Manipulating Crystallization for Simultaneous Improvement of Impact Strength and Heat Resistance of Plasticized Poly(l-lactic acid) and Poly(butylene succinate) Blends
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Blend Preparation
2.3. Annealing Procedure
2.4. Characterizations and Testing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Stress-Strain Behaviors
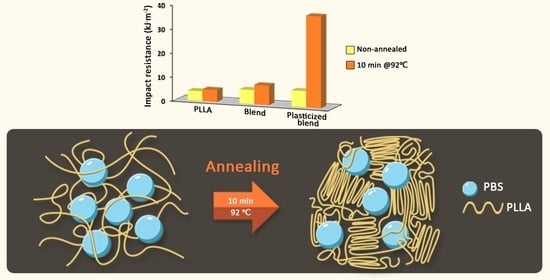
3.2. Impact Resistance
3.3. Discussion on Impact Performance and Crystalline Morphology
3.4. Discussion on Impact Performance and Phase Morphology
3.5. Overall Mechanical and Thermal Properties of PLLA-Based Blends
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Garlotta, D. A Literature Review of Poly(Lactic Acid). J. Polym. Environ. 2001, 9, 63–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Hu, H.; Wang, X.; Yu, X.; Zhou, W.; Peng, S. Super tough poly(lactic acid) blends: A comprehensive review. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 13316–13368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Guo, B.-H. Poly(butylene succinate) and its copolymers: Research, development and industrialization. Biotechnol. J. 2010, 5, 1149–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiqah, S.A.; Khalina, A.; Harmaen, A.S.; Tawakkal, I.A.; Zaman, K.; Asim, M.; Nurrazi, M.N.; Lee, C.H. A Review on Properties and Application of Bio-Based Poly(Butylene Succinate). Polymers 2021, 13, 1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.W.; Im, S.S. Phase behavior and morphology in blends of poly(L-lactic acid) and poly(butylene succinate). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 86, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Thomas, N.L. Blending poly(butylene succinate) with poly(lactic acid): Ductility and phase inversion effects. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 71, 534–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, S.; Kopitzky, R.; Tolga, S.; Kabasci, S. Polylactide (PLA) and Its Blends with Poly(butylene succinate) (PBS): A Brief Review. Polymers 2019, 11, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yokohara, T.; Yamaguchi, M. Structure and properties for biomass-based polyester blends of PLA and PBS. Eur. Polym. J. 2008, 44, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrowska, J.; Sadurski, W.; Paluch, M.; Tyński, P.; Bogusz, J. The effect of poly(butylene succinate) content on the structure and thermal and mechanical properties of its blends with polylactide. Polym. Int. 2019, 68, 1271–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likittanaprasong, N.; Seadan, M.; Suttiruengwong, S. Impact property enhancement of poly (lactic acid) with different flexible copolymers. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 87, 012069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Supthanyakul, R.; Kaabbuathong, N.; Chirachanchai, S. Random poly(butylene succinate-co-lactic acid) as a multi-functional additive for miscibility, toughness, and clarity of PLA/PBS blends. Polymer 2016, 105, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Han, L.; Han, C.; Xu, K.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, M.; Dong, L. Improvement in toughness and crystallization of poly(L-lactic acid) by melt blending with ethylene/methyl acrylate/glycidyl methacrylate terpolymer. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2013, 53, 2498–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Sun, B.; Bian, X.; Li, G.; Chen, X. High Melt Strength and High Toughness PLLA/PBS Blends by Copolymerization and in Situ Reactive Compatibilization. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, D.; Liu, Z.; Lan, X.; Wu, F.; Xie, B.; Yang, M. Morphology, rheology, crystallization behavior, and mechanical properties of poly(lactic acid)/poly(butylene succinate)/dicumyl peroxide reactive blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 39580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, M.; Ohya, T.; Iida, K.; Hayashi, H.; Hirano, K.; Fukuda, H. Increased impact strength of biodegradable poly(lactic acid)/poly(butylene succinate) blend composites by using isocyanate as a reactive processing agent. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 106, 1813–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, C.; Ma, P. Toughening modification of PLLA/PBS blends via in situ compatibilization. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2009, 49, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, F.; Yu, Q.; Ni, C.; Gu, X.; Li, Y.; You, J. Fabrication of PLLA with High Ductility and Transparence by Blending with Tiny Amount of PVDF and Compatibilizers. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2019, 304, 1970030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gu, X.; Ni, C.; Li, F.; Li, Y.; You, J. Improvement of PLLA Ductility by Blending with PVDF: Localization of Compatibilizers at Interface and Its Glycidyl Methacrylate Content Dependency. Polymers 2020, 12, 1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H.; Ikada, Y. Properties and morphologies of poly(l-lactide): 1. Annealing condition effects on properties and morphologies of poly(l-lactide). Polymer 1995, 36, 2709–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, V.; Zhang, K.; Misra, M.; Mohanty, A.K. Overcoming the Fundamental Challenges in Improving the Impact Strength and Crystallinity of PLA Biocomposites: Influence of Nucleating Agent and Mold Temperature. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 11203–11214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, H.; Zhang, W.; Deng, H.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, Q. Control of Crystal Morphology in Poly(l-lactide) by Adding Nucleating Agent. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 1233–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srithep, Y.; Nealey, P.; Turng, L.-S. Effects of annealing time and temperature on the crystallinity and heat resistance behavior of injection-molded poly(lactic acid). Polym. Eng. Sci. 2013, 53, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyama, H.T. Super-tough poly(lactic acid) materials: Reactive blending with ethylene copolymer. Polymer 2009, 50, 747–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajornprai, T.; Sirisinha, K. Effect of thermal annealing on crystal evolution and multiple melting behaviors of molded poly(L-lactic acid) and poly(butylene succinate) blends upon heating investigated by TMDSC. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tábi, T.; Sajó, I.E.; Szabó, F.; Luyt, A.S.; Kovács, J.G. Crystalline structure of annealed polylactic acid and its relation to processing. eXPRESS Polym. Lett. 2010, 4, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, P.M.; Mariatti, M.; Zulkifli, A.; Todo, M. Changes in the crystallinity and mechanical properties of poly(l-lactic acid)/poly(butylene succinate-co-l-lactate) blend with annealing process. Polym. Bull. 2011, 67, 815–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Guo, H.; Li, J.; Huang, S.; Li, H.; Meng, Y.; Yu, D.; de Claville Christiansen, J.; Jiang, S. Temperature dependence of poly(lactic acid) mechanical properties. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 113762–113772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, E.W.; Sterzel, H.J.; Wegner, G. Investigation of the structure of solution grown crystals of lactide copolymers by means of chemical reactions. Kolloid-Z. Z. Polym. 1973, 251, 980–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S. Phase structure and adhesion in polymer blends: A criterion for rubber toughening. Polymer 1985, 26, 1855–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortelny, I.; Ujcic, A.; Fambri, L.; Slouf, M. Phase Structure, Compatibility, and Toughness of PLA/PCL Blends: A Review. Front. Mater. 2019, 6, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bai, H.; Huang, C.; Xiu, H.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, Q. Toughening of poly(l-lactide) with poly(ε-caprolactone): Combined effects of matrix crystallization and impact modifier particle size. Polymer 2013, 54, 5257–5266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, J. Research progress in toughening modification of poly(lactic acid). J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2011, 49, 1051–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Misra, M.; Mohanty, A.K. Super Toughened Poly(lactic acid)-Based Ternary Blends via Enhancing Interfacial Compatibility. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 1955–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, P.; Kai, W.; Zhu, B.; Dong, T.; Inoue, Y. Polymorphous Crystallization and Multiple Melting Behavior of Poly(l-lactide): Molecular Weight Dependence. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 6898–6905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartier, L.; Okihara, T.; Ikada, Y.; Tsuji, H.; Puiggali, J.; Lotz, B. Epitaxial crystallization and crystalline polymorphism of polylactides. Polymer 2000, 41, 8909–8919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotek, J.; Raab, M.; Baldrian, J.; Grellmann, W. The effect of specific β-nucleation on morphology and mechanical behavior of isotactic polypropylene. