Selective Adsorption and Separation of Proteins by Ligand-Modified Nanofiber Fabric
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of CB-Modified PVA Nanofiber Fabric
2.3. BHb Adsorption Studies
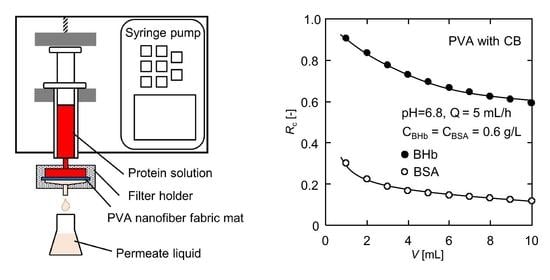
2.4. Selective Separation of Binary BHb–BSA Solution
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of the PVA Nanofiber Fabrics
3.2. Static Adsorption Isotherm of BHb
3.3. BHb Dynamic Adsorption Performance
3.4. Effect of pH on BHb and BSA Adsorption
3.5. Selective Separation of Binary BHb–BSA Solution
3.6. Desorption and Reusability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Watson, H. Biological membranes. Essays Biochem. 2015, 59, 43–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buehler, M.J.; Yung, Y.C. Deformation and failure of protein materials in physiologically extreme conditions and disease. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhlman, B.; Bradley, P. Advances in protein structure prediction and design. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 681–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefani, M.; Dobson, C.M. Protein aggregation and aggregate toxicity: New insights into protein folding, misfolding diseases and biological evolution. J. Mol. Med. 2003, 81, 678–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cournia, Z.; Allen, T.W.; Andricioaei, I.; Antonny, B.; Baum, D.; Brannigan, G.; Buchete, N.V.; Deckman, J.T.; Delemotte, L.; del Val, C.; et al. Membrane protein structure, function, and dynamics: A perspective from experiments and theory. J. Membr. Biol. 2015, 248, 611–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pace, C.N.; Grimsley, G.R.; Scholtz, J.M. Protein ionizable groups: pK values and their contribution to protein stability and solubility. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 13285–13289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Stern, D.; Lock, L.L.; Mills, J.; Ou, S.H.; Morrow, M.; Xu, X.; Ghose, S.; Li, Z.J.; Cui, H. Emerging biomaterials for downstream manufacturing of therapeutic proteins. Acta Biomater. 2019, 95, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Sharma, N.; Ranjan, R.; Kumar, S.; Bhat, Z.F.; Jeong, D.K. Perspective of membrane technology in dairy industry: A review. Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 26, 1347–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kapoor, S.; Rafiq, A.; Sharma, S. Protein engineering and its applications in food industry. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 2321–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, A.; Wu, H.S.; Wang, S.S. Engineering problems in protein crystallization. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 68, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, R.; Carvalho, A.L.; Roque, A.C.A. Renaissance of protein crystallization and precipitation in biopharmaceuticals purification. Biotechnol. Adv. 2017, 35, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Qian, H.; Qi, X. Targeted separation of antibacterial peptide from protein hydrolysate of anchovy cooking wastewater by equilibrium dialysis. Food Chem. 2015, 168, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, M.; Ye, Y.; Chen, V. Separation and concentration of milk proteins with a submerged membrane vibrational system. J. Memb. Sci. 2017, 524, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hage, D.S.; Anguizola, J.A.; Bi, C.; Li, R.; Matsuda, R.; Papastavros, E.; Pfaunmiller, E.; Vargas, J.; Zheng, X. Pharmaceutical and biomedical applications of affinity chromatography: Recent trends and developments. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2012, 69, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iritani, E.; Mukai, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Murase, T. Flux decline behavior in dead-end microfiltration of protein solutions. J. Memb. Sci. 1995, 103, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukai, Y.; Iritani, E.; Murase, T. Fractionation characteristics of binary protein mixtures by ultrafiltration. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1998, 33, 169–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iritani, E.; Mukai, Y. Approach from physicochemical aspects in membrane filtration. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 1997, 14, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, C.; Gallos, T.; Alekseev, Y.; Ayturk, E.; Pearl, S. Protein concentration with single-pass tangential flow filtration (SPTFF). J. Memb. Sci. 2011, 384, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emin, C.; Kurnia, E.; Katalia, I.; Ulbricht, M. Polyarylsulfone-based blend ultrafiltration membranes with combined size and charge selectivity for protein separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 193, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Ye, H.; Yu, T.