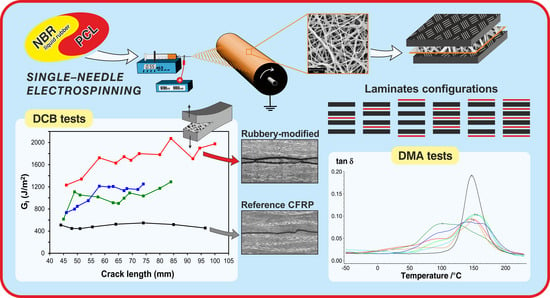
Rubbery-Modified CFRPs with Improved Mode I Fracture Toughness: Effect of Nanofibrous Mat Grammage and Positioning on Tanδ Behaviour
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Solutions, Blend Preparation and Nanofibrous Mats Electrospinning
2.3. Tensile Testing of Rubbery Nanofibrous Mats
2.4. CFRPs Production and Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Nanofibrous Mat Characterization: Morphology, Grammage and Tensile Properties
3.2. Damping Evaluation of CFRP Laminates via Analysis of Tanδ Behaviour
3.3. Mode I Interlaminar Fracture Toughness: DCB Tests, Crack Path and Delamination Surfaces Characterization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bagheri, R.; Marouf, B.T.; Pearson, R.A. Rubber-toughened epoxies: A critical review. Polym. Rev. 2009, 49, 201–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldona, E.B.; De Leon, A.C.C.; Pajarito, B.B.; Advincula, R.C. A Review on Rubber-Enhanced Polymeric Materials. Polym. Rev. 2017, 57, 311–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riew, C.K.; Siebert, A.R.; Smith, R.W.; Fernando, M.; Kinloch, A.J. Toughened Epoxy Resins: Preformed Particles as Tougheners for Adhesives and Matrices. In Toughened Plastics II; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1996; Volume 252, pp. 33–44. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, R.J.J.; Rozenberg, B.A.; Pascault, J. Reaction-Induced Phase Separation in Modified Thermosetting Polymers; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Wise, C.W.; Cook, W.D.; Goodwin, A.A. CTBN rubber phase precipitation in model epoxy resins. Polymer 2000, 41, 4625–4633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Narita, Y. Analysis and optimal design for the damping property of laminated viscoelastic plates under general edge conditions. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 45, 972–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthelot, J.M.; Assarar, M.; Sefrani, Y.; Mahi, A. El Damping analysis of composite materials and structures. Compos. Struct. 2008, 85, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheri, M.R. The effect of layup and boundary conditions on the modal damping of FRP composite panels. J. Compos. Mater. 2011, 45, 1411–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishi, H.; Kuwata, M.; Matsuda, S.; Asami, T.; Murakami, A. Damping properties of thermoplastic-elastomer interleaved carbon fiber-reinforced epoxy composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2004, 64, 2517–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patle, V.K.; Kumar, R.; Sharma, A.; Dwivedi, N.; Muchhala, D.; Chaudhary, A.; Mehta, Y.; Mondal, D.P.; Srivastava, A.K. Three dimension phenolic resin derived carbon-CNTs hybrid foam for fire retardant and effective electromagnetic interference shielding. Compos. Part C Open Access 2020, 2, 100020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Du, J.; Li, J.; Huang, X.; Kang, T.; Zhang, C.; Wang, S.; Ajao, O.O.; Wang, W.J.; Liu, P. Polymer nanocomposites with aligned two-dimensional materials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2021, 114, 101360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Huang, C.; Wang, L.; Liang, L.; Cheng, Y.; Fei, W.; Li, Y. Recent Progress in Graphene/Polymer Nanocomposites. Adv. Mater. 2020, 2001105, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsen, B.B.; Kinloch, A.J.; Mohammed, R.D.; Taylor, A.C.; Sprenger, S. Toughening mechanisms of nanoparticle-modified epoxy polymers. Polymer 2007, 48, 530–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, T.H.; Kinloch, A.J.; Masania, K.; Taylor, A.C.; Sprenger, S. The mechanisms and mechanics of the toughening of epoxy polymers modified with silica nanoparticles. Polymer 2010, 51, 6284–6294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tahan Latibari, S.; Mehrali, M.; Mottahedin, L.; Fereidoon, A.; Metselaar, H.S.C. Investigation of interfacial damping nanotube-based composite. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 50, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montazeri, A.; Montazeri, N. Viscoelastic and mechanical properties of multi walled carbon nanotube/epoxy composites with different nanotube content. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 2301–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowski, E.; Soliman, E.; Kandil, U.F.; Taha, M.R. Interlaminar fracture toughness of CFRP laminates incorporating multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Polymers 2015, 7, 1020–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zakaria, M.R.; Akil, H.M.; Omar, M.F.; Abdullah, M.M.A.B.; Rahman, A.A.A.; Othman, M.B.H. Improving flexural and dielectric properties of carbon fiber epoxy composite laminates reinforced with carbon nanotubes interlayer using electrospray deposition. Compos. Part C Open Access 2020, 3, 100075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cai, S.; Huang, X. Multi-scaled enhancement of damping property for carbon fiber reinforced composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 143, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, R.; Najafabadi, M.A.; Saghafi, H.; Zarouchas, D. Fracture and fatigue behavior of carbon/epoxy laminates modified by nanofibers. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2020, 137, 106015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Liu, A.; Jia, H.; Liu, F.; Zhang, J.; Guo, J.; Wei, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, D.; Li, S. A Review on the Methods of Interlaminar Properties Using Nanomaterials to Reinforce Carbon Fiber Epoxy Composites. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1622, 012053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Heijden, S.; Daelemans, L.; De Schoenmaker, B.; De Baere, I.; Rahier, H.; Van Paepegem, W.; De Clerck, K. Interlaminar toughening of resin transfer moulded glass fibre epoxy laminates by polycaprolactone electrospun nanofibres. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2014, 104, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akangah, P.; Lingaiah, S.; Shivakumar, K. Effect of Nylon-66 nano-fiber interleaving on impact damage resistance of epoxy/carbon fiber composite laminates. Compos. Struct. 2010, 92, 1432–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, T.; Lin, T.; Wang, C.H. Phase morphology of nanofibre interlayers: Critical factor for toughening carbon/epoxy composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2012, 72, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, D.; Bologna, F.; Scarselli, G.; Ivankovic, A.; Murphy, N. Mode-II fracture behaviour of aerospace-grade carbon fibre/epoxy composites interleaved with thermoplastic veils. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 191, 108065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteserín, C.; Blanco, M.; Murillo, N.; Pérez-Márquez, A.; Maudes, J.; Gayoso, J.; Laza, J.M.; Aranzabe, E.; Vilas, J.L. Effect of different types of electrospun polyamide 6 nanofibres on the mechanical properties of carbon fibre/epoxy composites. Polymers 2018, 10, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ognibene, G.; Latteri, A.; Mannino, S.; Saitta, L.; Recca, G.; Scarpa, F.; Cicala, G. Interlaminar toughening of epoxy carbon fiber reinforced laminates: Soluble versus non-soluble veils. Polymers 2019, 11, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brugo, T.M.; Maccaferri, E.; Cocchi, D.; Mazzocchetti, L.; Giorgini, L.; Fabiani, D.; Zucchelli, A. Self-sensing hybrid composite laminate by piezoelectric nanofibers interleaving. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 212, 108673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merighi, S.; Mazzocchetti, L.; Benelli, T.; Maccaferri, E.; Zucchelli, A.; D’Amore, A.; Giorgini, L. A New Wood Surface Flame-Retardant Based on Poly-m-Aramid Electrospun Nanofibers. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2019, 59, 2541–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzetti, R.; Zucchelli, A. Electrospun nano fibers as reinforcement for composite laminates materials–A review. Compos. Struct. 2017, 182, 711–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maccaferri, E.; Mazzocchetti, L.; Benelli, T.; Brugo, T.M.; Zucchelli, A.; Giorgini, L. Rubbery nanofibrous interleaves enhance fracture toughness and damping of CFRP laminates. Mater. Des. 2020, 195, 109049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, C.; Wilson, J.; Trendafilova, I.; Yang, L. Vibratory behaviour of glass fibre reinforced polymer (GFRP) interleaved with nylon nanofibers. Compos. Struct. 2017, 176, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Chase, G.G. Electrospun elastic acrylonitrile butadiene copolymer fibers. Polymer 2016, 97, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Fong, H.; Tian, M. Electrospun composite nanofibers of polybutadiene rubber containing uniformly distributed Ag nanoparticles. Mater. Lett. 2012, 84, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, X.; Chase, G.G. Filtration performance of electrospun acrylonitrile-butadiene elastic fiber mats in solid aerosol filtration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 186, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thielke, M.W.; Bruckner, E.P.; Wong, D.L.; Theato, P. Thiol-ene modification of electrospun polybutadiene fibers crosslinked by UV irradiation. Polymer 2014, 55, 5596–5599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr-Phillips, T.E.; Woehling, V.; Agniel, R.; Nguyen, G.T.M.; Vidal, F.; Kilmartin, P.; Plesse, C.; Travas-Sejdic, J. Electrospun rubber fibre mats with electrochemically controllable pore sizes. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 4249–4258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.S.; Hong, J.P.; Seo, Y.S.; Chung, S.M.; Nah, C. Fabrication and characterization of electrospun polybutadiene fibers crosslinked by UV irradiation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 101, 2333–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Hu, Q.; Wu, H.; Zhang, L.; Fong, H.; Zhang, L. Formation and morphological stability of polybutadiene rubber fibers prepared through combination of electrospinning and in-situ photo-crosslinking. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 3076–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Y.; Hsieh, H.C.; Chen, J.Y.; Shih, C.C.; Lee, W.Y.; Chiang, Y.C.; Chen, W.C. Fabrication and Application of Highly Stretchable Conductive Fiber-Based Electrode of Epoxy/NBR Electrospun Fibers Spray-Coated with AgNW/PU Composites. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2019, 220, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Nie, H.; Liu, D.; He, A. Retardation of cold flow in immiscible rubber blends by tailoring their microstructures. Polym. Int. 2017, 66, 1473–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Filippo, M.; Alessi, S.; Palmese, G.; Dispenza, C. Electrospun rubber/thermoplastic hybrid nanofibers for localized toughening effects in epoxy resins. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 48501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccaferri, E.; Mazzocchetti, L.; Benelli, T.; Brugo, T.M.; Zucchelli, A.; Giorgini, L. Rubbery nanofibers by co-electrospinning of almost immiscible NBR and PCL blends. Mater. Des. 2020, 186, 108210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccaferri, E.; Cocchi, D.; Mazzocchetti, L.; Benelli, T.; Brugo, T.M.; Giorgini, L.; Zucchelli, A. How nanofibers carry the load: Towards a universal and reliable approach for tensile testing of polymeric nanofibrous membranes, Macromolecular Engineering and Materials, accepted paper. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2021, 2100183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccaferri, E.; Mazzocchetti, L.; Benelli, T.; Zucchelli, A.; Giorgini, L. Morphology, thermal, mechanical properties and ageing of nylon 6,6/graphene nanofibers as Nano2 materials. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 166, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D5528-01 2001. Standard Test Method for Mode I Interlaminar Fracture Toughness of Unidirectional Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Matrix Composites. Am. Soc. Test. Mater. 2014, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzocchetti, L.; Benelli, T.; Maccaferri, E.; Merighi, S.; Belcari, J.; Zucchelli, A.; Giorgini, L. Poly-m-aramid electrospun nanofibrous mats as high-performance flame retardants for carbon fiber reinforced composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 145, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
















| Nanofibrous Mat | NBR Content (wt%) | Mat Thickness (μm) | Mat Grammage (g/m2) | Nanofiber Diameter (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n-60/40_5 | 60 | 10 ± 1 | 5.3 ± 0.3 | 258 ± 29 |
| n-60/40_10 | 60 | 20 ± 2 | 9.6 ± 0.5 | 252 ± 38 |
| n-60/40_20 | 60 | 40 ± 2 | 19.7 ± 1.1 | 265 ± 41 |
| DCB Specimen | Nanofibrous Mat | Specimen Width (b) (mm) | Specimen Length (mm) | Initial Delamination Length (a0) (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-Ref C-60/40_5 | – n-60/40_5 | 20 | 140 | 45 |
| C-60/40_10 C-60/40_20 | n-60/40_10 n-60/40_20 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maccaferri, E.; Mazzocchetti, L.; Benelli, T.; Brugo, T.M.; Zucchelli, A.; Giorgini, L. Rubbery-Modified CFRPs with Improved Mode I Fracture Toughness: Effect of Nanofibrous Mat Grammage and Positioning on Tanδ Behaviour. Polymers 2021, 13, 1918. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13121918
Maccaferri E, Mazzocchetti L, Benelli T, Brugo TM, Zucchelli A, Giorgini L. Rubbery-Modified CFRPs with Improved Mode I Fracture Toughness: Effect of Nanofibrous Mat Grammage and Positioning on Tanδ Behaviour. Polymers. 2021; 13(12):1918. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13121918
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaccaferri, Emanuele, Laura Mazzocchetti, Tiziana Benelli, Tommaso Maria Brugo, Andrea Zucchelli, and Loris Giorgini. 2021. "Rubbery-Modified CFRPs with Improved Mode I Fracture Toughness: Effect of Nanofibrous Mat Grammage and Positioning on Tanδ Behaviour" Polymers 13, no. 12: 1918. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13121918
APA StyleMaccaferri, E., Mazzocchetti, L., Benelli, T., Brugo, T. M., Zucchelli, A., & Giorgini, L. (2021). Rubbery-Modified CFRPs with Improved Mode I Fracture Toughness: Effect of Nanofibrous Mat Grammage and Positioning on Tanδ Behaviour. Polymers, 13(12), 1918. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13121918