Structural Behavior of High-Strength Concrete Slabs Reinforced with GFRP Bars
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Program
2.1. Experimental Study
2.1.1. Concrete Mix
2.1.2. Compressive Strength Test
2.1.3. GFRP Bars
2.1.4. Description of Tested Slabs
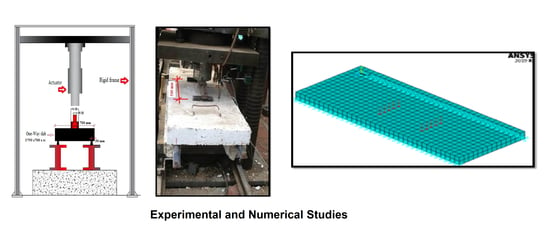
2.2. Test Setup
3. Experimental Results and Discussion
3.1. Ultimate Load
3.2. Ultimate Deflection
3.3. Crack Pattern and Mode of Failure
4. Nonlinear Finite Element Analysis (NLFEA)
4.1. Modeling
4.2. NLFE Ultimate Load
4.3. NLFE Deflection
4.4. Crack Pattern and Mode of Failure
5. Comparisons between Experimental and NLFEA Results
5.1. Comparison between Experimental and NLFE Ultimate Loads
5.2. Comparison between Experimental and NLFE Deflections
5.3. Comparison between Experimental and NLFE Crack Patterns and Mode of Failure
6. Conclusions
- Using reinforcement areas of the GFRP bars less than or equal to µb led to brittle failure in GFRP bars and concrete crushing with rupture GFRP bars, respectively.
- The behavior of the tested GFRP-reinforced slabs was bilinear elastic until failure.
- There was an enhancement in deflections and crack patterns for slabs reinforced using GFRP bars, especially for equal reinforcement areas.
- The NLFEA obtained an acceptable agreement with the experimental study in terms of the ultimate loads, ultimate deflection, and crack pattern.
- The agreement between the experimental and analytical study was approximately 86.0% with a standard deviation of 0.04 and a coefficient of variance of 0.0015.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rizkalla, S.; Hassan, T.; Hassan, N. Design Recommendations for the Use of FRP for Reinforcement and Strengthening of Concrete Structures. J. Prog. Struct. Eng. Mater. 2003, 50, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Salakawy, E.; Benmokrane, B.; Desgagné, G. FRP Composite Bars for the Concrete Deck Slab of Wotton Bridge. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2003, 30, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benmokrane, B.; El-Salakawy, E.; El-Ragaby, A.; Lackey, T. Designing and Testing of Concrete Bridge Decks Reinforced with Glass FRP Bars. J. Bridge Eng. 2006, 11, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benmokrane, B.; El-Salakawy, E.; El-Ragaby, A.; El-Gamal, S. Performance Evaluation of Innovative Concrete Bridge Deck Slabs Reinforced with Fibre-Reinforced Polymer Bars. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2007, 34, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ospina, C.E.; Nanni, A. Current FRP Reinforced Concrete Design Trends in ACI 440.1R. In Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Fiber Reinforced Polymer Reinforcement for Concrete Structures, FRPRCS-8, Patras, Greece, 16–18 July 2007. [Google Scholar]
- American Concrete Institute. Guide for the Design and Construction of Concrete Reinforced with FRP Bars, ACI 440.1R07; ACI Committee 440: Farmington Hills, MI, USA, 2006; pp. 1023–1034. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Masmoudi, R.; Benmokrane, B. Behaviour of one-way concrete slabs reinforced with CFRP grid reinforcements. Constr. Build. Mater. 2004, 18, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, D.-Y.; Banthia, N.; Yoon, Y.-S. Flexural behavior of ultra-high-performance fiber-reinforced concrete beams reinforced with GFRP and steel rebars. Eng. Struct. 2016, 111, 246–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benmokrane, B.; Chaallal, O.; Masmoudi, R. Flexural response of concrete beams reinforced with FRP reinforcing bars. ACI Struct. J. 1995, 91, 46–55. [Google Scholar]