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Xin, Q.; Wang, S.; Ding, X.; Li, H. Similarly sized protein separation of charge-selective ethylene-vinyl alcohol copolymer membrane by grafting dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadar, S.S.; Pawar, R.G.; Rathod, V.K. Recent advances in enzyme extraction strategies: A comprehensive review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 101, 931–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.B.; Xu, W.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, Y.L.; Yung, K.L.; Diao, D.; Fung, K.H.; Hao, J. Multifunctional water drop energy harvesting and human motion sensor based on flexible dual-mode nanogenerator incorporated with polymer nanotubes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 24030–24038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.B.; Xu, W.; Tian, W.; Han, J.C.; Zhao, C.H.; Wu, H.L.; Hao, J. Ultrasonic-assisted ultrafast fabrication of polymer nanowires for high performance triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2020, 71, 104593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.B.; Xu, W.; Hao, J. Energy device applications of synthesized 1D polymer nanomaterials. Small 2017, 13, 1701820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Yamaguchi, K.; Nagaishi, T.; Murai, M.; Kim, M.; Wei, K.; Zhang, K.Q.; Kim, I.S. Enhancement of mechanical properties of polymeric nanofibers by controlling crystallization behavior using a simple freezing/thawing process. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 43994–44000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mamun, A.; Blachowicz, T.; Sabantina, L. Electrospun nanofiber mats for filtering applications—Technology, structure and materials. Polymers 2021, 13, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, K.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. Functional nanofibers for environmental applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 5326–5334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.Y.; Bae, J.H.; Hasegawa, Y.; An, S.; Kim, I.S.; Lee, H.; Kim, M. Thiol-functionalized cellulose nanofiber membranes for the effective adsorption of heavy metal ions in water. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 234, 115881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliabadi, M.; Irani, M.; Ismaeili, J.; Piri, H.; Parnian, M.J. Electrospun nanofiber membrane of PEO/Chitosan for the adsorption of nickel, cadmium, lead and copper ions from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 220, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, B.; Barakat, N.A.M.; Pant, H.R.; Park, M.; Saud, P.S.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, H.Y. Synthesis and photocatalytic activities of CdS/TiO2 nanoparticles supported on carbon nanofibers for high efficient adsorption and simultaneous decomposition of organic dyes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 434, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, X.; Huang, Y.; Dargaville, T.R.; Fan, Y.; Cui, Z.; Zhu, H. Modified alumina nanofiber membranes for protein separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 120, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lan, T.; Shao, Z.Q.; Wang, J.Q.; Gu, M.J. Fabrication of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles decorated cellulose triacetate nanofibers for protein adsorption by coaxial electrospinning. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 260, 818–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Duan, C.; Yan, Z.; Si, Y.; Liu, L.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Electrospun nanofibrous composite materials: A versatile platform for high efficiency protein adsorption and separation. Compos. Commun. 2018, 8, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, P.; Schreuder-Gibson, H.; Rivin, D. Transport properties of porous membranes based on electrospun nanofibers. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2001, 187, 469–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Fu, Q.; Si, Y.; Liu, L.; Yin, X.; Ji, F.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Electrospun regenerated cellulose nanofiber based metal-chelating affinity membranes for protein adsorption. Compos. Commun. 2018, 10, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Show, P.L.; Ooi, C.W.; Lee, X.J.; Yang, C.L.; Liu, B.L.; Chang, Y.K. Batch and dynamic adsorption of lysozyme from chicken egg white on dye-affinity nanofiber membranes modified by ethylene diamine and chitosan. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 1711–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, I.S.; Song, C.P.; Ooi, C.W.; Tey, B.T.; Lee, Y.H.; Chang, Y.K. Purification of lysozyme from chicken egg white using nanofiber membrane immobilized with Reactive Orange 4 dye. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 134, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Mukai, Y. Dynamic adsorption behaviors of protein on Cibacron Blue-modified PVA nanofiber fabrics. J. Text. Eng. 2021, 67, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Sumi, T.; Mukai, Y. Development of Cibacron Blue-enhanced affinity nanofiber fabric for protein adsorption. J. Fiber Sci. Technol. 2020, 76, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Bora, N.; Rohman, M.A.; Sharma, R.; Jha, A.N.; Singha Roy, A. Molecular recognition of bio-active flavonoids quercetin and rutin by bovine hemoglobin: An overview of the binding mechanism, thermodynamics and structural aspects through multi-spectroscopic and molecular dynamics simulation studies. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 21668–21684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, D.C.; Ho, J.X. Structure of serum albumin. Adv. Protein Chem. 1994, 45, 153–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, S.M.; Sette, G.; Phan, Q. Electrochemical probing of selective haemoglobin binding in hydrogel-based molecularly imprinted polymers. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 9203–9208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peters, T. Serum albumin. Adv. Protein Chem. 1985, 37, 161–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruckenstein, E.; Zeng, X. Albumin separation with Cibacron Blue carrying macroporous chitosan and chitin affinity membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 1998, 142, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavuz, H.; Duru, E.; Genç, Ö.; Denizli, A. Cibacron Blue F3GA incorporated poly(methylmethacrylate) beads for albumin adsorption in batch system. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2003, 223, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang-Schenkelberg, J.; Fieg, G.; Waluga, T. Molecular insight into affinity interaction between Cibacron Blue and proteins. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 9691–9697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Agarwal, G.P. Interactions of proteins with immobilized metal ions: A comparative analysis using various isotherm models. Anal. Biochem. 2001, 288, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.; Shao, Z.Q.; Gu, M.J.; Zhou, Z.W.; Wang, Y.L.; Wang, W.J.; Wang, F.J.; Wang, J.Q. Electrospun nanofibrous cellulose diacetate nitrate membrane for protein separation. J. Memb. Sci. 2015, 489, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, L.; Zheng, J.; Xu, J. Preparation of magnetic carbon nanotubes with hierarchical copper silicate nanostructure for efficient adsorption and removal of hemoglobin. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 375, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Tan, S.; Liang, Q.; Guan, H.; Han, Q.; Ding, M. Selective separation of bovine hemoglobin using magnetic mesoporous rare-earth silicate microspheres. Talanta 2019, 204, 792–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Yang, C.; Yohannes, A.; Yao, S. Acidic ionic liquid modified silica gel for adsorption and separation of bovine serum albumin (BSA). RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 107452–107462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Yu, H.; Karunakaran, M.; Pradeep, N.; Nunes, S.P.; Peinemann, K.V. Selective separation of similarly sized proteins with tunable nanoporous block copolymer membranes. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tuzmen, N.; Kalburcu, T.; Uygun, D.A.; Akgol, S.; Denizli, A. A novel affinity disks for bovine serum albumin purification. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 175, 454–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Mukai, Y. Selective Adsorption and Separation of Proteins by Ligand-Modified Nanofiber Fabric. Polymers 2021, 13, 2313. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13142313
Liu S, Mukai Y. Selective Adsorption and Separation of Proteins by Ligand-Modified Nanofiber Fabric. Polymers. 2021; 13(14):2313. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13142313
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Song, and Yasuhito Mukai. 2021. "Selective Adsorption and Separation of Proteins by Ligand-Modified Nanofiber Fabric" Polymers 13, no. 14: 2313. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13142313
APA StyleLiu, S., & Mukai, Y. (2021). Selective Adsorption and Separation of Proteins by Ligand-Modified Nanofiber Fabric. Polymers, 13(14), 2313. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13142313