI | 1,5-Diisocyanatopentane | 4538-42-5 | Mitsui Chemicals |
| IPDI | Isophorone diisocyanate | 4098-71-9 | Tokyo Chemical Industry |
| 1,4-H6-XDI | 1,4-bis(isocyanatomethyl)cyclohexane | 10347-54-3 | Mitsui Chemicals |
| DBTDL | Dibutyltin dilaurate | 77-58-7 | Fujifilm Wako Pure Chemical Corporation |
| PTHF | Poly(tetrahydrofuran) | 25190-06-1 | Hodogaya Chemical |
| TMP | 2-(hydroxymethyl)-2-ethylpropane-1,3-diol | 77-99-6 | Tokyo Chemical Industry |
| BYK-088 | — | — | BYK Japan |
| Irganox 245 | Triethylene glycol bis(3-tert-butyl-4-hydroxy-5-methylphenyl)propionate | 36443-68-2 | BASF Japan |
| Sample Name | AR-1 | AR-2 *1 | AR-3 | AR-4 | AL-1 | AL-2 | AL-3 | AL-4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diisocyanate name | TODI | TODI/MDI | MDI | 1,3-XDI | H12-MDI | PDI | IPDI | 1,4-H6-XDI |
| PTHF(g) | 99 | |||||||
| TMP(g) | 0.99 | |||||||
| Diisocyanate(g) | 29.4 | 9.11/19.2 | 27.8 | 20.9 | 29.2 | 17.1 | 24.7 | 21.6 |
| Riso | 0.227 | 0.071/0.150 | 0.218 | 0.173 | 0.226 | 0.146 | 0.198 | 0.177 |
| Sample Name | AR-1 | AR-2 | AR-3 | AR-4 | AL-1 | AL-2 | AL-3 | AL-4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type of diisocyanate | TODI | TODI/MDI | MDI | 1,3-XDI | H12-MDI | PDI | IPDI | 1,4-H6-XDI |
| Photoelastic constant (10−12/Pa) | 10200 | 4860 | 3510 | 1650 | 1850 | 1380 | 1190 | 1410 |
| Elasto-optical constant (10−6) | 30700 | 22800 | 17300 | 5860 | 6620 | 5930 | 4870 | 6650 |
| Young’s modulus (106 Pa) | 3.01 | 4.69 | 4.93 | 3.55 | 3.58 | 4.3 | 4.09 | 4.72 |
| Glass transition temperature (K) | 239.5 | 240.8 | 241.8 | 221.9 | 238.5 | 215.3 | 231.7 | 224.3 |
| Diisocyanate | Polarizability in 630 nm Light (arb. unit) | (Py + Pz)/2 | α | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PX | Py | Pz | |||
| TODI | 488 | 218 | 171 | 194.5 | 293.5 |
| 173 *1 | 217 *1 | 195 | 293 | ||
| 149 *2 | 240 *2 | 194.5 | 293.5 | ||
| MDI | 382 | 197 | 191 | 194 | 188 |
| H12-MDI | 300 | 201 | 200 | 200.5 | 99.5 |
| 1,3-XDI | 215 | 171 | 143 | 157 | 58 |
| PDI | 172 | 119 | 132 | 125.5 | 46.5 |
| IPDI | 216 | 213 | 167 | 190 | 26 |
| 1,4-H6XDI | 184 | 178 | 155 | 166.5 | 17.5 |
| Sample Name | AR-1 | AR-2 | AR-3 | AR-4 | AL-1 | AL-2 | AL-3 | AL-4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D (g/cm3) | 1.06 | 1.063 | 1.063 | 1.048 | 1.033 | 1.028 | 1.028 | 1.034 |
| Riso | 0.227 | 0.22 | 0.218 | 0.173 | 0.226 | 0.146 | 0.198 | 0.177 |
| M (g/mol) | 264.3 | – | 250.3 | 188.2 | 262.4 | 154.2 | 222.3 | 194.2 |
| α | 293.5 | – | 188 | 58 | 99.5 | 46.5 | 26 | 17.5 |
| α × D × Riso/M | 0.2672 | 0.2033 * | 0.174 | 0.0559 | 0.0885 | 0.0453 | 0.0238 | 0.0165 |
| E (10−6) | 30700 | 22800 | 17300 | 5860 | 6620 | 5930 | 4870 | 6650 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mitsuzuka, M.; Kinbara, Y.; Fukuhara, M.; Nakahara, M.; Nakano, T.; Takarada, J.; Wang, Z.; Mori, Y.; Kageoka, M.; Tawa, T.; et al. Relationship between Photoelasticity of Polyurethane and Dielectric Anisotropy of Diisocyanate, and Application of High-Photoelasticity Polyurethane to Tactile Sensor for Robot Hands. Polymers 2021, 13, 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010143
Mitsuzuka M, Kinbara Y, Fukuhara M, Nakahara M, Nakano T, Takarada J, Wang Z, Mori Y, Kageoka M, Tawa T, et al. Relationship between Photoelasticity of Polyurethane and Dielectric Anisotropy of Diisocyanate, and Application of High-Photoelasticity Polyurethane to Tactile Sensor for Robot Hands. Polymers. 2021; 13(1):143. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010143
Chicago/Turabian StyleMitsuzuka, Masahiko, Yuho Kinbara, Mizuki Fukuhara, Maki Nakahara, Takashi Nakano, Jun Takarada, Zhongkui Wang, Yoshiki Mori, Masakazu Kageoka, Tsutomu Tawa, and et al. 2021. "Relationship between Photoelasticity of Polyurethane and Dielectric Anisotropy of Diisocyanate, and Application of High-Photoelasticity Polyurethane to Tactile Sensor for Robot Hands" Polymers 13, no. 1: 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010143
APA StyleMitsuzuka, M., Kinbara, Y., Fukuhara, M., Nakahara, M., Nakano, T., Takarada, J., Wang, Z., Mori, Y., Kageoka, M., Tawa, T., Kawamura, S., & Tajitsu, Y. (2021). Relationship between Photoelasticity of Polyurethane and Dielectric Anisotropy of Diisocyanate, and Application of High-Photoelasticity Polyurethane to Tactile Sensor for Robot Hands. Polymers, 13(1), 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010143