- Masmoudi, R.; Theriault, M.; Benmokrane, B. Flexural behavior of concrete beams reinforced with deformed fiber reinforced plastic reinforcing rods. ACI Struct. J. 1998, 95, 665–675. [Google Scholar]
- Alsayed, S.H. Flexural behavior of concrete beams reinforced with GFRP bars. Cem. Concr. Compos. 1998, 20, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toutanji, H.A.; Saafi, M. Flexural behavior of concrete beams reinforced with glass fiber-reinforced polimer (GFRP) bars. ACI Struct. J. 2000, 97, 712–719. [Google Scholar]
- Toutanji, H.; Deng, Y. Deflection and crack-width prediction of concrete beams reinforced with glass FRP rods. Constr. Build. Mater. 2003, 17, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiagarajan, G. Experimental and analytical behavior of carbon fiber-based rods as flexural reinforcement. J. Compos. Constr. 2003, 7, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yost, J.R.; Gross, S.P.; Dinehart, D.W. Effective moment of inertia for glass fiber reinforced concrete beams. ACI Struct. J. 2003, 100, 732–739. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, M.A.; Mansur, M.A.; Paramasivam, P. Behavior of aramid fiber-reinforced polymer reinforced high strength concrete beams under bending. J. Compos. Constr. 2005, 9, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashour, A.F. Flexural and shear capacities of concrete beams reinforced with GFRP bars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2006, 20, 1005–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayal, R.; Rasheed, H.A. Tension stiffening model for concrete beams reinforced with steel and FRP bars. J. Mater. Civil Eng. 2006, 18, 831–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, I.F.; Ashour, A.F. Flexural performance of FRP reinforced concrete beams. Compos. Struct. 2012, 94, 1616–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kara, I.F.; Ashour, A.F. Moment distribution in continuous FRP reinforced concrete beams. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 49, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kara, I.F.; Ashour, A.F.; Dundar, C. Deflection of concrete structures reinforced with FRP bars. Compos. Part B 2013, 44, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kassem, C.; Farghaly, A.S.; Benmokrane, B. Evaluation of flexural behavior and serviceability performance of concrete beams reinforced with FRP bars. J. Compos. Constr. 2011, 15, 682–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sunna, R.; Pilakoutas, K.; Hajirasouliha, I.; Guadagnini, M. Deflection behavior of FRP reinforced concrete beams and slabs: An experimental investigation. Compos. Part B 2012, 43, 2125–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barris, C.; Torres, L.; Comas, J.; Mias, C. Cracking and deflections in GFRP RC beams: An experimental study. Compos. Part B 2013, 55, 580–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahroug, M.E.M.; Ashour, A.F.; Lam, D. Experimental response and code modelling of continuous concrete slabs reinforced with BFRP bars. Compos. Struct. 