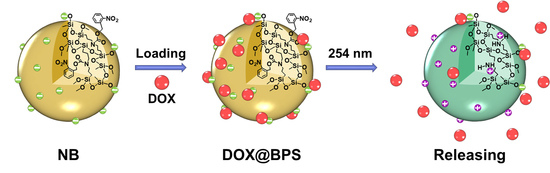
Precise Controlled Target Molecule Release through Light-Triggered Charge Reversal Bridged Polysilsesquioxane Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Synthesis of o-Nitrobenzyl Chloroformate
2.2.2. o-Nitrobenzyl Bis-trimethoxysilylpropyl Carbamate (o–NB)
2.2.3. Bridged Polysilsesquioxane Nanoparticles (BPS)
2.2.4. Photoreaction of the o–NB
2.2.5. Light-Triggered Charge Reversal of BPS
2.2.6. Drug Loading and Light-Triggered Drug Release In Vitro
2.3. Characterization Techniques
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characteristic of Photoresponsive o–NB
3.2. Synthesis and Characteristic of BPS
3.3. Light-Triggered Charge Reversal of BPS
3.4. Drug Loading and Light-Triggered Drug Release In Vitro
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mura, S.; Nicolas, J.; Couvreur, P. Stimuli-responsive nanocarriers for drug delivery. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 991–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganta, S.; Devalapally, H.; Shahiwala, A.; Amiji, M. A review of stimuli-responsive nanocarriers for drug and gene delivery. J. Control. Release 2008, 126, 187–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, T.; Kohane, D.S. Nanoscale systems for local drug delivery. Nano Today 2019, 28, 100765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thananukul, K.; Kaewsaneha, C.; Opaprakasit, P.; Lebaz, N.; Errachid, A.; Elaissari, A. Smart gating porous particles as new carriers for drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 174, 425–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora-Huertas, C.E.; Fessi, H.; Elaissari, A. Polymer-based nanocapsules for drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 385, 113–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khizar, S.; Ahmad, N.M.; Ahmed, N.; Manzoor, S.; Elaissari, A. Encapsulation of doxorubicin in magnetic-polymer hybrid colloidal particles of Eudragit E100 and their hyperthermia and drug release studies. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2020, 31, 1732–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofridam, F.; Tarhini, M.; Wei, L.; Lebaz, N.; Gagniere, E.; Mangin, D.; Dumas, E.; Ghnimi, S.; Gharsallaoui, A.; Errachid, A.; et al. Stimuli-Responsive Polymer Coatings; Polymer Coatings: Technologies and Applications, 11th ed.; Mavinkere, R.S., Parameswaranpillai, J., Siengchin, S., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021; pp. 199–225. [Google Scholar]
- Marturano, V.; Cerruti, P.; Giamberini, M.; Tylkowski, B.; Ambrogi, V. Light-responsive polymer micro-and nano-capsules. Polymers 2017, 9, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Lorenzo, C.; Bromberg, L.; Concheiro, A. Light-sensitive intelligent drug delivery systems. Photochem. Photobiol. 2009, 85, 848–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barhoumi, A.; Liu, Q.; Kohane, D.S. Ultraviolet light-mediated drug delivery: Principles, applications, and challenges. J. Control. Release 2015, 219, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rwei, A.Y.; Wang, W.; Kohane, D.S. Photoresponsive nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nano Today 2015, 10, 451–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Kohane, D.S. External triggering and triggered targeting strategies for drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 17020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruskowitz, E.R.; Deforest, C.A. Photoresponsive biomaterials for targeted drug delivery and 4D cell culture. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2018, 3, 17087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, C.P.; Rooney, C.; Edwards, C.R.; Jones, D.S.; Gorman, S.P. Light-triggered molecule-scale drug dosing devices. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 9572–9573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.K. Photocleavable linkers: Design and applications in nanotechnology; In Photonanotechnology for Therapeutics and Imaging, 9th ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 243–275. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Chen, C.; Lai, J.; Chen, J.; Mu, X.; Zheng, J.; Zhao, Y. Molecule-scale controlled-release system based on light-responsive silica nanoparticles. Chem. Commun. 2008, 23, 2662–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, Q.; Huang, Q.; Li, C.; Bao, C.; Liu, Z.; Li, F.; Zhu, L. Anticancer drug release from a mesoporous silica based nanophotocage regulated by either a one- or two-photon process. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 10645–10647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, S.; Puvvada, N.; Kumar, B.N.P.; Rajput, S.; Pathak, A.; Mandal, M.; Singh, N.D.P. Photoresponsive coumarin-tethered multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles for release of anticancer drug. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 5232–5238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karthik, S.; Jana, A.; Saha, B.; Kalyani, B.K.; Ghosh, S.K.; Zhao, Y.; Singh, N.D.P. Synthesis and in vitro evaluation of charge reversal photoresponsive quinoline tethered mesoporous silica for targeted drug delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 7971–7977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zangabad, P.S.; Mirkiani, S.; Shahsavari, S.; Masoudi, B.; Masroor, M.; Hamed, H.; Jafari, Z.; Taghipour, Y.D.; Hashemi, H.; Karimi, M.; et al. Stimulus-responsive liposomes as smart nanoplatforms for drug delivery applications. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2018, 7, 95–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Y.; Gong, X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, F.; Fu, C.; Li, P.; Zou, L.; Zhao, G. Activated charge-reversal polymeric nano-system: The promising strategy in drug delivery for cancer therapy. Polymers 2016, 8, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, X.; Li, C.; Shen, X. Charge-reversal nanocarriers: An emerging paradigm for smart cancer nanomedicine. J. Control. Release 2020, 319, 46–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, L.; Jiang, C. Charge-reversal nanoparticles novel targeted drug delivery carriers. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2016, 6, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, Z.; Pan, S.; Gao, P.; Sheng, H.; Li, L.; Shi, L.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, X. Stimuli-responsive charge-reversal nano drug delivery system: The promising targeted carriers for tumor therapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 575, 118841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhu, T.; Miao, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, W. Dual-responsive doxorubicin-loaded nanomicelles for enhanced cancer therapy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 18, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, M.; Zhang, W.G.; Wang, C.H.; Wang, F.; You, Y.Z.; Zhang, W.J.; Hong, C.Y. Polymerization-Induced Self-Assembly to Produce Prodrug Nanoparticles with Reduction-Responsive Camptothecin Release and pH-Responsive Charge-Reversible Property. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2020, 41, 2000260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhu, D.; Zhou, Z.; Piao, Y.; Tang, J.; Shen, Y. Glutathione-Specific and Intracellularly Labile Polymeric Nanocarrier for Efficient and Safe Cancer Gene Delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 14825–14838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Liu, Q.; Chen, L.; Li, M.; Yin, J.; Zhu, X.; Chen, D. A pH-Sensitive Self-Assembled and Carrier-Free Nanoparticle Based on Charge Reversal for Enhanced Synergetic Chemo-Phototherapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2020, 9, 2000899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Liu, P. pH-responsive surface charge reversal carboxymethyl chitosan-based drug delivery system for pH and reduction dual-responsive triggered DOX release. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 236, 116093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Wan, L.; Yuan, Y.; Kuang, Y.; Xu, X.; Liao, T.; Liu, J.; Xu, Z.Q.; Jiang, B.; Li, C. pH/GSH-Dual-Sensitive Hollow Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticle-Based Drug Delivery System for Targeted Cancer Therapy. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 3375–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, N.; Li, W.; Liu, D.; Wu, S.; Song, B.; Ma, J.; Chen, D.; Hu, H. Tumor Microenvironment Stimuli-Responsive Nanoparticles for Programmed Anticancer Drug Delivery. Mol. Pharm. 2020, 17, 1516–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; He, K.; Li, J.; Shen, T.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yuan, C.; Dai, L. Dual pH-responsive charge-reversal and photo-crosslinkable polymer nanoparticles for controlled drug release. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2020, 31, 849–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Song, F.; Liu, Y.; Tian, J.; Liu, C.; Li, R.; Zhang, Q. A dual pH-sensitive liposomal system with charge-reversal and NO generation for overcoming multidrug resistance in cancer. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 3814–3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, G.; You, C.C.; Kim, B.J.; Turingan, R.S.; Forbes, N.S.; Martin, C.T.; Rotello, V.M. Light-regulated release of DNA and its delivery to nuclei by means of photolabile gold nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 3165–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatieiev, Y.; Croissant, J.G.; Alsaiari, S.; Moosa, B.A.; Anjum, D.H.; Khashab, N.M. Photoresponsive Bridged Silsesquioxane Nanoparticles with Tunable Morphology for Light-Triggered Plasmid DNA Delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 24993–24997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foster, A.A.; Greco, C.T.; Green, M.D.; Epps, T.H.; Sullivan, M.O. Light-mediated activation of siRNA release in diblock copolymer assemblies for controlled gene silencing. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2015, 4, 760–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Zheng, J.; Zeng, Q.; Zhang, T.; Xing, D. Light-responsive charge-reversal nanovector for high-efficiency in vivo CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing with controlled location and time. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 2399–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shea, K.J.; Loy, D.A. Bridged Polysilsesquioxanes. Molecular-Engineered Hybrid Organic—Inorganic Materials. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 3306–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croissant, J.G.; Fatieiev, Y.; Khashab, N.M. Degradability and Clearance of Silicon, Organosilica, Silsesquioxane, Silica Mixed Oxide, and Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1604634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Lin, S.; Yang, S. Photo-responsive degradable hollow mesoporous organosilica nanoplatforms for drug delivery. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 18, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatieiev, Y.; Croissant, J.G.; Julfakyan, K.; Deng, L.; Anjum, D.H.; Gurinov, A.; Khashab, N.M. Enzymatically degradable hybrid organic-inorganic bridged silsesquioxane nanoparticles for in vitro imaging. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 15046–15050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, L.C.; Yonamine, Y.; Lee, S.H.; Van Der Veer, W.E.; Shea, K.J. Light-triggered charge reversal of organic-silica hybrid nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 11072–11075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomina, V.V.; Stolyarchuk, N.V.; Katelnikovas, A.; Misevicius, M.; Kanuchova, M.; Kareiva, A.; Beganskienė, A.; Melnyk, I.V. Preparation and luminescence properties of europium(III)-loaded aminosilica spherical particles. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 608, 125552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hu, J.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Li, Y. Fabrication of high-performance lithium ion battery anode materials from polysilsesquioxane nanotubes. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 859, 157801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Hu, R.; Zhu, Q.; Zhan, J.; Liu, H.; Yao, B. Improved selective extraction of 3,3′-dichlorobenzidine by molecularly imprinted polysiloxane microspheres. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2012, 10, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doustkhah, E.; Tahawy, R.; Simon, U.; Tsunoji, N.; Ide, Y.; Hanaor, D.A.H.; Assadi, M.H.N. Bispropylurea bridged polysilsesquioxane: A microporous MOF-like material for molecular recognition. Chemosphere 2021, 276, 130181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.J.; Song, J.; Ahmed, K.; Rahim, A.; Onófrio Volpe, P.L.; Rehman, F. Mesoporous silica MCM-41, SBA-15 and derived bridged polysilsesquioxane SBA-PMDA for the selective removal of textile reactive dyes from wastewater. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 298, 111957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Zhang, M.; Wu, M.; Yang, L.; Liu, R.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, T.; Song, C.; Liu, G.; Zhu, Q. Precise Controlled Target Molecule Release through Light-Triggered Charge Reversal Bridged Polysilsesquioxane Nanoparticles. Polymers 2021, 13, 2392. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13152392
Zhang X, Zhang M, Wu M, Yang L, Liu R, Zhang R, Zhao T, Song C, Liu G, Zhu Q. Precise Controlled Target Molecule Release through Light-Triggered Charge Reversal Bridged Polysilsesquioxane Nanoparticles. Polymers. 2021; 13(15):2392. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13152392
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xin, Mengmeng Zhang, Mingyue Wu, Linchuan Yang, Rui Liu, Rui Zhang, Tongtong Zhao, Ci Song, Gang Liu, and Qingzeng Zhu. 2021. "Precise Controlled Target Molecule Release through Light-Triggered Charge Reversal Bridged Polysilsesquioxane Nanoparticles" Polymers 13, no. 15: 2392. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13152392
APA StyleZhang, X., Zhang, M., Wu, M., Yang, L., Liu, R., Zhang, R., Zhao, T., Song, C., Liu, G., & Zhu, Q. (2021). Precise Controlled Target Molecule Release through Light-Triggered Charge Reversal Bridged Polysilsesquioxane Nanoparticles. Polymers, 13(15), 2392. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13152392