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 85, 1174–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivsa-Art, W.; Fujii, K.; Nomura, K.; Aso, Y.; Ohara, H.; Yamane, H. The effect of poly(ethylene glycol) as plasticizer in blends of poly(lactic acid) and poly(butylene succinate). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 43044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Deng, C.; Lin, G.-P.; Wang, Y.-Z. Super Toughened and High Heat-Resistant Poly(Lactic Acid) (PLA)-Based Blends by Enhancing Interfacial Bonding and PLA Phase Crystallization. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 5643–5655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S. Chain structure, phase morphology, and toughness relationships in polymers and blends. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1990, 30, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S. Control of intrinsic brittleness and toughness of polymers and blends by chemical structure: A review. Polym. Int. 1992, 29, 229–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, V.; Mohanty, A.K.; Misra, M. Perspective on Polylactic Acid (PLA) based Sustainable Materials for Durable Applications: Focus on Toughness and Heat Resistance. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2899–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Deng, C.; Wang, Y.-z. Improving the impact property and heat-resistance of PLA/PC blends through coupling molecular chains at the interface. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2015, 26, 1247–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, H.-T.; Huang, S.-Y.; Chen, Y.-F.; Kuo, M.-T.; Chiang, T.-Y.; Chang, C.-Y.; Wang, Y.-H. Heat Treatment Effects on the Mechanical Properties and Morphologies of Poly (Lactic Acid)/Poly (Butylene Adipate-co-terephthalate) Blends. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2013, 2013, 951696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oral, M.A.; Ersoy, O.G.; Serhatli, E.İ. Effect of acrylonitrile–butadiene–styrene/polyethylene terephthalate blends on dimensional stability, morphological, physical and mechanical properties and after aging at elevated temperature. J. Plast. Film Sheeting 2018, 34, 394–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Sample | Annealing Temperature (°C) | Modulus (MPa) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation (%) | Impact Strength (kJ∙m−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLLA | - | 2045.24 ± 157.34 | 68.48 ± 1.64 | 12.60 ± 3.00 | 4.02 ± 0.17 |
| 75 | 2197.41 ± 56.18 | 74.38 ± 2.14 | 6.48 ± 0.31 | 3.92 ± 0.06 | |
| 92 | 2218.89 ± 81.38 | 76.10 ± 1.76 | 6.69 ± 0.48 | 4.92 ± 0.48 | |
| 152 | 2402.50 ± 82.47 | 67.33 ± 4.72 | 5.15 ± 0.69 | 3.75 ± 0.13 | |
| Blend | - | 1781.23 ± 118.90 | 55.69 ± 1.08 | 356.99 ± 14.11 | 5.85 ± 0.04 |
| 75 | 1586.70 ± 58.20 | 56.03 ± 1.83 | 213.75 ± 69.96 | 6.92 ± 0.31 | |
| 92 | 1728.59 ± 55.20 | 59.11 ± 1.45 | 14.31 ± 2.84 | 8.13 ± 0.63 | |
| 152 | 1940.16 ± 97.20 | 55.80 ± 1.73 | 10.09 ± 2.35 | 5.27 ± 0.34 | |
| Plasticized blend | - | 1655.07 ± 98.70 | 48.55 ± 0.55 | 380.77 ± 21.98 | 6.75 ± 0.53 |
| 75 | 1665.07 ± 46.94 | 53.12 ± 1.81 | 52.04 ± 10.33 | 32.89 ± 1.64 | |
| 92 | 1587.34 ± 97.31 | 50.17 ± 1.31 | 32.04 ± 11.25 | 38.34 ± 2.22 | |
| 152 | 1893.70 ± 83.01 | 49.43 ± 1.75 | 18.98 ± 3.20 | 7.16 ± 1.16 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kajornprai, T.; Suttiruengwong, S.; Sirisinha, K. Manipulating Crystallization for Simultaneous Improvement of Impact Strength and Heat Resistance of Plasticized Poly(l-lactic acid) and Poly(butylene succinate) Blends. Polymers 2021, 13, 3066. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13183066
Kajornprai T, Suttiruengwong S, Sirisinha K. Manipulating Crystallization for Simultaneous Improvement of Impact Strength and Heat Resistance of Plasticized Poly(l-lactic acid) and Poly(butylene succinate) Blends. Polymers. 2021; 13(18):3066. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13183066
Chicago/Turabian StyleKajornprai, Todsapol, Supakij Suttiruengwong, and Kalyanee Sirisinha. 2021. "Manipulating Crystallization for Simultaneous Improvement of Impact Strength and Heat Resistance of Plasticized Poly(l-lactic acid) and Poly(butylene succinate) Blends" Polymers 13, no. 18: 3066. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13183066
APA StyleKajornprai, T., Suttiruengwong, S., & Sirisinha, K. (2021). Manipulating Crystallization for Simultaneous Improvement of Impact Strength and Heat Resistance of Plasticized Poly(l-lactic acid) and Poly(butylene succinate) Blends. Polymers, 13(18), 3066. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13183066