2014, 107, 664–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahroug, M.E.M.; Ashour, A.F.; Lam, D. Tests of continuous concrete slabs reinforced with carbon fibre reinforced polymer bars. Compos. Part B 2014, 66, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dundar, C.; Tanrikulu, A.K.; Frosch, J.R. Prediction of load-deflection behavior of multi-span FRP and steel reinforced concrete beams. Compos. Struct. 2015, 132, 680–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, G.; Wu, Z.; Dong, Z.; Xie, Q. Evaluation of prestressed basalt fiber and hybrid fiber reinforced polymer tendons under marine environment. Mater. Des. 2014, 64, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xian, G.; Li, H. Water absorption and distribution in a pultruded unidirectional carbon/glass hybrid rod under hydraulic pressure and elevated temperatures. Polymers 2018, 10, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Demakos, C.B.; Kyriazopoulos, A.; Pnevmatikos, N.; Drivas, D. Experimental investigation, and numerical simulation of curved frame structures. Procedia Struct. Integr. 2018, 10, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papavasileiou, G.S.; Pnevmatikos, N.G. Optimized design of steel buildings against earthquake and progressive collapse using cables. Int. J. Progress. Sci. Technol. 2018, 6, 213–220. [Google Scholar]
- ECP 208. Egyptian Code of Practice for Design Principles of the Use of Fiber Reinforced Polymers in Construction; Permanent Committee, HBNRC: Giza, Egypt, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Janus, O.; Girgle, F.; Kostiha, V.; Stepanek, P. Effect of Surface Treatment and Test Configuration on Bond Behaviour of GFRP Rebars. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Fibre-Reinforced Polymer (FRP) Composites in Civil Engineering (CICE 2018), Paris, France, 17–19 July 2018; pp. 17–19. [Google Scholar]
- Achillides, Z.; Pilakoutas, K. Bond behaviour of fibre reinforced polymer bars under direct pullout conditions. J. Compos. Constr. 2007, 8, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANSYS. “Engineering Analysis System User’s Manual” 2005, Vol. 1&2, and Theoretical Manual; Revision 8.0; Swanson Analysis System Inc.: Houston, PA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
























| Materials | Per m3of Concrete (fcu = 60 MPa) |
|---|---|
| Cement | 575 kg/m3 |
| Coarse aggregate | 1100 kg/m3 |
| Fine aggregate | 580 kg/m3 |
| Water | 138 kg/m3 |
| Silica fume | 50 kg/m3 |
| Superplasticizer | 18 kg/m3 |
| Cubes | Compressive Strength (MPa) |
|---|---|
| 28 Days | |
| C−1 | 63.9 |
| C−2 | 68.2 |
| C−3 | 66.7 |
| Average | 66.3 |
| Diameter (mm) | Tensile Strength (MPa) |
|---|---|
| 8 | 490 |
| 10 | 650 |
| 12 | 750 |
| Specimen Group | Specimen ID | Thickness (mm) | Diameter (mm) | Reinforcement Ratio % | RFT. Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | SP1 | 100 | ⌀ 8 | 0.16 µb | Steel |
| SP2 | 100 | ⌀ 10 | 0.24 µb | Steel | |
| Group I | SP3 | 100 | ⌀ 8 | 0.80 µfb | GFRP |
| SP4 | 100 | ⌀ 8 | 1.00 µfb | GFRP | |
| SP5 | 100 | ⌀ 8 | 1.20 µfb | GFRP | |
| Group II | SP6 | 120 | ⌀ 8 | 1.20 µfb | GFRP |
| SP7 | 120 | ⌀ 10 | 1.20 µfb | GFRP | |
| SP8 | 120 | ⌀ 12 | 1.20 µfb | GFRP | |
| Group III | SP9 | 150 | ⌀ 8 | 1.20 µfb | GFRP |
| SP10 | 150 | ⌀ 10 | 1.20 µfb | GFRP | |
