Electrospun PVDF Nanofibers for Piezoelectric Applications: A Review of the Influence of Electrospinning Parameters on the β Phase and Crystallinity Enhancement
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Production of Nanofibers
3. Experimental Setup and Process Parameters of Electrospinning
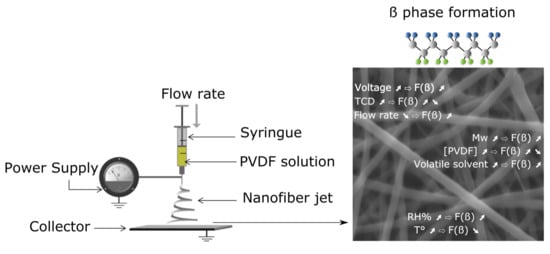
4. Effect of Electrospinning Parameters on the β Phase and the Crystallinity of PVDF Nanofibers
4.1. Process Parameters
4.1.1. Voltage
4.1.2. TCD
4.1.3. Flow Rate
4.1.4. Type of Collector
4.2. Solution Parameters
4.2.1. PVDF Molecular Weight
4.2.2. PVDF Concentration
4.2.3. Solvent
4.3. Ambient Parameters
4.3.1. RH
4.3.2. Working Temperature
5. Introduction of Nanoparticles to the Structure of Nanofibers for Improving the β Phase
5.1. Inorganic Nanomaterials
5.2. Organic Nanomaterials
6. Piezoelectric Properties on Nanofibrous Membranes
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sirohi, J.; Chopra, I. Fundamental understanding of piezoelectric strain sensors. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2000, 11, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Bai, Z.; Cao, Y.; Dong, M.; Jiang, K.; Zhou, Y.; Tao, Y.; Gu, S.; Xu, J.; Yin, X.; et al. Enhanced piezoelectric performance of BiCl3/PVDF nanofibers-based nanogenerators. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhasssan, Z.A.; Burezq, Y.S.; Nair, R.; Shehata, N. Polyvinylidene difluoride piezoelectric electrospun nanofibers: Review in synthesis, fabrication, characterizations, and applications. J. Nanomater. 2018, 2018, 8164185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.Y.; Domnner, M.; Chang, C.; Lin, L.W. Piezoelectric nanofibers for energy scavenging applications. Nano Energy 2012, 1, 356–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, P.; Lopes, A.C.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Electroactive phases of poly (vinylidene fluoride): Determination, processing and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 683–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persano, L.; Dagdeviren, C.; Su, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Girardo, S.; Pisignano, D.; Huang, Y.; Rogers, J.A. High performance piezoelectric devices based on aligned arrays of nanofibers of poly (vinylidenefluoride-co-trifluoroethylene). Nat Commun. 2013, 4, 1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persano, L.; Camposeo, A.; Pisignano, D. Active polymer nanofibers for photonics, electronics, energy generation and micromechanics. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2015, 43, 48–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shvetsova, N.A.; Shcherbinin, S.A.; Lugovaya, M.A.; Reznichenko, A.N.; Rybyanets, A.N. Method of electromechanical characterization of ferroelectric materials. Ferroelectrics 2020, 561, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trolier-McKinstry, S.; Zhang, S.; Bell, A.J.; Tan, X. High-performance piezoelectric crystals, ceramics, and films. Ann. Rev. Mater. Res. 2018, 48, 191–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shepelin, N.A.; Glushenkov, A.M.; Lussini, V.C.; Fox, P.J.; Dicinoski, G.W.; Shapter, J.G.; Ellis, A.V. New developments in composites, copolymer technologies and processing techniques for flexible fluoropolymer piezoelectric generators for efficient energy harvesting. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 1143–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadi, A.; Hosseini, S.M.; Mohseni, M. Investigation of the electromagnetic microwaves absorption and piezoelectric properties of electrospun Fe3O4-GO/PVDF hybrid nanocomposites. Org. Electron. 2018, 59, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paquin, F.; Rivnay, J.; Salleo, A.; Stingelin, N.; Silva, C. Multi-phase semicrystalline microstructures drive exciton dissociation in neat plastic semiconductors. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 10715–10722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wan, C.; Bowen, C.R. Multiscale-structuring of polyvinylidene fluoride for energy harvesting: The impact of molecular-, micro- and macro-structure. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 3091–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruan, L.; Yao, X.; Chang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Qin, G.; Zhang, X. Properties and applications of the beta phase poly (vinylidene fluoride). Polymers 2018, 10, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nunes-Pereira, J.; Sencadas, V.; Correia, V.; Rocha, J.G.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Energy harvesting performance of piezoelectric electrospun polymer fibers and polymer/ceramic composites. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2013, 196, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kakimoto, K.; Fukata, K.; Ogawa, H. Fabrication of fibrous BaTiO3-reinforced PVDF composite sheet for transducer application. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2013, 200, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalani, S.; Kohandani, R.; Bagherzadeh, R. Flexible electrospun PVDF–BaTiO3 hybrid structure pressure sensor with enhanced efficiency. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 35090–35098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Lye, S.W.; Miao, J. Measurement of impact characteristics in a string using electrospun PVDF nanofibers strain sensors. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.M.; Silva, M.M.