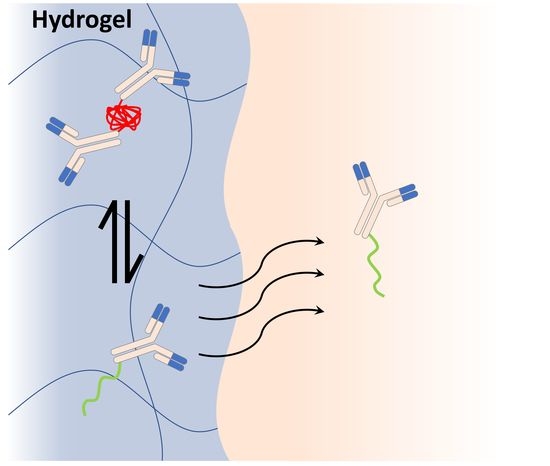
Modulating the Thermoresponse of Polymer-Protein Conjugates with Hydrogels for Controlled Release
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Selection of Polymer Components for Hydrogel and Antibody Conjugates
3.2. Synthesis and Characterization of PEGMA-Antibody Conjugates
3.3. Controlled Release of PEGMA-Protein Conjugates from pCB Hydrogels
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pelegri-O’Day, E.M.; Lin, E.-W.; Maynard, H.D. Therapeutic Protein–Polymer Conjugates: Advancing Beyond PEGylation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 14323–14332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekladious, I.; Colson, Y.L.; Grinstaff, M.W. Polymer–drug conjugate therapeutics: Advances, insights and prospects. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 273–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobo, I.; Li, M.; Sumerlin, B.S.; Perrier, S. Smart hybrid materials by conjugation of responsive polymers to biomacro-molecules. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Sun, F.; Liu, S.; Jiang, S. Anti-PEG antibodies in the clinic: Current issues and beyond PEGylation. J. Control. Release 2016, 244, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basu, A.; Kunduru, K.R.; Abtew, E.; Domb, A.J. Polysaccharide-Based Conjugates for Biomedical Applications. Bioconjugate Chem. 2015, 26, 1396–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joh, D.Y.; Zimmers, Z.; Avlani, M.; Heggestad, J.T.; Aydin, H.B.; Ganson, N.; Kumar, S.; Fontes, C.M.; Achar, R.K.; Hershfield, M.S.; et al. Architectural Modification of Conformal PEG-Bottlebrush Coatings Minimizes Anti-PEG Antigenicity While Preserving Stealth Properties. Adv. Health Mater. 2019, 8, e1801177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Simakova, A.; Ganson, N.J.; Li, X.; Luginbuhl, K.M.; Ozer, I.; Liu, W.; Hershfield, M.S.; Matyjaszewski, K.; Chilkoti, A. A brush-polymer/exendin-4 conjugate reduces blood glucose levels for up to five days and eliminates poly(ethylene glycol) antigenicity. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bebis, K.; Jones, M.W.; Haddleton, D.M.; Gibson, M.I. Thermoresponsive behaviour of poly[(oligo(ethyleneglycol methacrylate)]s and their protein conjugates: Importance of concentration and solvent system. Polym. Chem. 2011, 2, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Johansen, P.; Zabel, F.; Leroux, J.C.; Gauthier, M.A. Semi-permeable coatings fabricated from comb-polymers efficiently protect proteins in Vivo. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, M.; Tirino, P.; Radivojevic, M.; Phillips, D.J.; Gibson, M.; Leroux, J.-C.; Gauthier, M.A. Molecular Sieving on the Surface of a Protein Provides Protection Without Loss of Activity. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 23, 2007–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Bonde, J.S.; Ye, L. Temperature and pH Controlled Self-Assembly of a Protein-Polymer Biohybrid. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2018, 219, 1700597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilroy, C.A.; Roberts, S.; Chilkoti, A. Fusion of fibroblast growth factor 21 to a thermally responsive biopolymer forms an injectable depot with sustained anti-diabetic action. J. Control. Release 2018, 277, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luginbuhl, K.M.; Schaal, J.; Umstead, B.; Mastria, E.; Li, X.; Banskota, S.; Arnold, S.; Feinglos, M.; D’Alessio, D.; Chilkoti, A. One-week glucose control via zero-order release kinetics from an injectable depot of glucagon-like peptide-1 fused to a thermosensitive biopolymer. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 1, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnusson, J.P.; Khan, A.; Pasparakis, G.; Saeed, A.O.; Wang, W.; Alexander, C. Ion-sensitive ‘isothermal’ responsive polymers prepared in water. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 10852–10853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoaib, M.M.; Huynh, V.; Shad, Y.; Ahmed, R.; Jesmer, A.H.; Melacini, G.; Wylie, R.G. Controlled degradation of low-fouling poly(oligo(ethylene glycol)methyl ether methacrylate) hydrogels. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 18978–18988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santi, D.V.; Schneider, E.; Reid, R.; Robinson, L.; Ashley, G.W. Predictable and tunable half-life extension of therapeutic agents by controlled chemical release from macromolecular conjugates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 6211–6216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huynh, V.; Jesmer, A.H.; Shoaib, M.M.; Wylie, R.G. Influence of Hydrophobic Cross-Linkers on Carboxybetaine Co-polymer Stimuli Response and Hydrogel Biological Properties. Langmuir 2019, 35, 1631–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, V.; Wylie, R.G. Displacement Affinity Release of Antibodies from Injectable Hydrogels. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 30648–30660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, V.; Wylie, R.G. Competitive Affinity Release for Long-Term Delivery of Antibodies from Hydrogels. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 3406–3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keefe, A.J.; Jiang, S. Poly(zwitterionic)protein conjugates offer increased stability without sacrificing binding affinity or bioactivity. Nat. Chem. 2011, 4, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erfani, A.; Seaberg, J.; Aichele, C.P.; Ramsey, J.D. Interactions between Biomolecules and Zwitterionic Moieties: A Review. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 2557–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Yang, J.; Wang, H.-F.; Wang, Z.; Huang, X.; Wang, Z.; Niu, G.; Walker, A.R.H.; Chen, X. Glucose oxidase-catalyzed growth of gold nanoparticles enables quantitative detection of attomolar cancer biomarkers. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 5800–5806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moatsou, D.; Li, J.; Ranji, A.; Pitto-Barry, A.; Ntai, I.; Jewett, M.C.; O’Reilly, R.K. Self-Assembly of Temperature-Responsive Protein–Polymer Bioconjugates. Bioconjug. Chem. 2015, 26, 1890–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandy, A.; Chakraborty, S.; Nandi, S.; Bhattacharyya, K.; Mukherjee, S. Structure, Activity, and Dynamics of Human Serum Albumin in a Crowded Pluronic F127 Hydrogel. J. Phys. Chem. B 2019, 123, 3397–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Liu, K.; Xu, B.; Yao, Y.; Li, W.; Yan, J.; Zhang, A. Confined microenvironments from thermoresponsive dendronized polymers. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2020, 41, 2000325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Barnes, R.; Lin, Y.; Jeon, B.-J.; Najafi, S.; Delaney, K.T.; Fredrickson, G.H.; Shea, J.-E.; Hwang, D.S.; Han, S. Dehydration entropy drives liquid-liquid phase separation by molecular crowding. Commun. Chem. 2020, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakota, K.; Tabata, D.; Sekiya, H. Macromolecular Crowding Modifies the Impact of Specific Hofmeister Ions on the Coil–Globule Transition of PNIPAM. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 10334–10340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Wu, P. On the Thermally Reversible Dynamic Hydration Behavior of Oligo(ethylene glycol) Methacrylate-Based Polymers in Water. Macromolecules 2012, 46, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Tang, H.; Wu, P. In Depth Analysis on the Unusual Multistep Aggregation Process of Oligo(ethylene glycol) Methacrylate-Based Polymers in Water. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 4728–4737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amsden, B. Solute Diffusion within Hydrogels. Mechanisms and Models. Macromolecules 1998, 31, 8382–8395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soontornworajit, B.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y. Aptamer-Functionalized In Situ Injectable Hydrogel for Controlled Protein Release. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 2724–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vulic, K.; Shoichet, M.S. Tunable Growth Factor Delivery from Injectable Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 134, 882–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashley, G.W.; Henise, J.; Reid, R.; Santi, D.V. Hydrogel drug delivery system with predictable and tunable drug release and degradation rates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 2318–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huynh, V.; Ifraimov, N.; Wylie, R.G. Modulating the Thermoresponse of Polymer-Protein Conjugates with Hydrogels for Controlled Release. Polymers 2021, 13, 2772. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13162772
Huynh V, Ifraimov N, Wylie RG. Modulating the Thermoresponse of Polymer-Protein Conjugates with Hydrogels for Controlled Release. Polymers. 2021; 13(16):2772. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13162772
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuynh, Vincent, Natalie Ifraimov, and Ryan G. Wylie. 2021. "Modulating the Thermoresponse of Polymer-Protein Conjugates with Hydrogels for Controlled Release" Polymers 13, no. 16: 2772. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13162772
APA StyleHuynh, V., Ifraimov, N., & Wylie, R. G. (2021). Modulating the Thermoresponse of Polymer-Protein Conjugates with Hydrogels for Controlled Release. Polymers, 13(16), 2772. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13162772