| SP11 | 150 | ⌀ 12 | 1.20 µfb | GFRP |
| Specimen Group | Specimen ID | First Crack (kN) | Ultimate Load (kN) | Ultimate Deflection Δu (mm) | Mode of Failure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | SP1 | 75 | 148.00 | 6.75 | FF |
| SP2 | 75 | 139.00 | 4.89 | FF | |
| Group I | SP3 | 50 | 87.85 | 2.74 | GR |
| SP4 | 80 | 149.30 | 4.91 | GR + TF | |
| SP5 | 85 | 154.40 | 3.72 | CCT | |
| Group II | SP6 | 100 | 180.70 | 7.91 | CCT |
| SP7 | 120 | 149.30 | 4.91 | GR | |
| SP8 | 125 | 129.30 | 4.79 | GR | |
| Group III | SP9 | 100 | 313.75 | 11.03 | GR |
| SP10 | 150 | 256.02 | 6.55 | CCT | |
| SP11 | 200 | 212.10 | 7.80 | CCT |
| Specimen Group | Specimen ID | First Crack (kN) | Ultimate Load (kN) | ΔNLFA (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | SP1 | 50 | 133.30 | 6.10 |
| SP2 | 50 | 118.40 | 4.15 | |
| Group I | SP3 | 50 | 76.42 | 2.38 |
| SP4 | 50 | 119.40 | 3.92 | |
| SP5 | 50 | 138.92 | 3.35 | |
| Group II | SP6 | 70 | 153.60 | 6.72 |
| SP7 | 70 | 134.40 | 4.41 | |
| SP8 | 70 | 112.40 | 4.16 | |
| Group III | SP9 | 82 | 247.86 | 8.71 |
| SP10 | 82 | 215.05 | 5.50 | |
| SP11 | 82 | 193.10 | 7.10 |
| Specimen Group | Spec. ID | Experimental Load (kN) | Analytical Load (kN) | Δ (mm) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Crack | Ult. Load | First Crack | Ult. Load | Δexp | ΔNLFE | First Crack | Ult. Load | |||
| Control | SP1 | 75 | 148.00 | 50 | 133.30 | 6.75 | 6.10 | 0.67 | 0.90 | 0.90 |
| SP2 | 75 | 139.00 | 50 | 118.40 | 4.89 | 4.15 | 0.67 | 0.85 | 0.84 | |
| Group I | SP3 | 50 | 87.85 | 50 | 76.42 | 2.74 | 2.38 | 1.0 | 0.87 | 0.87 |
| SP4 | 80 | 149.30 | 50 | 119.40 | 4.91 | 3.92 | 0.62 | 0.80 | 0.79 | |
| SP5 | 85 | 154.40 | 50 | 138.92 | 3.72 | 3.35 | 0.59 | 0.90 | 0.90 | |
| Group II | SP6 | 100 | 180.70 | 70 | 153.60 | 7.91 | 6.72 | 0.70 | 0.85 | 0.85 |
| SP7 | 120 | 149.30 | 70 | 134.40 | 4.91 | 4.41 | 0.58 | 0.90 | 0.89 | |
| SP8 | 125 | 129.30 | 70 | 112.40 | 4.79 | 4.16 | 0.56 | 0.87 | 0.87 | |
| Group III | SP9 | 100 | 313.75 | 82 | 247.86 | 11.03 | 8.71 | 0.82 | 0.79 | 0.79 |
| SP10 | 150 | 256.02 | 82 | 215.05 | 6.55 | 5.50 | 0.55 | 0.83 | 0.84 | |
| SP11 | 200 | 212.10 | 82 | 193.10 | 7.80 | 7.10 | 0.41 | 0.91 | 0.91 | |
| Average | 0.65 | 0.86 | 0.86 | |||||||
| Variance | 0.019 | 0.0015 | 0.0016 | |||||||
| Standard Deviation | 0.15 | 0.04 | 0.041 | |||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adam, M.A.; Erfan, A.M.; Habib, F.A.; El-Sayed, T.A. Structural Behavior of High-Strength Concrete Slabs Reinforced with GFRP Bars. Polymers 2021, 13, 2997. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13172997
Adam MA, Erfan AM, Habib FA, El-Sayed TA. Structural Behavior of High-Strength Concrete Slabs Reinforced with GFRP Bars. Polymers. 2021; 13(17):2997. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13172997
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdam, Maher A., Abeer M. Erfan, Fatma A. Habib, and Taha A. El-Sayed. 2021. "Structural Behavior of High-Strength Concrete Slabs Reinforced with GFRP Bars" Polymers 13, no. 17: 2997. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13172997
APA StyleAdam, M. A., Erfan, A. M., Habib, F. A., & El-Sayed, T. A. (2021). Structural Behavior of High-Strength Concrete Slabs Reinforced with GFRP Bars. Polymers, 13(17), 2997. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13172997