Preparation of Polyetherimide Nanoparticles by a Droplet Evaporation-Assisted Thermally Induced Phase-Separation Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
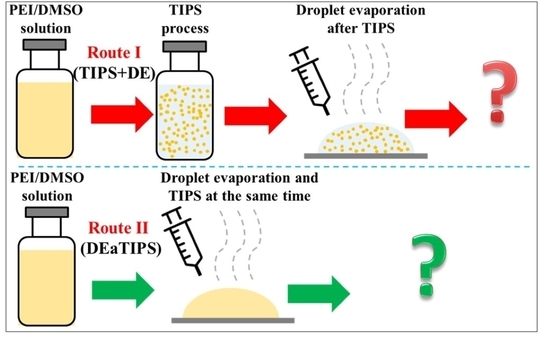
2.2. Preparation of the PEI/DMSO Solution
2.3. TIPS Process
2.4. Droplet Evaporation Process
2.5. Preparation of the PEI Nanoparticles
2.6. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Contact Angle and Surface Tension Test of Different Samples
3.2. PEI Micro or Nanoparticle Preparation in Route I
3.2.1. DLS Test of the PEI/DMSO Suspension
3.2.2. Optical Microscope Observation of the Samples in Route I
3.2.3. SEM Microscope Observation and Particle Size Distribution of the Samples in Route I
3.3. PEI Micro or Nanoparticle Preparation in Route II
3.3.1. Optical Microscope Observation of the Samples in Route II
3.3.2. SEM Microscope Observation and Particle Size Distribution of the Samples in Route II
3.3.3. TEM Microscope Observation of the Samples in Route II
3.4. Effect of Stirring on Particle Growth in the TIPS Process
4. Conclusions
- Circulation flows in the droplet evaporation can suppress the growth of particles. At 25 °C, the growth of some particles is suppressed, while some is not; while at 30 °C, the growth of almost all particles is suppressed; PEI solid nanoparticles with 193 nm average particle size, good uniformity, good separation and good roundness were obtained.
- A stirring process was designed to create circulation flows, which significantly suppressed the growth of particles. Therefore, it indirectly proves that the circulation flows of droplet evaporation can suppress the growth of particles in route II.
- Route I is less sensitive to temperature than route II. Samples in route I were still the accumulations of micro and nanoparticles until 40 °C instead of 30 °C in route II, although the particle size distribution was not uniform.
- A film structure would appear instead of particles when the evaporation temperature exceeds a certain value in both routes.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Fu, H.; Peng, A.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, J.; Ma, Y. Distinct nanostructures from isomeric molecules of bis(iminopyrrole) benzenes: Effects of molecular structures on nanostructural morphologies. Chem. Commun. 2007, 16, 1623–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Middha, E.; Liu, B. Solvent Magic for Organic Particles. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 2675–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korokhin, R.A.; Solodilov, V.I.; Zvereva, U.G.; Solomatin, D.V.; Bamborin, M.Y. Epoxy polymers modified with polyetherimide. Part II: Physicomechanical properties of modified epoxy oligomers and carbon fiber reinforced plastics based on them. Polym. Bull. 2020, 77, 2039–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, J.P.; Geckeler, K.E. Polymer nanoparticles: Preparation techniques and size-control parameters. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 887–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lu, Y.C.; Luo, G.S. Modified nanoprecipitation method for polysulfone nanoparticles preparation. Soft Mater. 2014, 10, 3414–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, D.; Rieger, J. Organic nanoparticles in the aqueous phase-theory, experiment, and use. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 4330–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrado, I.; Abdalrazeq, M.; Pezzella, C.; Di Girolamo, R.; Porta, R.; Sannia, G.; Giosafatto, C.V.L. Design and Characterization of Poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyhexanoate) Nanoparticles and Their Grafting in Whey Protein-based Nanocomposites. Food Hydrocolloid. 2021, 110, 106167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fessi, H.; Puisieux, F.; Devissaguet, J.P.; Ammoury, N.; Benita, S. Nanocapsule Formation by Interfacial Polymer Deposition following Solvent Displacement. Int. J. Pharm. 1989, 55, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, G.; Baby, T.; Chen, D.; Weitz, D.A.; Zhao, C.X. Stable Polymer Nanoparticles with Exceptionally High Drug Loading by Sequential Nanoprecipitation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 4720–4728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milosavljevic, V.; Jelinkova, P.; Jimenez Jimenez, A.M.; Moulick, A.; Haddad, Y.; Buchtelova, H.; Adam, V. Alternative Synthesis Route of Biocompatible Polyvinylpyrrolidone Nanoparticles and Their Effect on Pathogenic Microorganisms. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Foster, D.; Dhinojwala, A. Continuous Production of Polymer Nanoparticles Using a Membrane-based Flow Cell. J. Colloid Interfaces Sci. 2017, 501, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Demirdogen, R.E.; Emen, F.M.; Ocakoglu, K.; Murugan, P.; Sudesh, K.; Avşare, G. Green Nanotechnology for Synthesis and Characterization of Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) Nanoparticles for Sustained Bortezomib Release Using Supercritical CO2 Assisted Particle Formation Combined with Electrodeposition. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, W.H.; Lobuglio, T.M. A New Technique for Preparing Monodisperse Polymer Particles. II. Phase Separation Mechanisms. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1994, 54, 1363–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.H.; Aghajani, M.; Wang, M.Y.; Martinez, J.; Ding, Y.F. Patterning flat-sheet Poly(vinylidene fluoride) membrane using templated thermally induced phase separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 616, 118627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wei, Y.M.; Xu, Z.L.; Guo, R.Q.; Zhao, L.B. Preparation and characterization of polyethersulfone microporous membrane via thermally induced phase separation with low critical solution temperature system. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 437, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, K.; Deckers, J.; Boury, S.; Neirinck, B.; Kruth, J.P.; Vleugels, J. Preparation and indirect selective laser sintering of alumina/PA microspheres. Ceram. Int. 2012, 38, 1241–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.H.; Lloyd, T.B. A New Technique for Preparing Monodisperse Polymer Particles. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1992, 45, 1783–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.J. Nano/micro Spherical Poly (Methyl Methacrylate) Particle Formation by Cooling from Polymer Solution. Powder Technol. 2005, 154, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuyama, H.; Kuwana, M.; Kitamura, Y. Formation of polypropylene particles via thermally induced phase separation. Polymer 2000, 41, 8673–8679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Y.; Khan, A.; Adewole, J.K.; Naim, M.; Basha, S.I.; Aziz, M.D. Biomass derived carboxylated carbon nanosheets blended polyetherimide membranes for enhanced CO2/CH4 Separation. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2020, 75, 103156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Zhou, Y.H.; Zhang, T.D.; Zhang, C.H.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Q.G.; Chi, Q.G. Ultrahigh Discharge Efficiency and Excellent Energy Density in Oriented Core-shell Nanofiber-polyetherimide Composites. Energy Storage Mater. 2020, 25, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, G.W.; Tan, B.; Mcgrath, J.E. Solvent-resistant polyetherimide network systems via phenylethynylphthalic anhydride endcapping. High Perform. Polym. 1994, 6, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri–Tar, F.; Sahimi, M.; Tsotsis, T.T. Preparation of Polyetherimide Nanoparticles by an Electrospray Technique. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 3348–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraud, I.; Franceschi-Messant, S.; Perez, E.; Lacabanne, C.; Dantras, E. Preparation of aqueous dispersion of thermoplastic sizing agent for carbon fiber by emulsion/solvent evaporation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 266, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, X.; Zhang, P.; Shu, M.; Gong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Tian, X. Water vapor induced phase separation: A simple and efficient method for fabricating polyetherimide microspheres. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 105363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Zhang, H.P. Polyetherimide nanoparticle preparation from a polyetherimide/dimethyl sulfoxide solution by a simplified cooling-down method. Polym. Plast. Technol. Mater. 2021, 60, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajiya, T.; Monteux, C.; Narita, T.; Lequeux, F.; Doi, M. Contact-line recession leaving a macroscopic polymer film in the drying droplets of water-poly(N,N-dimethylacrylamide) (PDMA) solution. Langmuir 2009, 25, 6934–6939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.D.; Midya, J.; Kappl, M.; Butt, H.J.; Nikoubashman, A. Segregation in drying binary colloidal droplets. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 4972–4979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Park, S.B.; Kim, J.H.; Zin, W.C. Polymer transports inside evaporating water droplets at various substrate temperatures. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 15375–15383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khellil, S. Patterns from drying drops. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 206, 372–381. [Google Scholar]
- Kajiya, T.; Kobayashi, W.; Okuzono, T.; Doi, M. Controlling the drying and film formation processes of polymer solution droplets with addition of small amount of surfactants. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 15460–15466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshitake, Y.; Yasumatsu, S.; Kaneda, M.; Nakaso, K.; Fukai, J. Structure of circulation flows in polymer solution droplets receding on flat surfaces. Langmuir 2010, 26, 3923–3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uno, K.; Hayashi, K.; Hayashi, T.; Ito, K.; Kitano, H. Particle adsorption in evaporating droplets of polymer latex dispersions on hydrophilic and hydrophobic surfaces. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1998, 276, 810–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.K.; Cheng, J.T.; Collier, C.P.; Srijanto, B.R.; Briggs, D.P. Evaporation of squeezed water droplets between two parallel hydrophobic/superhydrophobic surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 576, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deegan, R.D.; Bakajin, O.; Dupont, T.F.; Huber, G.; Witten, T.A. Capillary flow as the cause of ring stains from dried liquid drops. Nature 1997, 389, 827–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneda, M.; Hyakuta, K.; Takao, Y.; Ishizuka, H.; Fukai, J. Internal flow in polymer solution droplets deposited on a lyophobic surface during a receding process. Langmuir 2008, 24, 9102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Askounis, A.; Sefiane, K.; Shanahan, M.; Shanahan, M.E.R. Effect of particle geometry on triple line motion of nano-fluid drops and deposit nano-structuring. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 222, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]












| Samples | Surface Tension (mN/m) | Contact Angle (°) | Droplet Diameter (d: mm) | Droplet Height (h: mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMSO | 39.1 ± 0.4 | 70.9 ± 1.3 | 3.5 | 1.2 |
| 20-TIPS + DE | 39.3 ± 0.1 | 70.6 ± 1.0 | 3.4 | 1.2 |
| 60-TIPS + DE | 39.0 ± 0.1 | 71.0 ± 1.1 | 3.7 | 1.2 |
| DEaTIPS | 39.1 ± 0.4 | 73.7 ± 1.3 | 3.5 | 1.2 |
| Samples | Particle Size Distribution of Samples at Different Evaporation Temperature | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 °C | 30 °C | 40 °C | 50 °C | |
| 20-TIPS + DE | 463 ± 217 nm | 769 ± 207 nm | 856 ± 201 nm | Film structure |
| 60-TIPS + DE | 682 ± 181 nm | 721 ± 262 nm | 753 ± 201 nm | Film structure |
| DEaTIPS | 231 ± 150 nm | 193 ± 44 nm | Film structure | Film structure |
| 20-TIPS(Stirring) + DE | - | 387 ± 288 nm | - | - |
| 60-TIPS(Stirring) + DE | - | 1048 ± 536 nm | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, P.; Zhang, H.; Lu, H. Preparation of Polyetherimide Nanoparticles by a Droplet Evaporation-Assisted Thermally Induced Phase-Separation Method. Polymers 2021, 13, 1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13101548
Zhu P, Zhang H, Lu H. Preparation of Polyetherimide Nanoparticles by a Droplet Evaporation-Assisted Thermally Induced Phase-Separation Method. Polymers. 2021; 13(10):1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13101548
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Peng, Huapeng Zhang, and Hongwei Lu. 2021. "Preparation of Polyetherimide Nanoparticles by a Droplet Evaporation-Assisted Thermally Induced Phase-Separation Method" Polymers 13, no. 10: 1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13101548
APA StyleZhu, P., Zhang, H., & Lu, H. (2021). Preparation of Polyetherimide Nanoparticles by a Droplet Evaporation-Assisted Thermally Induced Phase-Separation Method. Polymers, 13(10), 1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13101548