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Battery separators based on vinylidene fluoride (VDF) polymers and copolymers for lithium ion battery applications. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 11404–11417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wan, C.C. Review of gel-type polymer electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 1999, 77, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, J.C.; Dias, J.P.; Lanceros-Mendez, S.; Costa, C.M. Recent advances in poly (vinylidene fluoride) and its copolymers for lithium-ion battery separators. Membranes 2018, 8, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khalifa, M.; Janakiraman, S.; Ghosh, S.; Venimadhav, A.; Anandhan, S. PVDF/halloysite nanocomposite-based non-wovens as gel polymer electrolyte for high safety lithium ion battery. Polym. Compos. 2018, 40, 2320–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, R.; Ribeiro, C.; Lopes, A.C.; Martins, P.; Sencadas, V.; Soares, R.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Osteoblast, fibroblast and in vivo biological response to poly (vinylidene fluoride) based composite materials. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2013, 24, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ribeiro, C.; Panadero, J.A.; Sencadas, V.; Lanceros-Mendez, S.; Tamano, M.N.; Moratal, D.; Salmeron-Sanchez, M.; Gomez Ribelles, J.L. Fibronectin adsorption and cell response on electroactive poly (vinylidene fluoride) films. Biomed. Mater. 2012, 7, 035004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senthil Kumar, R.; Sarathi, T.; Venkataraman, K.K.; Bhattacharyya, A. Enhanced piezoelectric properties of polyvinylidene fluoride nanofibers using carbon nanofiber and electrical poling. Mater. Lett. 2019, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Wang, X.G.; Lin, T. Electrical power generator from randomly oriented electrospun poly (vinylidene fluoride) nanofibre membranes. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 11088–11091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haddadi, S.A.; Ghaderi, S.; Amini, M.; Ramazani, S.A.A. Mechanical and piezoelectric characterizations of electrospun PVDF-nanosilica fibrous scaffolds for biomedical applications. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 15710–15716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koç, M.; Paralı, L.; Şan, O. Fabrication and vibrational energy harvesting characterization of flexible piezoelectric nanogenerator (PEN) based on PVDF/PZT. Polym. Test. 2020, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liao, C.; Tjong, S.C. Electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride-based fibrous scaffolds with piezoelectric characteristics for bone and neural tissue engineering. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, J.H.; Zhu, B.K.; Xu, Y.Y. Structure and ionic conductivity of porous polymer electrolytes based on PVDF-HFP copolymer membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 281, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.H.; Chen, S.L.; Elumalai, N.K.; Prabhakaran, M.P.; Zong, Y.; Vijila, C.; Allakhverdiev, S.I.; Ramakrishna, S. Biological, chemical, and electronic applications of nanofibers. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2013, 298, 822–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roebben, G.; Emons, H.; Reiners, G.; Decker, J.E.; Steele, A.G. Nanotechnology Standards. Nanotechnology 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barhate, R.S.; Loong, C.K.; Ramakrishna, S. Preparation and characterization of nanofibrous filtering media. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 283, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barhate, R.S.; Ramakrishna, S. Nanofibrous filtering media: Filtration problems and solutions from tiny materials. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 296, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopal, R.; Kaur, S.; Ma, Z.W.; Chan, C.; Ramakrishna, S.; Matsuura, T. Electrospun nanofibrous filtration membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 281, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Ouyang, Y.; Xiao, R. Fabrication and morphology development of isotactic polypropylene nanofibers from isotactic polypropylene/polylactide blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 123, 2859–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaarour, B.; Tina, H.; Zhu, L.; Jin, X. Branched nanofibers with tiny diameters for air filtration via one-step electrospinning. J. Ind. Text. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidouny, L.; Abou-Daher, M.; Tehrani-Bagha, A.R.; Ghali, K.; Ghaddar, N. Electrospun nanofibrous polyvinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene membranes for oil–water separation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.H.; Kang, H.W. Surface energy characteristics of zeolite embedded PVDF nanofiber films with electrospinning process. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 387, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nain, A.S.; Wong, J.C.; Amon, C.; Sitti, M. Drawing suspended polymer micro-/nanofibers using glass micropipettes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reneker, D.H.; Yarin, A.L. Electrospinning jets and polymer nanofibers. Polymer 2008, 49, 2387–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, Y.; Lv, Y.; Che, R.; Wu, H.; Zhang, X.; Gu, D.; Zheng, G.; Zhao, D. Two-dimensional mesoporous carbon nanosheets and their derived graphene nanosheets: Synthesis and efficient lithium ion storage. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 1524–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.-J.; Persano, L.; Camposeo, A.; Jang, J.-S.; Koo, W.-T.; Kim, S.-J.; Cho, H.-J.; Kim, I.-D.; Pisignano, D. Electrospun nanostructures for high performance chemiresistive and optical sensors. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2017, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janakiraman, S.; Surendran, A.; Biswal, R.; Ghosh, S.; Anandhan, S.; Venimadhav, A. Electrochemical characterization of a polar β-phase poly (vinylidene fluoride) gel electrolyte in sodium ion cell. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 833, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbarnia, A.; Khan, W.S.; Ghazinezami, A.; Asmatulu, R. Investigating the thermal, mechanical, and electrochemical properties of PVdF/PVP nanofibrous membranes for supercapacitor applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lin, Y.; Liang, L.; Voigt, J.A.; Huber, D.L.; Tian, Z.R.; Coker, E.; McKenzie, B.; McDermott, M.J. Templateless assembly of molecularly aligned conductive polymer nanowires: A new approach for oriented nanostructures. Chemistry 2003, 9, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Zhu, J.; Sun, H.; Xu, Y.; Liu, T.; Qian, C. A brief review on piezoelectric PVDF nanofibers prepared by electrospinning. Ferroelectrics 2018, 526, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.R. Nanomaterials: A membrane-based synthetic approach. Science 1994, 266, 1961–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansarizadeh, M.; Haddadi, S.A.; Amini, M.; Hasany, M.; Ramazani SaadatAbadi, A. Sustained release of CIP from TiO2-PVDF/starch nanocomposite mats with potential application in wound dressing. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Zhang, H.M.; Zhong, H.X.; Zhang, J.L. Nitrogen-doped carbon xerogel: A novel carbon-based electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction reaction in proton exchange membrane (PEM) fuel cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 3389–3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Huang, S.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, W. In situ preparation of 2D MoS2 nanosheets vertically supported on TiO2/PVDF flexible fibers and their photocatalytic performance. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 375606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Huang, H.; Meng, X.H.; Zeng, Y.C. Fabrication of helical microfibers from melt blown polymer blends. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2018, 56, 970–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agubra, V.A.; De la Garza, D.; Gallegos, L.; Alcoutlabi, M. ForceSpinning of polyacrylonitrile for mass production of lithium-ion battery separators. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, Z.M.; Lu, B.B.; Mei, S.Q.; Xu, Q.; Liu, F. Research on parametric model for polycaprolactone nanofiber produced by centrifugal spinning. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2018, 40, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, M.Q.; Kou, R.; Lu, L.L.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, X.W.; Liu, G.M.; Zheng, Y.M.; Yu, S.H. Unique necklace-like phenol formaldehyde resin nanofibers: Scalable templating synthesis, casting films, and their superhydrophobic property. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 5086–5092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondarçuhu, T.; Joachim, C. Drawing a single nanofibre over hundreds of microns. Europhys. Lett. 1998, 42, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitesides, G.M.; Grzybowski, B. Self-assembly at all scales. Science 2002, 295, 2418–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jayanarayanan, K.; Thomas, S.; Joseph, K. Morphology, static and dynamic mechanical properties of in situ microfibrillar composites based on polypropylene/poly (ethylene terephthalate) blends. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2008, 39, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Xi, P.; Cheng, B.W. High efficiency fabrication of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene submicron filaments/sheets by flash-spinning. J. Polym. Eng. 2016, 36, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferri, A.; Rault, F.; Da Costa, A.; Cochrane, C.; Boudriaux, M.; Lemort, G.; Campagne, C.; Devaux, E.; Courtois, C.; Desfeux, R. Local electrical characterization of PVDF textile filament. Fibers Polym. 2019, 20, 1333–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Peng, H.; Wang, W.; Liu, T. Crystallization behavior of poly(ε-caprolactone)/layered double hydroxide nanocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 116, 2658–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.H.; Nirmala, R.; Kim, T.W.; Navamathavan, R.; Kim, H.Y.; Park, S.J. Highly aligned poly (vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoro propylene) nanofibers via electrospinning technique. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 16, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.; Tarbutton, J.A. Electric poling-assisted additive manufacturing process for PVDF polymer-based piezoelectric device applications. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, W.A.; Kotaki, M.; Liu, Y.; Lu, X.H. Morphology, polymorphism behavior and molecular orientation of electrospun poly(vinylidene fluoride) fibers. Polymer 2007, 48, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reneker, D.H.; Yarin, A.L.; Fong, H.; Koombhongse, S. Bending instability of electrically charged liquid jets of polymer solutions in electrospinning. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 87, 4531–4547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.L.; Li, Y.; Xu, J.T.; Fan, Z.Q. Cooperative effect of electrospinning and nanoclay on formation of polar crystalline phases in poly (vinylidene fluoride). ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 1759–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Srinivas, V.; Madras, G.; Bose, S. Outstanding dielectric constant and piezoelectric coefficient in electrospun nanofiber mats of PVDF containing silver decorated multiwall carbon nanotubes: Assessing through piezoresponse force microscopy. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 6251–6258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asai, H.; Kikuchi, M.; Shimada, N.; Nakane, K. Effect of melt and solution electrospinning on the formation and structure of poly (vinylidene fluoride) fibres. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 17593–17598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, J.; Niu, H.T.; Wang, H.X.; Wang, X.G.; Lin, T. Enhanced mechanical energy harvesting using needleless electrospun poly (vinylidene fluoride) nanofibre webs. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 2196–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Navarro, N.; González-González, V.; Moreno-Cortez, I.E.; Garza-Navarro, M.A. Electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride nanofibers by bubble electrospinning technique. Mater. Lett. 2016, 167, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, H.A.; Khan, K.R. Study on the various types of needle based and needleless electrospinning system for nanofiber production. Int. J. Text. Sci. 2017, 6, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaarour, B.; Zhu, L.; Jin, X.Y. Controlling the surface structure, mechanical properties, crystallinity, and piezoelectric properties of electrospun PVDF nanofibers by maneuvering molecular weight. Soft Mater. 2019, 17, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.F.; He, A.H.; Li, J.X.; Han, C.C. Polymorphism control of poly (vinylidene fluoride) through electrospinning. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2007, 28, 2159–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafari, E.; Jiang, X.; Lu, N. Surface morphology and beta-phase formation of single polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) composite nanofibers. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2017, 1, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehata, N.; Elnabawy, E.; Abdelkader, M.; Hassanin, A.H.; Salah, M.; Nair, R.; Ahmad Bhat, S. Static-aligned piezoelectric poly (Vinylidene Fluoride) Electrospun nanofibers/MWCNT composite membrane: Facile method. Polymers 2018, 10, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, Z.M.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. A review on polymer nanofibers by electrospinning and their applications in nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 2223–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szentivanyi, A.; Chakradeo, T.; Zernetsch, H.; Glasmacher, B. Electrospun cellular microenvironments: Understanding controlled release and scaffold structure. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damaraju, S.M.; Wu, S.; Jaffe, M.; Arinzeh, T.L. Structural changes in PVDF fibers due to electrospinning and its effect on biological function. Biomed. Mater. 2013, 8, 045007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.; Hu, X.G.; Dai, C.S.; Yi, T.F. Crystal structures of electrospun PVDF membranes and its separator application for rechargeable lithium metal cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. B Solid State Mater. Adv. Technol. 2006, 131, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiyong, H.; Yinda, Z.; Hele, Z.; Yuanyuan, G.; Xudong, Y. Mixed effect of main electrospinning parameters on the β-phase crystallinity of electrospun PVDF nanofibers. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 085019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.Z.; Li, J.Q.; Yuan, X.Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Sheng, J. Preparation and properties of electrospun poly (vinylidene fluoride) membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 97, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, M.; Matsumoto, H.; Danno, T.; Minagawa, M.; Irisawa, T.; Shioya, M.; Tanioka, A. Control of diameter, morphology, and structure of PVDF nanofiber fabricated by electrospray deposition. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2006, 44, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motamedi, A.S.; Mirzadeh, H.; Hajiesmaeilbaigi, F.; Bagheri-Khoulenjani, S.; Shokrgozar, M. Effect of electrospinning parameters on morphological properties of PVDF nanofibrous scaffolds. Prog. Biomater. 2017, 6, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, J.; Baek, I.; Choi, H. Efficacy of piezoelectric electrospun nanofiber membrane for water treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 307, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garain, S.; Jana, S.; Sinha, T.K.; Mandal, D. Design of in situ poled Ce(3+)-doped electrospun PVDF/graphene composite nanofibers for fabrication of nanopressure sensor and ultrasensitive acoustic nanogenerator. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 4532–4540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasipour, M.; Khajavi, R.; Yousefi, A.A.; Yazdanshenas, M.E.; Razaghian, F. The piezoelectric response of electrospun PVDF nanofibers with graphene oxide, graphene, and halloysite nanofillers: A comparative study. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2017, 28, 15942–15952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaarour, B.; Zhu, L.; Huang, C.; Jin, X. Controlling the secondary surface morphology of electrospun PVDF nanofibers by regulating the solvent and relative humidity. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ribeiro, C.; Sencadas, V.; Ribelles, J.L.G.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Influence of processing conditions on polymorphism and nanofiber morphology of electroactive poly (vinylidene fluoride) electrospun membranes. Soft Mater. 2010, 8, 274–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiyong, H.; Yuanyuan, G.; Hele, Z.; Yinda, Z.; Xudong, Y. Effect of electrospinning parameters on piezoelectric properties of electrospun PVDF nanofibrous mats under cyclic compression. J. Text. Inst. 2017, 109, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Lye, S.W.; Miao, J. PVDF Nanofiber sensor for vibration measurement in a string. Sensors 2019, 19, 3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andrew, J.S.; Clarke, D.R. Effect of electrospinning on the ferroelectric phase content of polyvinylidene difluoride fibers. Langmuir 2008, 24, 670–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhtari, F.; Shamshirsaz, M.; Latifi, M. Investigation of β phase formation in piezoelectric response of electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride nanofibers: LiCl additive and increasing fibers tension. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2016, 56, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, B.J.; Liu, Y.; Yang, R.; Wang, Z.L. Hybrid nanogenerator for concurrently harvesting biomechanical and biochemical energy. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 3647–3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Diani, J.; Liu, Y.P.; Gall, K. Finite strain 3D thermoviscoelastic constitutive model for shape memory polymers. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2006, 46, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.H.; Kang, H.W. Advanced electrospinning using circle electrodes for freestanding PVDF nanofiber film fabrication. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 455, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, F.; Shamshirsaz, M.; Latifi, M.; Asadi, S. Comparative evaluation of piezoelectric response of electrospun PVDF (polyvinilydine fluoride) nanofiber with various additives for energy scavenging application. J. Text. Inst. 2017, 108, 906–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi Varposhti, A.; Yousefzadeh, M.; Kowsari, E.; Latifi, M. Enhancement of β-phase crystalline structure and piezoelectric properties of flexible PVDF/ionic liquid surfactant composite nanofibers for potential application in sensing and self-powering. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2020, 305, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, L.M.M.; Bretas, R.E.S.; Gregorio, R. Effect of solution concentration on the electrospray/electrospinning transition and on the crystalline phase of PVDF. Mater. Sci. Appl. 2010, 1, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Z.P.; Wu, X.F. Electrospinning superhydrophobic-superoleophilic fibrous PVDF membranes for high-efficiency water-oil separation. Mater. Lett. 2015, 160, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, R.F.; Chen, S.; Lin, Y.; He, Y.F.; Gu, Y.C. Preparation and piezoelectric investigation of electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride fibrous membrane. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 16, 12337–12343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benz, M.; Euler, W.B. Determination of the crystalline phases of poly (vinylidene fluoride) under different preparation conditions using differential scanning calorimetry and infrared spectroscopy. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 89, 1093–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lins, L.C.; Wianny, F.; Livi, S.; Dehay, C.; Duchet-Rumeau, J.; Gerard, J.F. Effect of polyvinylidene fluoride electrospun fiber orientation on neural stem cell differentiation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2017, 105, 2376–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yee, W.A.; Nguyen, A.C.; Lee, P.S.; Kotaki, M.; Liu, Y.; Tan, B.T.; Mhaisalkar, S.; Lu, X.H. Stress-induced structural changes in electrospun polyvinylidene difluoride nanofibers collected using a modified rotating disk. Polymer 2008, 49, 4196–4203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abolhasani, M.M.; Azimi, S.; Fashandi, H. Enhanced ferroelectric properties of electrospun poly (vinylidene fluoride) nanofibers by adjusting processing parameters. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 61277–61283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.M.; Chou, M.H.; Zeng, W.Y. Piezoelectric response of aligned electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride/carbon nanotube nanofibrous membranes. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.R.; Zheng, J.M.; Ren, G.Y.; Zhang, P.H.; Xu, C. A flexible piezoelectric force sensor based on PVDF fabrics. Smart Mater. Struct. 2011, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.H.; Pan, C.T.; Lin, L.W.; Huang, J.C.; Ou, Z.Y. Direct-write PVDF nonwoven fiber fabric energy harvesters via the hollow cylindrical near-field electrospinning process. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.P.; Yu, L.K.; Zheng, G.F.; Wang, L.Y.; Wu, D.Z.; Sun, D.H. Electrospinning-induced preferred dipole orientation in PVDF fibers. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 4342–4347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.; Fang, J.; Wang, H.X.; Lin, T. Effect of electrospinning parameters and polymer concentrations on mechanical-to-electrical energy conversion of randomly-oriented electrospun poly (vinylidene fluoride) nanofiber mats. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 14345–14350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafari, E.; Lu, N. Self-polarized electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) nanofiber for sensing applications. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 160, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Zhao, L.; Teh, K.S.; Jiang, Z. The radial piezoelectric response from three-dimensional electrospun PVDF micro wall structure. Materials 2020, 13, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Magniez, K.; De Lavigne, C.; Fox, B.L. The effects of molecular weight and polymorphism on the fracture and thermo-mechanical properties of a carbon-fibre composite modified by electrospun poly (vinylidene fluoride) membranes. Polymer 2010, 51, 2585–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, S.; Johnson, B.; Smith, A.L. Optimizing electrospinning parameters for piezoelectric PVDF nanofiber membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 563, 804–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servais, T.; Brocke, R.; Fatka, O. Variability in the Ordovician acritarch Dicrodiacrodium. Palaeontology 1996, 39, 389–405. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, G.C.; Zhao, L.Y.; Zhu, L.T.; Deng, X.Y.; Chen, W.L. Effect of experimental parameters on nanofiber diameter from electrospinning with wire electrodes. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 230, 012043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, G.J.; Zhang, L.F.; Su, R.; Wang, K.; Fong, H.; Zhu, L. Understanding polymorphism formation in electrospun fibers of immiscible Poly (vinylidene fluoride) blends. Polymer 2011, 52, 2228–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matabola, K.P.; Moutloali, R.M. The influence of electrospinning parameters on the morphology and diameter of poly (vinyledene fluoride) nanofibers- effect of sodium chloride. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 5475–5482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baji, A.; Mai, Y.W.; Li, Q.; Liu, Y. Electrospinning induced ferroelectricity in poly (vinylidene fluoride) fibers. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 3068–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaarour, B.; Zhu, L.; Huang, C.; Jin, X. Enhanced piezoelectric properties of randomly oriented and aligned electrospun PVDF fibers by regulating the surface morphology. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, M.; Kotaki, M. Fabrication of aligned piezoelectric nanofiber by electrospinning. IJN 2011, 8, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, K.; Kelarakis, A. Nanoclay-directed structure and morphology in PVDF electrospun membranes. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014, 367671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zaarour, B.; Zhang, W.X.; Zhu, L.; Jin, X.Y.; Huang, C. Maneuvering surface structures of polyvinylidene fluoride nanofibers by controlling solvent systems and polymer concentration. Text. Res. J. 2019, 89, 2406–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, D.; D’Souza, N.A. One-step fabrication of biomimetic PVDF-BaTiO3nanofibrous composite using DoE. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Wang, R.; Tian, M.; Qiu, C.Q.; Fane, A.G. Fabrication of polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) nanofiber membranes by electro-spinning for direct contact membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 425, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.H.; Wan, Y.; Sun, B.; Liu, L.Z.; Xu, W. Mechanical and electrical properties of electrospun PVDF/MWCNT ultrafine fibers using rotating collector. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lei, T.P.; Zhu, P.; Cai, X.M.; Yang, L.; Yang, F. Electrospinning of PVDF nanofibrous membranes with controllable crystalline phases. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2015, 120, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Wood, D.; Edmondson, D.; Yao, D.Y.; Erickson, A.E.; Tsao, C.T.; Revia, R.A.; Kim, H.; Zhang, M.Q. Electrospun uniaxially-aligned composite nanofibers as highly-efficient piezoelectric material. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 2734–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, D.; Kottapalli, A.G.P.; Chen, S.H.; Miao, J.M.; Kwok, C.Y.; Triantafyllou, M.S.; Warkiani, M.E.; Asadnia, M. Characterization of single polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) nanofiber for flow sensing applications. AIP Adv. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasipour, M.; Khajavi, R.; Yousefi, A.A.; Yazdanshenas, M.E.; Razaghian, F.; Akbarzadeh, A. Improving piezoelectric and pyroelectric properties of electrospun PVDF nanofibers using nanofillers for energy harvesting application. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2019, 30, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.W.; Kim, J.R.; Ahn, Y.R.; Jo, S.M.; Cairns, E.J. Characterization of electrospun PVdF fiber-based polymer electrolytes. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.L.; Wei, Q.F.; Wang, J.X.; Cai, Y.B.; Huang, Y.B. Effect of temperature on structure, morphology and crystallinity of PVDF nanofibers via electrospinning. E-Polymers 2008, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, T.; Safavi, M.A. Application of Taguchi method in optimization of desalination by vacuum membrane distillation. Desalination 2009, 249, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, C. One dimensional nanostructures electrospinning technique and unique nanofibers. One Dimens. Nanostruct. 2013, 1–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaarour, B.; Zhu, L.; Huang, C.; Jin, X.Y. Fabrication of a polyvinylidene fluoride cactus- like nanofiber through one- step electrospinning. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 42353–42360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szewczyk, P.K.; Gradys, A.; Kim, S.K.; Persano, L.; Marzec, M.; Kryshtal, A.; Busolo, T.; Toncelli, A.; Pisignano, D.; Bernasik, A.; et al. Enhanced piezoelectricity of electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride fibers for energy harvesting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 13575–13583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, T.H.; Lee, S.S.; Choi, G.J.; Park, I.K. Churros-like polyvinylidene fluoride nanofibers for enhancing output performance of triboelectric nanogenerators. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 17824–17832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slack, J.J.; Brodt, M.; Cullen, D.A.; Reeves, K.S.; More, K.L.; Pintauro, P.N. Impact of polyvinylidene fluoride on nanofiber cathode structure and durability in proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 054517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozza, E.S.; Monticelli, O.; Marsano, E.; Cebe, P. On the electrospinning of PVDF: Influence of the experimental conditions on the nanofiber properties. Polym. Int. 2013, 62, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, Y.; Lim, J.Y.; Hong, S.M.; Lee, J.; Ha, J.; Choi, H.J.; Seo, Y. Enhanced piezoelectric properties of electrospun poly (vinylidene fluoride)/multiwalled carbon nanotube composites due to high β-phase formation in poly (vinylidene fluoride). J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 11791–11799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.J.; Liu, Y.; Yan, J.; Wang, K.X.; Xie, B.L.; Hu, Y.X.; Kang, W.M.; Cheng, B.W. Electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride/fluorinated acrylate copolymer tree-like nanofiber membrane with high flux and salt rejection ratio for direct contact membrane distillation. Desalination 2019, 466, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.A.; Cho, Y.H.; Nam, S.E.; Park, A.; Park, Y.I.; Park, H. High performance thin-film nanocomposite forward osmosis membrane based on PVDF/bentonite nanofiber support. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 86, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.Z.; Zheng, J.M.; Xu, C.Y. Silver nanowire dopant enhancing piezoelectricity of electrospun PVDF nanofiber web. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Smart Materials and Nanotechnology in Engineering, Gold Coast, Australia, 10–12 July 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorayani Bafqi, M.S.; Bagherzadeh, R.; Latifi, M. Fabrication of composite PVDF-ZnO nanofiber mats by electrospinning for energy scavenging application with enhanced efficiency. J. Polym. Res. 2015, 22, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanmal, C.V.; Jog, J.P. Electrospun PVDF/BaTiO3 nanocomposites: Polymorphism and thermal emissivity studies. Int. J. Plast. Technol. 2011, 15, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bairagi, S.; Ali, S.W. Flexible lead-free PVDF/SM-KNN electrospun nanocomposite based piezoelectric materials: Significant enhancement of energy harvesting efficiency of the nanogenerator. Energy 2020, 198, 117385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, Z.-K.; Li, J.-S.; Yi, Y.-P.-Q.; Fan, Y.-Y.; Xu, L.-L.; Li, Y. Enhancement of β-phase crystal content of poly (vinylidene fluoride) nanofiber web by graphene and electrospinning parameters. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2020, 38, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.Y.; Jiang, P.K.; Kim, C.; Liu, F.; Yin, Y. Influence of aspect ratio of carbon nanotubes on crystalline phases and dielectric properties of poly (vinylidene fluoride). Eur. Polym. J. 2009, 45, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, C.; Guan, J.; Li, Y.; Li, J. Effect of a room-temperature ionic liquid on the structure and properties of electrospun poly (vinylidene fluoride) nanofibers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 4447–4457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Babel, A.; Jenekhe, S.A.; Xia, Y.N. Nanofibers of conjugated polymers prepared by electrospinning with a two-capillary spinneret. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 2062–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaarour, B.; Zhu, L.; Jin, X. Direct generation of electrospun branched nanofibers for energy harvesting. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2020, 31, 2659–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Yee, W.A.; Tjiu, W.C.; Liu, Y.; Kotaki, M.; Boey, Y.C.; Ma, J.; Liu, T.; Lu, X. Electrospinning of polyvinylidene difluoride with carbon nanotubes: Synergistic effects of extensional force and interfacial interaction on crystalline structures. Langmuir 2008, 24, 13621–13626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baji, A.; Mai, Y.W.; Li, Q.; Liu, Y. Nanoscale investigation of ferroelectric properties in electrospun barium titanate/polyvinylidene fluoride composite fibers using piezoresponse force microscopy. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2011, 71, 1435–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebrekrstos, A.; Madras, G.; Bose, S. Piezoelectric response in electrospun poly (vinylidene fluoride) fibers containing fluoro-doped graphene derivatives. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 5317–5326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fialka, J.; Benes, P. Comparison of methods for the measurement of piezoelectric coefficients. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2013, 62, 1047–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabriani, F.; Chytanya, K.; Giovanna, I.; Lanzara, G. Characterization of electrospun PVDF fibres for sensing and actuation. Proceedings 2018, 2, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al Halabi, F.; Gryshkov, O.; Kuhn, A.I.; Kapralova, V.M.; Glasmacher, B. Force induced piezoelectric effect of polyvinylidene fluoride and polyvinylidene fluoride-co-trifluoroethylene nanofibrous scaffolds. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2018, 41, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Chen, D.; Liang, C.; Lei, T.; Sun, D.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, L. Piezoelectric performance of aligned PVDF nanofibers fabricated by electrospinning and mechanical spinning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Nanotechnology, Beijing, China, 5–8 August 2013; pp. 962–966. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Huang, S.; Xiao, Z.; Yu, L.; Wang, L.; Sun, D.; Lin, L. Piezoelectric properties of PVDF nanofibers via non-uniform field electrospinning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Manipulation, Manufacturing and Measurement on the Nanoscale, 3M-NANO, Taipei, Taiwan, 27–31 October 2014; pp. 285–289. [Google Scholar]




| Type of Collector | Advantages | Disadvantages | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Static collector 1. Metal plate collector  | Simple equipment | Random distribution of nanofibers Not conducive to stretching the nanofibers Low F(β) | [91,92] |
2. Double-plate collector | Highly aligned nanofibers Enhance F(β) (compared with a mental plate collector) | [93,94,] | |
3. Circle electrode collector | Easy to transfer membranes to the target substrates High productivity | Random distribution of nanofibers Low F(β) | [95] |
| Rotating collector 1. Rotating drum collector  | Highly aligned nanofibers Enhance F(β) (compared with a mental plate collector) The large area of a nanofibrous membrane | [96,97] | |
2. Rotating disk collector | Highly aligned nanofibers Enhance F(β) (compared with all other collectors) | The small area of a nanofibrous membrane | [98,99,100] |
| Name of Nanomaterials | How to Improve the β Phase | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inorganic nanomaterials | LiCl | Improvement of the solution conductivity | [92] |
| AgNWs | Improvement of the solution conductivity | [142] | |
| ZnO | Improvement of the solution conductivity | [143] | |
| BaTiO3 | Local dipole field on the surface | [144] | |
| KNN | Beta-nucleating agent in PVDF | [145] | |
| Organic nanomaterials | Graphene | Electro-interactions | [82,146] |
| CNTs | Interfacial polarization | [85] | |
| [BMIM][PF6] | Strong interactions | [97] | |
| [OMD]Br | Strong interactions | [147] | |
| 2,3-dihydrodecafluoropentane | Hydrogen bonds | [148] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, Z.; Rault, F.; Lewandowski, M.; Mohsenzadeh, E.; Salaün, F. Electrospun PVDF Nanofibers for Piezoelectric Applications: A Review of the Influence of Electrospinning Parameters on the β Phase and Crystallinity Enhancement. Polymers 2021, 13, 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13020174
He Z, Rault F, Lewandowski M, Mohsenzadeh E, Salaün F. Electrospun PVDF Nanofibers for Piezoelectric Applications: A Review of the Influence of Electrospinning Parameters on the β Phase and Crystallinity Enhancement. Polymers. 2021; 13(2):174. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13020174
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Zhongchen, François Rault, Maryline Lewandowski, Elham Mohsenzadeh, and Fabien Salaün. 2021. "Electrospun PVDF Nanofibers for Piezoelectric Applications: A Review of the Influence of Electrospinning Parameters on the β Phase and Crystallinity Enhancement" Polymers 13, no. 2: 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13020174
APA StyleHe, Z., Rault, F., Lewandowski, M., Mohsenzadeh, E., & Salaün, F. (2021). Electrospun PVDF Nanofibers for Piezoelectric Applications: A Review of the Influence of Electrospinning Parameters on the β Phase and Crystallinity Enhancement. Polymers, 13(2), 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13020174