Effect of Material Properties on the Foaming Behaviors of PP-Based Wood Polymer Composites Prepared with the Application of Spherical Cavity Mixer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Platform
2.1. Structural Parameters of CTM
2.2. Effect of CTM Application
3. Experimental
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Samples
3.3. Characterization
3.3.1. Melt Flow Rate (MFR)
3.3.2. Rheological Property
3.3.3. Thermal Property
3.3.4. Micromorphology
3.3.5. Mechanical Property
4. Results and Discussion
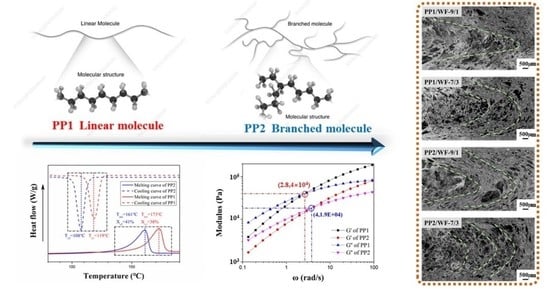
4.1. Effect of Molecular Structure on the Properties of Composites
4.1.1. Thermal Property
4.1.2. Melt Flow Rate
4.1.3. Rheological Property
4.1.4. Mechanical Property
4.2. Effect of Molecular Structure on the Microstructure of Samples
4.2.1. Dispersion State of Fillers
4.2.2. Cell Morphology on Axial Section
4.2.3. Cell morphology on Radial Section
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Compared with static mixer, CTM with a strong shear dispersion ability was more suitable for the dispersive mixing of materials with high viscosity, which was also improved by the increased radius and axial number of cavities. Meanwhile, the experimental results also demonstrated that the application of spherical CTM with the radius of 5 mm could effectively prevent the exposure of agglomerated WF on the sample surface and realize the uniform dispersion of fillers.
- (2)
- Affected by the molecular configuration, the linear molecular endowed PP1 with the triclinic crystals, which were about 10 °C higher than the trigonal crystals of PP2 with branched molecule. The smaller angular frequency of PP1 at the intersection of G’ and G” curves indicated the longer relaxation time and higher average molecular weight, which decreased the difficulty in the formation of entanglements and caused the much higher viscosity.
- (3)
- The addition of WF and linear molecular endowed PP1-based composites with higher viscosity at a shear rate lower than 100 s−1, which contributed to the smaller size and larger density of the bubbles. Moreover, the bubbles foamed in the shear flow field were gradually stretched into a flat ellipsoid shape and arranged along the flow direction for the radial velocity gradient.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hu, X.; Huang, J.; Chang, C.P.; Guo, Y. Relationship between forest resources and economic growth: Empirical evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 214, 848–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martone, M.; Rizzoli, P.; Wecklich, C.; González, C.; Bueso-Bello, J.L.; Valdo, P.; Schulze, D.; Zink, M.; Krieger, G.; Moreira, A. The global forest/non-forest map from TanDEM-X interferometric SAR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 205, 352–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cincinelli, A.; Scopetani, C.; Chelazzi, D.; Lombardini, E.; Martellini, T.; Katsoyiannis, A.; Fossi, M.C.; Corsolinid, S. Microplastic in the surface waters of the Ross Sea (Antarctica): Occurrence, distribution and characterization by FTIR. Chemosphere 2017, 175, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantia, F.P.L.; Morreale, M. Green composites: A brief review. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2011, 42, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, B.; Wang, Z. Optimizing torque rheometry parameters for assessing the rheological characteristics and extrusion processability of wood plastic composites. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2019, 32, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Rodrigue, D.; Riedl, B. Preparation and morphology of polypropylene/wood flour composite foams via extrusion. Polym. Compos. 2010, 26, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petchwattana, N.; Covavisaruch, S.J.M. Influences of particle sizes and contents of chemical blowing agents on foaming wood plastic composites prepared from poly(vinyl chloride) and rice hull. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 2844–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyvarinen, M.; Ronkanen, M.; Karki, T. The effect of the use of construction and demolition waste on the mechanical and moisture properties of a wood-plastic composite. Compos. Struct. 2019, 210, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, D. Thermoplastic moulding of Wood-Polymer Composites (WPC): A review on physical and mechanical behaviour under hot-pressing technique. Compos. Struct. 2021, 262, 113649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrentino, L.; Aurilia, M.; Iannace, S. Polymeric foams from high-performance thermoplastics. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2011, 30, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, J.; Waldman, F.; Suh, N. The production and analysis of microcellular thermoplastic foams. Annu. Technol. Conf.-Soc. Plast. Eng. 1982, 28, 674–676. [Google Scholar]
- Rachtanapun, P.; Selke, S.E.M.; Matuana, L.M. Microcellular foam of polymer blends of HDPE/PP and their composites with wood fiber. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 88, 2842–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, G.M.; Park, C.B.; Lin, W.S.; Guo, G.; Pop-Iliev, R. Expansion mechanisms of plastic/wood-flour composite foams with moisture, dissolved gaseous volatiles, and undissolved gas bubbles. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2003, 43, 1347–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Rizvi, G.; Park, C.B. Development of an extrusion system for producing fine-celled HDPE/wood-fiber composite foams using CO2 as a blowing agent. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2004, 23, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Toghiani, H.; Zhang, J.; Xue, Y.; Pittman, C.U., Jr. Studies of surface-modified wood flour/polypropylene composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 2143–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.X.; Zhang, J.; Lu, B.X.; Xin, Z.X.; Kang, C.K.; Kim, J.K. Effect of flame retardants on mechanical properties, flammability and foamability of PP/wood–fiber composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2012, 43, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauwendaal, C.J. Screw Extruder with Improved Dispersive Mixing. U.S. Patent 5932159 A, 3 August 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Fukumizu, S.; Inoue, K.; Kuriyama, A. Cavity Transfer Mixing Extruder. U.S. Patent 4695165, 22 September 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Grosso, G.; Hulsen, M.A.; Sarhangi Fard, A.; Overend, A.; Anderson, P.D. Mixing processes in the cavity transfer mixer: A thorough study. AIChE J. 2018, 64, 1034–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Yang, J.; Chen, C.; Yu, G.; Mao, Z. Analysis of the structure of high-efficiency dynamic mixer. J. Qingdao Univ. 1995, 10, 51–54. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Kong, L.; Li, J.; Du, Z.-Y. Assessment of Groove Type Dynamic Mixer with High Efficiency by Number of Striations. Plastics 2014, 43, 100–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Xin, C.; Yang, Z.; Yan, B.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; He, Y. Solid-state foaming of isotactic polypropylene and its composites with spherical or fibrous poly(butylenes terephthalate). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 41801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.L.; Liu, T.; Xu, Z.M.; Zhaoa, L.; Hubc, G.-H.; Yuana, W.-K. Effects of crystal structure on the foaming of isotactic polypropylene using supercritical carbon dioxide as a foaming agent. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2009, 48, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Tang, T.; Zhu, L.; Wei, K.; Qiao, L. The Investigation on Crystallization Behavior and Foamability of Long Chain Branched Polypropylene. Acta Polym. Sin. 2016, 4, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marigo, A.; Marega, C.; Causin, V.; Ferrari, P. Influence of thermal treatments, molecular weight, and molecular weight distribution on the crystallization of β-isotactic polypropylene. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 91, 1008–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Wu, Q.; Li, S.; Ou, R.; Wang, Q. Toughness and crystallization enhancement in wood fiber-reinforced polypropylene composite through controlling matrix nucleation. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 6542–6551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, S.H.; Asaad, J.N.; Iskander, B.A.; Tawfik, S.Y. Influence of some additives on the performance of wood flour/polyolefin composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 109, 2243–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Jiang, H.; Guo, L.; Shi, H. Comparative study on the effect of manchurian ash and larch wood flour on mechanical property, morphology, and rheology of HDPE/wood flour composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 107, 2520–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, N.; Xu, X.; Zhu, L.; Sheng, J.; Yan, X.-L. Rheological Behavior and Miscibility of Polypropylene and Poly(Ethylene-1-Octene) Blends. J. Tianjin Univ. 2009, 42, 861–866. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Q.; Wang, Y.; Liao, F.; Xia, J.; Miao, J. Structure and properties of impact PP copolymer K9928H with high melt flow rate via hydrogen as regulator. China Synth. Resin Plast. 2015, 32, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favelukis, M.; Tadmor, Z.; Semiat, R. Bubble growth in a viscous liquid in a simple shear flow. AIChE J. 1999, 45, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.H.; Han, C.D. A study of bubble nucleation in a mixture of molten polymer and volatile liquid in a shear flow field. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1988, 28, 1616–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xue, P.; Jia, M.; Zhang, R. Effect of Polymer Blends on the Properties of Foamed Wood-Polymer Composites. Materials 2019, 12, 1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]












| Sample | Weight (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PP1 | PP2 | WF | MAH-g-PP | Talc | AC | |
| 1 | 90 | / | 10 | 3.5 | 10 | 1 |
| 2 | 80 | / | 20 | 3.5 | 10 | 1 |
| 3 | 70 | / | 30 | 3.5 | 10 | 1 |
| 4 | 60 | / | 40 | 3.5 | 10 | 1 |
| 5 | / | 90 | 10 | 3.5 | 10 | 1 |
| 6 | / | 80 | 20 | 3.5 | 10 | 1 |
| 7 | / | 70 | 30 | 3.5 | 10 | 1 |
| 8 | / | 60 | 40 | 3.5 | 10 | 1 |
| Sample | ω (rad/s) | G’ (Pa) |
|---|---|---|
| PP1 | 4.28 | 19,729.37 |
| PP2 | 2.92 | 42,404.58 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Xue, P.; Zhang, W.; Hao, G.; Xiao, L.; Jiang, W. Effect of Material Properties on the Foaming Behaviors of PP-Based Wood Polymer Composites Prepared with the Application of Spherical Cavity Mixer. Polymers 2021, 13, 3179. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13183179
Wang S, Xue P, Zhang W, Hao G, Xiao L, Jiang W. Effect of Material Properties on the Foaming Behaviors of PP-Based Wood Polymer Composites Prepared with the Application of Spherical Cavity Mixer. Polymers. 2021; 13(18):3179. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13183179
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Suwei, Ping Xue, Wenxin Zhang, Gazi Hao, Lei Xiao, and Wei Jiang. 2021. "Effect of Material Properties on the Foaming Behaviors of PP-Based Wood Polymer Composites Prepared with the Application of Spherical Cavity Mixer" Polymers 13, no. 18: 3179. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13183179
APA StyleWang, S., Xue, P., Zhang, W., Hao, G., Xiao, L., & Jiang, W. (2021). Effect of Material Properties on the Foaming Behaviors of PP-Based Wood Polymer Composites Prepared with the Application of Spherical Cavity Mixer. Polymers, 13(18), 3179. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13183179