Reinforced Smart Foams Produced with Time-Profiled Magnetic Fields
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Foams Preparation
2.3. Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Foam Preparation and Morphology
3.2. Static Mechanical Behaviour in Compression
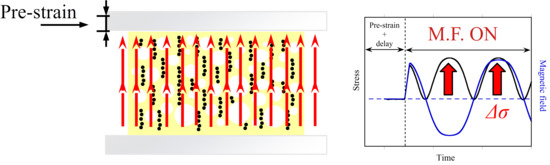
3.3. Magnetoelastic Behaviour
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Custom-Made Setup for the Production of Foams


Appendix A.2. Custom-Made Setup for the Magnetoelastic Characterization

Appendix A.3. Macroscopic Features of Foams
| Series | Sample | Particle Content (%) | Density (kg/m3) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| by Weight of Polymer | by Total Solid Volume | |||
| PU | 0 | 0.0 | 64.4 ± 2.1 | |
| A | RF | 25 | 3.3 | 88.0 ± 5.2 |
| AF_24_T0-10 | 25 | 3.3 | 91.5 ± 1.3 | |
| AF_48_T0-10 | 25 | 3.3 | 87.8 ± 1.0 | |
| AF_96_T0-10 | 25 | 3.3 | 92.0 ± 3.4 | |
| AF_189_T0-10 | 25 | 3.3 | 91.6 ± 4.8 | |
| B | AF_189_T0.5-10 | 25 | 3.3 | 84.9 ± 2.7 |
| AF_189_T1-10 | 25 | 3.3 | 93.8 ± 1.9 | |
| AF_189_T2-10 | 25 | 3.3 | 90.4 ± 2.2 | |
| C | AF_189_T0-1 | 25 | 3.3 | 87.1 ± 3.1 |
| AF_189_T0-2 | 25 | 3.3 | 81.6 ± 2.9 | |
References
- Elhajjar, R.; Law, C.T.; Pegoretti, A. Magnetostrictive polymer composites: Recent advances in materials, structures and properties. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2018, 97, 204–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.X.; Gong, X.L.; Wang, L.H. Development of an adaptive tuned vibration absorber with magnetorheological elastomer. Smart Mater. Struct. 2006, 15, N111–N116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Gong, X.; Fan, Y.; Xia, H. Physically crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels with magnetic field controlled modulus. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 6205–6512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plachy, T.; Kratina, O.; Sedlacik, M. Porous magnetic materials based on EPDM rubber filled with carbonyl iron particles. Compos. Struct. 2018, 192, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipcsei, G.; Csetneki, I.; Szilágyi, A.; Zrínyi, M. Magnetic field-responsive smart polymer composites. Adv. Polym. Sci. 2007, 206, 137–189. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, J.E.; Anderson, R.A.; Williamson, R.L. Generating strange magnetic and dielectric interactions: Classical molecules and particle foams. J. Chem. Phys. 2003, 118, 1557–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulichikhin, V.G.; Semakov, A.V.; Karbushev, V.V.; Plate, N.A.; Picken, S.J. The chaos-to-order transition in critical modes of shearing for polymer and nanocomposite melts. Polym. Sci. Ser. A 2006, 51, 1303–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Dong, X.; Ou, J. Magnetostrictive effect of magnetorheological elastomer. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2008, 320, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coquelle, E.; Bossis, G. Magnetostriction and piezoresistivity in elastomers filled with magnetic particles. J. Adv. Sci. 2005, 17, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.E.; Anderson, R.A.; Read, D.; Gulley, G. Magnetostriction of field-structured magnetoelastomers. Phys. Rev. E 2006, 74, 051507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stepanov, G.V.; Abramchuk, S.S.; Grishin, D.A.; Nikitin, L.V.; Kramarenko, E.Y.; Khokhlov, A.R. Effect of a homogeneous magnetic field on the viscoelastic behavior of magnetic elastomers. Polymer 2007, 48, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrentino, L.; Aurilia, M.; Forte, G.; Iannace, S. Composite Polymeric Foams Produced by Using Magnetic Field. Adv. Sci. Technol. 2008, 54, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrentino, L.; Aurilia, M.; Forte, G.; Iannace, S. Anisotropic mechanical behavior of magnetically oriented iron particle reinforced foams. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 119, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davino, D.; Mei, P.; Sorrentino, L.; Visone, C. Polymeric Composite Foams with Properties Controlled by the Magnetic Field. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 3043–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.; Wu, J.K.J.; Gong, X.L.X.; Fan, Y.C.Y.; Xia, H. Smart polyurethane foam with magnetic field controlled modulus and anisotropic compression property. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Auria, M.; Davino, D.; Pantani, R.; Sorrentino, L. Polymeric foam-ferromagnet composites as smart lightweight materials. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 055014. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.-L.; Li, X.-Q.; Liu, H.-Q.; Luo, Z.-M.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Z.-Q.; Fu, Q. Eco-friendly fabrication of sponge-like magnetically carbonaceous fiber aerogel for high-efficiency oil–water separation. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 30301–30310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Pan, Q. Versatile Fabrication of Ultralight Magnetic Foams and Application for Oil–Water Separation. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 6875–6883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, B.; Zhu, X.; Li, Y.; Men, X.; Li, P.; Zhang, Z. Versatile fabrication of magnetic superhydrophobic foams and application for oil–water separation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 482, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhou, X.; Jiang, W. Low-Cost and Superhydrophobic Magnetic Foam as an Absorbent for Oil and Organic Solvent Removal. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 9498–9506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Hao, G.; Xiao, L.; Yin, Q.; Xia, M.; Jiang, W. Robust magnetic polystyrene foam for high efficiency and removal oil from water surface. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 173, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaddoni Moghaddam, S.; Naimi-Jamal, M.R.; Rohlwing, A.; Hussein, F.B.; Abu-Zahra, N. High Removal Capacity of Arsenic from Drinking Water Using Modified Magnetic Polyurethane Foam Nanocomposites. J. Polym. Environ. 2019, 27, 1497–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarek, S. The giant volumetric magnetostriction of ferromagnetic composites with elastomer matrix. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 1999, 13, 865–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramchuk, S.; Kramarenko, E.; Grishin, D.; Stepanov, G.; Nikitin, L.V.; Filipcsei, G.; Khokhlov, A.R.; Zrínyi, M. Novel highly elastic magnetic materials for dampers and seals: Part II. Material behavior in a magnetic field. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2007, 18, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raikher, Y.L.; Stolbov, O.V. Magnetodeformation effect in a ferroelastic material. Tech. Phys. Lett. 2000, 26, 156–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borcea, L.; Bruno, O. On the magneto-elastic properties of elastomer-ferromagnet composites. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2001, 49, 2877–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kankanala, S.V.; Triantafyllidis, N. On finitely strained magnetorheological elastomers. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2004, 52, 2869–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diguet, G.; Beaugnon, E.; Cavaillé, J.Y. Shape effect in the magnetostriction of ferromagnetic composite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2010, 322, 3337–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coquelle, E.; Bossis, G.; Szabo, D.; Giulieri, F. Micromechanical analysis of an elastomer filled with particles organized in chain-like structure. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 41, 5941–5953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanov, G.V.; Borin, D.Y.; Raikher, Y.L.; Melenev, P.V.; Perov, N.S. Motion of ferroparticles inside the polymeric matrix in magnetoactive elastomers. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2008, 20, 204121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raikher, Y.L.; Stolbov, O.V. Numerical modeling of large field-induced strains in ferroelastic bodies: A continuum approach. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2008, 20, 204126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokander, M.; Stenberg, B. Performance of isotropic magnetorheological rubber materials. Polym. Test. 2003, 22, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varga, Z.; Filipcsei, G.; Zrínyi, M. Magnetic field sensitive functional elastomers with tuneable elastic modulus. Polymer 2006, 47, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.X.; Gong, X.L. Adaptive Tuned Vibration Absorber based on Magnetorheological Elastomer. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2007, 18, 1205–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Gong, X.; Chen, L.; Xia, H.; Hu, Z. Preparation and characterization of isotropic polyurethane magnetorheological elastomer through in situ polymerization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 114, 901–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böse, H.; Röder, R. Magnetorheological elastomers with high variability of their mechanical properties. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2009, 149, 012090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boczkowska, A.; Awietjan, S.F. Smart composites of urethane elastomers with carbonyl iron. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 4104–4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chertovich, A.V.; Stepanov, G.V.; Kramarenko, E.Y.; Khokhlov, A.R. New composite elastomers with giant magnetic response. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2010, 295, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safronov, A.P.; Terziyan, T.V.; Istomina, A.S.; Beketov, I.V. Swelling and contraction of ferrogels based on polyacrylamide in a magnetic field. Polym. Sci. Ser. A 2012, 54, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galipeau, E.; Ponte Castañeda, P. The effect of particle shape and distribution on the macroscopic behavior of magnetoelastic composites. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2012, 49, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brun, F.; Pacilè, S.; Accardo, A.; Kourousias, G.; Dreossi, D.; Mancini, L.; Tromba, G.; Pugliese, R. Enhanced and Flexible Software Tools for X-ray Computed Tomography at the Italian Synchrotron Radiation Facility Elettra. Fundam. Inform. 2015, 141, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Auria, M.; Davino, D.; Pantani, R.; Sorrentino, L. Magnetic field-structuring as versatile approach to shape the anisotropic mechanical response of composite foams. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020. accepted. [Google Scholar]
- Ivaneyko, D.; Toshchevikov, V.P.; Saphiannikova, M.; Heinrich, G. Magneto-sensitive Elastomers in a Homogeneous Magnetic Field: A Regular Rectangular Lattice Model. Macromol. Theory Simul. 2011, 20, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]













| Sample Series | Investigated Parameter | Processing Conditions | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CIP content (Volume %) | MF Strength (kA/m) | sON (min) | sOFF (min) | ||
| A | MF strength | 3.3 | 0–275 | 0 | 10 |
| B | sON | 3.3 | 189 | 0–2 | 10 |
| C | sOFF | 3.3 | 189 | 0 | 0–2 |
| Series | Sample | Compressive Modulus (kPa) | Yield Stress (σy) (kPa) | Strain at Yield (εy) (m/m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PU | 24.3 ± 1.5 | 1.99 ± 0.24 | 0.100 | |
| A | RF | 30.1 ± 1.6 | 2.39 ± 0.37 | 0.100 |
| AF_24_T0-10 | 108.8 ± 2.8 | 7.95 ± 0.61 | 0.100 | |
| AF_48_T0-10 | 146.8 ± 3.7 | 9.40 ± 0.73 | 0.100 | |
| AF_96_T0-10 | 255.3 ± 3.7 | 13.65 ± 0.85 | 0.130 ± 0.011 | |
| AF_189_T0-10 | 447.8 ± 7.6 | 14.85 ± 1.02 | 0.073 ± 0.008 | |
| B | AF_189_T0.5-10 | 302.2 ± 6.4 | 12.05 ± 0.72 | 0.105 ± 0.0007 |
| AF_189_T1-10 | 203.0 ± 2.3 | 10.50 ± 0.55 | 0.100 | |
| AF_189_T2-10 | 76.9 ± 1.2 | 5.04 ± 0.38 | 0.100 | |
| C | AF_189_T0-1 | 41.0 ± 0.1 | 3.84 ± 0.4 | 0.100 |
| AF_189_T0-2 | 89.9 ± 0.3 | 8.22 ± 1.01 | 0.173 ± 0.016 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Davino, D.; D’Auria, M.; Pantani, R.; Sorrentino, L. Reinforced Smart Foams Produced with Time-Profiled Magnetic Fields. Polymers 2021, 13, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010024
Davino D, D’Auria M, Pantani R, Sorrentino L. Reinforced Smart Foams Produced with Time-Profiled Magnetic Fields. Polymers. 2021; 13(1):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010024
Chicago/Turabian StyleDavino, Daniele, Marco D’Auria, Roberto Pantani, and Luigi Sorrentino. 2021. "Reinforced Smart Foams Produced with Time-Profiled Magnetic Fields" Polymers 13, no. 1: 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010024
APA StyleDavino, D., D’Auria, M., Pantani, R., & Sorrentino, L. (2021). Reinforced Smart Foams Produced with Time-Profiled Magnetic Fields. Polymers, 13(1), 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010024