Electrospun Shape-Stabilized Phase Change Materials Based on Photo-Crosslinked Polyethylene Oxide
Abstract
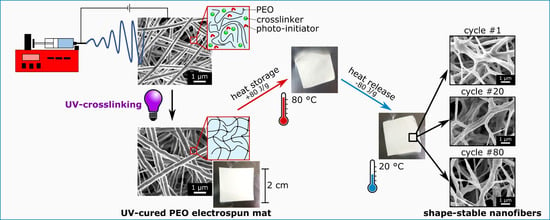
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.2.1. Electrospinning
2.2.2. Film Casting
2.2.3. Photo-Crosslinking
2.3. Characterization
2.3.1. Morphology
2.3.2. Photo-Crosslinking Efficiency
2.3.3. Mechanical and Dynamic-Mechanical Analysis
2.3.4. Heat Storage Properties and Long-Term Stability
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Crosslinking Efficiency and Fibrous Morphology
3.2. Mechanical and Dynamic-Mechanical Analysis
3.3. Heat Storage Properties and Long-Term Stability
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Si, Y.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Thermoconductive, moisture-permeable, and superhydrophobic nanofibrous membranes with interpenetrated boron nitride network for personal cooling fabrics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 32078–32089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, L.; Shou, D.; Park, H.; Zhao, D.; Wu, Y.S.; Hui, X.; Yang, R.; Kan, E.C.; Fan, J. Thermoelectric air conditioning undergarment for personal thermal management and HVAC energy saving. Energy Build. 2020, 226, 110374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Calleja, T.; Bonet-Aracil, M.; Gisbert-Payá, J.; Bou-Belda, E. Analysis of the influence of graphene and phase change microcapsules on thermal behavior of cellulosic fabrics. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 25, 101557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Liu, X. Soft-logic: Design and thermal-comfort evaluation of smart thermoregulatory fabric with pneumatic actuators. J. Text. Inst. 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, H.; Wei, Q. Regulating phase-change temperatures of form-stable phase-change ternary composite fibrous membranes consisting of polystyrene nanofibers and fatty acid eutectics via co-electrospinning method. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2020, 29, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredi, G.; Dorigato, A.; Fambri, L.; Pegoretti, A. Multifunctional structural composites for thermal energy storage. Multifunct. Mater. 2020, 3, 42001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farid, M.M.; Khudhair, A.M.; Razack, S.A.K.; Al-Hallaj, S. A review on phase change energy storage: Materials and applications. Energy Convers. Manag. 2004, 45, 1597–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredi, G.; Dorigato, A.; Fambri, L.; Pegoretti, A. Detailed experimental and theoretical investigation of the thermomechanical properties of epoxy composites containing paraffin microcapsules for thermal management. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2020, 60, 1202–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royo, P.; Ferreira, V.J.; Ure, Z.; Gledhill, S.; López-Sabirón, A.M.; Ferreira, G. Multiple-Criteria Decision Analysis and characterisation of phase change materials for waste heat recovery at high temperature for sustainable energy-intensive industry. Mater. Des. 2020, 186, 108215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudheer, R.; Prabhu, K.N. A Computer Aided Cooling Curve Analysis method to study phase change materials for thermal energy storage applications. Mater. Des. 2016, 95, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alehosseini, E.; Jafari, S.M. Nanoencapsulation of phase change materials (PCMs) and their applications in various fields for energy storage and management. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 283, 102226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Q.; Guo, P.; Zhu, J. Thermal management of electronic devices using pin-fin based cascade microencapsulated PCM/expanded graphite composite. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 149, 119199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldalbahi, A.; El-Naggar, M.E.; El-Newehy, M.H.; Rahaman, M.; Hatshan, M.R.; Khattab, T.A. Effects of Technical Textiles and Synthetic Nanofibers on Environmental Pollution. Polymers 2021, 13, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Hong, G.; Dong, D.; Song, W.; Zhang, X. Multiresponsive graphene-aerogel-directed phase-change smart fibers. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1801754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Xiao, X.; Fu, J.; Huan, C.; Qi, S.; Zhan, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, G. Novel smart textile with phase change materials encapsulated core-sheath structure fabricated by coaxial electrospinning. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 355, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.-F.; Wang, X.-Y.; Wang, S.-B.; Zhao, Y.-H.; Huang, Z. Fabrication and properties of microencapsulated-paraffin/gypsum-matrix building materials for thermal energy storage. Energy Convers. Manag. 2012, 55, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; He, Z.; Fang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z. Experimental and numerical investigations on a flexible paraffin/fiber composite phase change material for thermal therapy mask. Energy Storage Mater. 2017, 6, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Gaikwad, K.K.; Lee, Y.S. Phase change materials for advanced cooling packaging. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2018, 16, 845–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundararajan, S.; Kumar, A.; Chakraborty, B.C.; Samui, A.B.; Kulkarni, P.S. Poly (ethylene glycol)(PEG)-modified epoxy phase-change polymer with dual properties of thermal storage and vibration damping. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2018, 2, 688–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Jin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Du, K. Recent development on heat transfer and various applications of phase-change materials. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 287, 124432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Rao, Z.; Zhao, J.; Huo, Y.; Li, Y. Review on nanoencapsulated phase change materials: Preparation, characterization and heat transfer enhancement. Nano Energy 2015, 13, 814–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, M.; Coca-Clemente, J.A.; Shchukina, E.; Shchukin, D. Nanoencapsulated crystallohydrate mixtures for advanced thermal energy storage. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 13683–13691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Jia, S.; Niu, Y.; Lv, X.; Fu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, D.; Wang, B.; Li, Q. Bean-Pod-Inspired 3D-Printed Phase Change Microlattices for Solar-Thermal Energy Harvesting and Storage. Small 2021, 17, 2101093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaiselvam, S. Bifunctional nanoencapsulated eutectic phase change material core with SiO2/SnO2 nanosphere shell for thermal and electrical energy storage. Mater. Des. 2018, 154, 291–301. [Google Scholar]
- Pielichowska, K.; Pielichowski, K. Biodegradable PEO/cellulose-based solid–solid phase change materials. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2011, 22, 1633–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorigato, A.; Fredi, G.; Pegoretti, A. Thermo-mechanical behavior of novel wood laminae-thermoplastic starch biodegradable composites with thermal energy storage/release capability. Front. Mater. 2019, 6, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Ding, E.; Li, G. Study on transition characteristics of PEG/CDA solid–solid phase change materials. Polymer 2002, 43, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Naggar, M.E.; Abdelgawad, A.M.; Salas, C.; Rojas, O.J. Curdlan in fibers as carriers of tetracycline hydrochloride: Controlled release and antibacterial activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 154, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.-D.; Ding, E.-Y. Preparation and characterization of cross-linking PEG/MDI/PE copolymer as solid–solid phase change heat storage material. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2007, 91, 764–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; He, W.; Xu, J.; Jiang, M. Preparation and characterization of in situ grafted/crosslinked polyethylene glycol/polyvinyl alcohol composite thermal regulating fiber. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2015, 140, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundararajan, S.; Samui, A.B.; Kulkarni, P.S. Versatility of polyethylene glycol (PEG) in designing solid–solid phase change materials (PCMs) for thermal management and their application to innovative technologies. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 18379–18396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, C.; Jia, Y.; Wu, J.; Huang, Y.; Wang, L. Review on electrospun ultrafine phase change fibers (PCFs) for thermal energy storage. Appl. Energy 2018, 210, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, D.G.; Kandasubramanian, B. A review on polymeric-based phase change material for thermo-regulating fabric application. Polym. Rev. 2020, 60, 389–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherif, C.; Tran, N.H.A.; Kirsten, M.; Bruenig, H.; Vogel, R. Environmentally friendly and highly productive bi-component melt spinning of thermoregulated smart polymer fibres with high latent heat capacity. Express Polym. Lett. 2018, 12, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, H.M.; Leducq, D.; Pérez-Masia, R.; Lagaron, J.M.; Gogou, E.; Taoukis, P.; Alvarez, G. Heat transfer study of submicro-encapsulated PCM plate for food packaging application. Int. J. Refrig. 2015, 52, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Zhu, C.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Xia, Y. Integration of phase-change materials with electrospun fibers for promoting neurite outgrowth under controlled release. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1705563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darzi, M.E.; Golestaneh, S.I.; Kamali, M.; Karimi, G. Thermal and electrical performance analysis of co-electrospun-electrosprayed PCM nanofiber composites in the presence of graphene and carbon fiber powder. Renew. Energy 2019, 135, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Yu, X. Encapsulation of bio-based PCM with coaxial electrospun ultrafine fibers. Rsc Adv. 2012, 2, 5580–5584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golestaneh, S.I.; Mosallanejad, A.; Karimi, G.; Khorram, M.; Khashi, M. Fabrication and characterization of phase change material composite fibers with wide phase-transition temperature range by co-electrospinning method. Appl. Energy 2016, 182, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semnani Rahbar, R.; Maleki, H.; Kalantari, B. Fabrication of electrospun nanofibre yarn based on nylon 6/microencapsulated phase change materials. J. Exp. Nanosci. 2016, 11, 1402–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vitale, A.; Massaglia, G.; Chiodoni, A.; Bongiovanni, R.; Pirri, C.F.; Quaglio, M. Tuning Porosity and Functionality of Electrospun Rubber Nanofiber Mats by Photo-Crosslinking. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 24544–24551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wang, Q.; Wu, Q. UV-initiated crosslinking of electrospun poly (ethylene oxide) nanofibers with pentaerythritol triacrylate: Effect of irradiation time and incorporated cellulose nanocrystals. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 1779–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kianfar, P.; Vitale, A.; Dalle Vacche, S.; Bongiovanni, R. Enhancing properties and water resistance of PEO-based electrospun nanofibrous membranes by photo-crosslinking. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 56, 1879–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami, S.H.; Salovey, R. Crosslinked poly (ethylene oxide) hydrogels. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 88, 1451–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şimşek, M.; Çakmak, S.; Gümüşderelioğlu, M. Insoluble poly(ethylene oxide) nanofibrous coating materials: Effects of crosslinking conditions on the matrix stability. J. Polym. Res. 2016, 23, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kianfar, P.; Vitale, A.; Dalle Vacche, S.; Bongiovanni, R. Photo-crosslinking of chitosan/poly(ethylene oxide) electrospun nanofibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 217, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotaling, N.A.; Bharti, K.; Kriel, H.; Simon, C.G., Jr. DiameterJ: A validated open source nanofiber diameter measurement tool. Biomaterials 2015, 61, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pucić, I.; Jurkin, T. FTIR assessment of poly(ethylene oxide) irradiated in solid state, melt and aqeuous solution. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2012, 81, 1426–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredi, G.; Zimmerer, C.; Scheffler, C.; Pegoretti, A. Polydopamine-Coated Paraffin Microcapsules as a Multifunctional Filler Enhancing Thermal and Mechanical Performance of a Flexible Epoxy Resin. J. Compos. Sci. 2020, 4, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredi, G.; Dorigato, A.; Pegoretti, A. Dynamic-mechanical response of carbon fiber laminates with a reactive thermoplastic resin containing phase change microcapsules. Mech. Time-Depend. Mater. 2020, 24, 395–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredi, G.; Dorigato, A.; Fambri, L.; Unterberger, S.H.; Pegoretti, A. Effect of phase change microcapsules on the thermo-mechanical, fracture and heat storage properties of unidirectional carbon/epoxy laminates. Polym. Test. 2020, 91, 106747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredi, G.; Dorigato, A.; Pegoretti, A. Novel reactive thermoplastic resin as a matrix for laminates containing phase change microcapsules. Polym. Compos. 2019, 40, 3711–3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredi, G.; Dorigato, A.; Fambri, L.; Pegoretti, A. Multifunctional epoxy/carbon fiber laminates for thermal energy storage and release. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 158, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauziyah, N.A.; Hilmi, A.R.; Zainuri, M.; Asrori, M.Z.; Mashuri, M.; Jawaid, M.; Pratapa, S. Thermal and dynamic mechanical properties of polyethylene glycol/quartz composites for phase change materials. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 48130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, G.; Choi, J.H.; Lee, J.K. Thermal behavior and ion conductivity of polyethylene oxide/polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane nanocomposite electrolytes. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2015, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doytcheva, M.; Dotcheva, D.; Stamenova, R.; Orahovats, A.; Tsvetanov, C.; Leder, J. Ultraviolet-induced crosslinking of solid poly(ethylene oxide). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1997, 64, 2299–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Sample | Composition | Processing | Sample Form |
|---|---|---|---|
| PEO-E | PEO; BP | Electrospinning + UV irradiation | Fibrous mat |
| PEO-XL-E | PEO; BP; TMPTA | Electrospinning + UV irradiation | Fibrous mat |
| PEO-XL-C | PEO; BP; TMPTA | Casting + UV irradiation | Continuous film |
| Sample | C=C Conversion (%) | Gel Content (%) |
|---|---|---|
| PEO-XL-E | 44.6 ± 3.9 | 76.0 ± 3.3 |
| PEO-XL-C | 38.3 ± 5.2 | 95.8 ± 0.6 |
| Sample | |
|---|---|
| PEO-E | −17 ± 4 |
| PEO-XL-E | −20 ± 1 |
| PEO-XL-C | −28 ± 2 |
| Sample | (°C) | (J/g) | (°C) | (J/g) | (°C) | (J/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEO-E | 62.2 | 186.2 | 40.8 | 160.9 | 60.6 | 169.7 |
| PEO-XL-E | 63.8 | 161.2 | 41.1 | 102.5 | 58.8 | 112.3 |
| PEO-XL-C | 68.6 | 179.6 | 43.9 | 105.1 | 60.0 | 115.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fredi, G.; Kianfar, P.; Dalle Vacche, S.; Pegoretti, A.; Vitale, A. Electrospun Shape-Stabilized Phase Change Materials Based on Photo-Crosslinked Polyethylene Oxide. Polymers 2021, 13, 2979. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13172979
Fredi G, Kianfar P, Dalle Vacche S, Pegoretti A, Vitale A. Electrospun Shape-Stabilized Phase Change Materials Based on Photo-Crosslinked Polyethylene Oxide. Polymers. 2021; 13(17):2979. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13172979
Chicago/Turabian StyleFredi, Giulia, Parnian Kianfar, Sara Dalle Vacche, Alessandro Pegoretti, and Alessandra Vitale. 2021. "Electrospun Shape-Stabilized Phase Change Materials Based on Photo-Crosslinked Polyethylene Oxide" Polymers 13, no. 17: 2979. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13172979
APA StyleFredi, G., Kianfar, P., Dalle Vacche, S., Pegoretti, A., & Vitale, A. (2021). Electrospun Shape-Stabilized Phase Change Materials Based on Photo-Crosslinked Polyethylene Oxide. Polymers, 13(17), 2979. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13172979