Effect of Modified Silica Fume Using MPTMS for the Enhanced EPDM Foam Insulation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Modification of Silica Fume Surface
2.3. Compounding and Vulcanization
2.4. Cure Characteristics and Mechanical Properties
2.5. EPDM Foam Structures and Compression Set
3. Results and Discussion
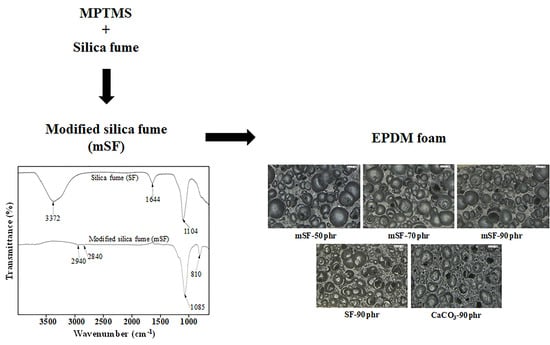
3.1. Characterization of the Modified Silica Fume (mSF)
3.2. Cure Characteristics
3.3. Mechanical Properties
3.4. EPDM Foam Structure and Properties
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spenadel, L. Heat aging performance of ethylene propylene elastomers in electrical insulation compounds. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1983, 56, 113–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamlin, C.; Dutta, N.; Roy-Choudhury, N.; Kehoe, D.; Matisons, J. Influence of ethylene-propylene ratio on the thermal degradation behavior of EPDM elastomers. Thermochim. Acta 2001, 367–368, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, P.K.; De, S.K. Studies of polymer-filler interaction, network structure, physical properties, and fracture of silica- and clay-filled EPDM rubber in the presence of a silane coupling agent. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1983, 56, 737–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Dipak, G.; Basu, K. Natural rubber–ethylene-propylene-diene rubber covulcanization: Effect of reinforcing fillers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 84, 1001–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spratte, T.; Plagge, J.; Wunde, M.; Klüppel, M. Investigation of strain-induced crystallization of carbon black and silica filled natural rubber composites based on mechanical and temperature measurements. Polymer 2017, 115, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.; Huang, J.; Guo, W.; Wu, C. Investigation of carbon black network in natural rubber with different bound rubber contents. J. Macromol. Sci. B. 2007, 46, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongsang, S.; Sombatsompop, N. Dynamic rebound behavior of silica/natural rubber composites: Fly ash particles and precipitated silica. J. Macromol. Sci. B. 2007, 46, 825–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Pal, K.; Kim, J.K. Effect of silica and silicone oil on the mechanical and thermal properties of silicone rubber. J. Macromol. Sci. B. 2011, 50, 1144–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesan, M.T. Effect of silica on uncompatibilized and compatibilized styrene butadiene rubber and nitrile rubber blends. Int. J. Polym. Mater. 2011, 60, 1130–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Ling, L.; Xie, J.; Ma, G.; Wang, B. Surface modification of nanosilica with 3-mercaptopropyl trimethoxysilane: Experimental and theoretical study on the surface interaction. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2014, 591, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Jia, Z.; Tang, Y.; Wu, L.; Luo, Y.; Jia, D. Novel functional silica nanoparticles for rubber vulcanization and reinforcement. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 144, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Sun, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Effect of nitrile rubber on properties of silica-filled natural rubber compounds. Polym. Test. 2005, 24, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staropoli, M.; Rogé, V.; Moretto, E.; Didierjean, J.; Michel, M.; Duez, B.; Steiner, P.; Thielen, G.; Lenoble, D.; Thomann, J.-S. Hybrid silica-based fillers in nanocomposites: Influence of isotropic/isotropic and isotropic/anisotropic fillers on mechanical properties of styrene-butadiene (SBR)-based rubber. Polymers 2021, 13, 2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.J.; Zhang, Y.D.; Wu, C.F.; Xie, L.S.; Ma, Y.L. Wet sliding abrasion of natural rubber composites filled with carbon black at different applied loads. J. Macromol. Sci. B. 2015, 54, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; He, H.; Jia, Y.; Shenghui, T.; Jian, C.; Jia, D.; Luo, Y. A comprehensive study on lignin as a green alternative of silica in natural rubber composites. Polym. Test. 2016, 54, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, H.; Mathialagan, M. Comparative study on the effect of partial replacement of silica or calcium carbonate by bentonite on the properties of EPDM composites. Polym. Test. 2012, 31, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Song, Q.; Qiao, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Song, Z. Good dispersion of hydrophilic nanoscale calcium carbonate particles in nitrile butadiene rubber matrix. Polymer 2011, 52, 3496–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, R.; Sreelekshmi, R.V.; Menon, A.R.R. Cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide modified kaolin as a reinforcing filler for natural rubber. J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, G.C.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Bhowmick, A.K. Influence of nanoclay on adhesion of EPDM vulcanizate. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2011, 31, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, F.; Cho, U.R. Effects of silane coupling agents on tribological properties of bentonite/nitrile butadiene rubber composites. Polym. Composite 2017, 38, 2347–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Sun, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, Y. Effects of silane coupling agents on the vulcanization characteristics of natural rubber. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 94, 1511–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.M.; Razzaghi-Kashani, M. Vulcanization kinetics of nano-silica filled styrene butadiene rubber. Polymer 2014, 55, 6426–6434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, C.S.J.; Bipinbal, P.K.; Sunil, K.N. Viscoelastic behavior of silica filled natural rubber composites—Correlation of shear with elongational testing. Polym. Test. 2017, 60, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sae-oui, P.; Sirisinha, C.; Thepsuwan, U.; Hatthapanit, K. Comparison of reinforcing efficiency between Si-69 and Si-264 in a conventional vulcanization system. Polym. Test. 2004, 23, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Dhanania, S.; Bhowmick, A.K. Reactive grafting of 3-octanoylthio-1-propyltriethoxysilane in styrene butadiene rubber: Characterization and its effect on silica reinforced tire composites. Polymer 2019, 179, 121693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sae-oui, P.; Sirisinha, C.; Thepsuwan, U.; Hatthapanit, K. Roles of silane coupling agents on properties of silica-filled polychloroprene. Eur. Polym. J. 2006, 42, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhothu, T.H.; Luyt, A.S.; Messort, M. Preparation and characterization of EPDM/silica nanocomposites prepared through non-hydrolytic sol-gel method in the absence and presence of a coupling agent. Express Polym. Lett. 2014, 8, 809–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Kim, J.S.; Lim, S.H.; Jang, S.H.; Kim, D.H.; Park, N.-H.; Jung, J.W.; Choi, J. The investigation of the silica-reinforced rubber polymers with the methoxy type silane. Polymers 2020, 12, 3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, H.; Nordin, R. Effect of epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) and ethylene-co-acrylic acid copolymer on properties of silica-filled natural rubber/recycle rubber powder blends. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2004, 43, 285–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suntako, R. Effect of zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized by a precipitation method on mechanical and morphological properties of the CR foam. B Mater. Sci. 2015, 28, 1033–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Materials | mSF-50 phr | mSF-70 phr | mSF-90 phr | SF-90 phr | CaCO3-90 phr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Keltan 8550C | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| N-550 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| mSF | 50 | 70 | 90 | - | - |
| SF | - | - | - | 90 | - |
| Omyacarb 1T | - | - | - | - | 90 |
| ZnO | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Stearic acid | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| PS-430T | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| EM-80MA | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| TMTD | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| ZDMC | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| MBTS | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Sulphur | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| Properties | mSF-50 phr | mSF-70 phr | mSF-90 phr | SF-90 phr | CaCO3-90 phr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore OO) | 58 ± 1 | 62 ± 1 | 67 ± 1 | 65 ± 1 | 55 ± 1 |
| Tensile strength (MPa) | 6.26 ± 0.02 | 6.52 ± 0.01 | 7.45 ± 0.02 | 6.62 ± 0.03 | 5.58 ± 0.02 |
| Elongation at break (%) | 520 ± 10 | 470 ± 15 | 455 ± 10 | 460 ± 20 | 550 ± 10 |
| 100% Modulus (MPa) | 1.22 ± 0.01 | 1.51 ± 0.01 | 1.70 ± 0.01 | 1.62 ± 0.01 | 1.18 ± 0.01 |
| 300% Modulus (MPa) | 3.40 ± 0.02 | 3.98 ± 0.03 | 5.10 ± 0.03 | 4.98 ± 0.01 | 3.28 ± 0.01 |
| Specific gravity | 0.51 ± 0.01 | 0.54 ± 0.01 | 0.66 ± 0.01 | 0.64 ± 0.01 | 0.45 ± 0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suntako, R. Effect of Modified Silica Fume Using MPTMS for the Enhanced EPDM Foam Insulation. Polymers 2021, 13, 2996. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13172996
Suntako R. Effect of Modified Silica Fume Using MPTMS for the Enhanced EPDM Foam Insulation. Polymers. 2021; 13(17):2996. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13172996
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuntako, Rudeerat. 2021. "Effect of Modified Silica Fume Using MPTMS for the Enhanced EPDM Foam Insulation" Polymers 13, no. 17: 2996. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13172996
APA StyleSuntako, R. (2021). Effect of Modified Silica Fume Using MPTMS for the Enhanced EPDM Foam Insulation. Polymers, 13(17), 2996. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13172996